- 1python学习3. 无重复字符的最长子串(滑动窗口)_无重复字符的最长子串滑动窗口python
- 2访问github速度慢解决_腾讯vps访问github慢
- 3基于Wemos的避障小车_wemos d1控制电机 mixly
- 4TCP四次握手
- 5lstm网络一般训练多少轮_【论文推荐】黄伟等:针对设备端口链路的LSTM网络流量预测与链路拥塞方案...
- 6字节数组转字符串(Java)_字节数组转换成字符串
- 7大厂前端高频面试问题与答案精选
- 8NVIDIA Jetson Nano 深度学习开发环境配置及案例实践_jetson nano应用案例
- 9Math对象生成随机数与日期如何使用_const time = math.random() * 50000
- 10Eclipse中jsp异常The superclass "javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet" was not found on the Java Build Path_eclipse创建filter类httpfilter显示the super class does n
力扣java刷题学习(代码随想录学习)2_代码随想录java版本代码
赞
踩
二叉树
404.左叶子之和
//注意:左叶节点!层序遍历解决。 class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) { int res = 0; Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>(); que.add(root); TreeNode temp; while(!que.isEmpty()){ int len = que.size(); while(len-- > 0){ temp = que.poll(); //System.out.println(temp.val); if(temp.left != null){ que.add(temp.left); if(temp.left.left == null && temp.left.right == null) res += temp.left.val; } if(temp.right!=null) que.add(temp.right); } } return res; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
进
行
一
个
分
割
513.找树左下角的值
//层序遍历非常简单,队列中的第一个就是。 class Solution { public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) { int res = 0; Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<>(); que.add(root); TreeNode temp; while(!que.isEmpty()){ int len = que.size(); res = que.peek().val; while(len > 0){ temp = que.poll(); if(temp.left != null) que.add(temp.left); if(temp.right!=null) que.add(temp.right); len--; } } return res; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
进
行
一
个
分
割
112. 路径总和
本体可以说是求二叉树所有路径的衍生题,同样的解决思路。
//递归全,用来理解。 class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { if(root == null) return false; int paths = 0; return traversal(root,paths,targetSum); } public boolean traversal(TreeNode root, int paths,int targetSum){ paths += root.val; if(root.left == null && root.right == null){ if(paths == targetSum) return true ; else return false; } if(root.left != null) { if(traversal(root.left,paths,targetSum)) return true; } if(root.right !=null){ if(traversal(root.right,paths,targetSum)) return true; } return false; } } /*精简版本*/ class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { int paths = 0; return traversal(root,paths,targetSum); } public boolean traversal(TreeNode root, int paths,int targetSum){ if(root == null) return false; paths += root.val; if(root.left == null && root.right == null && paths == targetSum) return true ; return traversal(root.left,paths,targetSum) || traversal(root.right,paths,targetSum); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
进
行
一
个
分
割
113. 路径总和ii
深拷贝,浅拷贝的概念,不能直接给res赋值temp,引用类型赋值的话是把当前的地址传过去,所以后面对temp改动了,之前传进去的值也会随之改动,必须要新建一个ArrayList<>,把数据存在其中,再赋值。
//递归 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<>(); if(root == null)return res; temp.add(root.val); traversal(root, targetSum - root.val,res,temp); return res; } public void traversal(TreeNode root,int count, List<List<Integer>> res,List<Integer> temp){ if(root.left == null && root.right == null && count == 0){ List<Integer> temp2 = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i= 0;i<temp.size();i++){ temp2.add(temp.get(i)); } res.add(temp2); return ; } if(root.left != null){ temp.add(root.left.val); traversal(root.left,count - root.left.val,res,temp); temp.remove(temp.size() - 1); } if(root.right != null){ temp.add(root.right.val); traversal(root.right,count - root.right.val,res,temp); temp.remove(temp.size() - 1); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
进
行
一
个
分
割
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
//递归。 //做的时候遇到了问题,如果函数设置的是void,那最后得到的结果就是初始化的root,即0。 //个人分析原因是在下面的函数生成的TreeNode类,在函数调用结束之后,给实例化的对象清除掉了。 class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) { int len = inorder.length; TreeNode root = new TreeNode(); root = buildNode(inorder,postorder,0,len-1,0,len-1); return root; } public TreeNode buildNode(int[] inorder,int[] postorder,int inorStart, int inorFin,int postStart,int postFin){ if(inorStart > inorFin || postStart > postFin) return null; TreeNode temp = new TreeNode(); temp.val = postorder[postFin]; int i = 0; while(true){ if(inorder[inorStart + i] == temp.val) break; i++; } temp.left = buildNode(inorder,postorder,inorStart,inorStart+i-1,postStart,postStart+i-1); temp.right = buildNode(inorder,postorder,inorStart+i+1,inorFin,postStart+i,postFin-1); return temp; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
进
行
一
个
分
割
105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) { int len = preorder.length; TreeNode root = new TreeNode(); root = buildNode(preorder,inorder,0,len-1,0,len-1); return root; } public TreeNode buildNode(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int preStart, int preFin,int inoStart,int inoFin){ if(preStart > preFin || inoStart > inoFin) return null; TreeNode temp = new TreeNode(); temp.val = preorder[preStart]; int i = 0; while(true){ if(inorder[inoStart + i] == temp.val) break; i++; } temp.left = buildNode(preorder,inorder,preStart+1,preStart+i,inoStart,inoStart+i-1); temp.right = buildNode(preorder,inorder,preStart+i+1,preFin,inoStart+i+1,inoFin); return temp; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
