- 1解决Androidx中RecyclerView不能使用的方法_
- 2Python在金融大数据分析中的AI应用实战_python在金融大数据中有哪些应用?
- 3harmonyOS开发技巧(一)——封装hilog日志_export hilog怎么进行
- 4Object Detection︱RCNN、faster-RCNN框架的浅读与延伸内容笔记_rcnn进化
- 5keil5——安装教程附资源包_keil5安装教程
- 6C#WinForm POST方式提交给网页(与网页交互) (转)
- 7sqllab第三关通关笔记
- 8拉链表的制作_基于客户信息表制作月表拉链表
- 9医学图像目标跟踪论文阅读笔记 2024.03.08~2024.03.14
- 10ChatGLM-6B微调,P-Tuning,LoRA,Full parameter_chatglm 微调
Vue2.x 源码剖析之响应式原理_vue2源码阅读:响应式原理zhouweicsu
赞
踩
Study Notes
本博主会持续更新各种前端的技术,如果各位道友喜欢,可以关注、收藏、点赞下本博主的文章。
Vue.js 源码剖析-响应式原理
响应式处理的入口
- src/core/instance/init.js
- initState(vm) vm 状态的初始化
- 初始化了 _data、_props、methods 等
- src/core/instance/state.js
/* @flow */
import ...;
const sharedPropertyDefinition = {...};
export function proxy(target: Object, sourceKey: string, key: string) {...}
export function initState(vm: Component) {
vm._watchers = [];
const opts = vm.$options;
if (opts.props) initProps(vm, opts.props);
if (opts.methods) initMethods(vm, opts.methods);
// 判断options中是否存在data属性
if (opts.data) {
// 如果存在data属性,则给其添加响应式
initData(vm);
} else {
// 如果不存在data属性,则给给vue对象,添加_data属性,初始化为空对象,并给其添加响应式
observe((vm._data = {}), true /* asRootData */);
}
if (opts.computed) initComputed(vm, opts.computed);
if (opts.watch && opts.watch !== nativeWatch) {
initWatch(vm, opts.watch);
}
}
function initProps(vm: Component, propsOptions: Object) {...}
function initData(vm: Component) {
let data = vm.$options.data;
// 判断data是否是函数,如果是一个函数,则是组件中的data,将其this指向vue
// 不是函数,则判断是否存在。不存在则赋值为空对象
data = vm._data = typeof data === 'function' ? getData(data, vm) : data || {};
// 判断data是否是[object Object],如果不是,则将data赋值为空对象
// 并在非production环境下,抛出警告
if (!isPlainObject(data)) {
data = {};
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
warn(
'data functions should return an object:\n' +
'https://vuejs.org/v2/guide/components.html#data-Must-Be-a-Function',
vm,
);
}
// proxy data on instance
// 获取data的所有key值
const keys = Object.keys(data);
const props = vm.$options.props;
const methods = vm.$options.methods;
let i = keys.length;
while (i--) {
const key = keys[i];
// 在非production环境下,判断是否与methods里的方法存在同名,存在则抛出警告
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (methods && hasOwn(methods, key)) {
warn(
`Method "${key}" has already been defined as a data property.`,
vm,
);
}
}
// 在非production环境下,判断是否与props里的属性存在同名,存在则抛出警告
if (props && hasOwn(props, key)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
warn(
`The data property "${key}" is already declared as a prop. ` +
`Use prop default value instead.`,
vm,
);
} else if (!isReserved(key)) {
// 如果key的第一个字符不是$或者_,为其设置代理
proxy(vm, `_data`, key);
}
}
// observe data
// 将data转换为响应式数据
// true:告诉observe函数,其为根属性data
observe(data, true /* asRootData */);
}
function getData(data: Function, vm: Component): any {...}
const computedWatcherOptions = { lazy: true };
function initComputed(vm: Component, computed: Object) {...}
export function defineComputed(
target: any,
key: string,
userDef: Object | Function,
) {...}
function createComputedGetter(key) {...}
function initMethods(vm: Component, methods: Object) {...}
function initWatch(vm: Component, watch: Object) {...}
function createWatcher(
vm: Component,
keyOrFn: string | Function,
handler: any,
options?: Object,
) {...}
export function stateMixin(Vue: Class<Component>) {...}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- observe(value, asRootData)
- 负责为每一个 Object 类型的 value 创建一个 observer 实例
/* @flow */
import ...;
const arrayKeys = Object.getOwnPropertyNames(arrayMethods);
export const observerState = {
shouldConvert: true,
};
export class Observer {...}
function protoAugment(target, src: Object, keys: any) {...}
/* istanbul ignore next */
function copyAugment(target: Object, src: Object, keys: Array<string>) {...}
/**
* Attempt to create an observer instance for a value,
* returns the new observer if successfully observed,
* or the existing observer if the value already has one.
