热门标签
热门文章
- 1jupyter远程连接Linux服务器_jupyter里的linux命令
- 2鸿蒙Harmony应用开发—ArkTS声明式开发(容器组件:EffectComponent)
- 3顶级AI【数据】资源送给你!
- 4spring cloud config配置中心详细教程_项目中写cloud config的流程
- 5Axure原型部署到云服务器教程_axure部署到云服务器
- 6datatalble总结(一)_c# datatalble 分组
- 7[内附完整源码和文档] 基于SSH网上商城的设计与实现_基于ssh的网上商城系统的设计与实现
- 8c语言小游戏实践-贪吃蛇_请实现贪吃蛇移动的函数,考虑移动时分别当吃到果子和没有吃的果子的场景,同时
- 9Thinkphp+workman+redis实现多线程异步任务处理
- 10MVC5后台C#无法访问网络共享目录的解决办法_mvc发布后无法访问共享文件夹
当前位置: article > 正文
SVM学习(一)SVM模型训练与分类_svm训练
作者:weixin_40725706 | 2024-03-23 05:52:49
赞
踩
svm训练
SVM模型训练与分类
支持向量机(SVM):
一个能够将不同类样本在样本空间分隔的超平面。换句话说,给定一些标记好的训练本(监督式学习),SVM算法输出一个最优化的超分隔平面。本次利用VS2015+OpenCV3.4.1实现SVM算法,完成数据集的训练,生成XML文件,然后通过调用XML文件来实现图片的识别分类。即为分三个步骤:数据集的准备、数据集的模型训练以及利用训练好的模型进行测试分类。
目的:利用SVM算法实现手写体0和1的图片的识别分类。
步骤1:数据集的准备
在OpenCV的安装路径下,搜索digits,可以得到一张图片,图片大小为1000*2000,有0-9的10个数字,每5行为一个数字,总共50行,共有5000个手写数字,每个数字块大小为20×20。 下面将把这些数字中的0和1作为二分类的准备数据。其中0有500张,1有500张。
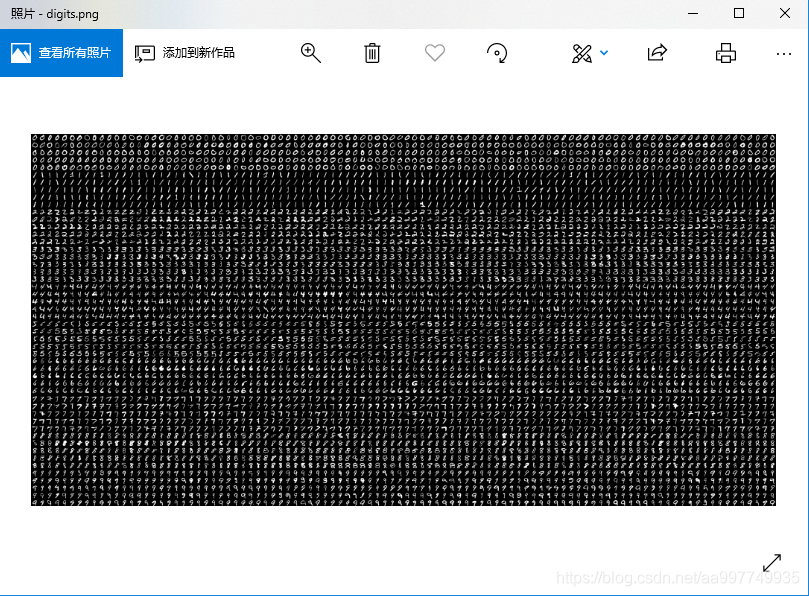
用下面的代码将图片准备好,在写入路径提前建立好文件夹:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <iostream> using namespace std; using namespace cv; int main() { char ad[128] = { 0 }; int filename = 0, filenum = 0; Mat img = imread("F:\\Opencv3_4_1\\opencv\\sources\\samples\\data\\digits.png"); Mat gray; cvtColor(img, gray, CV_BGR2GRAY); int b = 20; int m = gray.rows / b; //原图为1000*2000 int n = gray.cols / b; //裁剪为5000个20*20的小图块 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int offsetRow = i*b; //行上的偏移量 if (i % 5 == 0 && i != 0) { filename++; filenum = 0; } for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { int offsetCol = j*b; //列上的偏移量 sprintf_s(ad, "D:\\data\\%d\\%d.jpg", filename, filenum++); //截取20*20的小块 Mat tmp; gray(Range(offsetRow, offsetRow + b), Range(offsetCol, offsetCol + b)).copyTo(tmp); imwrite(ad, tmp); } } return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
最后可以得到这样的结果