进
行
一
个
分
割
654.最大二叉树
//递归 class Solution { public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) { TreeNode root = new TreeNode(); int len = nums.length; root = constructNode(nums,0,len-1); return root; } public TreeNode constructNode(int[] nums,int start,int fin){ if(start > fin) return null; int i = 0; int max = -1; int j = 0; //一定要注意while内的判断条件,一定是start+i小于fin,否则会出现过界问题。 while(start+i<=fin){ if(max < nums[start+i]) { max = nums[start+i]; j = start+i; } i++; } TreeNode root = new TreeNode(max); root.left = constructNode(nums,start,j-1); root.right = constructNode(nums,j+1,fin); return root; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
进
行
一
个
分
割
617.合并二叉树
//递归非常简单。
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null && root2 == null) return null;
if(root1 == null && root2 != null) return root2;
if(root1 != null && root2 == null) return root1;
root1.val += root2.val;
root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left);
root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right);
return root1;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
进
行
一
个
分
割
700.二叉搜索树中的搜索
//递归
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root == null) return null;
TreeNode temp = new TreeNode();
if(root.val > val) temp = searchBST(root.left,val);
if(root.val < val) temp = searchBST(root.right,val);
if(root.val == val) temp = root;
return temp;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
//迭代
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
while(root != null){
if(root.val == val) break;
else if(root.val < val) root = root.right;
else if(root.val > val) root = root.left;
}
return root;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
进
行
一
个
分
割
98.验证二叉搜索树
//中序遍历,左中右,如果是二叉搜索树的话一定是从小到大,有一个不符合就是错误。
class Solution {
Integer pre;//这是一个类。
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);
if(pre != null && root.val <= pre){
return false;
}
pre = root.val;
boolean right = isValidBST(root.right);
return left && right;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
进
行
一
个
分
割
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
//通过中序遍历解决,二叉搜索树,在中序条件下是一个有序递增数组。 class Solution { TreeNode pre;// 记录上一个遍历的结点 int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) { travel(root); return result; } public void travel(TreeNode root){ if(root == null) return; travel(root.left); if(pre != null){ result = Math.min(result,(root.val - pre.val)); } pre = root; travel(root.right); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
进
行
一
个
分
割
501.二叉搜索树中的众数
class Solution { List<Integer> answer = new ArrayList<Integer>(); int base , count , max; public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) { travel(root); int[] aaa = new int[answer.size()]; for (int i = 0; i < answer.size(); i++) { aaa[i] = answer.get(i); } return aaa; } private void travel(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return; travel(root.left); update(root.val); travel(root.right); } private void update(int x) { //count初始是0,如果第一个节点就是0,直接让count变成1。 if (x == base) ++count; else { base = x; count = 1; } if (count == max) answer.add(base); if (count > max) { answer.clear(); max = count; answer.add(base); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
进
行
一
个
分
割
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
//通过递归求路径,模拟栈的操作,把路径存入ArrayList中。 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { List<TreeNode> routeOne = new ArrayList<TreeNode>(); List<TreeNode> routeTwo = new ArrayList<TreeNode>(); findRoute(root,p,routeOne); findRoute(root,q,routeTwo); TreeNode temp; TreeNode res = null; int len = (routeOne.size() > routeTwo.size()) ? routeTwo.size():routeOne.size(); for(int i = len - 1; i>=0; i--){ temp = routeOne.get(i); if(routeTwo.contains(temp)) { res = temp; break; } } return res; } public void findRoute(TreeNode root, TreeNode res,List route){ if(root == null) return; route.add(root); if(root == res) return; findRoute(root.left,res,route); if(route.get(route.size() - 1) == res) return; findRoute(root.right,res,route); if(route.get(route.size() - 1) == res) return; route.remove(root); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
进
行
一
个
分
割
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
//递归方法 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if(root == null) return null; if(p.val < q.val){ if(root.val >= p.val && root.val <= q.val) return root; if(p.val < root.val && q.val < root.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q); if(p.val > root.val && q.val > root.val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q); } if(p.val > q.val){ return lowestCommonAncestor(root,q,p); } return null; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
while (root != null) {
if (root.val > q.val && root.val > p.val) {
root = root.left;
} else if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {
root = root.right;
} else {
return root;
}
}
return null;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
进
行
一
个
分
割
701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作
