- 1springboot集成flowable-ui最新版本_springboot集成flowableui
- 2MySQL零基础从入门到精通,看完这篇直接毕业!(图文并茂,实战教学)_mysql创建学生表并存储案例
- 3基于jeecgboot-vue3的Flowable流程-待办任务(一)_vue3集成flowable
- 4大数据TensorFlow深度学习——基于BERT+LSTM+CRF深度学习识别模型医疗知识图谱问答可视化系统(完整系统源码+PPT+详细开发文档+论文+源码解析)_bert模型医疗知识问答
- 5Android BatteryStats服务功耗统计流程详解_android 应用耗电量的统计方法和工具
- 6简单好用的python可视化-Streamlit_python streamlit
- 7PaddleOCR基于PaddleHub Serving的在线服务部署_paddlehub ocr
- 8git 文件修改不区分大小写 设置git的敏感_core.ignorecase=true
- 9langchain-Agent代理详解_langchain agent
- 10RHEL8_Linux_ssh远程登录系统和远程拷贝_rhel ssh远程连接提示activate the web console
Python技能练习!值得你看的28道常见题型汇总!(附答案解析)_python练习题
赞
踩
今天给大家分享30道Python练习题,建议大家先独立思考一下解题思路,再查看答案。 【文末有惊喜】
1.已知一个字符串为 “hello_world_yoyo”,如何得到一个队列
[“hello”,”world”,”yoyo”] ?
使用 split 函数,分割字符串,并且将数据转换成列表类型:
test = 'hello_world_yoyo'``print(test.split("_"))``12
- 1
结果:
['hello', 'world', 'yoyo']
- 1
2. 有个列表 [“hello”, “world”, “yoyo”],如何把列表里面的字符串联起来,得到字符串 “hello_world_yoyo”?
使用 join 函数将数据转换成字符串:
test = ["hello", "world", "yoyo"]``print("_".join(test))
- 1
结果:
hello_world_yoyo
- 1
如果不依赖 python 提供的 join 方法,还可以通过 for 循环,然后将字符串拼接,但是在用“+”连接字符串时,结果会生成新的对象,使用 join 时结果只是将原列表中的元素拼接起来,所以 join 效率比较高。
for 循环拼接如下:
test = ["hello", "world", "yoyo"]``# 定义一个空字符串``j = ''``# 通过 for 循环打印出列表中的数据``for i in test:` `j = j + "_" + i``# 因为通过上面的字符串拼接,得到的数据是“_hello_world_yoyo”,前面会多一个下划线_,所以把这个下划线去掉``print(j.lstrip("_"))
- 1
3. 把字符串 s 中的每个空格替换成”%20”,输入:s = “We are happy.”,输出:“We%20are%20happy.”。
使用 replace 函数,替换字符换即可:
s = 'We are happy.'``print(s.replace(' ', '%20'))``12
- 1
结果:
We%20are%20happy.
- 1
4. Python 如何打印 99 乘法表?
for 循环打印:
for i in range(1, 10):` `for j in range(1, i+1):` `print('{}x{}={}\t'.format(j, i, i*j), end='')` `print()
- 1
while 循环实现:
i = 1``while i <= 9:` `j = 1` `while j <= i:` `print("%d*%d=%-2d"%(i,j,i*j),end = ' ') # %d: 整数的占位符,'-2'代表靠左对齐,两个占位符` `j += 1` `print()` `i += 1
- 1
结果:
1x1=1` `1x2=2 2x2=4` `1x3=3 2x3=6 3x3=9` `1x4=4 2x4=8 3x4=12 4x4=16` `1x5=5 2x5=10 3x5=15 4x5=20 5x5=25` `1x6=6 2x6=12 3x6=18 4x6=24 5x6=30 6x6=36` `1x7=7 2x7=14 3x7=21 4x7=28 5x7=35 6x7=42 7x7=49` `1x8=8 2x8=16 3x8=24 4x8=32 5x8=40 6x8=48 7x8=56 8x8=64` `1x9=9 2x9=18 3x9=27 4x9=36 5x9=45 6x9=54 7x9=63 8x9=72 9x9=81
- 1
5. 从下标 0 开始索引,找出单词 “welcome” 在字符串“Hello, welcome to my world.” 中出现的位置,找不到返回 -1。
