- 1【软件逆向-自动化】逆向工具大全
- 2素数判断_i*1.0>sqrt(n)
- 3浅谈云计算的意义_云计算产生的背景及意义
- 4linux找出占用内存,占用CPU资源最多的前10个进程_linux top 前10资源
- 5Ant-Design-Vue中,a-form-model嵌套table,并且支持动态添加输入框还支持表单校验
- 6vue封装一个多行文本展开收起的组件_vue文字的展开与收起 插件
- 7printf格式控制符_printf("%15.0s\n",country)
- 8数据库备份和还原 mysqldump(重点,重点,重点)分库备份_mysql mydumper备份的是完整数据库吗
- 9golang 面试题(十二)chan缓存池_chan面试go
- 10最小调整次数【C语言】_c语言求最小排序次数
详解tensorflow训练自己的数据集实现CNN图像分类_tensorflow1.x训练自己的数据集resnet图像分类
赞
踩
出处: https://www.jb51.net/article/134623.htm
利用卷积神经网络训练图像数据分为以下几个步骤
1.读取图片文件
2.产生用于训练的批次
3.定义训练的模型(包括初始化参数,卷积、池化层等参数、网络)
4.训练
1 读取图片文件
- def get_files(filename):
- class_train = []
- label_train = []
- for train_class in os.listdir(filename):
- for pic in os.listdir(filename+train_class):
- class_train.append(filename+train_class+'/'+pic)
- label_train.append(train_class)
- temp = np.array([class_train,label_train])
- temp = temp.transpose()
- #shuffle the samples
- np.random.shuffle(temp)
- #after transpose, images is in dimension 0 and label in dimension 1
- image_list = list(temp[:,0])
- label_list = list(temp[:,1])
- label_list = [int(i) for i in label_list]
- #print(label_list)
- return image_list,label_list

这里文件名作为标签,即类别(其数据类型要确定,后面要转为tensor类型数据)。
然后将image和label转为list格式数据,因为后边用到的的一些tensorflow函数接收的是list格式数据。
2 产生用于训练的批次
- def get_batches(image,label,resize_w,resize_h,batch_size,capacity):
- #convert the list of images and labels to tensor
- image = tf.cast(image,tf.string)
- label = tf.cast(label,tf.int64)
- queue = tf.train.slice_input_producer([image,label])
- label = queue[1]
- image_c = tf.read_file(queue[0])
- image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_c,channels = 3)
- #resize
- image = tf.image.resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(image,resize_w,resize_h)
- #(x - mean) / adjusted_stddev
- image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(image)
-
- image_batch,label_batch = tf.train.batch([image,label],
- batch_size = batch_size,
- num_threads = 64,
- capacity = capacity)
- images_batch = tf.cast(image_batch,tf.float32)
- labels_batch = tf.reshape(label_batch,[batch_size])
- return images_batch,labels_batch

首先使用tf.cast转化为tensorflow数据格式,使用tf.train.slice_input_producer实现一个输入的队列。
label不需要处理,image存储的是路径,需要读取为图片,接下来的几步就是读取路径转为图片,用于训练。
CNN对图像大小是敏感的,第10行图片resize处理为大小一致,12行将其标准化,即减去所有图片的均值,方便训练。
接下来使用tf.train.batch函数产生训练的批次。
最后将产生的批次做数据类型的转换和shape的处理即可产生用于训练的批次。
3 定义训练的模型
(1)训练参数的定义及初始化
- def init_weights(shape):
- return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape,stddev = 0.01))
- #init weights
- weights = {
- "w1":init_weights([3,3,3,16]),
- "w2":init_weights([3,3,16,128]),
- "w3":init_weights([3,3,128,256]),
- "w4":init_weights([4096,4096]),
- "wo":init_weights([4096,2])
- }
-
- #init biases
- biases = {
- "b1":init_weights([16]),
- "b2":init_weights([128]),
- "b3":init_weights([256]),
- "b4":init_weights([4096]),
- "bo":init_weights([2])
- }