//找空节点位置插入。 class Solution { public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) { if(root == null){ root = new TreeNode(val); return root; } TreeNode temp = root; while(temp != null){ if(val > temp.val) { if(temp.right == null){ temp.right = new TreeNode(val); break; } temp = temp.right; } else if(val < temp.val) { if(temp.left == null){ temp.left = new TreeNode(val); break; } temp = temp.left; } } return root; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
进
行
一
个
分
割
450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点
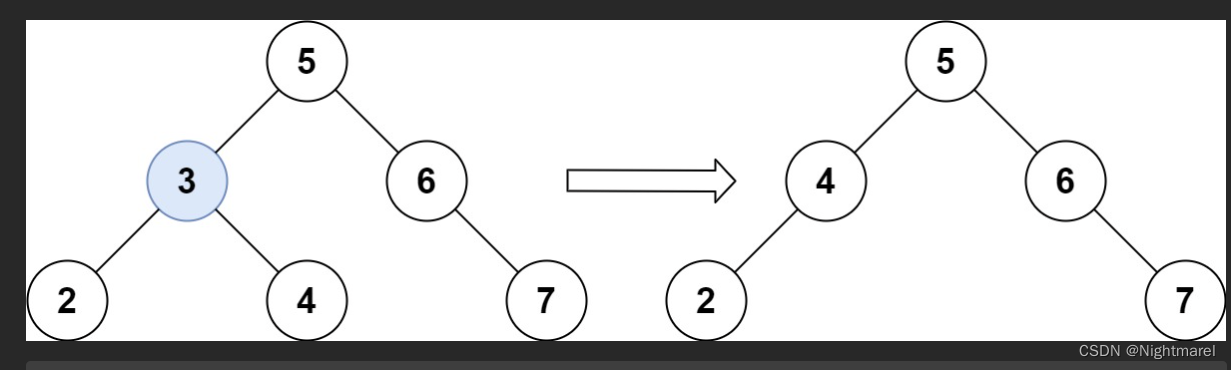
//疯狂的迭代。 /* 我的思路并不是从右子树中找到最小的代替,而是把删除节点3的右节点4移动上去,然后把右节点4的左子树连接到删除 节点左节点2的右子树上(因为一定大于删除节点左节点2上右子树的所有值,所以找到最右的节点连接上右子树)。 */ class Solution { public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) { if(root == null) return null; TreeNode temp = root; TreeNode pre = new TreeNode(); pre.left = root; while(temp != null && temp.val != key){ pre = temp; if(key < temp.val) temp = temp.left; else if(key > temp.val) temp = temp.right; if(temp == null) return root; if(key == temp.val) break; } TreeNode node; TreeNode a; if(pre.val >= key || temp == root){ //在左子树删除节点,最上最下分别是左节点为空,和右节点为空的情况。 //中间是对面描述的实现。 if(temp.left == null) pre.left = temp.right; else if(temp.right != null){ pre.left = temp.right; node = temp.right.left; pre.left.left = temp.left; a = pre.left.left;//这一部分就是为了找到右子树最右节点插入。 while(a.right != null){ a = a.right; } a.right = node; } else pre.left = temp.left; } else{ if(temp.left == null) pre.right = temp.right; else if(temp.right != null){ pre.right = temp.right; node = temp.right.left; pre.right.left = temp.left; a = pre.right.left; a = pre.right.left; while(a.right != null){ a = a.right; } a.right = node; } else pre.right = temp.left; } if(temp == root) return pre.left; return root; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
进
行
一
个
分
割
669. 修剪二叉搜索树
//递归方法,和450题类似。 class Solution { public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) { if (root == null) return root; root.left = trimBST(root.left,low,high); root.right = trimBST(root.right,low,high); if (root.val < low || root.val > high){ if (root.left == null) return root.right; else if (root.right == null) return root.left; else{ TreeNode cur = root.right; while (cur.left != null) cur = cur.left; cur.left = root.left; root = root.right; return root; } } /*删除放在下面就是450题递归方法。 if (root.val > key) root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key); if (root.val < key) root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key); */ return root; } } //个人理解版本 class Solution { public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) { if(root == null) return null; root.left = trimBST(root.left,low,high); root.right = trimBST(root.right,low,high); if((root.val < low || root.val > high) && root.left == null && root.right == null) return null; if((root.val < low || root.val > high) && root.left == null) return root.right; else if((root.val < low || root.val > high) && root.right == null) return root.left; if(root.val < low || root.val > high){ TreeNode a = root.right; while(a.left != null){ a = a.left; } a.left = root.left; return root.right; } return root; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
进
行
一
个
分
割
108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
//递归创建 class Solution { public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) { if(nums.length == 0) return null; TreeNode root = new TreeNode(); root = creTree(nums,0,nums.length-1); return root; } public TreeNode creTree(int[] nums,int sta,int fin){ int a = fin - sta + 1; if(sta > fin) return null; TreeNode root; if(a > 2){ int b = (a / 2) + sta; //System.out.println(b); root = new TreeNode(nums[b]); root.left = creTree(nums,sta,b-1); root.right = creTree(nums,b+1,fin); } else{ root = new TreeNode(nums[sta]); root.right = creTree(nums,sta+1,fin); } return root; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
进
行
一
个
分
割
538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
//左中右是中序遍历,二叉搜索树中序遍历是递增数组,右中左是递减的数组,符合这道题的做题方法。 class Solution { TreeNode pre = null; public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return null; convertBST(root.right); if(pre != null) { root.val = root.val + pre.val; } pre = root; convertBST(root.left); return root; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
进
行
一
个
分
割
回溯算法
77.组合
//staindex调整初始取值,可以想象成数组的下标,从下一个小标开始取值。 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { backtracking(n,k,1); return result; } public void backtracking(int n,int k,int staindex){ if(res.size() == k){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(res)); return ; } //后面的取值属于剪枝操作。 for(int i = staindex; i <= n - (k - res.size()) + 1 ; i++){ res.add(i); System.out.println("递归之前 => " + res); backtracking(n,k,i+1); res.removeLast(); System.out.println("递归之后 => " + res); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
