- 1机器学习——有监督学习和无监督学习
- 2###51单片机学习(1)-----单片机烧录软件的使用,以及如何建立一个工程项目
- 32017-2018-2 20179225《网络攻防与实践》 第7周作业
- 4YOLO发展史
- 5【Azure】Azure 中的基于角色的访问控制 (RBAC) 与基于属性的访问控制 (ABAC)
- 612.0 Zookeeper 数据同步流程
- 7unity引擎简介——(1)Unity3D游戏开发流程与规范_unity3d开发流程
- 8unity在shader中获取当前摄像机的方向向量_unity 获取相机看向的方向
- 9Codeforces Round #698 (Div. 2)(A ~ F)6题全,超高质量题解)【每日亿题】2021/2/4_d - cron codeforces - 698e
- 10React16源码: React中event事件触发的源码实现
数据结构(栈)
赞
踩
一.什么是栈
1.栈的定义
栈是一种特殊类型的线性表,它的特点是仅允许在其一端进行插入(入栈)和删除(弹出)操作。这一端称为栈顶,而相对的另一端称为栈底。
2.栈的特点
栈遵循“后进先出”(LIFO)的原则,也就是说新加入的元素总是位于栈顶,先入栈的元素总是最后出栈。
3.基本操作
- 入栈(Push):将元素推送到栈顶
- 出栈(Pop):删除栈顶元素
① 入栈
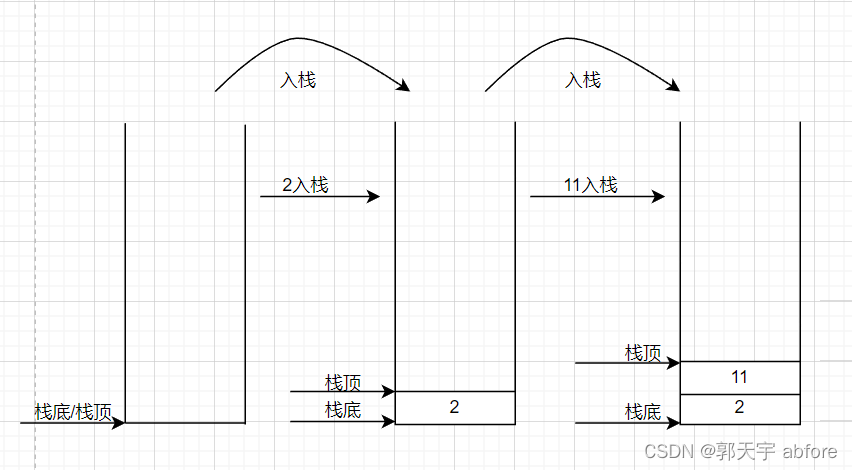
② 出栈

二. 栈的基本操作
1.顺序栈
顺序栈是一种使用数组实现的栈,也称为数组栈。其基本思路是通过数组来存储栈中的元素,并通过栈顶指针指示栈顶元素在数组中的位置。
- 代码实现
- public interface myStack<T>{
-
- // 入栈
- void push(T ele);
-
- // 出栈
- T pop();
-
- // 查看当前栈顶元素
- T peek();
-
- // 判断栈是否为空
- boolean isEmpty();
-
- // 获取栈内的元素个数
- int getSize();
-
- }
-
-
-
- public class MyArray<T> {
-
- private T[] arr;
- private int size;
- private int capacity; //容积
-
-
- // 构造方法
- public MyArray(int capacity) {
- // 入参判断
- if (capacity <= 0) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("输入容积异常!");
- }
- this.capacity = capacity;
- this.size = 0;
- this.arr = (T[]) new Object[this.capacity];
- }
-
- // 获取元素个数
- public int getSize() {
- return this.size;
- }
-
- // 获取容积
- public int getCapacity() {
- return this.capacity;
- }
-
- // 添加元素
- public void add(T item) {
- this.arr[this.size] = item;
- this.size++;
- }
-
- // 向指定位置添加元素
- public void addValueByIndex(int index, T value) {
- if (index < 0 || index > this.size) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常!");
- }
- if (this.size == this.capacity) {
- resize(this.capacity * 2);
- }
- for (int i = this.size - 1; i >= index; i--) {
- this.arr[i + 1] = this.arr[i];
- }
- this.arr[index] = value;
- this.size++;
- }
-
- // 扩容
- private void resize(int newCapacity) {
- T[] newArr = (T[]) new Object[newCapacity];
-
- for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
- newArr[i] = this.arr[i];
- }
- // 改变容器与容积
- this.arr = newArr;
- this.capacity = newCapacity;
- }
-
- // 判空
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return this.size == 0;
- }
-
- // 修改元素
- public void modifyValueByIndex(int index, T value) {
- // 入参判断
- if (index < 0 || index > capacity) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常!");
- }
- this.arr[index] = value;
- }
-
- // 获取指定位置的值
- public T getValueByIndex(int index) {
- // 入参判断
- if (index < 0 || index > capacity) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常!");