*/
// 如果不存在观察者实例,则创建观察者实例,并返回
// 存在,则直接返回现有的观察者实例
export function observe(value: any, asRootData: ?boolean): Observer | void {
// 如果value不是一个对象或者value是一个虚拟dom,则不往下执行,即不需为其转换为响应式数据
if (!isObject(value) || value instanceof VNode) {
return;
}
let ob: Observer | void;
// 如果value中存在__ob__属性,并且__ob__是Observer,则直接将value.__ob__赋值给ob
if (hasOwn(value, '__ob__') && value.__ob__ instanceof Observer) {
ob = value.__ob__;
} else if (
observerState.shouldConvert &&
!isServerRendering() &&
(Array.isArray(value) || isPlainObject(value)) &&
Object.isExtensible(value) &&
!value._isVue
) {
// observerState.shouldConvert为true
// 并且当前是浏览器环境
// 并且value是一个数组或者是'[object Object]'
// 并且value是可扩展的(可以在它上面添加新的属性)
// 并且value不是Vue实例
// 创建一个Observer对象,并赋值给ob
ob = new Observer(value);
}
// 如果处理的是根数据并且存在ob,则ob.vmCount++
if (asRootData && ob) {
ob.vmCount++;
}
return ob;
}
export function defineReactive(
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: ?Function,
shallow?: boolean,
) {...}
export function set(target: Array<any> | Object, key: any, val: any): any {...}
export function del(target: Array<any> | Object, key: any) {...}
function dependArray(value: Array<any>) {...}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
Observer
- Observer 类
- constructor()方法,初始化数据,并改变数组当前对象的原型属性
- walk()方法为对象做响应式处理
- observeArray()方法为数组做响应式处理
export class Observer {
// 数据对象
value: any;
// 依赖对象
dep: Dep;
// 实例计数器
// 以该对象在根$data的vms数
vmCount: number; // number of vms that has this object as root $data
// 构造函数,初始化数据
constructor(value: any) {
this.value = value;
this.dep = new Dep();
this.vmCount = 0;
// 将实例挂载到观察对象的__ob__属性
def(value, '__ob__', this);
// 如果观察对象是一个数组,将数组转换为响应式数据
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
const augment = hasProto
? protoAugment // 改变数组当前对象的原型属性
: copyAugment; // 改变数组当前对象的原型属性
// arrayKeys是对象的所有自身属性的属性名组成的数组
augment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys);
// 为数组中的每一个对象元素创建一个observer实例
this.observeArray(value);
} else {
// 遍历对象中的每一个属性,转换成getter/setter
this.walk(value);
}
}
/**
* Walk through each property and convert them into
* getter/setters. This method should only be called when
* value type is Object.
*/
walk(obj: Object) {
// 获取对象里的所有属性
const keys = Object.keys(obj);
// 遍历每一个属性,设置为响应式数据
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
defineReactive(obj, keys[i], obj[keys[i]]);
}
}
/**
* Observe a list of Array items.