//剪枝之前的输出 递归之前 => [1] 递归之前 => [1, 2] 递归之后 => [1] 递归之前 => [1, 3] 递归之后 => [1] 递归之前 => [1, 4] 递归之后 => [1] 递归之后 => [] 递归之前 => [2] 递归之前 => [2, 3] 递归之后 => [2] 递归之前 => [2, 4] 递归之后 => [2] 递归之后 => [] 递归之前 => [3] 递归之前 => [3, 4] 递归之后 => [3] 递归之后 => [] 递归之前 => [4] 递归之后 => [] //剪枝之后的输出 递归之前 => [1] 递归之前 => [1, 2] 递归之后 => [1] 递归之前 => [1, 3] 递归之后 => [1] 递归之前 => [1, 4] 递归之后 => [1] 递归之后 => [] 递归之前 => [2] 递归之前 => [2, 3] 递归之后 => [2] 递归之前 => [2, 4] 递归之后 => [2] 递归之后 => [] 递归之前 => [3] 递归之前 => [3, 4] 递归之后 => [3] 递归之后 => []
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
从上述输出可以看出来,剪掉了4的操作,因为组合两个数,当选到4的时候已经不可能进行组合只是浪费时间,所以剪掉4的操作。通过例子可以看出:
1.已经选择的元素个数:path.size();
2.还需要的元素个数为: k - path.size();
3.集合的上界应该是 : n - (k - path.size()) + 1。
进
行
一
个
分
割
216.组合总和III
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); int num = 0; public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3(int k, int n) { backTracking(k,n,1); return result; } public void backTracking(int k, int n,int startIndex){ if(path.size() == k && num == n){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } //if((num + startIndex) > n) return; //下面的剪枝更好 for(int i = startIndex; i <= n - num;i++){ if(i > 9) break; path.add(i); num += i; backTracking(k,n,i+1); path.removeLast(); num -= i; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
进
行
一
个
分
割
17.电话号码的字母组合
class Solution { List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); //每次迭代获取一个字符串,所以会设计大量的字符串拼接,所以这里选择更为高效的 StringBuild StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder(); public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) { if (digits.length() == 0){ return list; } String[] numString = {"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"}; backTracking(digits,numString,0); return list; } public void backTracking(String digits,String[] numString,int num){ if(temp.length() == digits.length()){ list.add(temp.toString()); return; } String str = numString[digits.charAt(num) - '0']; for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++){ temp.append(str.charAt(i)); backTracking(digits,numString,num+1); temp.deleteCharAt(temp.length() - 1); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
进
行
一
个
分
割
39. 组合总和
//先进行排序可以更好的在后面跳出循环,如果不排序的话,只能在下一次递归函数中跳出,浪费时间。 class Solution { int num = 0; List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { if(candidates.length == 1 && candidates[0] != target){ return result; } Arrays.sort(candidates); // 先进行排序 backTracking(candidates, target, 0); return result; } public void backTracking(int[] candidates,int target,int staIndex){ if(num == target){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for(int i = staIndex;i < candidates.length;i++){ if(num + candidates[i] > target) break; path.add(candidates[i]); num += candidates[i]; backTracking(candidates,target,i); path.removeLast(); num -= candidates[i]; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
进
行
一
个
分
割
40.组合总和II
//不用标记数组的方法 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); int num = 0; public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) { if(candidates.length == 1 && candidates[0] != target) return result; Arrays.sort(candidates); backTracking(candidates,target,0); return result; } public void backTracking(int[] candidates, int target,int idx){ if(num == target){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } if(num > target) return; for(int i = idx;i < candidates.length;i++){ // i > idx 这么设计的原因是在同层循环中不选择使用同样的数字。 /* 如12225,这一组数字从1开始迭代可以得到122,idx也是从0-2,当回溯之后,idx变成1,只想第一个2,这个 时候回到第二层的迭代for循环,i满足大于idx,并且两个同样的2,就不会再取。 */ if(i > idx && candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]) continue; path.add(candidates[i]); num += candidates[i]; backTracking(candidates,target,i+1); path.removeLast(); num -= candidates[i]; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
//使用标记数组。 class Solution { LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>(); boolean[] used; int sum = 0; public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) { used = new boolean[candidates.length]; // 加标志数组,用来辅助判断同层节点是否已经遍历 Arrays.fill(used, false); // 为了将重复的数字都放到一起,所以先进行排序 Arrays.sort(candidates); backTracking(candidates, target, 0); return ans; } // used[i - 1] == true,说明同一树枝candidates[i - 1]使用过 //可以理解为上一个迭代函数使用过 // used[i - 1] == false,说明同一树层candidates[i - 1]使用过 //可以理解为本次迭代的for函数中使用过 private void backTracking(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex) { if (sum == target) { ans.add(new ArrayList(path)); } for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) { if (sum + candidates[i] > target) { break; } // 出现重复节点,同层的第一个节点已经被访问过,所以直接跳过 if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]) { continue; } used[i] = true; sum += candidates[i]; path.add(candidates[i]); // 每个节点仅能选择一次,所以从下一位开始 backTracking(candidates, target, i + 1); used[i] = false; sum -= candidates[i]; path.removeLast(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
进
行
一
个
分
割
131.分割回文串
对本题的思考总结:题目要求找到所有的分割方案,也就是当起始位置大于等于字符串的长度就是找完一种分割方案,即本题的中止条件。
要求是回文串,所以for循环中判断是回文才可以添加,不是回文进行下一次循环(注同上)。
分割如下图:
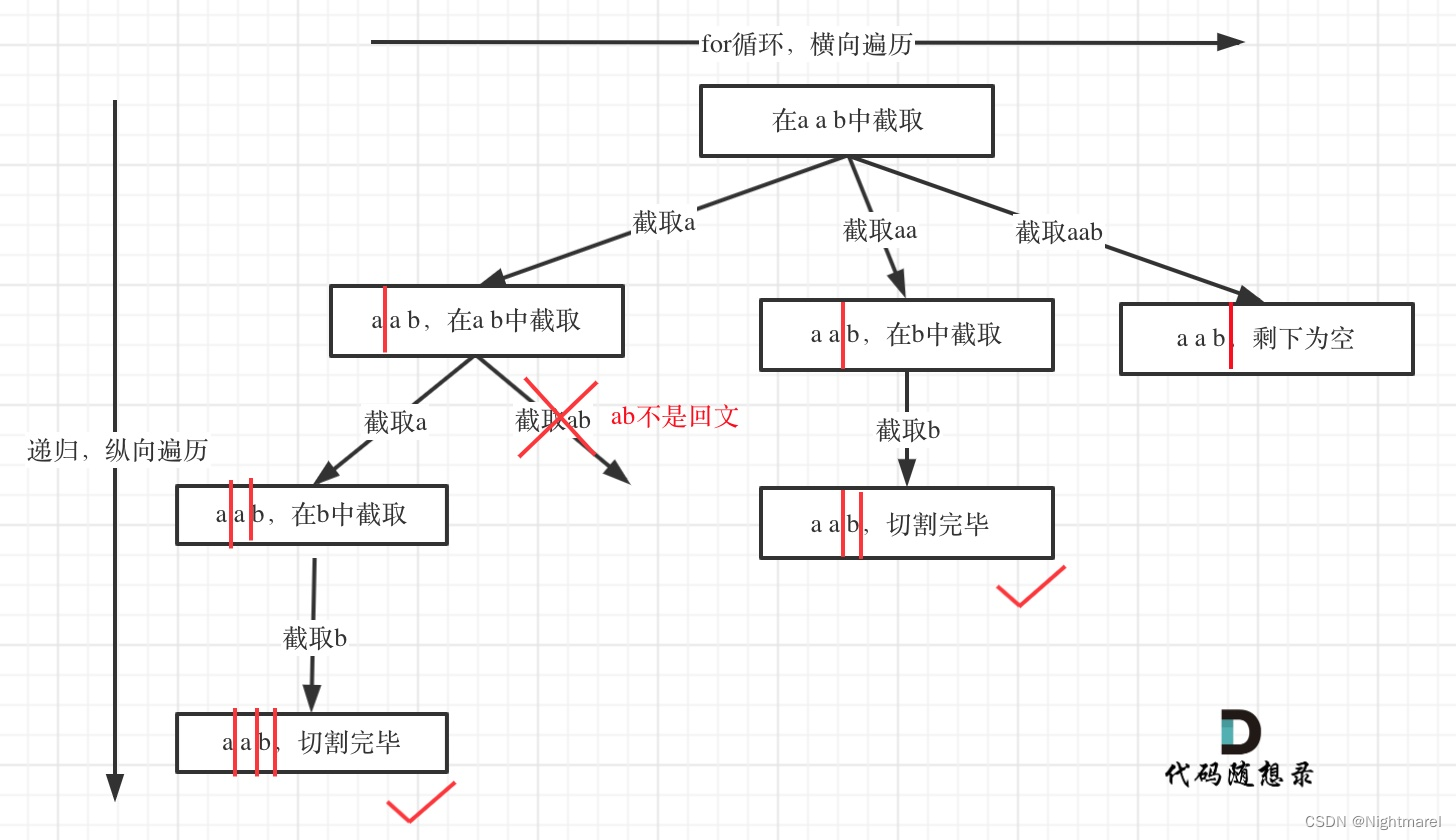