- }
- return this.arr[index];
- }
-
- // 查询指定的值在数组中是否存在,存在返回索引,不存在返回-1
- public int containsValue(T value) {
- for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
- if (value.equals(this.arr[i])) {
- return i;
- }
- }
- return -1;
- }
-
- // 删除指定位置的元素
- public T deleteValueByIndex(int index) {
- // 入参判断
- if (index < 0 || index > capacity) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引异常");
- }
- // 1.找到删除的位置的元素
- T deValue = this.arr[index];
- // 2.将删除元素之后的元素前移
- for (int j = index + 1; j < this.size; j++) {
- this.arr[j - 1] = this.arr[j];
- }
- this.size--;
- // 判断是否缩容
- if (this.size <= this.capacity / 4 && this.capacity / 2 > 0) {
- resize(this.capacity / 2);
- }
- return deValue;
- }
-
- public T removeFromLast() {
- T delVal = this.arr[this.size - 1];
- this.size--;
- return delVal;
- }
-
- public T getValue() {
- return getValueByIndex(this.size - 1);
- }
-
-
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- sb.append("{");
- for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
- sb.append(this.arr[i]);
- if (i < this.size - 1) {
- sb.append(",");
- }
- }
- sb.append("}");
- return sb.toString();
- }
-
- }
-
-
-
-
- // 以数组为栈的数据存储结构
- public class ArrStack<T> implements myStack<T> {
- private MyArray<T> data;
- int size;
-
- public ArrStack() {
- this.data = new MyArray<>(100);
- this.size = 0;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void push(T ele) {
- this.data.add(ele);
- this.size++;
- }
-
- @Override
- public T pop() {
- if(this.data.isEmpty()){
- return null;
- }
- return this.data.removeFromLast();
- }
-
- @Override
- public T peek() {
- return this.data.getValue();
- }
-
- @Override
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return this.size == 0;
- }
-
- @Override
- public int getSize() {
- return this.size;
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.Random;
-
- public class StackTest<T> {
-
- public void test(myStack<T> stack, ArrayList<T> list){
- long startTime = System.nanoTime();
- // 入栈
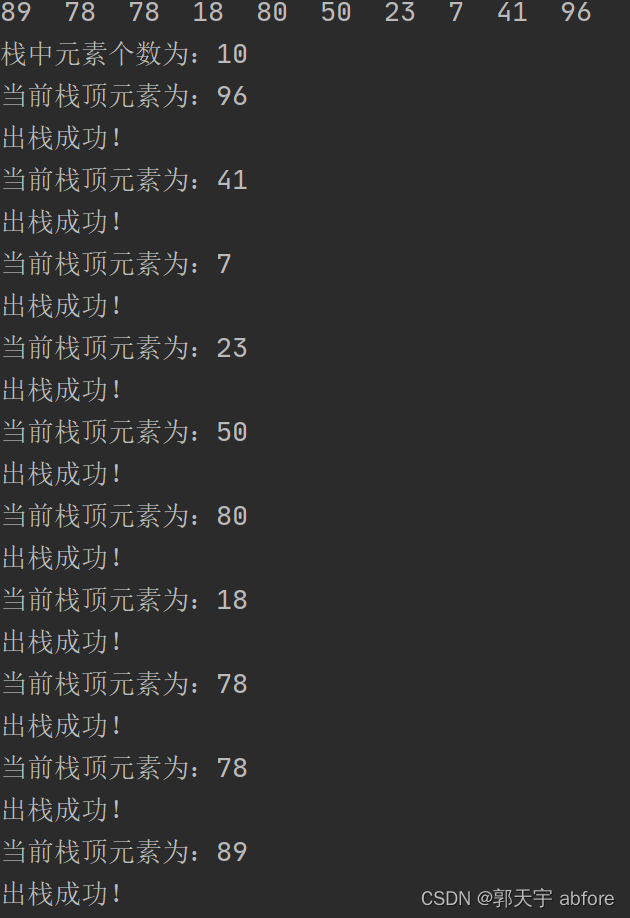
- for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
- stack.push(list.get(i));
- System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
- }
- System.out.println();
- // 获取栈中元素个数
- System.out.println("栈中元素个数为:" + stack.getSize());
- // 出栈
- for (int i = 0; i < stack.getSize(); i++) {
- // 查看栈顶元素
- System.out.println("当前栈顶元素为:" + stack.peek());
- stack.pop();
- if(!stack.isEmpty()){
- System.out.println("出栈成功!");
- }
- }
-
- long endTime = System.nanoTime();