*/
observeArray(items: Array<any>) {
for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i]);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
对象响应式处理
- defineReactive
- 为一个对象定义一个响应式的属性,每一个属性对应一个 dep 对象
- 如果该属性的值是对象,继续调用 observe
- 如果给属性赋的新值是一个对象,继续调用 observe
- 如果数据更新发送通知
// 在对象上定义响应式属性
export function defineReactive(
obj: Object,
key: string,
val: any,
customSetter?: ?Function,
shallow?: boolean,
) {
// 创建依赖对象实例,其作用是为当前属性(key)收集依赖
const dep = new Dep();
// 获取obj对象的属性描述符
const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key);
// 当且仅当该属性的 configurable 键值为 true 时
// 该属性的描述符才能够被改变,同时该属性也能从对应的对象上被删除。
// 如果存在属性描述符,并且configurable为false,即不可被转换为响应式数据,则不继续往下执行
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return;
}
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
// 提供预定义的存取器函数
const getter = property && property.get;
const setter = property && property.set;
// 当shallow为false或者不存在时
// observe会判断val是否是递归观察子对象
// 并将对象属性都转换为getter/setter,返回子观察对象
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val);
// 当且仅当该属性的 enumerable 键值为 true 时,该属性才会出现在对象的枚举属性中。
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter() {
// 如果存在用户设置的getter,将getter的this指向obj,并赋值给value
// 否则直接将传入的val赋值给value
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
// 如果存在当前依赖目标,即watcher对象,则建立依赖
// 在src/core/observer/index.js中的mountComponent方法,创建了watcher对象
// 在watcher对象的构造函数中,创建了Dep.target
if (Dep.target) {
// 为当前属性收集依赖
dep.depend();
// 如果存在子观察对象,则建立子对象的依赖关系
if (childOb) {
// 为当前子对象收集依赖
childOb.dep.depend();
// 如果value是数组,则特殊处理收集数组对象依赖
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value);
}
}
}
// 返回属性值
return value;
},
set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
// 如果新值等于旧值或者新值和旧值都为NaN,则不继续往下执行
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || (newVal !== newVal && value !== value)) {
return;
}
// 如果传入customSetter参数时,并且在非production环境时,调用customSetter方法
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter();
}
// 如果存在用户设置的setter,则将setter的this指向obj,并将newVal传入
// 否则直接newVal赋值给val
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal);
} else {
val = newVal;
}
// 当shallow为false或者不存在时
// observe会判断newVal是否是是递归观察子对象,返回子观察对象
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal);
// 派发更新(发布更新通知)
dep.notify();
},
});
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
数组响应式处理
在 observer 构造函数中
// 如果观察对象是一个数组,将数组转换为响应式数据
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
const augment = hasProto
? protoAugment // 改变数组当前对象的原型属性
: copyAugment; // 改变数组当前对象的原型属性
// arrayKeys是对象的所有自身属性的属性名组成的数组
augment(value, arrayMethods, arrayKeys);
// 为数组中的每一个对象元素创建一个observer实例
this.observeArray(value);
} else {
// 遍历对象中的每一个属性,转换成getter/setter
this.walk(value);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 改变数组当前对象的原型属性
/*
* not type checking this file because flow doesn't play well with
* dynamically accessing methods on Array prototype
*/
import { def } from '../util/index';
const arrayProto = Array.prototype;
// 使用数组的原型创建一个新的对象
export const arrayMethods = Object.create(arrayProto);
/**
* Intercept mutating methods and emit events
*/
// 修改数组元素的方法
['push', 'pop', 'shift', 'unshift', 'splice', 'sort', 'reverse'].forEach(
function (method) {
// cache original method
// 缓存数组的原方法
const original = arrayProto[method];
// 调用Object.defineProperty()方法,重写数组的方法
def(arrayMethods, method, function mutator(...args) {
// 执行原数组的原方法,并改变其this指向
const result = original.apply(this, args);
// 获取数组对象的__ob__属性
const ob = this.__ob__;
// 获取数组新增的元素
let inserted;
switch (method) {
case 'push':
case 'unshift':
inserted = args;
break;
case 'splice':
inserted = args.slice(2);
break;
}
// 如果存在新增元素,重新遍历数组元素设置为响应式数据
if (inserted) ob.observeArray(inserted);
// notify change
// 调用数组的ob对象发送更新通知
ob.dep.notify();
return result;
});
},
);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
Dep 类
- 在 defineReactive() 的 getter 中创建 dep 对象,当存在 Dep.target , 调用 dep.depend()
- dep.depend() 内部调用 Dep.target.addDep(this),也就是 watcher 的 addDep() 方法,它内部最终调用 dep.addSub(this),把订阅者(Watcher)添加到 dep 的 subs 数组中,当数据变化的时候调用 watcher 对象的 update() 方法
- 什么时候设置的 Dep.target? 通过简单的案例调试观察。调用 mountComponent() 方法的时候,创建了渲染 watcher 对象,执行 watcher 中的 get() 方法
- get() 方法内部调用 pushTarget(this),把当前 Dep.target = watcher,同时把当前 watcher 入栈,因为有父子组件嵌套的时候先把父组件对应的 watcher 入栈,再去处理子组件的 watcher,子组件的处理完毕后,再把父组件对应的 watcher 出栈,继续操作
- Dep.target 用来存放目前正在使用的 watcher。全局唯一,并且一次也只能有一个 watcher 被使用
/* @flow */
import type Watcher from './watcher';
import { remove } from '../util/index';
let uid = 0;
/**
* A dep is an observable that can have multiple
* directives subscribing to it.