class Solution { List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<String> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<String>> partition(String s) { backTracking(s,0); return result; } public void backTracking(String s,int idx){ //如果起始位置大于s的大小,说明找到了一组分割方案 if(idx >= s.length()){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for(int i = idx; i < s.length();i++){ if(isPalindrome(s, idx, i)){ String str = s.substring(idx,i+1); path.add(str); } else continue; backTracking(s,i+1); path.removeLast(); } } //判断是不是回文 public boolean isPalindrome(String s,int idx,int end){ for(int i = idx, j = end; i < j;i++,j--){ if(s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)){ return false; } } return true; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
进
行
一
个
分
割
93.复原IP地址
class Solution { List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(); public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) { //大于12,或者小于4都无法凑成ip地址 if (s.length() > 12 || s.length() < 4) return result;//算是剪枝 backTracking(s,0,0); return result; } public void backTracking(String s,int idx,int pointNum){ //pint是点,一个ip地址有3个点,当为3时证明已经分割完成。 if(pointNum == 3){ //如果是ip地址,那一定是整个字符串都分完。 if(isHefa(s,idx,s.length()-1)) result.add(s); return; } for(int i = idx;i < s.length();i++){ if(isHefa(s,idx,i)){ //在s上改节省空间 s = s.substring(0, i + 1) + "." + s.substring(i + 1); pointNum++; backTracking(s, i + 2, pointNum);// 插入逗点之后下一个子串的起始位置为i+2 pointNum--; s = s.substring(0, i + 1) + s.substring(i + 2); } else break;//只要有不符合的直接结束,一定不可能分配成ip地址了 } } public boolean isHefa(String s,int idx,int end){ if(idx > end) return false; if(end-idx > 0){ if(s.charAt(idx) == '0') return false; } String str = s.substring(idx,end+1); int num = Integer.parseInt(str); if(num >= 0 && num <= 255) return true; else return false; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
进
行
一
个
分
割
78.子集
/*子集,实际上只要小于等于数组本身的长度就到了结束条件。 另一方面本体就类似于数组,进行多组合(长度不可大于数组本身)。例:[1,2,3] 组合出 1,12,123,13,2,23,3。 */ class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { if(nums.length == 0) return result; backtracking(nums,0); return result; } public void backtracking(int[] nums, int idx){ if (idx >= nums.length){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } else{ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); } for(int i = idx;i < nums.length;i++){ path.add(nums[i]); backtracking(nums,i+1); path.removeLast(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
进
行
一
个
分
割
90.子集II
//让数组有序就可以避免414出现的问题,会出现41和14两种子集,重复了。 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) { if(nums.length == 0) return result; Arrays.sort(nums); backtracking(nums,0); return result; } public void backtracking(int[] nums, int idx){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); for(int i = idx;i < nums.length;i++){ //i > idx 的目的是只判断同循环且在idx后的数字,是否与前面相同。 if(i > idx && nums[i-1] == nums[i]) continue; path.add(nums[i]); backtracking(nums,i+1); path.removeLast(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
进
行
一
个
分
割
491.递增子序列
用used数组表示这个数被使用过,同层就不可以再用。
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) { if(nums.length == 0) return result; backtracking(nums,0); return result; } public void backtracking(int[] nums, int idx){ if(path.size() >= 2) result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); int[] used = new int[201]; for(int i = idx;i < nums.length;i++){ if (!path.isEmpty() && nums[i] < path.peekLast() || (used[nums[i] + 100] == 1)) continue; used[nums[i] + 100] = 1; path.add(nums[i]); backtracking(nums, i + 1); path.removeLast(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
进
行
一
个
分
割
46.全排列
类似的思路,used数组考虑之前迭代已经用过的数不可以再被使用。
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); int[] used; public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { used = new int[nums.length]; backtracking(nums); return result; } public void backtracking(int[] nums){ if(path.size() == nums.length){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++){ if(path.isEmpty() || (!path.isEmpty() && used[i] != 1)){ path.add(nums[i]); used[i] = 1; } else continue; backtracking(nums); path.removeLast(); used[i] = 0; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
进
行
一
个
分
割
47.全排列 II
class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); int[] used = new int[21]; public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) { Arrays.sort(nums); backtracking(nums); return result; } public void backtracking(int[] nums){ if(path.size() == nums.length){ result.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); return; } for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++){ // used[i - 1] == 1,说明同⼀树枝nums[i - 1]使⽤过 // used[i - 1] == 0,说明同⼀树层nums[i - 1]使⽤过 // 如果同⼀树层nums[i - 1]使⽤过则直接跳过 if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == 0) { continue; } if (used[i] == 0){ used[i] = 1; path.add(nums[i]); backtracking(nums); path.removeLast(); used[i] = 0; } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
进
行
一
个
分
割
332.重新安排行程
