- 1C语言自定义数据类型(C语言十)_c语言类型是在哪里定义的
- 2ECharts 点击非图表区域的点击事件不触发问题_chart.getzr()不起作用
- 3Springboot+thymeleaf动态修改权限菜单_thymeleaf动态导航栏
- 4Python_文本分析入门_SnowNLP(1)_snownlp函数
- 5Huggingface中Transformer模型使用_huggingface transformer库
- 6FPGA_ZYNQ_XADC_fpga自带adc是多少位的
- 7adb查看设备信息_adb查看设备制造商
- 8Ubuntu配置DNS服务器--bind_ubuntu bind
- 9【华为OD机试】芯片资源限制(贪心算法—Java&Python&C++&JS实现)
- 10xtrabackup全量增量备份+全量增量恢复+binlog增量恢复
复现论文之对YOLOV7添加可变卷积网络与注意力机制_yolov7颈部嵌入sa注意力模块
赞
踩
首先,让我们先看一看这篇论文主要的修改地方

这篇论文中,在yolov7的backbone最后一个部分引入了可变卷积结构,我们先来了解一下yolov7的大概结构是什么样子的。

仔细观察两副图,我们可以看到论文其实是对yolov7最后stage5部分的Transition_Block和Multi_Concat_Block进行了变换,在这里引入了可变卷积结构。
其次,论文在neck中引入了SimAm注意力机制,注意力机制的添加可以参考我的上一篇文章:
接下来我们继续替换backbone结构中的 Transition_Block和Multi_Concat_Block。
首先我们需要知道在yolov7中Transition_Block和Multi_Concat_Block是具体是什么样子的:

