- 1vscode 好用的插件推荐_vscode tabnine
- 2git合并多条提交记录_git合并提交记录
- 3阿里云服务器Ubuntu系统安装配置PyTorch版深度学习环境_ubantu配置python运行环境
- 4【STM32 + HAL库】之 1 --- CubeMX 下载、安装_stm32cubemx下载
- 5简单整理SpringCloudAlibaba+SpringSecurity+JWT_springcloudalibaba+springsctiry
- 6WinServer2022 服务器之WSL(Linux 子系统)安装实践_适用于 linux 的 windows 子系统没有已安装的分发版。
- 7Android相机支持的预览格式详解_getsupportedpreviewformats
- 8操作系统课堂笔记_操作系统笔记
- 9TypeError [ERR_UNKNOWN_FILE_EXTENSION] [ERR_UNKNOWN_FILE_EXTENSION]: Unknown file extension “.json“_typeerror [err_unknown_file_extension]: unknown fi
- 10工作中常用工具推荐及资源分享_can i use前端兼容性自查工具下载安装
【学习笔记】简单的连通性状压DP——插头DP(不学以为是天书)
赞
踩
哈希链表
众所周知,哈希是有冲突的可能性的,而且在状态数越多,冲突的概率就越高。目前掌握的处理方案有多哈希,但仍有冲突的可能;
STL
\text{STL}
STL 直接整个记录下来,自带大常数和
log
\text{log}
log。
插头 DP 都不用,而是采取了哈希链表的方法。
具体而言就是将轮廓线上插头状态按一定的规则哈希成一个整数后,甩到其对应的链上。
形象地说,就是开了一定的哈希桶,然后哈希后的整数取模桶数,得到一个桶的编号,接着把这个轮廓线相应信息装成结构体,放到这个桶里。显然这个桶里很有可能有其余的轮廓线状态,那么就直接接在最后一个的后面。用前向星,数组来做。应该不会有人要刚vector吧
桶数随意,但肯定是越大且是个质数更好,因为后面定位轮廓线哈希位置的时候,是要从其所在桶里面开始一个一个遍历比较的,如果一个桶内太多轮廓线状态,遍历时间复杂度就有点要命了。
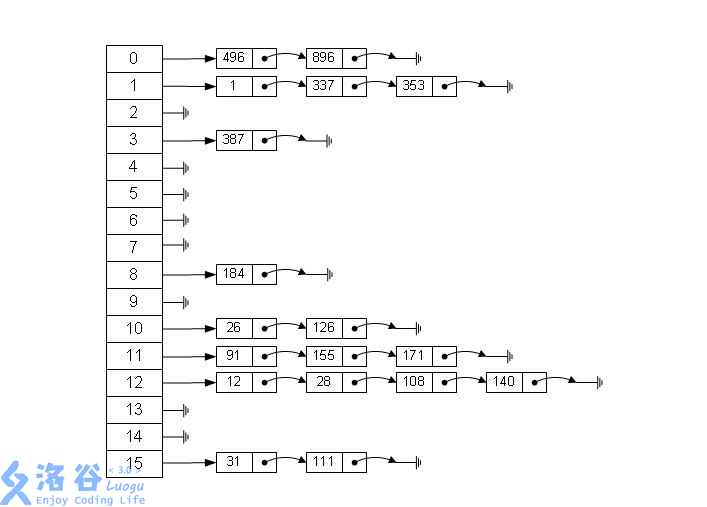
#define mod 299989
struct HashTable { int sta[2], dp[2], nxt; }Hash[300000];
void insert( int sta, int val ) {
int key = sta % mod;
for( int i = head[key];i;i = Hash[i].nxt )
if( sta == Hash[i].sta[now] ) { Hash[i].dp[now] += val; return; }
++ cnt[now];
Hash[cnt[now]].sta[now] = sta;
Hash[cnt[now]].dp[now] = val;
Hash[cnt[now]].nxt = head[key];
head[key] = cnt[now];
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
插头DP
概念
插头DP ,是一类基于连通性的状态压缩动态规划,用状压DP来处理联通问题。本质就是状压。
常见的联通问题:多回路问题、路径问题、简单回路问题、广义路径问题、生成树问题。
插头DP 一般是 逐格转移 的,少有逐行转移。
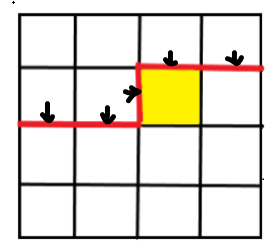
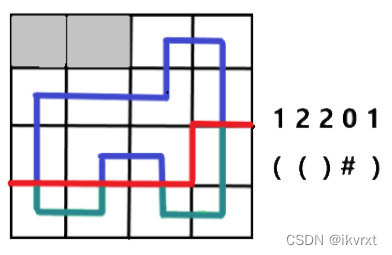
而逐格转移就是将格子划分成已转移的格子和未转移的格子,我们将起到这样分类作用的工具叫做 轮廓线。
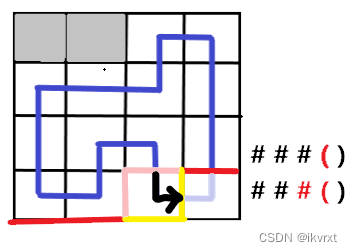
如图,红色线就是此时的轮廓线,当前在处理的格子是黄色格子,也就是说当前处理的格子也被划分到未转移的格子集合中。
不难发现, m m m 列却有 m + 1 m+1 m+1 个插头 / 轮廓线。
既然叫做 插头DP,那么什么又是插头呢?插头就是一个格子上下左右四个方向的插头,如图。
前面提到了主要是用来解决连通性问题的,一个格子与其余格子联通,怎么联通的
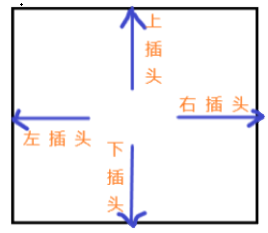
这个插头可以帮助我们知道两个相邻格子是怎样连接的,比如这个格子是和上面格子联通的,那么就是一条上下边,是通过这个格子的上插头完成的。还有如果这个格子恰好是联通的拐点,就是通过相邻插头,比如从左插头联通这个格子又从下插头连出去。
一个格子有四个插头,一个存在的插头表示 在它代表的方向上 能与相邻的格子连接(联通)。不存在就不能。
要求一个回路,也就意味着最后所有的非障碍格子通过插头连接成了一个连通块,那么久需要转移时记录格子的连通情况。
我们递推的时候就是依据轮廓线上插头的存在性,求出所有能转移到的合法状态。
形象地理解,每个格子可以看作一块块拼图,插头就是两块拼图之间的衔接。
在逐格转移中一般只记录轮廓线上的插头存在性,因为这些才与后面的格子是有可能直接相连的。

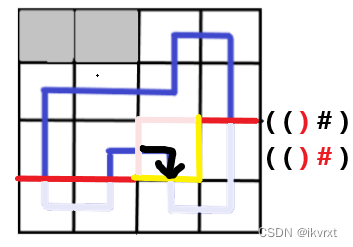
转移到新格子后,轮廓线也会相应的移动。如图。不难发现,同行内的移动只跟当前处理格子的左插头和上插头有关,并且是转移到自己的右插头和下插头。如果换行,发现唯一一个竖着的特殊插头是不会有的。但不影响,后面会提到。
所以当前格子合法状态至于上一次处理的格子有关,这里就可以采用滚动数组优化了,减少空间花费。
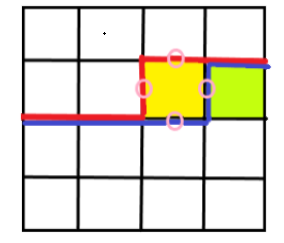
一般是设 d p [ i ] [ j ] [ s t a ] : ( i , j ) dp[i][j][sta]:(i,j) dp[i][j][sta]:(i,j) 位置时状态是 s t a sta sta 的方案数 / 代价和 等等。状压的就是轮廓线状态。
括号表示法 / 最小表示法
记录当前的联通状态 / 轮廓线上的插头状态,准确地讲是记录轮廓线上的状态,一般有两种方法。
括号表示法
当前已经联通的轮廓线上的插头,靠左边的是左括号,靠右边的是右括号。没有插头就另设字符。