class Solution { List<String> result; LinkedList<String> path = new LinkedList<>(); boolean[] used; public List<String> findItinerary(List<List<String>> tickets) { //先把tickets排序,排序的方法是对目的地由小到大排序。 Collections.sort(tickets, (a, b) -> a.get(1).compareTo(b.get(1))); used = new boolean[tickets.size()]; path.add("JFK"); backtracking(tickets); return result; } //使用boolean返回的原因是,最初已经对目标进行了排序,第一个结果就是正确的,后续如果继续遍历结果是错的。 public boolean backtracking(List<List<String>> tickets){ if(path.size() == tickets.size() + 1){ result = new LinkedList<>(path); return true; } for (int i = 0; i < tickets.size(); i++) { if (!used[i] && tickets.get(i).get(0).equals(path.getLast())){ path.add(tickets.get(i).get(1)); used[i] = true; if (backtracking(tickets)){ return true; } used[i] = false; path.removeLast(); } } return false; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
//用map的方式实现。两个Str分别是始发地,目的地,int代表的是到目的地的次数。 class Solution { Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();; LinkedList<String> res = new LinkedList<>(); public List<String> findItinerary(List<List<String>> tickets) { for(List<String> t : tickets){ Map<String, Integer> temp; if(map.containsKey(t.get(0))){ temp = map.get(t.get(0)); //一定是getOrDefault方法,因为目的地不一定只有一个,如果有多个,可能是还没添加到map中。 temp.put(t.get(1), temp.getOrDefault(t.get(1), 0) + 1); } else{ temp = new TreeMap<>();//升序Map temp.put(t.get(1), 1); } map.put(t.get(0), temp); } res.add("JFK"); backtracking(tickets.size()); return res; } public boolean backtracking(int ticketNum){ if(res.size() == ticketNum + 1){ return true; } String last = res.getLast(); //可能会出现没有目的地的情况,到了那个城市之后再没去过其他城市,会出现null。 if(map.get(last) == null) return false; //对键值进行映射,映射的是目的地城市(可能会有多个目的地城市)。 for(Map.Entry<String, Integer> target : map.get(last).entrySet()){ int count = target.getValue(); if(count > 0){ res.add(target.getKey()); target.setValue(count - 1); if(backtracking(ticketNum)) return true; res.removeLast(); target.setValue(count); } } return false; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
进
行
一
个
分
割
51. N皇后
class Solution { List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) { char[][] chessboard = new char[n][n]; for(char[] c : chessboard){ Arrays.fill(c,'.');//给数组全部填充上· } backtracking(chessboard,n,0); return result; } public void backtracking(char[][] chessboard,int n,int row){ //结束条件,因为在循环中已经判断该位置是否可以放皇后了,如果进入迭代那就一定是正确的位置。 if(row == n){ result.add(Array2List(chessboard)); return; } for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ if(isValid(chessboard, row, i, n)){ chessboard[row][i] = 'Q'; backtracking(chessboard, n, row+1); chessboard[row][i] = '.'; } } } public boolean isValid(char[][] chessboard,int row,int col,int n){ //按顺序迭代放入皇后的,在本行之后的没开始,所以只需要检查之前行的就可以。 // 检查列 for(int i=0; i<row; i++){ if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') { return false; } } // 检查\方向的对角线 for(int i=row-1, j=col-1; i>=0 && j>=0; i--, j--){ if(chessboard[i][j] == 'Q'){ return false; } } // 检查/方向的对角线 for(int i=row-1, j=col+1; i>=0 && j<=n-1; i--, j++){ if(chessboard[i][j] == 'Q'){ return false; } } return true; } public List Array2List(char[][] chessboard){ List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(char[] c : chessboard){ list.add(String.copyValueOf(c)); } return list; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
进
行
一
个
分
割
37. 解数独
class Solution { public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) { solveSudokuHelper(board); } private boolean solveSudokuHelper(char[][] board){ //「一个for循环遍历棋盘的行,一个for循环遍历棋盘的列, // 一行一列确定下来之后,递归遍历这个位置放9个数字的可能性!」 for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){ // 遍历行 for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++){ // 遍历列 if (board[i][j] != '.'){ // 跳过原始数字 continue; } for (char k = '1'; k <= '9'; k++){ // (i, j) 这个位置放k是否合适 if (isValidSudoku(i, j, k, board)){ board[i][j] = k; if (solveSudokuHelper(board)){ // 如果找到合适一组立刻返回 return true; } board[i][j] = '.'; } } // 9个数都试完了,都不行,那么就返回false return false; // 因为如果一行一列确定下来了,这里尝试了9个数都不行,说明这个棋盘找不到解决数独问题的解! // 那么会直接返回, 「这也就是为什么没有终止条件也不会永远填不满棋盘而无限递归下去!」 } } // 遍历完没有返回false,说明找到了合适棋盘位置了 return true; } /** * 判断棋盘是否合法有如下三个维度: * 同行是否重复 * 同列是否重复 * 9宫格里是否重复 */ private boolean isValidSudoku(int row, int col, char val, char[][] board){ // 同行是否重复 for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){ if (board[row][i] == val){ return false; } } // 同列是否重复 for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++){ if (board[j][col] == val){ return false; } } // 9宫格里是否重复 int startRow = (row / 3) * 3; int startCol = (col / 3) * 3; for (int i = startRow; i < startRow + 3; i++){ for (int j = startCol; j < startCol + 3; j++){ if (board[i][j] == val){ return false; } } } return true; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
进
行
一
个
分
割
贪心算法
455.分发饼干
//满足最多的孩子,从最容易满足的开始,从小到大满足。
class Solution {
public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
Arrays.sort(g);
Arrays.sort(s);
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < s.length;i++){
if(s[i] >= g[result]) result++;
//有饼干多孩子少的问题,要判断result。
if(result >= g.length) break;
}
return result;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
进
行
一
个
分
割
376.摆动序列
//贪心算法,尽可能的找不同的坡度。 //算法是求最大子序列,所以保存最后一个坡度,寻找下一个坡度,求出最大子序列。 class Solution { public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) { if (nums.length <= 1) { return nums.length; } //当前差值 int curDiff = 0; //上一个差值 int preDiff = 0; int count = 1; for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) { //得到当前差值 curDiff = nums[i] - nums[i - 1]; //如果当前差值和上一个差值为一正一负 //等于0的情况表示初始时的preDiff if ((curDiff > 0 && preDiff <= 0) || (curDiff < 0 && preDiff >= 0)) { count++; preDiff = curDiff; } } return count; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