def test():` `message = 'Hello, welcome to my world.'` `world = 'welcome'` `if world in message:` `return message.find(world)` `else:` `return -1`` ``print(test())``
- 1
结果:
7
- 1
6. 统计字符串“Hello, welcome to my world.” 中字母 w 出现的次数。
def test():` `message = 'Hello, welcome to my world.'` `# 计数` `num = 0` `# for 循环 message` `for i in message:` `# 判断如果 ‘w’ 字符串在 message 中,则 num +1` `if 'w' in i:` `num += 1` `return num`` ``print(test())``# 结果``2
- 1
7. 输入一个字符串 str,输出第 m 个只出现过 n 次的字符,如在字符串 gbgkkdehh 中,找出第 2 个只出现 1 次的字符,输出结果:d
def test(str_test, num, counts):` `"""` `:param str_test: 字符串` `:param num: 字符串出现的次数` `:param count: 字符串第几次出现的次数` `:return:` `"""` `# 定义一个空数组,存放逻辑处理后的数据` `list = []`` ` `# for循环字符串的数据` `for i in str_test:` `# 使用 count 函数,统计出所有字符串出现的次数` `count = str_test.count(i, 0, len(str_test))` `# 判断字符串出现的次数与设置的counts的次数相同,则将数据存放在list数组中` `if count == num:` `list.append(i)`` ` `# 返回第n次出现的字符串` `return list[counts-1]`` ``print(test('gbgkkdehh', 1, 2))``结果:``d
- 1
8. 判断字符串 a = “welcome to my world” 是否包含单词 b = “world”,包含返回 True,不包含返回 False。
def test():` `message = 'welcome to my world'` `world = 'world'` `if world in message:` `return True` `return False`` ``print(test())`` ``结果:``True
- 1
9. 从 0 开始计数,输出指定字符串 A = “hello” 在字符串 B = “hi how are you hello world, hello yoyo!”中第一次出现的位置,如果 B 中不包含 A,则输出 -1。
def test():` `message = 'hi how are you hello world, hello yoyo!'` `world = 'hello'` `return message.find(world)`` ``print(test())`` ``结果:``15
- 1
10. 从 0 开始计数,输出指定字符串 A = “hello”在字符串 B = “hi how are you hello world, hello yoyo!”中最后出现的位置,如果 B 中不包含 A,则输出 -1。
def test(string, str):` `# 定义 last_position 初始值为 -1` `last_position = -1` `while True:` `position = string.find(str, last_position+1)` `if position == -1:` `return last_position` `last_position = position`` ``print(test('hi how are you hello world, hello yoyo!', 'hello'))`` ``结果:``28
- 1
11. 给定一个数 a,判断一个数字是否为奇数或偶数。
while True:` `try:` `# 判断输入是否为整数` `num = int(input('输入一个整数:'))` `# 不是纯数字需要重新输入` `except ValueError:`` print("输入的不是整数!")` `continue` `if num % 2 == 0:` `print('偶数')` `else:` `print('奇数')` `break`` ``结果:``输入一个整数:100``偶数
- 1
12. 输入一个姓名,判断是否姓王。
def test():` `user_input = input("请输入您的姓名:")`` ` `if user_input[0] == '王':` `return "用户姓王"`` ` `return "用户不姓王"`` ``print(test())`` ``结果:``请输入您的姓名:王总``用户姓王
- 1
13. 如何判断一个字符串是不是纯数字组成?