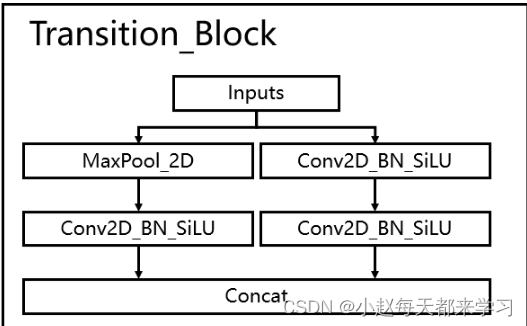
可以看到Transition_Block有着非常多的卷积过程,类似于残差结构,而在Multi_Concat_Block中左边是maxpool操作过程,右边是两次卷积,都会使特征图维度变小,最后进行Concat。
随后我们来看看论文中修改的地方:
论文中在Transition_Block中对右边连续的卷积进行了替换,替换为了可变性卷积结构;
在Multi_Concat_Block中将两个卷积中后面的一个卷积替换为了可变性卷积结构,接下来我们在代码中看看怎么体现:
首先我们先导入我们的可变卷积结构代码:
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
-
-
- class DeformConv2d(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, inc, outc, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=None, modulation=False):
- """
- Args:
- modulation (bool, optional): If True, Modulated Defomable Convolution (Deformable ConvNets v2).
- """
- super(DeformConv2d, self).__init__()
- self.kernel_size = kernel_size
- self.padding = padding
- self.stride = stride
- self.zero_padding = nn.ZeroPad2d(padding)
- # conv则是实际进行的卷积操作,注意这里步长设置为卷积核大小,因为与该卷积核进行卷积操作的特征图是由输出特征图中每个点扩展为其对应卷积核那么多个点后生成的。
- self.conv = nn.Conv2d(inc, outc, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=kernel_size, bias=bias)
- # p_conv是生成offsets所使用的卷积,输出通道数为卷积核尺寸的平方的2倍,代表对应卷积核每个位置横纵坐标都有偏移量。
- self.p_conv = nn.Conv2d(inc, 2 * kernel_size * kernel_size, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride)
- nn.init.constant_(self.p_conv.weight, 0)
- self.p_conv.register_backward_hook(self._set_lr)
-
- self.modulation = modulation # modulation是可选参数,若设置为True,那么在进行卷积操作时,对应卷积核的每个位置都会分配一个权重。
- if modulation:
- self.m_conv = nn.Conv2d(inc, kernel_size * kernel_size, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=stride)
- nn.init.constant_(self.m_conv.weight, 0)
- self.m_conv.register_backward_hook(self._set_lr)
-
- @staticmethod
- def _set_lr(module, grad_input, grad_output):
- grad_input = (grad_input[i] * 0.1 for i in range(len(grad_input)))
- grad_output = (grad_output[i] * 0.1 for i in range(len(grad_output)))
-
- def forward(self, x):
- offset = self.p_conv(x)
- if self.modulation:
- m = torch.sigmoid(self.m_conv(x))
-
- dtype = offset.data.type()
- ks = self.kernel_size
- N = offset.size(1) // 2
-
- if self.padding:
- x = self.zero_padding(x)
-
- # (b, 2N, h, w)
- p = self._get_p(offset, dtype)
-
- # (b, h, w, 2N)
- p = p.contiguous().permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- q_lt = p.detach().floor()
- q_rb = q_lt + 1
-
- q_lt = torch.cat([torch.clamp(q_lt[..., :N], 0, x.size(2) - 1), torch.clamp(q_lt[..., N:], 0, x.size(3) - 1)],
- dim=-1).long()
- q_rb = torch.cat([torch.clamp(q_rb[..., :N], 0, x.size(2) - 1), torch.clamp(q_rb[..., N:], 0, x.size(3) - 1)],
- dim=-1).long()
- q_lb = torch.cat([q_lt[..., :N], q_rb[..., N:]], dim=-1)
- q_rt = torch.cat([q_rb[..., :N], q_lt[..., N:]], dim=-1)
-
- # clip p
- p = torch.cat([torch.clamp(p[..., :N], 0, x.size(2) - 1), torch.clamp(p[..., N:], 0, x.size(3) - 1)], dim=-1)
-
- # bilinear kernel (b, h, w, N)
- g_lt = (1 + (q_lt[..., :N].type_as(p) - p[..., :N])) * (1 + (q_lt[..., N:].type_as(p) - p[..., N:]))
- g_rb = (1 - (q_rb[..., :N].type_as(p) - p[..., :N])) * (1 - (q_rb[..., N:].type_as(p) - p[..., N:]))
- g_lb = (1 + (q_lb[..., :N].type_as(p) - p[..., :N])) * (1 - (q_lb[..., N:].type_as(p) - p[..., N:]))
- g_rt = (1 - (q_rt[..., :N].type_as(p) - p[..., :N])) * (1 + (q_rt[..., N:].type_as(p) - p[..., N:]))
-
- # (b, c, h, w, N)
- x_q_lt = self._get_x_q(x, q_lt, N)
- x_q_rb = self._get_x_q(x, q_rb, N)
- x_q_lb = self._get_x_q(x, q_lb, N)
- x_q_rt = self._get_x_q(x, q_rt, N)
-
- # (b, c, h, w, N)
- x_offset = g_lt.unsqueeze(dim=1) * x_q_lt + \
- g_rb.unsqueeze(dim=1) * x_q_rb + \
- g_lb.unsqueeze(dim=1) * x_q_lb + \
- g_rt.unsqueeze(dim=1) * x_q_rt
-
- # modulation
- if self.modulation:
- m = m.contiguous().permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
- m = m.unsqueeze(dim=1)
- m = torch.cat([m for _ in range(x_offset.size(1))], dim=1)
- x_offset *= m
-
- x_offset = self._reshape_x_offset(x_offset, ks)
- out = self.conv(x_offset)
-
- return out
-
- def _get_p_n(self, N, dtype):
- # 由于卷积核中心点位置是其尺寸的一半,于是中心点向左(上)方向移动尺寸的一半就得到起始点,向右(下)方向移动另一半就得到终止点
- p_n_x, p_n_y = torch.meshgrid(
- torch.arange(-(self.kernel_size - 1) // 2, (self.kernel_size - 1) // 2 + 1),
- torch.arange(-(self.kernel_size - 1) // 2, (self.kernel_size - 1) // 2 + 1))
- # (2N, 1)
- p_n = torch.cat([torch.flatten(p_n_x), torch.flatten(p_n_y)], 0)
- p_n = p_n.view(1, 2 * N, 1, 1).type(dtype)
-
- return p_n
-
- def _get_p_0(self, h, w, N, dtype):
- # p0_y、p0_x就是输出特征图每点映射到输入特征图上的纵、横坐标值。
- p_0_x, p_0_y = torch.meshgrid(
- torch.arange(1, h * self.stride + 1, self.stride),
- torch.arange(1, w * self.stride + 1, self.stride))
-
- p_0_x = torch.flatten(p_0_x).view(1, 1, h, w).repeat(1, N, 1, 1)
- p_0_y = torch.flatten(p_0_y).view(1, 1, h, w).repeat(1, N, 1, 1)
- p_0 = torch.cat([p_0_x, p_0_y], 1).type(dtype)
-
- return p_0
-
- # 输出特征图上每点(对应卷积核中心)加上其对应卷积核每个位置的相对(横、纵)坐标后再加上自学习的(横、纵坐标)偏移量。
- # p0就是将输出特征图每点对应到卷积核中心,然后映射到输入特征图中的位置;
- # pn则是p0对应卷积核每个位置的相对坐标;
- def _get_p(self, offset, dtype):
- N, h, w = offset.size(1) // 2, offset.size(2), offset.size(3)
-
- # (1, 2N, 1, 1)
- p_n = self._get_p_n(N, dtype)
- # (1, 2N, h, w)
- p_0 = self._get_p_0(h, w, N, dtype)
- p = p_0 + p_n + offset
- return p
-
- def _get_x_q(self, x, q, N):
- # 计算双线性插值点的4邻域点对应的权重
- b, h, w, _ = q.size()
- padded_w = x.size(3)
- c = x.size(1)
- # (b, c, h*w)
- x = x.contiguous().view(b, c, -1)
-
- # (b, h, w, N)
- index = q[..., :N] * padded_w + q[..., N:] # offset_x*w + offset_y
- # (b, c, h*w*N)
- index = index.contiguous().unsqueeze(dim=1).expand(-1, c, -1, -1, -1).contiguous().view(b, c, -1)
-
- x_offset = x.gather(dim=-1, index=index).contiguous().view(b, c, h, w, N)
-
- return x_offset
-
- @staticmethod
- def _reshape_x_offset(x_offset, ks):
- b, c, h, w, N = x_offset.size()
- x_offset = torch.cat([x_offset[..., s:s + ks].contiguous().view(b, c, h, w * ks) for s in range(0, N, ks)],
- dim=-1)
- x_offset = x_offset.contiguous().view(b, c, h * ks, w * ks)
-
- return x_offset