// DP class Solution { public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) { // 0 i 作为波峰的最大长度 // 1 i 作为波谷的最大长度 int dp[][] = new int[nums.length][2]; dp[0][0] = dp[0][1] = 1; for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){ //i 自己可以成为波峰或者波谷 dp[i][0] = dp[i][1] = 1; for (int j = 0; j < i; j++){ if (nums[j] > nums[i]){ // i 是波谷 dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i][1], dp[j][0] + 1); } if (nums[j] < nums[i]){ // i 是波峰 dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i][0], dp[j][1] + 1); } } } return Math.max(dp[nums.length - 1][0], dp[nums.length - 1][1]); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
进
行
一
个
分
割
53. 最大子序和
如果 -2 1 在一起,计算起点的时候,一定是从 1 开始计算,因为负数只会拉低总和,这就是贪心贪的地方!
局部最优:当前“连续和”为负数的时候立刻放弃,从下一个元素重新计算“连续和”,因为负数加上下一个元素 “连续和”只会越来越小。
全局最优:选取最大“连续和”
局部最优的情况下,并记录最大的“连续和”,可以推出全局最优。

class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++){
count += nums[i];
//一定要先判断和max的大小,如果遇到全是负数的数组,只会取其中最大的。
if(count > max) max = count;
//对count进行重置
if(count <= 0) count = 0;
}
return max;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
进
行
一
个
分
割
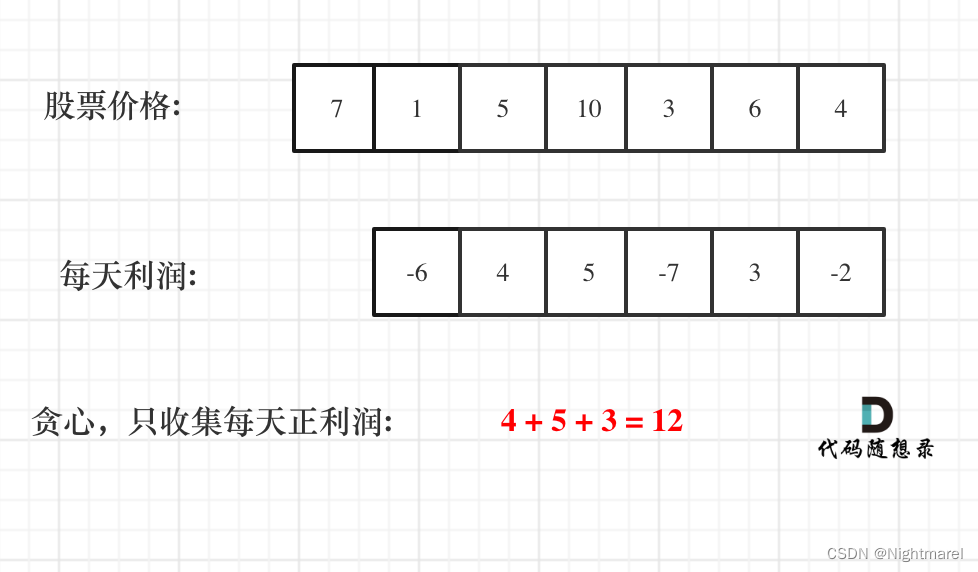
122.买卖股票的最佳时机 II
利润是可以分解的,即:假如第 0 天买入,第 3 天卖出,那么利润为:prices[3] - prices[0]。
相当于(prices[3] - prices[2]) + (prices[2] - prices[1]) + (prices[1] - prices[0])。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if (prices == null || prices.length == 0) {return 0;}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < prices.length - 1; i++){
if(prices[i] < prices[i+1]){
res += prices[i+1] - prices[i];
}
}
return res;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
进
行
一
个
分
割
55. 跳跃游戏
看覆盖范围,只要能覆盖到最后的下标就能达到。
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int cover = 0;
if (nums.length == 1) return true;
//i<=cover控制你能到达的范围,如果第一个数就是0,那么直接无法到达。
//相当于你只能从你的覆盖范围内取值,去更新你的覆盖范围。
for(int i = 0;i <= cover;i++){
//更新最大覆盖范围。
cover = Math.max(i + nums[i],cover);
if(cover >= nums.length-1) return true;
}
return false;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
进
行
一
个
分
割
45.跳跃游戏 II
同样是看下标覆盖问题
class Solution { public int jump(int[] nums) { int result = 0; // 当前覆盖的最远距离下标 int end = 0; // 下一步覆盖的最远距离下标 int temp = 0; //最大能到的范围就是nums.length-2,到了这个点就一定可以到最后,所以直接让res++就可以。 //如果第二次直接覆盖到结果,end一定是大于等于结果,但是i限制在最后的前一位,res只会加一次。 for (int i = 0; i <nums.length - 1; ++i) { temp = Math.max(temp, i + nums[i]); // 可达位置的改变次数就是跳跃次数 if (i == end) { end = temp; result++; } } return result; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
进
行
一
个
分
割
1005.K次取反后最大化的数组和
class Solution { public int largestSumAfterKNegations(int[] nums, int k) { Arrays.sort(nums);//排序之后可以更好的取负。 int num = 0; int res = 0; //找负数个数。 for(int i = 0; i < nums.length;i++){ if(nums[i] < 0) num++; else break; } //进行正负转换,只取最小的,如果num小就转换所有负数,如果k小就转换k个负数。 int min = Math.min(k,num); for(int i = 0; i < min;i++){ nums[i] = -nums[i]; } k = k - min; //k不为零还需要进行符号变换。 if(k!=0){ Arrays.sort(nums);//只找最小的进行符号变换 while(k > 0){ nums[0] = -nums[0]; k--; } } for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++){ res += nums[i]; } return res; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
进
行
一
个
分
割
134. 加油站
首先如果总油量减去总消耗大于等于零那么一定可以跑完一圈,说明 各个站点的加油站 剩油量rest[i]相加一定是大于等于零的。
i从0开始累加rest[i],和记为curSum,一旦curSum小于零,说明[0, i]区间都不能作为起始位置,因为这个区间选择任何一个位置作为起点,到i这里都会断油,那么起始位置从i+1算起,再从0计算curSum。
class Solution { public int canCompleteCircuit(int[] gas, int[] cost) { int curSum = 0; int totalSum = 0; int index = 0; for (int i = 0; i < gas.length; i++) { curSum += gas[i] - cost[i]; totalSum += gas[i] - cost[i]; if (curSum < 0) { index = i + 1 ; curSum = 0; } } //总消耗小于0,不可能完整走一圈 if (totalSum < 0) return -1; return index; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
进
行
一
个
分
割
135. 分发糖果
分两个阶段
1、起点下标1 从左往右,只要右边比左边大,右边的糖果 = 左边 + 1
2、起点下标 ratings.length - 2 从右往左, 只要左边比右边大,此时左边的糖果应该取本身的糖果数(符合比它左边大)和右边糖果数 + 1 二者的最大值,这样才符合它比它左边的大,也比它右边大
class Solution { public int candy(int[] ratings) { int len = ratings.length; int[] candyVec = new int[len]; candyVec[0] = 1; for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) { candyVec[i] = (ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1]) ? candyVec[i - 1] + 1 : 1; } for (int i = len - 2; i >= 0; i--) { if (ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1]) { candyVec[i] = Math.max(candyVec[i], candyVec[i + 1] + 1); } } int ans = 0; for (int num : candyVec) { ans += num; } return ans; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
进
行
一
个
分
割
860.柠檬水找零
class Solution { public boolean lemonadeChange(int[] bills) { int five = 0; int ten = 0; for(int i = 0; i < bills.length;i++){ if(bills[i] == 5) five++; if(bills[i] == 10){ five--; ten++; } if(bills[i] == 20){ if(ten > 0){ ten--; five--; } else five -= 3; } if(five < 0) return false; } return true; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
进
行
一
个
分
割
406.根据身高重建队列
类似上面的题,要考虑两个维度,先完成一个维度之后再完成第二个,最好先按身高排序。
此时我们可以确定一个维度了,就是身高,前面的节点一定都比本节点高!
那么只需要按照k为下标重新插入队列就可以了,为什么呢?