*/
export default class Dep {
// 静态属性,Watcher对象
static target: ?Watcher;
// dep实例id
id: number;
// dep实例对应的Watcher对象/订阅者数组
subs: Array<Watcher>;
// 构造函数,初始化数据
constructor() {
this.id = uid++;
this.subs = [];
}
// 添加新的订阅者Watcher对象
addSub(sub: Watcher) {
this.subs.push(sub);
}
// 移除订阅者Watcher对象
removeSub(sub: Watcher) {
remove(this.subs, sub);
}
// 将观察对象和Watcher对象建立依赖
depend() {
// 如果存在target,则把dep对象添加到watcher的依赖中
if (Dep.target) {
Dep.target.addDep(this);
}
}
// 发布通知
notify() {
// stabilize the subscriber list first
// 克隆数组
const subs = this.subs.slice();
// 调用每个订阅者的update方法实现更新
for (let i = 0, l = subs.length; i < l; i++) {
subs[i].update();
}
}
}
// Dep.target 用来存放目前正在使用的watcher
// 全局唯一,并且一次也只能有一个watcher被使用
// the current target watcher being evaluated.
// this is globally unique because there could be only one
// watcher being evaluated at any time.
Dep.target = null;
const targetStack = [];
// 入栈并将当前 watcher 赋值给Dep.target
export function pushTarget(_target: Watcher) {
// 每一个组件都有一个mountComponent函数
// mountComponent函数创建了watcher对象
// 所以每一个组件对应一个watcher对象
// 如果A组件嵌套B组件,当我们渲染A组件时,发现存在子组件,则先渲染子组件,将A组件渲染挂起
// 所以这里需要将A组件的Dep.target入栈
// 当子组件渲染结束后,将其弹出栈,并继续执行A组件渲染
// 总结:
// 父子组件嵌套的时候先把父组件对应的watcher入栈,再去处理子组件的watcher。
// 子组件处理完毕后,再把父组件对应的watcher出栈,继续操作
if (Dep.target) targetStack.push(Dep.target);
Dep.target = _target;
}
// 出栈操作
export function popTarget() {
Dep.target = targetStack.pop();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
Watcher 类
- Watcher 分为三种,Computed Watcher、用户 Watcher (侦听器)、渲染 Watcher
- 什么时候渲染 Watcher?在 src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 中的 mountComponent 方法中创建
- Watcher 的构造函数初始化,处理 expOrFn (渲染 watcher 和侦听器处理不同)
- 调用 this.get() ,它里面调用 pushTarget() 方法,接下来执行 this.getter.call(vm, vm) (对于渲染 watcher 调用 updateComponent),如果是用户 watcher 会获取属性的值(触发 get 操作)
- 当数据更新的时候,dep 中调用 notify() 方法,notify() 中调用 watcher 的 update() 方法
- update() 中调用 queueWatcher()
- queueWatcher() 是一个核心方法,去除重复操作,调用 flushSchedulerQueue() 刷新队列并执行 watcher
- flushSchedulerQueue() 中对 watcher 排序,遍历所有 watcher ,如果存在 before,触发生命周期的钩子函数 beforeUpdate,执行 watcher.run(),它内部调用 this.get(),然后调用 this.cb() (渲染 watcher 的 cb 是 noop)