- System.out.println("总耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0 + "s");
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
-
- StackTest<Integer> t = new StackTest<>();
- ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
- ArrStack<Integer> arrStack = new ArrStack<>();
- LinkedStack<Integer> stack = new LinkedStack<>();
- Random random = new Random();
- for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
- list.add(random.nextInt(100));
- }
- t.test(arrStack,list);
- }
- }

2.链表栈
链栈是一种基于链表实现的栈,其特点是无需事先分配固定长度的存储空间,栈的长度可以动态增长或缩小,避免了顺序栈可能存在的空间浪费和存储溢出问题。
- 代码实现(与上述顺序栈相比,只是数据存储的存储采用了链表的方式)
- import java.util.Optional;
-
- public class LinkedStack<T> implements myStack<T>{
- private LinkedList<T> data;
- public LinkedStack() {
- this.data = new LinkedList<>();
- }
-
- @Override
- public void push(T ele) {
- this.data.addInHead(ele);
- }
-
-
- @Override
- public T pop() {
- return (T) this.data.deleteHead();
- }
-
- @Override
- public T peek() {
- Optional<T> optional = this.data.getHead();
- if(optional.isPresent()){
- return (T) optional;
- }else{
- throw new RuntimeException();
- }
- }
-
- @Override
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return this.data.isEmpty();
- }
-
- @Override
- public int getSize() {
- return this.data.getSize();
- }
- }
-
-
-
- import java.util.Optional;
-
- public class LinkedList<T> {
-
- class Node<T> {
- T data;
- Node next;
-
- public Node(T data) {
- this.data = data;
- this.next = null;
- }
-
- public Node(T data, Node next) {
- this.data = data;
- this.next = next;
- }
-
- }
-
- private Node head;
- private int size;
-
- public LinkedList() {
- this.head = new Node(null);
- this.size = 0;
- }
-
- // 判空
- public boolean isEmpty() {
- return this.size == 0;
-
- }
-
- // 向头部添加元素
- public void addInHead(T data) {
- addInAny(0, data);
- }
-
- // 向尾部添加元素
- public void addInTail(T data) {
- addInAny(this.size, data);
- }
-
- // 向任意位置添加元素
- public void addInAny(int index, T data) {
- if (index < 0 || index > this.size) {
- throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("非法索引!");
- }
- Node node = new Node(data);
- // 寻找插入位置的前驱结点
- Node pre = this.head;
- for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
- pre = pre.next;
- }
- node.next = pre.next;
- pre.next = node;
- this.size++;
- }
-
- // 从链表中查找指定元素
- public boolean contains(T data) {
- Node curNode = this.head.next;
- while (curNode != null) {
- if (curNode.data.equals(data)) {
- return true;
- }
- curNode = curNode.next;
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- // 删除头结点