CNN的每层是y=wx+b的决策模型,卷积层产生特征向量,根据这些特征向量带入x进行计算,因此,需要定义卷积层的初始化参数,包括权重和偏置。其中第8行的参数形状后边再解释。
(2)定义不同层的操作
- def conv2d(x,w,b):
- x = tf.nn.conv2d(x,w,strides = [1,1,1,1],padding = "SAME")
- x = tf.nn.bias_add(x,b)
- return tf.nn.relu(x)
-
- def pooling(x):
- return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize = [1,2,2,1],strides = [1,2,2,1],padding = "SAME")
-
- def norm(x,lsize = 4):
- return tf.nn.lrn(x,depth_radius = lsize,bias = 1,alpha = 0.001/9.0,beta = 0.75)
这里只定义了三种层,即卷积层、池化层和正则化层
(3)定义训练模型
- def mmodel(images):
- l1 = conv2d(images,weights["w1"],biases["b1"])
- l2 = pooling(l1)
- l2 = norm(l2)
- l3 = conv2d(l2,weights["w2"],biases["b2"])
- l4 = pooling(l3)
- l4 = norm(l4)
- l5 = conv2d(l4,weights["w3"],biases["b3"])
- #same as the batch size
- l6 = pooling(l5)
- l6 = tf.reshape(l6,[-1,weights["w4"].get_shape().as_list()[0]])
- l7 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(l6,weights["w4"])+biases["b4"])
- soft_max = tf.add(tf.matmul(l7,weights["wo"]),biases["bo"])
- return soft_max
模型比较简单,使用三层卷积,第11行使用全连接,需要对特征向量进行reshape,其中l6的形状为[-1,w4的第1维的参数],因此,将其按照“w4”reshape的时候,要使得-1位置的大小为batch_size,这样,最终再乘以“wo”时,最终的输出大小为[batch_size,class_num]
(4)定义评估量
- def loss(logits,label_batches):
- cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=label_batches)
- cost = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)
- return cost
-
- 首先定义损失函数,这是用于训练最小化损失的必需量
- def get_accuracy(logits,labels):
- acc = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits,labels,1)
- acc = tf.cast(acc,tf.float32)
- acc = tf.reduce_mean(acc)
- return acc
评价分类准确率的量,训练时,需要loss值减小,准确率增加,这样的训练才是收敛的。
(5)定义训练方式
- def training(loss,lr):
- train_op = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(lr,0.9).minimize(loss)
- return train_op
有很多种训练方式,可以自行去官网查看,但是不同的训练方式可能对应前面的参数定义不一样,需要另行处理,否则可能报错。
4 训练
- def run_training():
- data_dir = 'C:/Users/wk/Desktop/bky/dataSet/'
- image,label = inputData.get_files(data_dir)
- image_batches,label_batches = inputData.get_batches(image,label,32,32,16,20)
- p = model.mmodel(image_batches)
- cost = model.loss(p,label_batches)
- train_op = model.training(cost,0.001)
- acc = model.get_accuracy(p,label_batches)
-
- sess = tf.Session()
- init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
- sess.run(init)
-
- coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
- threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess = sess,coord = coord)
-
- try:
- for step in np.arange(1000):
- print(step)
- if coord.should_stop():
- break
- _,train_acc,train_loss = sess.run([train_op,acc,cost])
- print("loss:{} accuracy:{}".format(train_loss,train_acc))
- except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
- print("Done!!!")
- finally:
- coord.request_stop()
- coord.join(threads)
- sess.close()

神经网络训练的时候,我们需要将模型保存下来,方便后面继续训练或者用训练好的模型进行测试。因此,我们需要创建一个saver保存模型。
- def run_training():
- data_dir = 'C:/Users/wk/Desktop/bky/dataSet/'
- log_dir = 'C:/Users/wk/Desktop/bky/log/'
- image,label = inputData.get_files(data_dir)
- image_batches,label_batches = inputData.get_batches(image,label,32,32,16,20)
- print(image_batches.shape)
- p = model.mmodel(image_batches,16)
- cost = model.loss(p,label_batches)
- train_op = model.training(cost,0.001)
- acc = model.get_accuracy(p,label_batches)
-
- sess = tf.Session()
- init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
- sess.run(init)
- saver = tf.train.Saver()
- coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
- threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess = sess,coord = coord)
-
- try:
- for step in np.arange(1000):
- print(step)
- if coord.should_stop():
- break
- _,train_acc,train_loss = sess.run([train_op,acc,cost])
- print("loss:{} accuracy:{}".format(train_loss,train_acc))
- if step % 100 == 0:
- check = os.path.join(log_dir,"model.ckpt")
- saver.save(sess,check,global_step = step)
- except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
- print("Done!!!")
- finally:
- coord.request_stop()
- coord.join(threads)
- sess.close()