哪些数组操作可以触发视图更新
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
arr: [2, 3, 5],
},
});
// 在浏览器控制台分别执行下面的代码
// 会更新视图
// vm.arr.push(8)
// 数据已改变,但不会更新视图
// vm.arr[0] = 100
// 将数组清空,也不会更新视图
// vm.arr.length = 0
// 将数组第一位删除,并重新赋值为100,这时会更新视图
// vm.arr.splice(0,1,100)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
总结
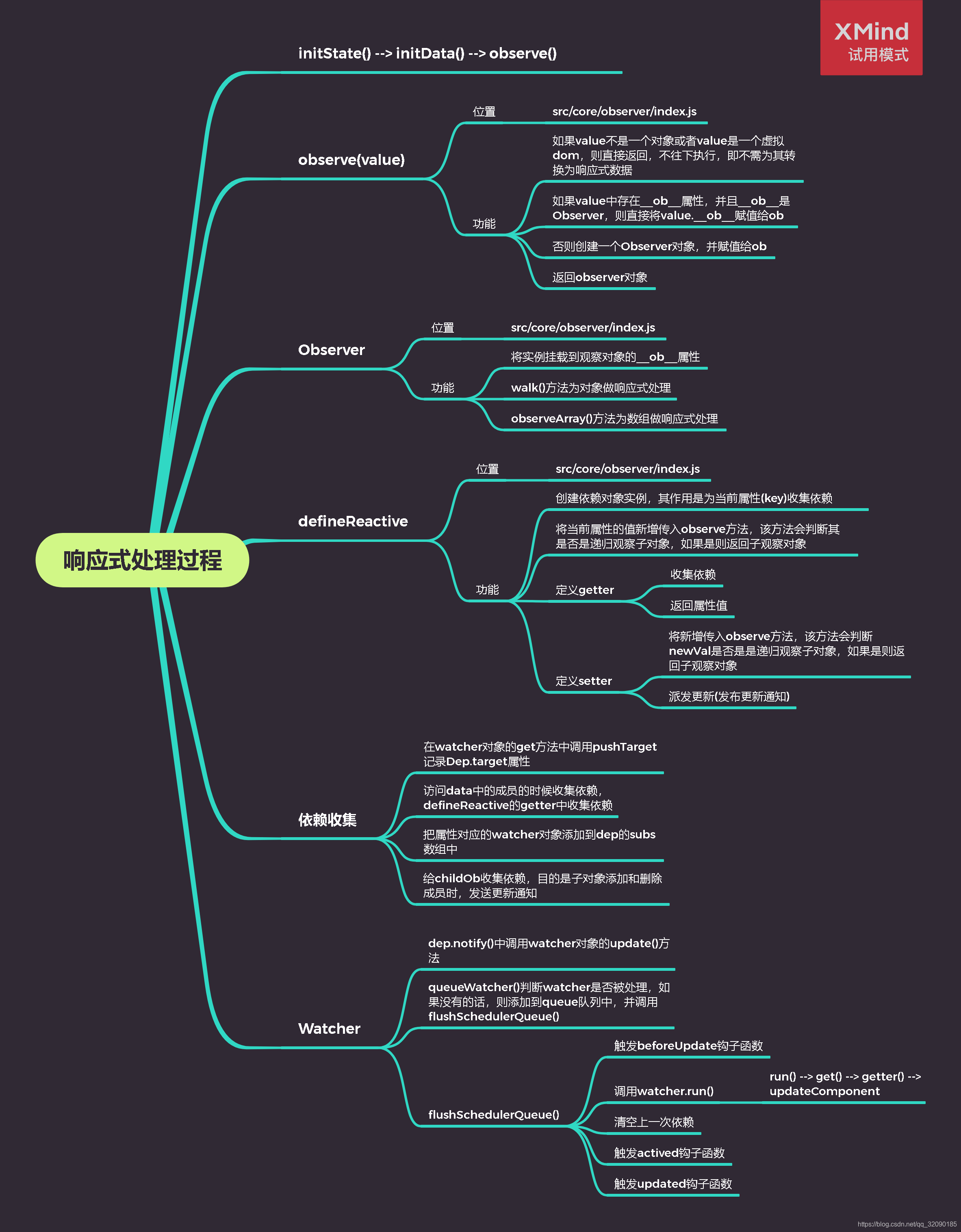
实例方法/数据
Vue.set(target, propertyName/index, value)
-
参数:
- {Object | Array} target
- {string | number} propertyName/index
- {any} value
-
返回值:设置的值。
-
用法:
向响应式对象中添加一个 property,并确保这个新 property 同样是响应式的,且触发视图更新。它必须用于向响应式对象上添加新 property,因为 Vue 无法探测普通的新增 property (比如 this.myObject.newProperty = ‘hi’)
注意对象不能是 Vue 实例,或者 Vue 实例的根数据对象。
- 示例
Vue.set(obj, 'foo', 'test');
- 1
vm.$set(target, propertyName/index, value)
-
参数:
- {Object | Array} target
- {string | number} propertyName/index
- {any} value
-
返回值:设置的值。
-
用法:
这是全局 Vue.set 的别名。
-
示例
vm.$set(obj, 'foo', 'test');
- 1
接单
小编承接外包,有意者可加
QQ:1944300940

微信号:wxid_g8o2y9ninzpp12

源码分析
-
Vue.set()
-
vm.$set()
在 src/core/instance/index.js 中的引用了在 src/core/instance/state.js 中的 stateMixin 方法,该方法定义了$set
-
上诉两个方法都指向 src/core/observer/index.js 中的 set()方法
export function set(target: Array<any> | Object, key: any, val: any): any {
// 如果目标是数组,并且key 是合法的索引
if (Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
// 通过Math.max返回最大值,并赋值给target.length
target.length = Math.max(target.length, key);
// 通过 splice 对key位置的元素进行替换
// splice 在 src/core/observer/array.js中进行了响应式的处理
target.splice(key, 1, val);
return val;
}
// 如果target中已存在key属性,则直接赋值
if (hasOwn(target, key)) {
target[key] = val;
return val;
}
// 获取 target 中的 observer 对象
const ob = (target: any).__ob__;
// 如果target是vue实例或者是$data,则直接返回
if (target._isVue || (ob && ob.vmCount)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
warn(
'Avoid adding reactive properties to a Vue instance or its root $data ' +
'at runtime - declare it upfront in the data option.',
);
return val;
}
// 如果不存在ob,那么target 不是一个响应式对象,则直接赋值并返回
if (!ob) {
target[key] = val;
return val;
}
// 把 key 设置为响应式属性
defineReactive(ob.value, key, val);
// 发送更新通知
ob.dep.notify();
return val;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