- public Optional deleteHead() {
- if (this.head.next == null) {
- return Optional.empty();
- }
- Node delNode = this.head.next;
- this.head.next = delNode.next;
- delNode.next = null;
- return Optional.ofNullable(delNode.data);
- }
-
- // 删除尾节点
- public Optional deleteTail() {
- if (this.head.next == null) {
- return Optional.empty();
- }
- Node curNode = this.head.next;
- while (curNode.next.next != null) {
- curNode = curNode.next;
- }
- Node delNode = curNode.next;
- curNode.next = delNode.next;
- delNode.next = null;
- this.size--;
- return Optional.ofNullable(delNode.data);
- }
-
- // 删除指定位置的元素
- public Optional deleteInIndex(int index) {
- if (this.head == null) {
- return Optional.empty();
- }
- if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
- throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引异常!");
- }
- Node pre = this.head;
- // 找删除结点的前驱结点
- int i = 0;
- while (i < index) {
- pre = pre.next;
- i++;
- }
- Node delNode = pre.next;
- pre.next = delNode.next;
- delNode.next = null;
- this.size--;
- return Optional.ofNullable(delNode.data);
- }
-
- // 根据值删除元素
- public int deleteByData(T val) {
- int count = 0;
- Node pre = this.head;
- while (pre.next != null) {
- Node curNode = pre.next;
- if (curNode.data.equals(val)) {
- pre.next = pre.next.next;
- curNode.next = null;
- this.size--;
- count++;
- } else {
- pre = pre.next;
- }
- }
- return count;
- }
-
-
- // 获取元素个数
- public int getSize() {
- return this.size;
- }
-
- // 获取链表头结点
- public Optional getHead() {
- if (this.head.next == null) {
- return Optional.empty();
-
- }
- return Optional.ofNullable(this.head.next.data);
- }
-
-
- //获取链表尾结点
- public Optional getTail() {
- if (this.head.next == null) {
- return Optional.empty();
- }
- Node curNode = this.head.next;
- while (curNode != null) {
- curNode = curNode.next;
- if (curNode.next == null)
- break;
- }
- return Optional.ofNullable(curNode.data);
- }
-
- // 获取任意位置的元素
- public Optional getIndex(int index) {
- if (this.head.next == null) {
- return Optional.empty();
- }
- if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
- throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引异常!");
- }
- Node curNode = this.head.next;
- int i = 0;
- while (i < index) {
- curNode = curNode.next;
- i++;
- }
- return Optional.ofNullable(curNode.data);
- }
-
-
- // 重写toString方法
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- Node curNode = this.head.next;
- while (curNode != null) {
- sb.append(curNode.data + "--->");
- curNode = curNode.next;
- }
