- 1SpringCloud 学习笔记总结 (一)_springcloud d版
- 2latex图片排版技巧总结_latex subfloat
- 3python 异步socket编程
- 4Unity3D内嵌html网页+通信
- 5SpringBoot 统一功能处理:用户登录权限校验-拦截器、异常处理、数据格式返回...
- 6python如何在一个py文件中运行另一个py文件的代码_python运行一个内嵌文件
- 7c++与c语言中*p++,*++p,(*p)++,*(p++),*(++p)_p++与c++的相同之处
- 8计算右侧小于当前元素的个数
- 9操作系统课堂笔记_操作系统笔记
- 10弹性搜索引擎Elasticsearch:本地部署与远程访问指南_es 部署访问
使用Keras进行时间序列预测回归问题的LSTM实现_时间序列预测和回归分析lstm
赞
踩
基本简介
LSTM_learn
使用Keras进行时间序列预测回归问题的LSTM实现
数据
数据来自互联网,这些数据用于预测航空公司的人数,我们使用LSTM网络来解决这个问题
关于此处模型构建,只对keras部分代码做重点的介绍
模型构建与编译
def build_model(): # input_dim是输入的train_x的最后一个维度,train_x的维度为(n_samples, time_steps, input_dim) model = Sequential() #部分注释是对于老版本的kreas,支持,2.2.2不支持 # model.add(LSTM(input_dim=1, output_dim=50, return_sequences=True)) #2.2.2 keras model.add(LSTM(input_shape=(None, 1), units=100, return_sequences=False)) #① # model.add(LSTM(units=100, return_sequences=False)) # model.add(Dense(output_dim=1)) model.add(Dense(units=1)) model.add(Activation('linear')) model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='rmsprop') return model
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
①上面代码是建立了一个序列模型,采用的lstm,这里面关于参数这里要重点说明,return_sequences=True与False,比如说在我们设置。model.add(LSTM(input_shape=(None, 1), units=100, return_sequences=False))中就不需要执行 model.add(LSTM(units=100, return_sequences=False)),但是在我们执行model.add(LSTM(input_shape=(None, 1), units=100, return_sequences=True))时后面是必须要接, model.add(LSTM(units=100, return_sequences=False))的
具体原因及扩展原因如下:
Understand the Difference Between Return Sequences and Return States for LSTMs in Keras
Kears LSTM API 中给出的两个参数描述
return_sequences:默认 False。在输出序列中,返回单个 hidden state值还是返回全部time step 的 hidden state值。 False 返回单个, true 返回全部。
return_state:默认 False。是否返回除输出之外的最后一个状态。
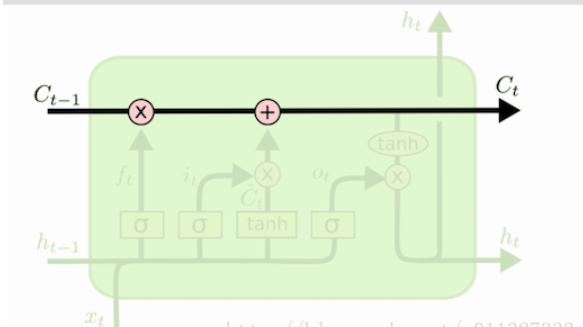
区别 cell state 和 hidden state
LSTM 的网络结构中,直接根据当前 input 数据,得到的输出称为 hidden state。
还有一种数据是不仅仅依赖于当前输入数据,而是一种伴随整个网络过程中用来记忆,遗忘,选择并最终影响 hidden state 结果的东西,称为 cell state。 cell state 就是实现 long short memory 的关键。
如图所示, C 表示的就是 cell state。h 就是hidden state。(选的图不太好,h的颜色比较浅)。整个绿色的矩形方框就是一个 cell。
cell state 是不输出的,它仅对输出 hidden state 产生影响。
通常情况,我们不需要访问 cell state,除非想设计复杂的网络结构时。例如在设计 encoder-decoder 模型时,我们可能需要对 cell state 的初始值进行设定。
keras 中设置两种参数的讨论
1.return_sequences=False && return_state=False
h = LSTM(X)
- 1
Keras API 中,return_sequences和return_state默认就是false。此时只会返回一个hidden state 值。如果input 数据包含多个时间步,则这个hidden state 是最后一个时间步的结果
2.return_sequences=True && return_state=False
LSTM(1, return_sequences=True)
- 1
输出的hidden state 包含全部时间步的结果。
3.return_sequences=False && return_state=True
lstm1, state_h, state_c = LSTM(1, return_state=True)
- 1
lstm1 和 state_h 结果都是 hidden state。在这种参数设定下,它们俩的值相同。都是最后一个时间步的 hidden state。 state_c 是最后一个时间步 cell state结果。
为什么要保留两个值一样的参数? 马上看配置4就会明白
为了便于说明问题,我们给配置3和配置4一个模拟的结果,程序结果参考reference文献。
[array([[ 0.10951342]], dtype=float32), # lstm1
array([[ 0.10951342]], dtype=float32), # state_h
array([[ 0.24143776]], dtype=float32)] # state_c
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
3.return_sequences=True && return_state=True
lstm1, state_h, state_c = LSTM(1, return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
- 1
此时,我们既要输出全部时间步的 hidden state ,又要输出 cell state。
lstm1 存放的就是全部时间步的 hidden state。
state_h 存放的是最后一个时间步的 hidden state
state_c 存放的是最后一个时间步的 cell state
一个输出例子,假设我们输入的时间步 time step=3
[array([[[-0.02145359],
[-0.0540871 ],
[-0.09228823]]], dtype=float32),
array([[-0.09228823]], dtype=float32),
array([[-0.19803026]], dtype=float32)]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