之后我们打开yolov7的nets文件夹,在文件夹里有一个backbone.py文件,我们将其打开,翻到下面可以看到定义好了的Transition_Block和Multi_Concat_Block函数:
- class Multi_Concat_Block(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, c1, c2, c3, n=4, e=1, ids=[0]):
- super(Multi_Concat_Block, self).__init__()
- c_ = int(c2 * e)
-
- self.ids = ids
- self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
- self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
- self.cv3 = nn.ModuleList(
- [Conv(c_ if i ==0 else c2, c2, 3, 1) for i in range(n)]
- )
- self.cv4 = Conv(c_ * 2 + c2 * (len(ids) - 2), c3, 1, 1)
-
- def forward(self, x):
- x_1 = self.cv1(x)
- x_2 = self.cv2(x)
-
- x_all = [x_1, x_2]
- # [-1, -3, -5, -6] => [5, 3, 1, 0]
- for i in range(len(self.cv3)):
- x_2 = self.cv3[i](x_2)
- x_all.append(x_2)
-
- out = self.cv4(torch.cat([x_all[id] for id in self.ids], 1))
- return out
-
- class Transition_Block(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, c1, c2):
- super(Transition_Block, self).__init__()
- self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c2, 1, 1)
- self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c2, 1, 1)
- self.cv3 = Conv(c2, c2, 3, 2)
-
- self.mp = MP()
-
- def forward(self, x):
- # 160, 160, 256 => 80, 80, 256 => 80, 80, 128
- x_1 = self.mp(x)
- x_1 = self.cv1(x_1)
-
- # 160, 160, 256 => 160, 160, 128 => 80, 80, 128
- x_2 = self.cv2(x)
- x_2 = self.cv3(x_2)
-
- # 80, 80, 128 cat 80, 80, 128 => 80, 80, 256
- return torch.cat([x_2, x_1], 1)

这里小编建议大家复制一份原函数,在复制的函数上进行修改,不会破坏其他层的正常运行。
下面是修改之后的Transition_Block和Multi_Concat_Block函数:
- class Multi_Concat_Block_DeformConv(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, c1, c2, c3, n=4, e=1, ids=[0]):
- super(Multi_Concat_Block_DeformConv, self).__init__()
- c_ = int(c2 * e)
-
- self.ids = ids
- self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
- self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
- self.cv3 = nn.ModuleList(
- [DeformConv2d(c_ if i == 0 else c2, c2, 3, 1) for i in range(n)]
- )
- # 这里将Conv替换成了DeformConv()函数,符合原论文中的结构
- self.cv4 = Conv(c_ * 2 + c2 * (len(ids) - 2), c3, 1, 1)
-
- def forward(self, x):
- x_1 = self.cv1(x)
- x_2 = self.cv2(x)
-
- x_all = [x_1, x_2]
- # [-1, -3, -5, -6] => [5, 3, 1, 0]
- for i in range(len(self.cv3)):
- x_2 = self.cv3[i](x_2)
- x_all.append(x_2)
-
- out = self.cv4(torch.cat([x_all[id] for id in self.ids], 1))# 最后torch.cat堆叠之后再cv4卷积
- return out
-
- class Transition_Block_DeformConv(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, c1, c2):
- super(Transition_Block_DeformConv, self).__init__()
- self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c2, 1, 1)
- self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c2, 1, 1)
- self.cv3 = Conv(c2, c2, 3, 2)
- self.DeformConv = DeformConv2d(c2, c2, 3, 2)# 定义可变卷积
-
- self.mp = MP()
-
- def forward(self, x):
- # 160, 160, 256 => 80, 80, 256 => 80, 80, 128
- x_1 = self.mp(x)
- x_1 = self.cv1(x_1)
-
- # 160, 160, 256 => 160, 160, 128 => 80, 80, 128
- x_2 = self.cv2(x)
- # x_2 = self.cv3(x_2)
- x_2 = self.DeformConv(x_2)# 加了一个可变卷积代替原来的cv3
-
- # 80, 80, 128 cat 80, 80, 128 => 80, 80, 256
- return torch.cat([x_2, x_1], 1)