轮廓线上从左到右 a , b , c , d a,b,c,d a,b,c,d 插头,如果 a , c a,c a,c 连通,并且与 b b b 不连通,那么 b , d b,d b,d 一定不连通。这个性质对所有的棋盘模型的问题都适用。
感性理解这很显然。
从左到右的排序是从左边的第一条轮廓线走到右边第一条轮廓线依次经历轮廓线的顺序。
最小表示法
同样地,从左到右的顺序,找到第一个不是障碍的轮廓线插头,然后找到跟这个插头联通的其余轮廓线插头,标记为第一个连通块,然后找第二个不是障碍且没有标记的插头,以此类推。
最小表示法比较好写,但括号表示法似乎时间更优秀。括号表示法是要每种情况分类讨论的,回路到还好只有三种状态,只用讨论九种,要是简单路径就会涉及到单独插头的问题,就是讨论十六种了。写挂的概率直线飙升。
最小表示法是有些情况可以合并成一个写。
且括号表示法的状态修改较为麻烦,都不一样,所以无法合并情况,而最小表示法比较暴力直接解码重编。
竖着的那条轮廓线比较特殊,所以我一般把它放到第 0 0 0 位。
例题
由于涉及到哈希压缩,一般都是用位运算,所以有些题目虽然是列的上限是 5 5 5 这种,我们也习惯开成 8 8 8 位的,这在最小表示法中很常见。
当你题目做多了过后,就会发现基本上都是一样的框架的感觉。
洛谷插头dp板题
此题就用括号表示法来做吧。
-
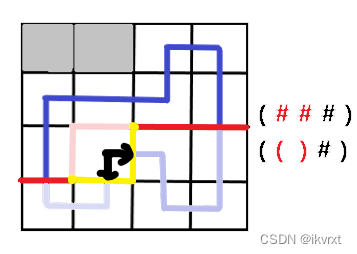
新建一个连通块
这个新建是就当前已操作过的格子而言的,但本题肯定是最后会联通成一个的,否则就不合法了。
能新建联通块当且仅当这个格子的上边轮廓线和左边轮廓线都没有插头。如图。
-
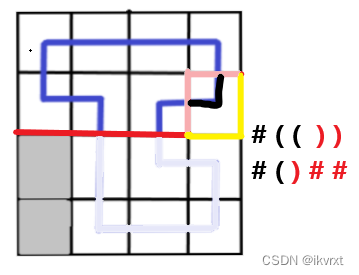
合并两个联通块
那么肯定是两个轮廓线都指了插头,这里必须做合并操作,不然就无法形成回路。
- 合并的是两个不同连通块的右括号,那么就要找两个右括号相对应的左括号更靠右的一个,变成右括号。
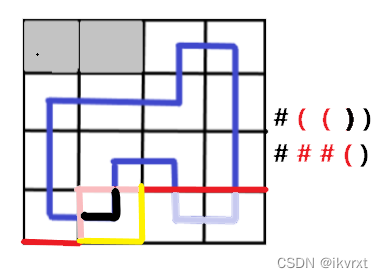
- 合并的是两个不同连通块的左括号,那么就要找两个左括号相对应的右括号更靠左的一个,变成左括号。
-
合并的是两个联通块的左右括号,直接擦去即可。
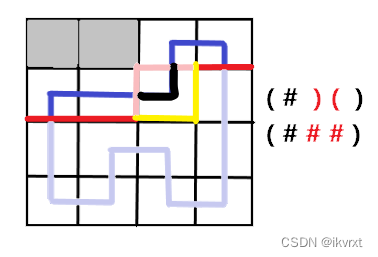 最后一个格子肯定是也是合并的这个类型,形成了完整的一条回路,这个时候还需要判断是否轮廓上一个插头都不存在,是否合法,然后统计答案。
最后一个格子肯定是也是合并的这个类型,形成了完整的一条回路,这个时候还需要判断是否轮廓上一个插头都不存在,是否合法,然后统计答案。
-
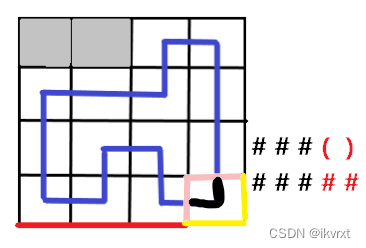
延续之前的联通情况。
-
不拐弯。
不拐弯最简单,不用改轮廓线情况,直接插入就行。
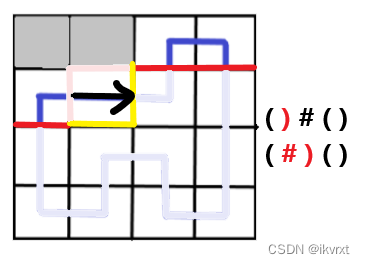
注意虽然下面这张图的括号表示法看似发生了改变,但是前面我提过,我喜欢把竖着个特殊轮廓线放在第 0 0 0 位,所以是没有改变的。
具体可见代码。
有的人就喜欢在 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j) 时, j j j 代表格子横着的轮廓线, j − 1 j-1 j−1 代表特殊的竖轮廓线。那可能就需要修改??
-
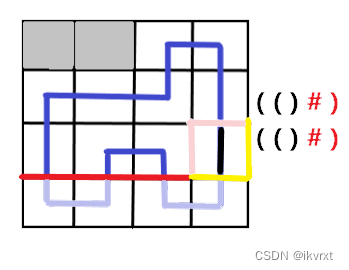
拐弯的。
拐弯的其实也简单,就是直接延续。虽然括号表示法看起来没有变化,但实际上是有轮廓线改变的。
具体可见代码。
-
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define mod 298999 #define int long long int n, m; int lst, now;//滚动 int head[300000], cnt[2]; //滚动的总合法方案数 bool mp[15][15]; //0 1 2 没有插头 左括号 右括号 struct HashTable { int sta[2], dp[2], nxt; }Hash[300000]; void insert( int sta, int val ) { int key = sta % mod; for( int i = head[key];i;i = Hash[i].nxt ) if( sta == Hash[i].sta[now] ) { Hash[i].dp[now] += val; return; } ++ cnt[now]; Hash[cnt[now]].sta[now] = sta; Hash[cnt[now]].dp[now] = val; Hash[cnt[now]].nxt = head[key]; head[key] = cnt[now]; }; struct node { int s[15]; }; node unZip( int sta ) { //解压 node code; code.s[0] = sta & 3; //单独的竖直轮廓线 for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) code.s[i] = ( sta >> ( i << 1 ) ) & 3; return code; } int Zip( node code ) { //压缩 int sta = 0; for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) sta |= ( code.s[i] << ( i << 1 ) ); sta |= code.s[0]; return sta; } signed main() { int ans = 0, Endx, Endy; scanf( "%lld %lld", &n, &m ); char ch[20]; for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) { scanf( "%s", ch + 1 ); for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) if( ch[j] == '.' ) mp[i][j] = 1, Endx = i, Endy = j; } insert( 0, 1 ); for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) { for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) { lst = now, now ^= 1, cnt[now] = 0; memset( head, 0, sizeof( head ) ); for( int k = 1;k <= cnt[lst];k ++ ) { node code = unZip( Hash[k].sta[lst] ); int Left = code.s[0], Up = code.s[j]; //左插头 上插头 int dp = Hash[k].dp[lst]; if( ! mp[i][j] ) { if( ! Left and ! Up ) insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( ! Left and ! Up ) { if( mp[i + 1][j] and mp[i][j + 1] ) { code.s[0] = 2, code.s[j] = 1; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } else if( ! Left and Up ) { if( mp[i + 1][j] ) insert( Zip( code ), dp ); if( mp[i][j + 1] ) { code.s[0] = Up, code.s[j] = 0; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } else if( Left and ! Up ) { if( mp[i][j + 1] ) insert( Zip( code ), dp ); if( mp[i + 1][j] ) { code.s[0] = 0, code.s[j] = Left; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } else if( Left == 1 and Up == 1 ) { //不属于同一个连通块 都是左括号 //得连起来 然后与这两个左括号匹配的右括号中较近的一个改成左括号 方法使用括号匹配 //显然肯定是左插头的匹配括号在右 呈包含关系 int p, tot = 1; for( p = j + 1;p <= m;p ++ ) { if( code.s[p] == 1 ) tot ++; if( code.s[p] == 2 ) tot --; if( ! tot ) break; } code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0, code.s[p] = 1; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( Left == 2 and Up == 2 ) { //显然肯定是上插头的匹配括号在左 呈包含关系 int p, tot = -1; for( p = j - 1;p;p -- ) { if( code.s[p] == 1 ) tot ++; if( code.s[p] == 2 ) tot --; if( ! tot ) break; } code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0, code.s[p] = 2; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( Left == 2 and Up == 1 ) { code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( Left == 1 and Up == 2 ) { //回路形成 code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0; bool flag = 0;//判断是否合法 for( int p = 0;p <= m;p ++ ) if( code.s[i] ) { flag = 1; break; } if( ! flag and i == Endx and j == Endy ) ans += dp; } } } } printf( "%lld\n", ans ); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
CITY
如果板题看懂了,就会发现这道题只是有些限制需要判定而已。直接改改就能过。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define mod 298999 #define int long long int n, m; int lst, now;//滚动 int head[300000], cnt[2]; //滚动的总合法方案数 int mp[15][15]; //0 1 2 没有插头 左括号 右括号 struct HashTable { int sta[2], dp[2], nxt; }Hash[300000]; void insert( int sta, int val ) { int key = sta % mod; for( int i = head[key];i;i = Hash[i].nxt ) if( sta == Hash[i].sta[now] ) { Hash[i].dp[now] += val; return; } ++ cnt[now]; Hash[cnt[now]].sta[now] = sta; Hash[cnt[now]].dp[now] = val; Hash[cnt[now]].nxt = head[key]; head[key] = cnt[now]; }; struct node { int s[15]; }; node unZip( int sta ) { //解压 node code; code.s[0] = sta & 3; //单独的竖直轮廓线 for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) code.s[i] = ( sta >> ( i << 1 ) ) & 3; return code; } int Zip( node code ) { //压缩 int sta = 0; for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) sta |= ( code.s[i] << ( i << 1 ) ); sta |= code.s[0]; return sta; } signed main() { int ans = 0, Endx, Endy; scanf( "%lld %lld", &n, &m ); char ch[20]; for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) { scanf( "%s", ch + 1 ); for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) { if( ch[j] == '#' ) continue; if( ch[j] == '.' ) mp[i][j] = 1; if( ch[j] == '-' ) mp[i][j] = 2; if( ch[j] == '|' ) mp[i][j] = 3; Endx = i, Endy = j; } } insert( 0, 1 ); for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) { for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) { lst = now, now ^= 1, cnt[now] = 0; memset( head, 0, sizeof( head ) ); for( int k = 1;k <= cnt[lst];k ++ ) { node code = unZip( Hash[k].sta[lst] ); int Left = code.s[0], Up = code.s[j]; //左插头 上插头 int dp = Hash[k].dp[lst]; if( ! mp[i][j] ) { if( ! Left and ! Up ) insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( ! Left and ! Up ) { if( mp[i][j] == 1 and mp[i + 1][j] and mp[i][j + 1] ) { code.s[0] = 2, code.s[j] = 1; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } else if( ! Left and Up ) { if( ( mp[i][j] == 3 or mp[i][j] == 1 ) and mp[i + 1][j] ) insert( Zip( code ), dp ); if( mp[i][j] == 1 and mp[i][j + 1] ) { code.s[0] = Up, code.s[j] = 0; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } else if( Left and ! Up ) { if( ( mp[i][j] == 1 or mp[i][j] == 2 ) and mp[i][j + 1] ) insert( Zip( code ), dp ); if( mp[i][j] == 1 and mp[i + 1][j] ) { code.s[0] = 0, code.s[j] = Left; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } else if( Left == 1 and Up == 1 and mp[i][j] == 1 ) { //不属于同一个连通块 都是左括号 //得连起来 然后与这两个左括号匹配的右括号中较近的一个改成左括号 方法使用括号匹配 //显然肯定是左插头的匹配括号在右 呈包含关系 int p, tot = 1; for( p = j + 1;p <= m;p ++ ) { if( code.s[p] == 1 ) tot ++; if( code.s[p] == 2 ) tot --; if( ! tot ) break; } code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0, code.s[p] = 1; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( Left == 2 and Up == 2 and mp[i][j] == 1 ) { //显然肯定是上插头的匹配括号在左 呈包含关系 int p, tot = -1; for( p = j - 1;p;p -- ) { if( code.s[p] == 1 ) tot ++; if( code.s[p] == 2 ) tot --; if( ! tot ) break; } code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0, code.s[p] = 2; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( Left == 2 and Up == 1 and mp[i][j] == 1 ) { code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( Left == 1 and Up == 2 and mp[i][j] == 1 ) { //回路形成 code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0; bool flag = 0;//判断是否合法 for( int p = 0;p <= m;p ++ ) if( code.s[i] ) { flag = 1; break; } if( ! flag and i == Endx and j == Endy ) ans += dp; } } } } printf( "%lld\n", ans ); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
ParkII
这道题就是求一条简单路径,那么就不要求一定是个回路,这个时候如果采取括号表示法讨论就有点多了。