利用 Python 提供的类型转行,将用户输入的数据转换成浮点数类型,如果转换抛异常,则判断数字不是纯数字组成。
def test(num):` `try:` `return float(num)` `except ValueError:` `return "请输入数字"`` ``print(test('133w3'))
- 1
14. 将字符串 a = “This is string example….wow!” 全部转成大写,字符串 b = “Welcome To My World” 全部转成小写。
a = 'This is string example….wow!'``b = 'Welcome To My World'`` ``print(a.upper())``print(b.lower())
- 1
15. 将字符串 a = “ welcome to my world ”首尾空格去掉
Python 提供了strip() 方法,可以去除首尾空格,rstrip() 去掉尾部空格,lstrip() 去掉首部空格,replace(" ", “”) 去掉全部空格。
a = ' welcome to my world '``print(a.strip())
- 1
还可以通过递归的方式实现:
def trim(s):` `flag = 0` `if s[:1]==' ':` `s = s[1:]` `flag = 1` `if s[-1:] == ' ':` `s = s[:-1]` `flag = 1` `if flag==1:` `return trim(s)` `else:` `return s``print(trim(' Hello world! '))
- 1
通过 while 循环实现:
def trim(s):` `while(True):` `flag = 0` `if s[:1]==' ':` `s = s[1:]` `flag = 1` `if s[-1:] == ' ':` `s = s[:-1]` `flag = 1` `if flag==0:` `break` `return s``print(trim(' Hello world! '))
- 1
16. 将字符串 s = “ajldjlajfdljfddd”,去重并从小到大排序输出”adfjl”。
def test():` `s = 'ajldjlajfdljfddd'` `# 定义一个数组存放数据` `str_list = []` `# for循环s字符串中的数据,然后将数据加入数组中` `for i in s:` `# 判断如果数组中已经存在这个字符串,则将字符串移除,加入新的字符串` `if i in str_list:` `str_list.remove(i)`` ` `str_list.append(i)` `# 使用 sorted 方法,对字母进行排序` `a = sorted(str_list)` `# sorted方法返回的是一个列表,这边将列表数据转换成字符串` `return "".join(a)`` ``print(test())`` ``结果:``adfjl
- 1
17. 打印出如下图案(菱形):

def test():` `n = 8` `for i in range(-int(n/2), int(n/2) + 1):` `print(" "*abs(i), "*"*abs(n-abs(i)*2))`` ``print(test())`` ``结果:` `**` `****` `******` `********` `******` `****` `**
- 1
18. 给一个不多于 5 位的正整数(如 a = 12346),求它是几位数和逆序打印出各位数字。
class Test:`` ` `# 计算数字的位数` `def test_num(self, num):` `try:` `# 定义一个 length 的变量,来计算数字的长度` `length = 0` `while num != 0:` `# 判断当 num 不为 0 的时候,则每次都除以10取整` `length += 1` `num = int(num) // 10` `if length > 5:` `return "请输入正确的数字"` `return length` `except ValueError:` `return "请输入正确的数字"`` ` `# 逆序打印出个位数` `def test_sorted(self, num):` `if self.test_num(num) != "请输入正确的数字":` `# 逆序打印出数字` `sorted_num = num[::-1]` `# 返回逆序的个位数` `return sorted_num[-1]`` ``print(Test().test_sorted('12346'))`` ``结果:``1
- 1
19. 如果一个 3 位数等于其各位数字的立方和,则称这个数为水仙花数。例如:153 = 13 + 53 + 33,因此 153 就是一个水仙花数。那么如何求 1000 以内的水仙花数(3 位数)。
def test():` `for num in range(100, 1000):` `i = num // 100` `j = num // 10 % 10` `k = num % 10` `if i ** 3 + j ** 3 + k ** 3 == num:` `print(str(num) + "是水仙花数")``test()``20. 求 1+2+3…+100 相加的和。``i = 1``for j in range(101):` `i = j + i`` ``print(i)`` ``结果:``5051
- 1
20. 计算 1-2+3-4+5-…-100 的值。
def test(sum_to):` `# 定义一个初始值` `sum_all = 0` `# 循环想要计算的数据` `for i in range(1, sum_to + 1):` `sum_all += i * (-1) ** (1 + i)` `return sum_all`` ``if __name__ == '__main__':` `result = test(sum_to=100)` `print(result)`` ``-50
- 1
21. 现有计算公式 13 + 23 + 33 + 43 + …….+ n3,如何实现:当输入 n = 5 时,输出 225(对应的公式 : 13 + 23 + 33 + 43 + 53 = 225)。
def test(n):` `sum = 0` `for i in range(1, n+1):` `sum += i*10+i` `return sum``print(test(5))``结果:``225
- 1
22. 已知 a 的值为“hello”,b 的值为“world”,如何交换 a 和 b 的值,得到 a 的值为“world”,b 的值为”hello”?
a = 'hello'``b = 'world'`` ``c = a``a = b``b = c``print(a, b)
- 1
23. 如何判断一个数组是对称数组?