Vue.delete(target, propertyName/index)
-
参数:
- {Object | Array} target
- {string | number} propertyName/index
仅在 2.2.0+ 版本中支持 Array + index 用法。
-
用法:
删除对象的 property。如果对象是响应式的,确保删除能触发更新视图。这个方法主要用于避开 Vue 不能检测到 property 被删除的限制,但是你应该很少会使用它。
在 2.2.0+ 中同样支持在数组上工作。
目标对象不能是一个 Vue 实例或 Vue 实例的根数据对象。
vm.$delete(target, propertyName/index)
-
参数:
- {Object | Array} target
- {string | number} propertyName/index
-
用法:
这是全局 Vue.delete 的别名。
源码分析
-
Vue.delete()
-
vm.$delete()
在 src/core/instance/index.js 中的引用了在 src/core/instance/state.js 中的 stateMixin 方法,该方法定义了$delete
-
上诉两个方法都指向 src/core/observer/index.js 中的 del()方法
export function del(target: Array<any> | Object, key: any) {
// 如果目标是数组,并且key 是合法的索引
if (Array.isArray(target) && isValidArrayIndex(key)) {
// 通过 splice 对key位置的元素进行删除
// splice 在 src/core/observer/array.js中进行了响应式的处理
target.splice(key, 1);
return;
}
// 获取 target 中的 observer 对象
const ob = (target: any).__ob__;
// 如果target是vue实例或者是$data,则直接返回
if (target._isVue || (ob && ob.vmCount)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
warn(
'Avoid deleting properties on a Vue instance or its root $data ' +
'- just set it to null.',
);
return;
}
// 如果target不存在key属性,则直接返回
if (!hasOwn(target, key)) {
return;
}
// 删除target的key属性
delete target[key];
// 如果不存在ob,那么target 不是一个响应式对象,则直接返回
if (!ob) {
return;
}
// 发送更新通知
ob.dep.notify();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
vm.$watch(expOrFn, callback, [options])
-
功能
- 观察 Vue 实例变化的一个表达式或计算属性函数。回调函数得到的参数为新值和旧值。表达式只接受监督的键路径。对于更复杂的表达式,用一个函数取代。
-
参数
-
{string | Function} expOrFn:要监视的 $data 中的属性,可以是表达式或函数
-
{Function | Object} callback:数据变化后执行的函数
-
函数:回调函数
-
对象:具有 handler 属性(字符串或者函数),如果该属性为字符串则 methods 中相应的定义
-
-
{Object} [options]:可选的选项
-
{boolean} deep:布尔类型,深度监听
-
{boolean} immediate:布尔类型,是否立即执行一次回调函数
-
-
返回值:{Function} unwatch
注意:在变更 (不是替换) 对象或数组时,旧值将与新值相同,因为它们的引用指向同一个对象/数组。Vue 不会保留变更之前值的副本。
-
-
示例
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
a: '1',
b: '2',
msg: 'Hello Vue',
user: {
firstName: '诸葛',
lastName: '亮',
},
},
});
// expOrFn 是表达式
vm.$watch('msg', function (newVal, oldVal) {
console.log(newVal, oldVal);
});
