- 1【正则】正则表达式基础知识大全
- 2机器学习|优化算法 | 评估方法|分类模型性能评价指标 | 正则化_智能优化算法性能评估的方法
- 3正则表达式使用大全_如何通过正则表达式筛选出katex中的数学公式
- 4查看服务器哪些端口开放指令_查看开放端口情况的命令
- 5mysql 常用查询语句(持续更新)_mysql查询语句
- 6面试测试岗要求20k+在准一线、二线城市意味着需要什么水平?来看看我的面试过程….
- 7sqlserver数据库连接失败的几种原因和处理方法_sql server连接失败
- 8程序员的思维修炼:开发认知潜能的九堂课_ghjv95
- 9【数据分析入门】人工智能、数据分析和深度学习是什么关系?如何快速入门 Python Pandas?_深度学习和数据分析有什么区别
- 10【Vue前端】使用 videojs 做 hls 直播流遇到的问题及解决方案总结(销毁、反复加载视频流、http-flv 低延时优化解决方向)_the element or id supplied is not valid. (videojs)
LeetCode--160.相交链表
赞
踩
相交链表
注:题目来源LeetCode。
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
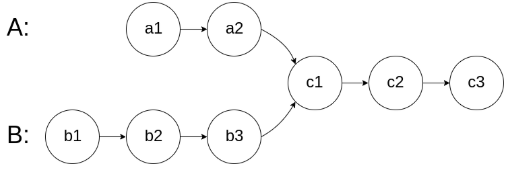
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例1
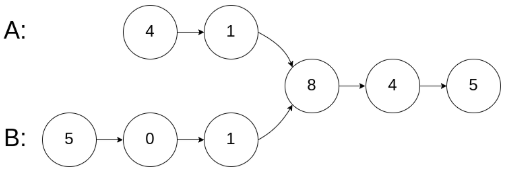
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2,skipB=3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
示例2
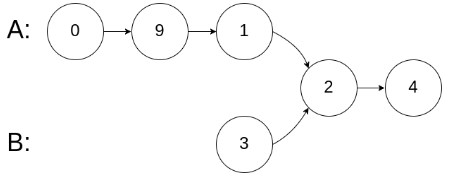
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
示例3
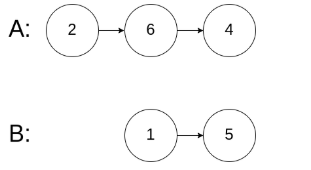
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
题目含义:
有两个单链表,如果这两个单聊表有相交的点,则说明这两个但单链表是相交链表,返回相交的节点。如果这两个单链表没有相交的点,则说明其不是相交链表,返回null。
方法一:
思路
暴力法 直接遍历
时间复杂度 O(m*n) 空间复杂度O(1)
双重循环遍历,当两个链表有相同的节点时,返回该节点,否则返回null。
代码
// 01暴力法 双重循环 public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { // 如果两个链表任意一个为空,则返回null if (headA == null || headB == null) { return null; } ListNode temp = headB; while (headA != null) { while (temp != null) { // 如果找到了相等的节点,则返回该节点,headA和temp是一样的 if (headA == temp) { return headA; } temp = temp.next; } headA = headA.next; // 遍历完headA之后temp需要重置为首节点 temp = headB; } return null; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
方法二:
思路
容器存储法
空间换时间
先遍历一遍第一个链表,将其节点存储在一个HashSet集合中,在遍历第二个链表,由于set集合是自动去重的,所以在遍第二个链表的时候判断第二个节点是否在集合中,如果在,说明是相交节点,返回该节点。如果遍历结束了还没有返回,则说明没有相交的节点,返回null。
代码
// 02优化时间复杂度 空间换时间 public ListNode getIntersectionNode2(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>(); while (headA != null) { set.add(headA); headA = headA.next; } while (headB != null) { if (set.contains(headB)) { return headB; } headB = headB.next; } return null; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
方法三:
思路
更少的空间复杂度
定义两个指针,指针A从链表A开始遍历,当遍历到最后一个节点时,接着遍历链表B。指针B从链表B开始遍历,当遍历到最后一个节点时,接着遍历链表A。形成两个环形链表(并且节点数是相同的),当两个环形链表相交时,说明是相交链表,否则返回null。
双指针法
链表A数据:4 1 8 4 5
链表B数据:5 0 1 8 4 5
4 1 8 4 5 -> 5 0 1 8 4 5
5 0 1 8 4 5 -> 4 1 8 4 5
pA指针 从A链表表头开始遍历 遍历到表尾时 开始遍历B链表表头
pB指针 从B链表表头开始遍历 遍历到表尾时 开始遍历A链表表头
如果两个链表相交 pA和pB一定相遇 且相遇的节点就是相交节点
时间复杂度 O(m+n) 空间复杂度O(1)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
代码
// 更少的空间复杂度 // 双指针法 public ListNode getIntersectionNode3(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null) { return null; } ListNode tempA = headA; ListNode tempB = headB; while (tempA != tempB) { if (tempA == null) { tempA = headB; } else { tempA = tempA.next; } if (tempB == null) { tempB = headA; } else { tempB = tempB.next; } } return tempA; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25