最小表示法就较好写一点,多压一个路径的端点数量即可,最后的合法结果一定有且只有两个端点。也就是单独插头。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define mod 298999 #define ll long long int n, m, num, lst, now; //num:单独插头的个数 int cnt[2], head[300000]; int v[105][10]; struct HashTable { int sta[2], nxt;ll dp[2]; }Hash[300000]; void insert( int sta, ll val ) { int key = sta % mod; for( int i = head[key];i;i = Hash[i].nxt ) if( Hash[i].sta[now] == sta ) { Hash[i].dp[now] = max( val, Hash[i].dp[now] ); return; } ++ cnt[now]; Hash[cnt[now]].sta[now] = sta; Hash[cnt[now]].dp[now] = val; Hash[cnt[now]].nxt = head[key]; head[key] = cnt[now]; } struct node { int s[15]; }; int vis[10]; int Zip( node code ) { int sta = 0, tot = 0; for( int i = 1;i <= 6;i ++ ) vis[i] = 0; for( int i = 0;i <= m;i ++, sta <<= 3 ) { if( ! code.s[i] ) continue; if( ! vis[code.s[i]] ) vis[code.s[i]] = ++ tot; //找最小表示 sta |= vis[code.s[i]]; } sta |= num; return sta; } node unZip( int sta ) { node code; num = sta & 7; for( int i = m;~ i;i -- ) sta >>= 3, code.s[i] = sta & 7; return code; } int main() { scanf( "%d %d", &n, &m ); for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) scanf( "%d", &v[i][j] ); insert( 0, 0 ); for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) { lst = now, now ^= 1, cnt[now] = 0; memset( head, 0, sizeof( head ) ); for( int k = 1;k <= cnt[lst];k ++ ) { node code = unZip( Hash[k].sta[lst] ); ll dp = Hash[k].dp[lst] + v[i][j]; int left = code.s[0], up = code.s[j]; if( left and up ) { if( left ^ up ) { //两个插头不是同一个连通块 在(i,j)位置合并两个连通块 code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0;//横着和竖着的轮廓线都要被擦掉 for( int p = 0;p <= m;p ++ ) if( code.s[p] == up ) code.s[p] = left; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } else if( left or up ) { //合并两种情况 int id = left + up; if( i < n ) { code.s[j] = id, code.s[0] = 0; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } if( j < m ) { code.s[0] = id, code.s[j] = 0; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } if( num < 2 ) { code.s[j] = code.s[0] = 0, num ++; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } else { insert( Zip( code ), Hash[k].dp[lst] );//两边都没有插头 可以选择不选这个格子 if( i < n and j < m ) {//一个新连通块的中转点 code.s[j] = code.s[0] = 6;//用最大的填 保证编号不与已存在的连通块冲突 insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } if( num < 2 ) { //直接做一个单独插头 不是路径的起点就是终点 num ++; if( i < n ) { code.s[j] = 6, code.s[0] = 0; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } if( j < m ) { code.s[j] = 0, code.s[0] = 6; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } } } } ll ans = -1e18; for( int i = 1;i <= cnt[now];i ++ ) if( ( Hash[i].sta[now] & 7 ) == 2 ) ans = max( ans, Hash[i].dp[now] ); printf( "%lld\n", ans ); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
Tony’s Tour
还要简单一点,稍微转化一下,在棋盘最后加入两行。
.####.
. . . . . .