vm.$watch('user.firstName', function (newVal, oldVal) {
console.log(newVal);
});
// expOrFn 是函数
vm.$watch(
function () {
return this.a + this.b;
},
function (newVal, oldVal) {
console.log(newVal);
},
);
// deep 是 true,消耗性能
vm.$watch(
'user',
function (newVal, oldVal) {
// 此时的 newVal 是 user 对象
console.log(newVal === vm.user);
},
{
deep: true,
},
);
// immediate 是 true
vm.$watch(
'msg',
function (newVal, oldVal) {
console.log(newVal);
},
{
immediate: true,
},
);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
三种类型的 Watcher 对象
-
没有静态方法,因为 $watch 方法中要使用 Vue 的实例
-
Watcher 分三种:计算属性 Watcher、用户 Watcher (侦听器)、渲染 Watcher
-
创建顺序:计算属性 Watcher、用户 Watcher (侦听器)、渲染 Watcher
-
源码分析
Vue.prototype.$watch = function (
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: any,
options?: Object
): Function {
// 获取 Vue 实例 this
const vm: Component = this
if (isPlainObject(cb)) {
// 如果 cb 是对象,则执行 createWatcher
return createWatcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
}
options = options || {}
// 标记为用户 watcher
options.user = true
// 创建用户 watcher 对象
const watcher = new Watcher(vm, expOrFn, cb, options)
if (options.immediate) {
// immediate 如果为 true,则立即执行一次 cb 回调,把this指向vue,并且当前值传入
cb.call(vm, watcher.value)
}
// 返回取消监听的方法
return function unwatchFn () {
watcher.teardown()
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
Vue.nextTick([callback, context])
-
参数:
-
{Function} [callback]
-
{Object} [context]
-
用法:
在下次 DOM 更新循环结束之后执行延迟回调。在修改数据之后立即使用这个方法,获取更新后的 DOM。
// 修改数据
vm.msg = 'Hello';
// DOM 还没有更新
Vue.nextTick(function () {
// DOM 更新了
});
// 作为一个 Promise 使用 (2.1.0 起新增,详见接下来的提示)
Vue.nextTick().then(function () {
// DOM 更新了
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
2.1.0 起新增:如果没有提供回调且在支持 Promise 的环境中,则返回一个 Promise。请注意 Vue 不自带 Promise 的 polyfill,所以如果你的目标浏览器不原生支持 Promise (IE:你们都看我干嘛),你得自己提供 polyfill。
- 参考:异步更新队列
vm.$nextTick([callback])
-
参数:
- {Function} [callback]
-
用法:
将回调延迟到下次 DOM 更新循环之后执行。在修改数据之后立即使用它,然后等待 DOM 更新。它跟全局方法 Vue.nextTick 一样,不同的是回调的 this 自动绑定到调用它的实例上。
2.1.0 起新增:如果没有提供回调且在支持 Promise 的环境中,则返回一个 Promise。请注意 Vue 不自带 Promise 的 polyfill,所以如果你的目标浏览器不是原生支持 Promise (IE:你们都看我干嘛),你得自行 polyfill。
-
示例
new Vue({
// ...