例如 [1,2,0,2,1],[1,2,3,3,2,1],这样的数组都是对称数组。用 Python 判断,是对称数组打印 True,不是打印 False。
def test():` `x = [1, 'a', 0, '2', 0, 'a', 1]` `# 通过下标的形式,将字符串逆序进行比对` `if x == x[::-1]:` `return True` `return False`` ``print(test())`` ``结果:``True
- 1
24. 如果有一个列表 a = [1,3,5,7,11],那么如何让它反转成 [11,7,5,3,1],并且取到奇数位值的数字 [1,5,11]?
def test():` `a = [1, 3, 5, 7, 11]` `# 逆序打印数组中的数据` `print(a[::-1])` `# 定义一个计数的变量` `count = 0` `for i in a:` `# 判断每循环列表中的一个数据,则计数器中会 +1` `count += 1` `# 如果计数器为奇数,则打印出来` `if count % 2 != 0:` `print(i)`` ``test()`` ``结果:``[11, 7, 5, 3, 1]``1``5``11
- 1
25. 对列表 a = [1, 6, 8, 11, 9, 1, 8, 6, 8, 7, 8] 中的数字从小到大排序。
a = [1, 6, 8, 11, 9, 1, 8, 6, 8, 7, 8]``print(sorted(a))`` ``结果:``[1, 1, 6, 6, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8, 9, 11]``27. 找出列表 L1 = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 3, 2, 5, 33, 88] 中最大值和最小值。``L1 = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 3, 2, 5, 33, 88]``print(max(L1))``print(min(L1))`` ``结果:``88``1
- 1
上面是通过 Python 自带的函数实现,如下,可以自己写一个计算程序:
class Test(object):`` ` `def __init__(self):` `# 测试的列表数据` `self.L1 = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 3, 2, 5, 33, 88]`` ` `# 从列表中取第一个值,对于数据大小比对` `self.num = self.L1[0]`` ` `def test_small_num(self, count):` `"""` `:param count: count为 1,则表示计算最大值,为 2 时,表示最小值` `:return:` `"""` `# for 循环查询列表中的数据` `for i in self.L1:` `if count == 1:` `# 循环判断当数组中的数据比初始值小,则将初始值替换` `if i > self.num:` `self.num = i` ` elif count == 2:` `if i < self.num:` `self.num = i` ` elif count != 1 or count != 2:` `return "请输入正确的数据"`` ` `return self.num`` ``print(Test().test_small_num(1))``print(Test().test_small_num(2))``结果:``88``1
- 1
26. 找出列表 a = [“hello”, “world”, “yoyo”, “congratulations”] 中单词最长的一个。
def test():` `a = ["hello", "world", "yoyo", "congratulations"]` ` # 统计数组中第一个值的长度` `length = len(a[0])` ` for i in a:` `# 循环数组中的数据,当数组中的数据比初始值length中的值长,则替换掉length的默认值` `if len(i) > length:` `length = i` `return length`` ``print(test())`` ``结果:``congratulations
- 1
27. 取出列表 L1 = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 3, 2, 5, 33, 88] 中最大的三个值。
def test():` `L1 = [1, 2, 3, 11, 2, 5, 3, 2, 5, 33, 88]` `return sorted(L1)[:3]`` ``print(test())`` ``结果:``[1, 2, 2]
- 1
28. 把列表 a = [1, -6, 2, -5, 9, 4, 20, -3] 中的数字绝对值。
deftest():` `a = [1, -6, 2, -5, 9, 4, 20, -3]` `# 定义一个数组,存放处理后的绝对值数据` `lists = []` `for i in a:` `# 使用 abs() 方法处理绝对值` `lists.append(abs(i))` `return lists`` ``print(test())`` ``结果:``[1, 6, 2, 5, 9, 4, 20, 3]
- 1
今天小编也给大家分享一份Python学习资料和公开课,里面的内容都是适合零基础小白的笔记和资料,不懂编程也能听懂、看懂。如果需要的话直接划到文末免费获得,让我们一起学习!