可以看到state_h 的值和lstm1的最后一个时间步的值相同。
state_c 则表示最后一个时间步的 cell state
Reference
https://machinelearningmastery.com/return-sequences-and-return-states-for-lstms-in-keras/
完整代码:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense, Activation
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
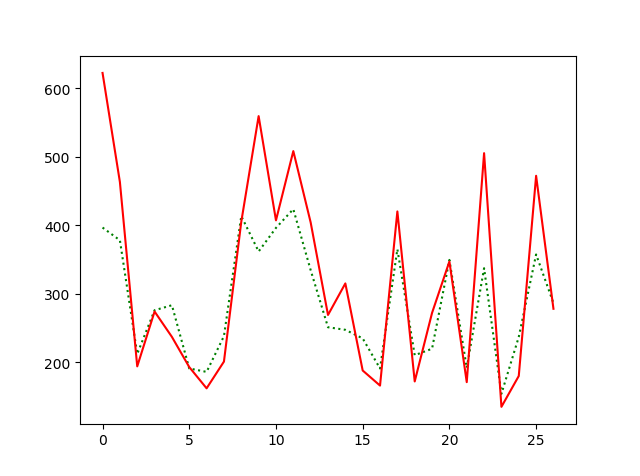
def load_data(file_name, sequence_length=10, split=0.8): df = pd.read_csv(file_name, sep=',', usecols=[1]) data_all = np.array(df).astype(float) scaler = MinMaxScaler() data_all = scaler.fit_transform(data_all) data = [] print("len(data_all)={}".format(len(data_all))) for i in range(len(data_all) - sequence_length - 1): print("i={}, (i + sequence_length + 1)={}".format(i, i + sequence_length + 1)) data.append(data_all[i: i + sequence_length + 1]) reshaped_data = np.array(data).astype('float64') np.random.shuffle(reshaped_data)#(133,11,1) # 对x进行统一归一化,而y则不归一化 #行全部取,11列中除了最后一列不取(133,10,1) x = reshaped_data[:, :-1] #行全部取,11列中只取最后一列(133,1) y = reshaped_data[:, -1] #分割数 split_boundary = int(reshaped_data.shape[0] * split) train_x = x[: split_boundary] test_x = x[split_boundary:] train_y = y[: split_boundary] test_y = y[split_boundary:] print("train_x={}, train_y={}, test_x={}, test_y={}".format(train_x.shape, train_y.shape, test_x.shape, test_y.shape,)) return train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, scaler def build_model(): # input_dim是输入的train_x的最后一个维度,train_x的维度为(n_samples, time_steps, input_dim) model = Sequential() # model.add(LSTM(input_dim=1, output_dim=50, return_sequences=True)) #2.2.2 keras model.add(LSTM(input_shape=(None, 1), units=100, return_sequences=False)) print(model.layers) # model.add(LSTM(units=100, return_sequences=False)) # model.add(Dense(output_dim=1)) model.add(Dense(units=1)) model.add(Activation('linear')) model.compile(loss='mse', optimizer='rmsprop') return model def train_model(train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y): model = build_model() try: # model.fit(train_x, train_y, batch_size=512, nb_epoch=30, validation_split=0.1) model.fit(train_x, train_y, batch_size=512, epochs=30, validation_split=0.1) predict = model.predict(test_x) predict = np.reshape(predict, (predict.size, )) except KeyboardInterrupt: print(predict) print(test_y) print("predict={},test_y={}".format(predict,test_y)) # print(test_y) try: fig = plt.figure(1) plt.plot(predict, 'r:') plt.plot(test_y, 'g-') plt.legend(['predict', 'true']) except Exception as e: print(e) return predict, test_y if __name__ == '__main__': train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, scaler = load_data('international-airline-passengers.csv') train_x = np.reshape(train_x, (train_x.shape[0], train_x.shape[1], 1)) test_x = np.reshape(test_x, (test_x.shape[0], test_x.shape[1], 1)) print("train_x.shape={},test_x.shape={}".format(train_x.shape,test_x.shape)) predict_y, test_y = train_model(train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y) #返回原来的对应的预测数值 predict_y = scaler.inverse_transform([[i] for i in predict_y]) test_y = scaler.inverse_transform(test_y) fig2 = plt.figure(2) plt.plot(predict_y, 'g:') plt.plot(test_y, 'r-') plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82

参考文献:
lstm中文网:https://keras.io/layers/recurrent/#lstm
https://blog.csdn.net/yyb19951015/article/details/79740869
https://blog.csdn.net/a819825294/article/details/54376781
https://blog.csdn.net/mebiuw/article/details/52705731
https://blog.csdn.net/hhtnan/article/details/80403146