这里要注意一点,在DeformConv2d和使用的时候的stride和padding一定要对应,否则会出现维度不正确的错误!
接下来我们改变backbone部分的dark5部分,下图是修改后的backbone代码:
- class Backbone(nn.Module):
- def __init__(self, transition_channels, block_channels, n, phi, pretrained=False):
- super().__init__()
- #-----------------------------------------------#
- # 输入图片是640, 640, 3
- #-----------------------------------------------#
- ids = {
- 'l' : [-1, -3, -5, -6],
- 'x' : [-1, -3, -5, -7, -8],
- }[phi]
- # 640, 640, 3 => 640, 640, 32 => 320, 320, 64
- self.stem = nn.Sequential(
- Conv(3, transition_channels, 3, 1),
- Conv(transition_channels, transition_channels * 2, 3, 2),
- Conv(transition_channels * 2, transition_channels * 2, 3, 1),
- )
- # 320, 320, 64 => 160, 160, 128 => 160, 160, 256
- self.dark2 = nn.Sequential(
- Conv(transition_channels * 2, transition_channels * 4, 3, 2),
- Multi_Concat_Block(transition_channels * 4, block_channels * 2, transition_channels * 8, n=n, ids=ids),
- )
- # 160, 160, 256 => 80, 80, 256 => 80, 80, 512
- self.dark3 = nn.Sequential(
- Transition_Block(transition_channels * 8, transition_channels * 4),
- Multi_Concat_Block(transition_channels * 8, block_channels * 4, transition_channels * 16, n=n, ids=ids),
- )
- # 80, 80, 512 => 40, 40, 512 => 40, 40, 1024
- self.dark4 = nn.Sequential(
- Transition_Block(transition_channels * 16, transition_channels * 8),
- Multi_Concat_Block(transition_channels * 16, block_channels * 8, transition_channels * 32, n=n, ids=ids),
- )
- # 40, 40, 1024 => 20, 20, 1024 => 20, 20, 1024
- self.dark5 = nn.Sequential(
- Transition_Block_DeformConv(transition_channels * 32, transition_channels * 16),
- Multi_Concat_Block_DeformConv(transition_channels * 32, block_channels * 8, transition_channels * 32, n=n, ids=ids),
- )
- # 这里我进行了修改,将原本的Transition_Block和Muti_Concat_Block中的Conv部分使用DeformConv进行了替换
- if pretrained:
- url = {
- "l" : 'https://github.com/bubbliiiing/yolov7-pytorch/releases/download/v1.0/yolov7_backbone_weights.pth',
- "x" : 'https://github.com/bubbliiiing/yolov7-pytorch/releases/download/v1.0/yolov7_x_backbone_weights.pth',
- }[phi]
- checkpoint = torch.hub.load_state_dict_from_url(url=url, map_location="cpu", model_dir="./model_data")
- self.load_state_dict(checkpoint, strict=False)
- print("Load weights from " + url.split('/')[-1])
-
- def forward(self, x):
- x = self.stem(x)
- x = self.dark2(x)
- #-----------------------------------------------#
- # dark3的输出为80, 80, 512,是一个有效特征层
- #-----------------------------------------------#
- x = self.dark3(x)
- feat1 = x
- #-----------------------------------------------#
- # dark4的输出为40, 40, 1024,是一个有效特征层
- #-----------------------------------------------#
- x = self.dark4(x)
- feat2 = x
- #-----------------------------------------------#
- # dark5的输出为20, 20, 1024,是一个有效特征层
- #-----------------------------------------------#
- x = self.dark5(x)
- feat3 = x
- return feat1, feat2, feat3

这样一来,在yolov7 backbone部分最后一个特征图的输出就得到了改变,里面Transition_Block和Multi_Concat_Block函数中的卷积发生了变换。
最后我们就可以开始训练啦

这里小编这里刚开始训练了几轮,结果还没出来。。。
大家也可以随机发挥,将其他部分的卷积也可以替换成可变卷积结构,不过最终的mAP值小编这里就不知道啦,哈哈哈。
感谢您的观看!


