在Java中我们通常把具备相同或相似功能的一些类放在同一个包中,当然 不同公司会有不同的命名方式,但大体都相同,一个好的命名应见名知义,提高代码可读性,以利于后期代码的修改与维护。下面基于我自己做项目中的一些感触谈谈自己对包命名规范的理解。
一Java包命名规范
| com.example.app.activitys | 用来组织Activity类 |
| com.example.app.base | 基础共享的类,如多个Activity共享的 BaseActivity或整个应用共享的MyApplication类 |
| com.example.app.adapter | 项目中用到的适配器类 |
| com.example.app.view | 自定义的View,如常用的TitleBarView |
| com.example.app.util | 工具类,如HttpUtil,ImageUtil,FileUtil |
| com.example.app.db | 数据库类,如DataBaseHelper,MessageDB |
| com.example.app.service | 服务类,如GetMsgService |
| com.example.app.constant | 常量类 |
| com.example.app.domain/modle/entity | 元素实体类,如对应注册用户信息的User类, 对应聊天信息的TextMessage类 |
| com.example.app.broadcast | 广播服务类 |
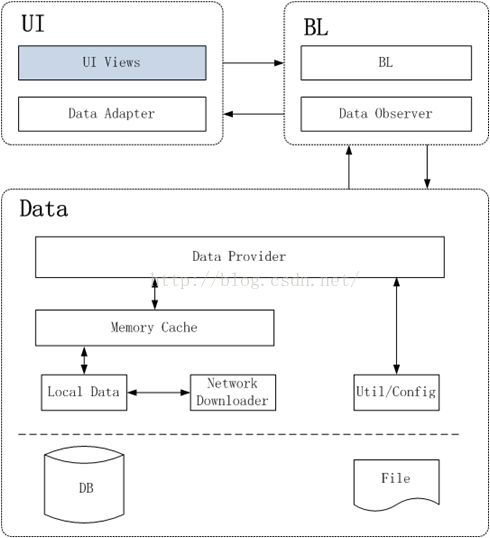
二常见项目框架
- <span> </span>public View getChildView(int groupPosition, int childPosition,boolean isLastChild, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
-
- GroupHolder holder = null;
- if (convertView == null) {
- convertView = LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(
- R.layout.fragment_constact_child, null);
- holder = new GroupHolder();
- holder.nameView = (TextView) convertView
- .findViewById(R.id.contact_list_item_name);
- holder.feelView = (TextView) convertView
- .findViewById(R.id.cpntact_list_item_state);
- holder.iconView = (ImageView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.icon);
- convertView.setTag(holder);
- } else {
- holder = (GroupHolder) convertView.getTag();
- }
-
- holder.iconView.setImageResource(R.drawable.head);
- holder.nameView.setText(getChild(groupPosition, childPosition)
- .toString());
- holder.feelView.setText(signString[groupPosition][childPosition]);
- return convertView;
- }
1. 加载大图片时,合理设置BitmapFactory.Options的值inSampleSize,减少图片内存占用;
2. 仅请求图片的大小,inJustDecodeBounds = true仅请求图片大小,而不会加载图片到内存;
3. 缓存图片:内存缓存使用lruCache,磁盘缓存使用 DiskLruCache;
4. 使用非UI线程加载图片,使用 AsyncTask;
5. 使用软引用SoftReference