methods: {
// ...
example: function () {
// 修改数据
this.message = 'changed';
// DOM 还没有更新
this.$nextTick(function () {
// DOM 现在更新了
// `this` 绑定到当前实例
this.doSomethingElse();
});
},
},
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 参考:异步更新队列
源码分析
在 src/core/instance/index.js 中调用 src/core/instance/render.js 中的 renderMixin 方法
- 手动调用 vm.$nextTick()
- 在 Watcher 的 queueWatcher 中执行 nextTick()
- src/core/util/env.js
export const nextTick = (function () {
const callbacks = [];
let pending = false;
let timerFunc;
function nextTickHandler() {
pending = false;
// 克隆回调函数数组
const copies = callbacks.slice(0);
// 将callbacks数组置为空数组
callbacks.length = 0;
// 遍历执行回调函数数组中的每一个回调函数
for (let i = 0; i < copies.length; i++) {
copies[i]();
}
}
// An asynchronous deferring mechanism.
// In pre 2.4, we used to use microtasks (Promise/MutationObserver)
// but microtasks actually has too high a priority and fires in between
// supposedly sequential events (e.g. #4521, #6690) or even between
// bubbling of the same event (#6566). Technically setImmediate should be
// the ideal choice, but it's not available everywhere; and the only polyfill
// that consistently queues the callback after all DOM events triggered in the
// same loop is by using MessageChannel.
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (typeof setImmediate !== 'undefined' && isNative(setImmediate)) {
timerFunc = () => {
setImmediate(nextTickHandler);
};
} else if (
typeof MessageChannel !== 'undefined' &&
(isNative(MessageChannel) ||
// PhantomJS
MessageChannel.toString() === '[object MessageChannelConstructor]')
) {
const channel = new MessageChannel();
const port = channel.port2;
channel.port1.onmessage = nextTickHandler;
timerFunc = () => {
port.postMessage(1);
};
} else if (typeof Promise !== 'undefined' && isNative(Promise)) {
/* istanbul ignore next */
// use microtask in non-DOM environments, e.g. Weex
const p = Promise.resolve();
timerFunc = () => {
p.then(nextTickHandler);
};
} else {
// fallback to setTimeout
timerFunc = () => {
setTimeout(nextTickHandler, 0);
};
}
return function queueNextTick(cb?: Function, ctx?: Object) {
let _resolve;
// 把 cb 加上异常处理存入 callbacks 数组中
callbacks.push(() => {
if (cb) {
try {
// 如果存在cb
// 将cb的this指向ctx,并调用 cb()
cb.call(ctx);
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, ctx, 'nextTick');
}
} else if (_resolve) {
_resolve(ctx);
}
});
if (!pending) {
pending = true;
timerFunc();
}
// $flow-disable-line
if (!cb && typeof Promise !== 'undefined') {
// 返回 promise 对象
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
_resolve = resolve;
});
}
};
})();
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85