- sb.append("null");
- return sb.toString();
- }
-
- }

三.栈的应用
栈常用来解决递归、括号匹配、表达式求值等问题。
1.例题一:有效的括号(20. 有效的括号 - 力扣(LeetCode))
① 题目分析:
我们遍历给定的字符串 s。当遇到一个左括号时,我们会期望在后续的遍历中,有一个相同类型的右括号将其闭合。由于后遇到的左括号要先闭合,因此我们可以将这个左括号放入栈中。
当我们遇到一个右括号时,我们需要将一个相同类型的左括号闭合。此时,我们可以取出栈顶的左括号并判断它们是否是相同类型的括号。如果不是相同的类型,或者栈中并没有左括号,那么字符串 s 无效。
② 代码实现
- import java.util.Stack;
-
- public class LeetCode_20 {
- public boolean isValid(String s) {
- Stack<Character> c = new Stack<>();
- // 入参判断
- if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
- return true;
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
- // 碰到左括号就入栈
- if (s.charAt(i) == '(' || s.charAt(i) == '[' || s.charAt(i) == '{') {
- c.push(s.charAt(i));
- }
- if (c.empty()) {
- return false;
- }
- // 没有相匹配的括号就return false
- if (((s.charAt(i) == ')' && c.pop() != '(') || (s.charAt(i) == ']' && c.pop() != '[') || (s.charAt(i) == '}' && c.pop() != '{'))) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return c.empty();
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s = "(()[]{}";
- LeetCode_20 leetCode_20 = new LeetCode_20();
- System.out.println(leetCode_20.isValid(s));
- }
- }



2.例题二:基本计算器II(227. 基本计算器 II - 力扣(LeetCode))
① 题目分析
由于乘除优先于加减计算,因此不妨考虑先进行所有乘除运算,并将这些乘除运算后的整数值放回原表达式的相应位置,则随后整个表达式的值,就等于所有整数加减后的值。
基于上述想法,我们可以用一个栈,保存这些进行乘除运算后的整数的值。对于加减号后的数字,将其直接入栈;对于乘除号后的数字,可以直接与栈顶元素计算,并替换栈顶元素为计算后的结果。
② 代码实现
- import java.util.Stack;
-
- public class LeetCode_227 {
- public int calculate(String s) {
- s = s.trim(); //去掉字符串两端的空格
- Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
- char c = '+';
- int num = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
- if (Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i))) { //判断当前字符是否是数字
- num = num * 10 + s.charAt(i) - '0'; //处理两位及两位以上的数字
- }
- // 判断当前字符是不是运算符号,对最后一个数字做特殊处理
- if ((!Character.isDigit(s.charAt(i)) && s.charAt(i) != ' ') || i == s.length() - 1) {
- switch (c) {
- case '+':
- stack.push(num);
- break;
- case '-':
- stack.push(-num);
- break;
- case '*':
- stack.push(stack.pop() * num);
- break;
- default:
- stack.push(stack.pop() / num);
- }
- c = s.charAt(i); //记录下当前的运算符号
- num = 0; //重置
- }
- }
- int res = 0;
- while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
- res += stack.pop();
- }
- return res;
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- String s = " 13+5 / 2 -3 ";
- LeetCode_227 leetCode_227 = new LeetCode_227();
- System.out.println("计算结果为:" + leetCode_227.calculate(s));
- }
- }


- 数据结构|队列的实现数据结构|队列的实现数据结构|队列的实现文章目录数据结构|队列的实现队列的概念及结构队列的实现队列的实现头文件,需要实现的接口Queue.h初始化队列队尾入队列【重点】队头出队列【重点】获取队列头部元素获取队列队尾元素获... [详细]