一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向路线就是把Python常用的技术点做整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
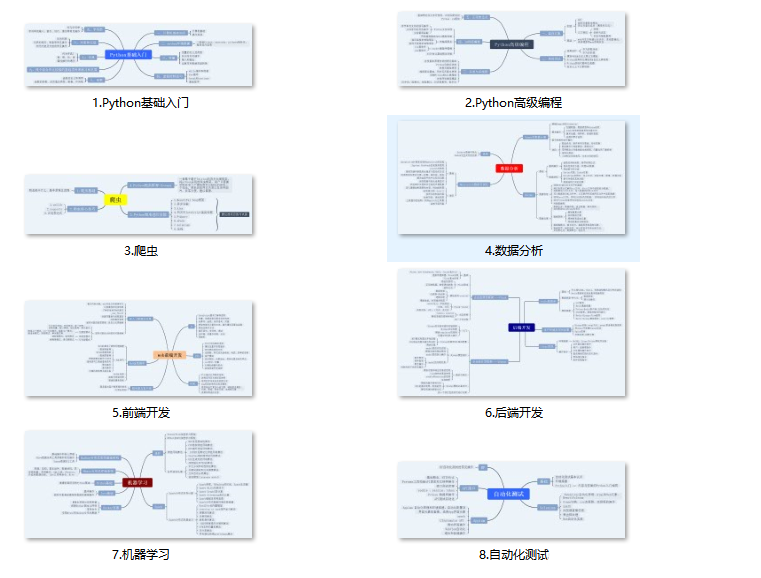
二、学习软件
工欲善其事必先利其器。学习Python常用的开发软件都在这里了,给大家节省了很多时间。
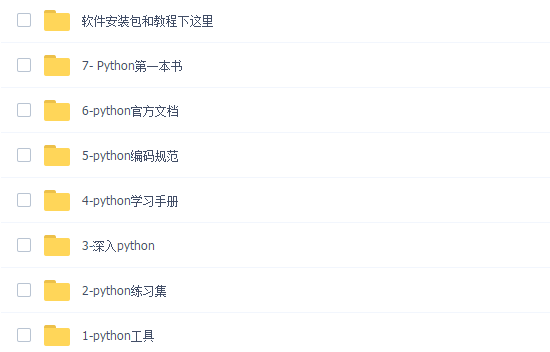
三、全套PDF电子书
书籍的好处就在于权威和体系健全,刚开始学习的时候你可以只看视频或者听某个人讲课,但等你学完之后,你觉得你掌握了,这时候建议还是得去看一下书籍,看权威技术书籍也是每个程序员必经之路。

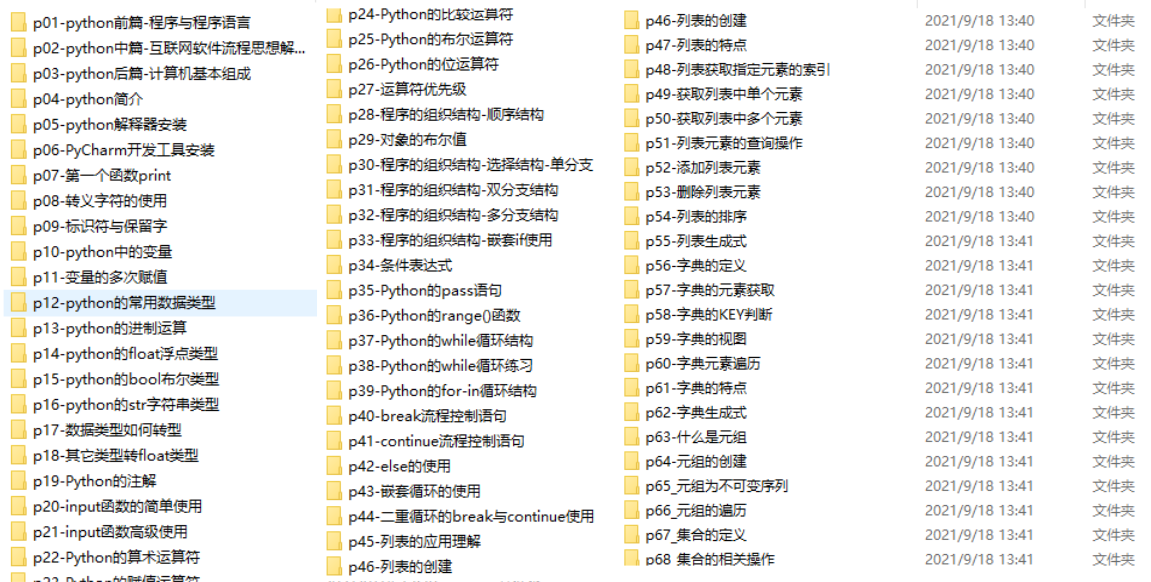
四、入门学习视频
我们在看视频学习的时候,不能光动眼动脑不动手,比较科学的学习方法是在理解之后运用它们,这时候练手项目就很适合了。