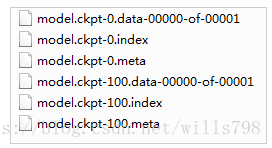
训练好的模型信息会记录在checkpoint文件中,大致如下:
model_checkpoint_path: "C:/Users/wk/Desktop/bky/log/model.ckpt-100"
all_model_checkpoint_paths: "C:/Users/wk/Desktop/bky/log/model.ckpt-0"
all_model_checkpoint_paths: "C:/Users/wk/Desktop/bky/log/model.ckpt-100"
其余还会生成一些文件,分别记录了模型参数等信息,后边测试的时候程序会读取checkpoint文件去加载这些真正的数据文件
构建好神经网络进行训练完成后,如果用之前的代码直接进行测试,会报shape不符合的错误,大致是卷积层的输入与图像的shape不一致,这是因为上篇的代码,将weights和biases定义在了模型的外面,调用模型的时候,出现valueError的错误。
因此,我们需要将参数定义在模型里面,加载训练好的模型参数时,训练好的参数才能够真正初始化模型。重写模型函数如下
- def mmodel(images,batch_size):
- with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope:
- weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
- shape = [3,3,3, 16],
- dtype = tf.float32,
- initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32))
- biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
- shape=[16],
- dtype=tf.float32,
- initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
- conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, weights, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding='SAME')
- pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
- conv1 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name= scope.name)
- with tf.variable_scope('pooling1_lrn') as scope:
- pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],
- padding='SAME', name='pooling1')
- norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9.0,
- beta=0.75,name='norm1')
- with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope:
- weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
- shape=[3,3,16,128],
- dtype=tf.float32,
- initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1,dtype=tf.float32))
- biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
- shape=[128],
- dtype=tf.float32,
- initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
- conv = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, weights, strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
- pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
- conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name='conv2')
- with tf.variable_scope('pooling2_lrn') as scope:
- norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, depth_radius=4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9.0,
- beta=0.75,name='norm2')
- pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(norm2, ksize=[1,2,2,1], strides=[1,1,1,1],
- padding='SAME',name='pooling2')
- with tf.variable_scope('local3') as scope:
- reshape = tf.reshape(pool2, shape=[batch_size, -1])
- dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value
- weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
- shape=[dim,4096],
- dtype=tf.float32,
- initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32))
- biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
- shape=[4096],
- dtype=tf.float32,
- initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
- local3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weights) + biases, name=scope.name)
- with tf.variable_scope('softmax_linear') as scope:
- weights = tf.get_variable('softmax_linear',
- shape=[4096, 2],
- dtype=tf.float32,
- initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.005,dtype=tf.float32))
- biases = tf.get_variable('biases',
- shape=[2],
- dtype=tf.float32,
- initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
- softmax_linear = tf.add(tf.matmul(local3, weights), biases, name='softmax_linear')
- return softmax_linear

测试训练好的模型
首先获取一张测试图像
- def get_one_image(img_dir):
- image = Image.open(img_dir)
- plt.imshow(image)
- image = image.resize([32, 32])
- image_arr = np.array(image)
- return image_arr
加载模型,计算测试结果
- def test(test_file):
- log_dir = 'C:/Users/wk/Desktop/bky/log/'
- image_arr = get_one_image(test_file)
-
- with tf.Graph().as_default():
- image = tf.cast(image_arr, tf.float32)
- image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(image)
- image = tf.reshape(image, [1,32, 32, 3])
- print(image.shape)
- p = model.mmodel(image,1)
- logits = tf.nn.softmax(p)
- x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape = [32,32,3])
- saver = tf.train.Saver()
- with tf.Session() as sess:
- ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(log_dir)
- if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
- global_step = ckpt.model_checkpoint_path.split('/')[-1].split('-')[-1]
- saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
- print('Loading success)
- else:
- print('No checkpoint')
- prediction = sess.run(logits, feed_dict={x: image_arr})
- max_index = np.argmax(prediction)
- print(max_index)

- 在本章中,我们涵盖了各种技术,您可能想知道应该使用哪些技术。这取决于任务,目前还没有明确的共识,但我发现表11-3中的配置在大多数情况下都能很好地工作,而不需要太多的超参数调整。尽管如此,请不要将这些默认值视为硬性规则!表11-3.默认DN... [详细]
赞
踩
- 小白入门深度学习,教你搭建一个简单的神经网络,五分钟入门_fashion_mnist.load_data()fashion_mnist.load_data()文章目录前言一、数据集加载以及数据集的预处理二、全连接网络层构建三、计算梯度和代价... [详细]
赞
踩
- 原文:BuildingMachineLearningProjectswithTensorFlow协议:CCBY-NC-SA4.0译者:飞龙本文来自【ApacheCN深度学习译文集】,采用译后编辑(MTPE)流程来尽可能提升效率。不要担心自己... [详细]
赞
踩
- Keras卷积神经网络识别手写数字卷积神经网络和多层感知机的差别就在于CNN多了卷积层和池化层,这两个层的层数可以自行设定,和用多层感知机相比只有建立卷积层那里不同fromkeras.datasetsimportmnistfromkeras... [详细]
赞
踩
- http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/vwSlxxD5Ov0XwQCKy1oyuQ深度学习大讲堂是由中科视拓运营的高质量原创内容平台,邀请学术界、工业界一线专家撰稿,致力于推送人工智能与深度学习最新技术、产品和活动信息!4.T... [详细]
赞
踩
- OpenCV实现手势音量控制:使用OpenCV和mediapipe库进行手势识别,并利用手势距离控制电脑音量。_info:createdtensorflowlitexnnpackdelegateforcpu.info:createdtens... [详细]
赞
踩
- 在Tensorflow训练模型时报错提示:failedtoallocate3.77G(4046333952bytes)fromdevice:CUDA_ERROR_OUT_OF_MEMORY:outofmemory虽然会报出显存溢出问题,但不... [详细]
赞
踩