将以上图片可以进行分类成训练集和测试集,方便后期进行训练和测试。要注意:训练中的图片不包含测试集合中的图片。
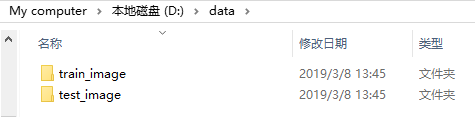
训练数据800张,0,1各400张;测试数据200张,0,1各100张
步骤2:模型的训练
数据准备完成之后,就可以用下面的代码训练了:
#include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <opencv/cv.h> #include <iostream> #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/ml/ml.hpp> #include <io.h> //查找文件相关函数 using namespace std; using namespace cv; using namespace cv::ml; void getFiles(string path, vector<string>& files); void getBubble(Mat& trainingImages, vector<int>& trainingLabels); void getNoBubble(Mat& trainingImages, vector<int>& trainingLabels); int main() { //获取训练数据 Mat classes; Mat trainingData; Mat trainingImages; vector<int> trainingLabels; //getBubble()与getNoBubble()将获取一张图片后会将图片(特征)写入 // 到容器中,紧接着会将标签写入另一个容器中,这样就保证了特征 // 和标签是一一对应的关系push_back(0)或者push_back(1)其实就是 // 我们贴标签的过程。 getBubble(trainingImages, trainingLabels); getNoBubble(trainingImages, trainingLabels); //在主函数中,将getBubble()与getNoBubble()写好的包含特征的矩阵拷贝给trainingData,将包含标签的vector容器进行类 //型转换后拷贝到trainingLabels里,至此,数据准备工作完成,trainingData与trainingLabels就是我们要训练的数据。 Mat(trainingImages).copyTo(trainingData); trainingData.convertTo(trainingData, CV_32FC1); Mat(trainingLabels).copyTo(classes); // 创建分类器并设置参数 Ptr<SVM> SVM_params = SVM::create(); SVM_params->setType(SVM::C_SVC); SVM_params->setKernel(SVM::LINEAR); //核函数 SVM_params->setDegree(0); SVM_params->setGamma(1); SVM_params->setCoef0(0); SVM_params->setC(1); SVM_params->setNu(0); SVM_params->setP(0); SVM_params->setTermCriteria(TermCriteria(TermCriteria::MAX_ITER + TermCriteria::EPS, 1000, 0.01)); Ptr<TrainData> tData = TrainData::create(trainingData, ROW_SAMPLE, classes); // 训练分类器 SVM_params->train(tData); //保存模型 SVM_params->save("svm.xml");//将训练好的模型保存在此文件中。 cout << "训练好了!!!" << endl; getchar(); return 0; } void getFiles(string path, vector<string>& files)//用来遍历文件夹下的所有文件。 { intptr_t hFile = 0; struct _finddata_t fileinfo; string p; int i = 30; if ((hFile = _findfirst(p.assign(path).append("\\*").c_str(), &fileinfo)) != -1) { do { if ((fileinfo.attrib & _A_SUBDIR)) { if (strcmp(fileinfo.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name, "..") != 0) getFiles(p.assign(path).append("\\").append(fileinfo.name), files); } else { files.push_back(p.assign(path).append("\\").append(fileinfo.name)); } } while (_findnext(hFile, &fileinfo) == 0); _findclose(hFile); } } //获取正样本 //并贴标签为1 void getBubble(Mat& trainingImages, vector<int>& trainingLabels) { char * filePath = "D:\\data\\train_image\\1"; //数字1样本路径 vector<string> files; getFiles(filePath, files); int number = files.size(); for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) { Mat SrcImage = imread(files[i].c_str()); SrcImage = SrcImage.reshape(1, 1); trainingImages.push_back(SrcImage); trainingLabels.push_back(1);//该样本为数字1 } } //获取负样本 //并贴标签为0 void getNoBubble(Mat& trainingImages, vector<int>& trainingLabels) { char * filePath = "D:\\data\\train_image\\0"; //数组0样本路径 vector<string> files; getFiles(filePath, files); int number = files.size(); for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) { Mat SrcImage = imread(files[i].c_str()); SrcImage = SrcImage.reshape(1, 1); trainingImages.push_back(SrcImage); trainingLabels.push_back(0); //该样本是数字0 } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
注意:此过程的主要目的是生成xml文件,此文件保存在该工程项目的根目录下。
步骤3:加载模型进行分类识别
将上一步生成的XML文件复制一份到该工程根目录下,否则无法加载。
测试代码如下所示:
#include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <opencv/cv.h> #include <iostream> #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> #include <opencv2/ml/ml.hpp> #include <io.h> using namespace std; using namespace cv; //using namespace ml; void getFiles(string path, vector<string>& files); int main() { int result0 = 0; int result1 = 0; char * filePath = "D:\\data\\test_image\\0"; vector<string> files; getFiles(filePath, files); int number = files.size(); cout <<"共有测试图片"<< number<<"张\n" << endl; Ptr<ml::SVM>svm = ml::SVM::load("svm.xml"); for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) { Mat inMat = imread(files[i].c_str()); Mat p = inMat.reshape(1, 1); p.convertTo(p, CV_32FC1); int response = (int)svm->predict(p); cout << "识别的数字为:" << response << endl; if (response == 0) { result0++; } else { result1++; } } cout << "识别的数字0的个数为:" << result0 << endl; cout << "识别的数字1的个数为:" << result1 << endl; getchar(); return 0; } void getFiles(string path, vector<string>& files) //用来遍历文件夹下所有文件 { intptr_t hFile = 0; /*long hFile = 0;*/ struct _finddata_t fileinfo; string p; if ((hFile = _findfirst(p.assign(path).append("\\*").c_str(), &fileinfo)) != -1) { do { if ((fileinfo.attrib & _A_SUBDIR)) { if (strcmp(fileinfo.name, ".") != 0 && strcmp(fileinfo.name, "..") != 0) getFiles(p.assign(path).append("\\").append(fileinfo.name), files); } else { files.push_back(p.assign(path).append("\\").append(fileinfo.name)); } } while (_findnext(hFile, &fileinfo) == 0); _findclose(hFile); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
本次的测试图片共100张,其中0有94张,1有6张。

下面展示测试效果:

可以看出测试效果还不错!
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/weixin_40725706/article/detail/293478
推荐阅读
相关标签