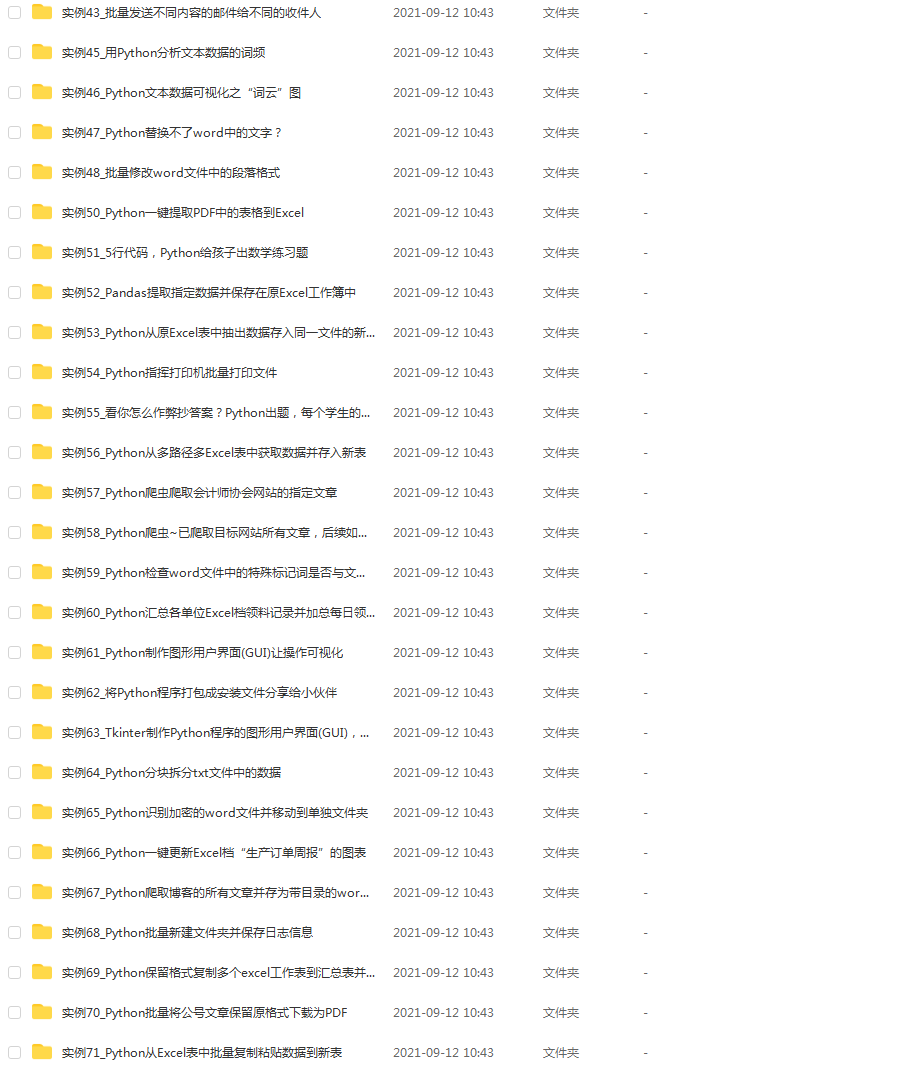
四、实战案例
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。
五、清华编程大佬出品《漫画看学Python》
用通俗易懂的漫画,来教你学习Python,让你更容易记住,并且不会枯燥乏味。

配套600集视频:

六、面试资料
我们学习Python必然是为了找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题是来自阿里、腾讯、字节等一线互联网大厂最新的面试资料,并且有阿里大佬给出了权威的解答,刷完这一套面试资料相信大家都能找到满意的工作。
如果你也想和我一起学习Python,欢迎关注我
点击下方链接即可免费获取Python全套资料,学习视频,热门书籍PDF版本
Copyright © 2003-2013 www.wpsshop.cn 版权所有,并保留所有权利。