就让起点和终点联通形成回路了,且这两行的走法之有一种。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define mod 298999 bool mp[15][15]; int head[300000], cnt[2]; int lst, now, n, m; struct HashTable { int sta[2], dp[2], nxt; }Hash[300000]; void insert( int sta, int val ) { int key = sta % mod; for( int i = head[key];i;i = Hash[i].nxt ) if( Hash[i].sta[now] == sta ) { Hash[i].dp[now] += val; return; } ++ cnt[now]; Hash[cnt[now]].sta[now] = sta; Hash[cnt[now]].dp[now] = val; Hash[cnt[now]].nxt = head[key]; head[key] = cnt[now]; } struct node { int s[15]; }; int Zip( node code ) { int sta = 0; for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) sta |= ( code.s[i] << ( i << 1 ) ); sta |= code.s[0]; return sta; } node unZip( int sta ) { node code; code.s[0] = sta & 3; for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) code.s[i] = ( sta >> ( i << 1 ) ) & 3; return code; } int main() { char ch[15]; while( scanf( "%d %d", &n, &m ) and n and m ) { memset( mp, 0, sizeof( mp ) ); //因为多组数据且后面没有判断是否(i+1,j)(i,j+1)在棋盘内 所以要全都清空 避免上一轮的mp有的地方为1 for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) { scanf( "%s", ch + 1 ); for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) if( ch[j] == '.' ) mp[i][j] = 1; else mp[i][j] = 0; } mp[n + 1][1] = mp[n + 1][m] = 1; for( int i = 2;i < m;i ++ ) mp[n + 1][i] = 0; for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) mp[n + 2][i] = 1; n += 2; now = 0, cnt[now] = 0; memset( head, 0, sizeof( head ) ); insert( 0, 1 ); int ans = 0; for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) { lst = now, now ^= 1, cnt[now] = 0; memset( head, 0, sizeof( head ) ); for( int k = 1;k <= cnt[lst];k ++ ) { node code = unZip( Hash[k].sta[lst] ); int left = code.s[0], up = code.s[j]; int dp = Hash[k].dp[lst]; if( ! mp[i][j] ) { if( ! left and ! up ) insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( ! left and ! up ) { if( mp[i + 1][j] and mp[i][j + 1] ) { code.s[0] = 2, code.s[j] = 1; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } else if( ! left and up ) { if( mp[i + 1][j] ) insert( Zip( code ), dp ); if( mp[i][j + 1] ) { code.s[0] = up, code.s[j] = 0; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } else if( left and ! up ) { if( mp[i][j + 1] ) insert( Zip( code ), dp ); if( mp[i + 1][j] ) { code.s[j] = left, code.s[0] = 0; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } } else if( left == 2 and up == 1 ) { code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( left == 1 and up == 1 ) { int p, tot = 1; for( p = j + 1;p <= m;p ++ ) { if( code.s[p] == 1 ) tot ++; if( code.s[p] == 2 ) tot --; if( ! tot ) break; } code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0, code.s[p] = 1; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( left == 2 and up == 2 ) { int p, tot = -1; for( p = j - 1;p;p -- ) { if( code.s[p] == 1 ) tot ++; if( code.s[p] == 2 ) tot --; if( ! tot ) break; } code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0, code.s[p] = 2; insert( Zip( code ), dp ); } else if( left == 1 and up == 2 ) { code.s[0] = code.s[j] = 0; bool flag = 1; for( int p = 0;p <= m;p ++ ) if( code.s[p] ) { flag = 0; break; } if( flag and i == n and j == m ) ans += dp; } } } printf( "%d\n", ans ); } return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
Efficient Tree