赞
踩
- 1.升序:建大堆;2.降序:建小堆。这种写法有两个缺点:1、先有一个堆的数据结构2、空间复杂度复杂度的消耗所以我们可以稍微改进一下,使得只要有一个数组就可以进行堆排序:假设要排一个升序:先使用向下调整的方式建一个大堆,然后再写一个循环,当e... [详细]
赞
踩
- 1.希尔排序是对直接插入排序的优化。2.当gap>1时都是预排序,目的是让数组更接近于有序。当gap==1时,数组已经接近有序的了,这样就会很快。这样整体而言,可以达到优化的效果。我们实现后可以进行性能测试的对比。【数据结构】八大排序目录1... [详细]
赞
踩
- 队列(Queue)是一种数据结构,是一种先进先出(First-In-First-Out,FIFO)的线性数据结构。它只允许在列表的一端进行插入操作(入队),在另一端进行删除操作(出队),即队头进行删除操作,队尾进行插入操作。队列常用的操作有... [详细]
赞
踩
- 生成树是通过对图的一次遍历(深度or广度)产生的,本质上是一棵树,它拥有连通图的所有顶点,且最少的边,同时一个图的生成树是它的极小连通子图,理论上说,如果这个图是一个连通图,那么连通分量和此时的极小图是一样的,但一般情况下,讨论连通分量是在... [详细]
赞
踩
- 在C语言中,结构体是一种用户自定义的数据类型,它允许我们将不同的数据类型组合在一起,创建一个具有自定义属性的复合数据类型。【数据结构】C语言结构体详解目录前言一、结构体的定义二、定义结构体变量三、结构体变量的初始化四、使用typedef声明... [详细]
赞
踩
- 先将第一个记录(设排序码为x)缓存,这样就空出了一个位置,改位置应该存放排序码不大于x的记录,将它放在第一个位置,这样,后面又空出一个位置,它应该放排序码大于x的记录,反过来又从第二个记录开始向右找一个排序码大于x的记录,将它放在后面空出的... [详细]
赞
踩
- 双向链表(DoublyLinkedList)是一种数据结构,它与单向链表相似,但每个节点不仅包含指向下一个节点的指针,还包含指向上一个节点的指针。双向链表的每个节点通常包含以下两个指针:-prev:指向上一个节点;-next:指向下一个节点... [详细]
赞
踩
- 无向图的边数组是一个对称矩阵。/*顶点类型应由用户定义*//*边上的权值类型应由用户定义*/#defineMAXVEX100 /*最大顶点数,应由用户定义*/#defineINFINITY65535 /*用65535来代表∞*... [详细]
赞
踩
- 特殊矩阵的压缩存储... [详细]
赞
踩
- 【数据结构】第二章——线性表(6)详细介绍了通过C语言实现单链表的基本操作……【数据结构】C语言实现单链表的基本操作单链表基本操作的实现导言一、查找操作1.1按位查找1.1.1按位查找的C语言实现1.1.2按位查找的时间复杂度1.2按值查找... [详细]
赞
踩
- 概念:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续非顺序的存储结构,但链表在逻辑上是连续的,顺序的,而数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针连接次序实现的。_单链表单链表文章目录一、单链表的定义及其结构1.1.概念1.2.单链表的结构1.3.单链表的特点二... [详细]
赞
踩
- 栈是一种先进后出(LIFO)的数据结构,在其中元素的的添加(称为“入栈”)和删除(称为“出栈”)仅在栈的顶部进行。因此,最后一个插入到栈中的元素是第一个从栈中删除的元素。它通常有两个主要操作:1.push:在栈的顶部插入一个元素。2.pop... [详细]
赞
踩
- 一,二叉树的顺序结构实现二叉树的顺序结构堆的概念及结构堆的接口实现堆的创建接口函数堆向上调整算法堆向下调整算法取堆顶元素建堆的时间复杂度堆的创建,向上调整建堆法向下调整建堆法,向上调整建堆的时间复杂度向下调整建堆的时间复杂度堆的应用堆排序建... [详细]
赞
踩
- 数据结构(DataStructure)是计算机存储、组织数据的方式,指相互之间存在一种或多种特定关系的数据元素的集合。算法(Algorithm)是定义良好的计算过程,它取一个或一组的值为输入,并产生出一个或一组值作为输出。简单来说算法就是一... [详细]
赞
踩
- 【数据结构】链队列的基本操作(C语言版)【数据结构】链队列的基本操作(C语言版)目录一、链队列1、链栈的定义:2、链栈的优缺点:二、链队列的基本操作算法(C语言) 1、宏定义 &nbs... [详细]
赞
踩
- 排序有内部排序和外部排序,这里八大排序就是内部排序,指直接插入,希尔,选择,堆排,冒泡,快排,归并,计数。附有动图解释和思维导图汇总_八大排序八大排序概述排序有内部排序和外部排序,内部排序是数据记录在内存中进行排序,这里八大排序就是内部排... [详细]
赞
踩
- 数组(Array)是一种用于存储多个相同类型的元素的数据结构。它可以被看作是一个容器,其中的元素按照一定的顺序排列,并且可以通过索引访问。数组的长度是固定的,一旦定义后,就不能再改变。矩阵(Matrix)是一个具有行和列的二维数组。它是由一... [详细]
赞
踩
- 注意:双链表不可随机存取,按位查找和按值查找操作都只能用遍历的方式实现,时间复杂度为。思路:从头结点开始,找到某个位序的前驱结点,对该前驱结点执行后插操作;思路:找到给定结点的前驱结点,再对该前驱结点执行后插操作;双链表的初始化(带头结点)... [详细]
赞
踩
- 数据量的增长与程序运行时间增长所呈现的比例函数,则称为时间渐进复杂度函数简称时间复杂度。链式存储的表状结构,链表可以分为:单向链表、双向链表、循环链表、内核链表。1.只要空间足够,理论上可以存放无限个数据。1.数据访问不太方便(空间不连续)... [详细]
赞
踩