也是轮廓线 D P DP DP 的题目,直接分类讨论就行。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define int long long #define mod 1000000007 struct node { int ans, cnt; node operator + ( node &now ) const { if( ans < now.ans ) return *this; else if( ans > now.ans ) return now; else return { ans, ( cnt + now.cnt ) % mod }; } node operator + ( int x ) { return { ans + x, cnt }; } node operator * ( int x ) { return { ans, cnt * x % mod }; }; }; int L[1000][1000], U[1000][1000]; int lst, now, n, m; int cnt[2], head[2500]; struct HASH { node dp[2]; int sta[2], nxt; }Hash[3000000]; void insert( int sta, node cost ) { int key = sta % 2333; for( int i = head[key];i;i = Hash[i].nxt ) if( Hash[i].sta[now] == sta ) { Hash[i].dp[now] = Hash[i].dp[now] + cost; return; } ++ cnt[now]; Hash[cnt[now]].sta[now] = sta; Hash[cnt[now]].dp[now] = cost; Hash[cnt[now]].nxt = head[key]; head[key] = cnt[now]; } int vis[10]; struct zip { int s[15]; zip(){ memset( s, 0, sizeof( s ) ); } /* 注意清空 因为第i行最后1列跳转到第i+行第1列的时候会访问到第0列的状态 呼应flag单独联通块的判断 */ }; int encode( zip code ) { int sta = 0, tot = 0; memset( vis, -1, sizeof( vis ) ); vis[0] = 0; for( int i = 1;i <= m;i ++ ) { if( vis[code.s[i]] == -1 ) vis[code.s[i]] = ++ tot; sta = ( sta << 3 ) | vis[code.s[i]]; } return sta; } zip decode( int sta ) { zip code; for( int i = m;i;i --, sta >>= 3 ) code.s[i] = sta & 7; return code; } signed main() { int T; scanf( "%lld", &T ); for( int t = 1;t <= T; t++ ) { scanf( "%lld %lld", &n, &m ); for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) for( int j = 2;j <= m;j ++ ) scanf( "%lld", &L[i][j] ); for( int i = 2;i <= n;i ++ ) for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) scanf( "%lld", &U[i][j] ); now = 0, cnt[now] = 0; memset( head, 0, sizeof( head ) ); insert( 0, { 0, 1 } ); for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) { lst = now, now ^= 1, cnt[now] = 0; memset( head, 0, sizeof( head ) ); for( int k = 1;k <= cnt[lst];k ++ ) { zip code = decode( Hash[k].sta[lst] ); int left = code.s[j - 1], up = code.s[j]; node dp = Hash[k].dp[lst]; bool flag = 1; for( int p = 0;p <= m;p ++ ) if( p ^ j and code.s[p] == up ) { flag = 0; break; } if( j > 1 and ! flag ) { code.s[j] = left; insert( encode( code ), { dp.ans + L[i][j], dp.cnt * 2 % mod } ); code.s[j] = up; } if( i > 1 ) insert( encode( code ), { dp.ans + U[i][j], dp.cnt * 2 % mod } ); if( ! flag ) { code.s[j] = 8; //赋值成不可能有的最小表示法到达的连通块编号数量 表示新开一个连通块 insert( encode( code ), dp ); code.s[j] = up; } if( i > 1 and j > 1 and left ^ up ) { for( int p = 0;p <= m;p ++ ) if( code.s[p] == left ) code.s[p] = up; insert( encode( code ), { dp.ans + U[i][j] + L[i][j], dp.cnt * 3 % mod } ); } } } node ans = { 0x7f7f7f7f, 0 }; for( int i = 1;i <= cnt[now];i ++ ) { bool flag = 1; zip code = decode( Hash[i].sta[now] ); for( int j = 1;j < m;j ++ ) flag &= ( code.s[j] == code.s[j + 1] ); if( flag ) ans = ans + Hash[i].dp[now]; } printf( "Case #%lld: %lld %lld\n", t, ans.ans, ans.cnt ); } return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
[CQOI2015]标识设计
BZOJ3934
将
L
L
L 形状的表示拆分成 一个只有下插头,一段上下插头,一个有上插头和右插头,一段左右插头,一个只有左插头 五个部分。
记录转折插头的个数和只有左插头的个数。
当转折插头个数有 3 3 3 个,只有左插头的个数已经有 2 2 2 个了。当现在这个格子成为左插头就形成了 3 3 3 个 L L L 标识。统计进入答案即可。
当然这一切都要在合法的情况下进行插头转移。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define int long long int lst, now, ans; int cnt[2], head[300000]; bool ch[50][50]; struct HashTable { int sta[2], dp[2], nxt; }Hash[700000]; void insert( int sta, int val ) { int key = sta % 299989; for( int i = head[key];i;i = Hash[i].nxt ) if( Hash[i].sta[now] == sta ) { Hash[i].dp[now] += val; return; } ++ cnt[now]; Hash[cnt[now]].sta[now] = sta; Hash[cnt[now]].dp[now] = val; Hash[cnt[now]].nxt = head[key]; head[key] = cnt[now]; } int zip( int x, int y, int z ) { return ( x << 4 ) | ( y << 2 ) | z; } signed main() { int n, m; char s[50]; scanf( "%lld %lld", &n, &m ); for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) { scanf( "%s", s + 1 ); for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) ch[i][j] = s[j] == '.'; } insert( 0, 1 ); for( int i = 1;i <= n;i ++ ) { for( int k = 1;k <= cnt[now];k ++ ) Hash[k].sta[now] = (Hash[k].sta[now] & 15) | (Hash[k].sta[now] >> 4 << 5); for( int j = 1;j <= m;j ++ ) { lst = now, now ^= 1, cnt[now] = 0; memset( head, 0, sizeof( head ) ); for( int k = 1;k <= cnt[lst];k ++ ) { int sta = Hash[k].sta[lst] >> 4, dp = Hash[k].dp[lst]; int left = sta >> j - 1 & 1, up = sta >> j & 1; int num = Hash[k].sta[lst] >> 2 & 3; int tot = Hash[k].sta[lst] & 3; if( up and left ) continue; //这个格子连出去两个格子 不合法 形成的是反L形 else if( ! ch[i][j] ) { if( ! left and ! up ) insert( zip(sta, num, tot), dp ); } else if( ! left and ! up ) { insert( zip(sta, num, tot), dp ); if( num < 3 and ch[i + 1][j] ) insert( zip((1 << j - 1) | sta, num + 1, tot), dp ); } else if( ! left and up ) { if( ch[i][j + 1] ) insert( zip(sta, num, tot), dp ); if( ch[i + 1][j] ) insert( zip(sta ^ (1 << j - 1) ^ (1 << j), num, tot), dp ); } else { if( ch[i][j + 1] ) insert( zip(sta ^ (1 << j - 1) ^ (1 << j), num, tot), dp ); if( num == 3 and tot == 2 ) ans += dp; else insert( zip(sta ^ (1 << j - 1), num, tot + 1), dp ); } } } } printf( "%lld\n", ans ); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 基于Anaconda虚拟环境写的python脚本,需要在windows10系统开机自启。_开机自启动conda开机自启动conda需求基于Anaconda虚拟环境写的python脚本,需要在windows10系统开机自启。方案1.写bat文... [详细]
赞
踩
- 如何在Ubuntu18.04.2LTS系统环境下运行,双击一个文件(快捷方式),运行一个程序,或者打开一个软件呢?1,首先,打开gedit软件,编写程序,如:gedit或者nautilus保存为test.sh文件。2选中文件,然后在屏幕左上... [详细]
赞
踩
- 之前发过几篇关于国产化相关的文章,把银河麒麟装进U盘、一问带你掌握通过storcli做RAID、统信UOS入门设置(简单使用说明)、国产操作系统统信UOS的简单故障维护等,包括今天发的国产PC,这些都和国产化、信创密不可分。国产化是国家级政... [详细]
赞
踩
- SHPR1寄存器:0xE000_ED18SHPR2寄存器:0xE000_ED1CPendsv:实现任务切换;SysTick:提供UcosIII的系统节拍。_ucosiiihardfaultucosiiihardfault目录*注意事项一、中... [详细]
赞
踩
- MCU进入HardFault的基础知识总结_stm32nmistm32nmi目录一、背景引入二、基础知识1.CortexM3内核2.寄存器组3.三级流水线4.异常一、背景引入在开发过程中,经常会遇到进入HardFault死循环的问题,主要原... [详细]
赞
踩
- 解决Cannotallocatememory【linux|java应用报错】Cannotallocatememory启动一个java应用报Cannotallocatememory,并且会生产一个hs_ess_pid.log文件。文件内容为:... [详细]
赞
踩
- CDN服务器会将JS文件缓存到多个地点的边缘服务器上,当用户请求访问时,就可以从离用户最近的边缘服务器获取缓存的JS文件,从而加快文件传输速度。服务器可以设置缓存时间,当某个JS文件被请求时,服务器会先检查该文件是否已缓存,如果已缓存且缓存... [详细]
赞
踩
- Jetsonnano环境搭建https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/downloadshttps://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/downloads1、基础设置1.1、使用... [详细]
赞
踩
- 在本文中,探讨了Python中利用PyPDF2和PyMuPDF这两个强大的PDF处理库进行文本提取的方法。通过PyPDF2,学习了基本的文本提取、指定页面范围提取以及文本搜索与高级提取的技巧。同时,探讨了如何将提取的文本保存到文本文件中,以... [详细]
赞
踩
- Python程序打包exe可执行软件教程_python打包exe还需要环境吗python打包exe还需要环境吗1、前言Python虽好,但是平时我们写的代码都是.py脚本文件,必须要在Python环境下才可以运行。如果一台电脑没有安装Pyt... [详细]
赞
踩
- Py2exe附带了完整的教程,可以用于您的应用程序。在样本位于Python\Lib\site-packages\py2exe\samples下。在作为一个简单的例子,这是我在我的应用程序中使用的setup.py来创建一个嵌入所有所需库的可执... [详细]
赞
踩
- 知识点线程安全,线程封闭,线程调度,同步容器,并发容器,AQS,J.U.C,等等高并发解决思路与手段扩容:水平扩容、垂直扩容缓存:Redis、Memcache、GuavaCache等队列:Kafka、RabitMQ、RocketMQ等应用拆... [详细]
赞
踩
- “::”作用域运算符(表明数据、方法的归属性问题)①程序与分析#include
usingnamespacestd;inta=10;//全局变量voidtest(){inta=20;//局部变量cout<<"局部变量a="... [详细] 赞
踩
- 之前的文章中介绍过STM32F0列的内部Flash读写《STM32CubeMX之内部Flash读写》,F1系列的也是一样的。而F4系列的单片机与F0和F1略有不同,HAL库对应的函数也不..._stm32f4内部flash读写stm32f4... [详细]
赞
踩
- c++支持在程序的任何地方定义变量,那么变量的作用域就极为重要,这些作用域是用大括号{}来划分的。例子:#include
usingnamespacestd;classA{ public: A(){cout<<"构造函数... [详细] 赞
踩
- 算法准备_leetcode30最佳算法leetcode30最佳算法本篇为LeetCode30刷,记录个人的学习记录,后续会补充字符串匹配No.1暴力算法(BF)采用逐个匹配的方法进行字符串的匹配,时间复杂度较为复杂,不推荐。No.2哈希值比... [详细]
赞
踩
- 项目中使用LPC1857单片机,这是一款NXP出的Cortex-M3内核MCU,我们做了一个bootload代码,用于IAP升级。在bootloader代码中我们使用了官方移植好的ucosIII系统,当检测到APP应用程序格式正确时,执行跳... [详细]
赞
踩
- NC248:左叶子之和(C++)NC248:左叶子之和(C++)1.题目描述2.题目分析我们以一个二叉树为例左叶子的特点是什么?是左节点并且没有左右孩子节点所以我们用leftnode保存root->lefe节点,判断条件为leftno... [详细]
赞
踩
- http://www.zhengdazhi.com/archives/1749书签栏信息收集二级域名查询,子域名查询-站长帮手网ZoomEye-CyberspaceSearchEngine360威胁情报中心SSL证书在线检测工具-中国数字证... [详细]
赞
踩
- 结构体的声明是有固定的结构的,所在位置一般在主函数的外面intx,y;//下面的数据类型是定义的结构体的数据类型//当然也可以一开始的时候就进行初始化如下:intx,y;}Node[N];//数组甚至还可以是单个变量。_运算符重构运算符重构... [详细]
赞
踩