class Solution { public int[][] reconstructQueue(int[][] people) { // 身高从大到小排(身高相同k小的站前面) Arrays.sort(people, (a, b) -> { if (a[0] == b[0]) return a[1] - b[1]; return b[0] - a[0]; }); LinkedList<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>(); for(int[] p : people){ que.add(p[1],p); } return que.toArray(new int[people.length][]); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
进
行
一
个
分
割
452. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球
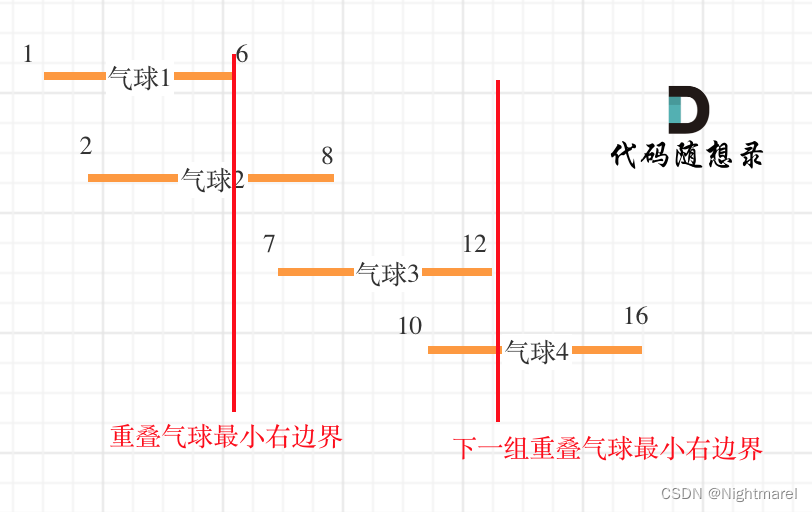
重点在于更新重叠气球最小右边界。
class Solution { public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) { // 根据气球直径的开始坐标从小到大排序 // 使用Integer内置比较方法,不会溢出 Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0])); int count = 1; // points 不为空至少需要一支箭 for (int i = 1; i < points.length; i++) { if (points[i][0] > points[i - 1][1]) { // 气球i和气球i-1不挨着,注意这里不是>= count++; // 需要一支箭 } else { // 气球i和气球i-1挨着 points[i][1] = Math.min(points[i][1], points[i - 1][1]); // 更新重叠气球最小右边界 } } return count; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
进
行
一
个
分
割
435. 无重叠区间
按照右边界排序,从左向右记录非交叉区间的个数。最后用区间总数减去非交叉区间的个数就是需要移除的区间个数了。
此时问题就是要求非交叉区间的最大个数。
这里记录非交叉区间的个数还是有技巧的,如图:
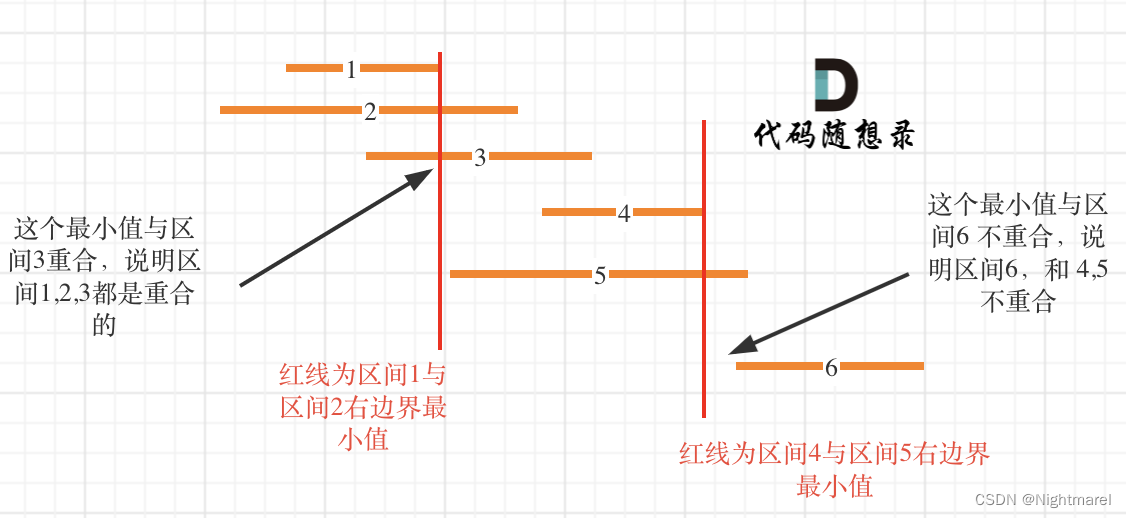
class Solution {
public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
//按右边界大小进行排序,右边界大的在后面,题目的要求是最少的区间让它不重叠,也就是右边界越大的一般来说所占据的区间越长。
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[1],b[1]));
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < intervals.length - 1;i++){
//判断右边界是否大于了下一个区间的左边界,如果大于了就清掉下一个,并把右边界赋值。
if(intervals[i][1] > intervals[i+1][0]){
count++;
intervals[i+1][1] = intervals[i][1];
}
}
return count;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
进
行
一
个
分
割
763.划分字母区间
思路如图: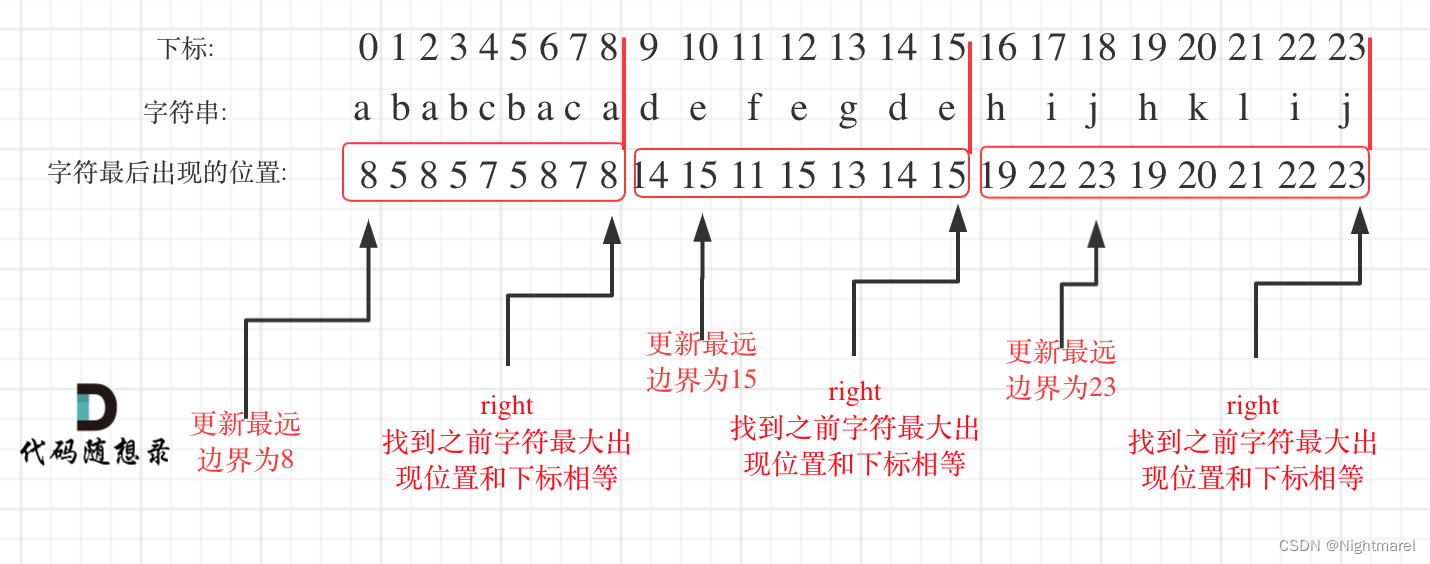
class Solution { public List<Integer> partitionLabels(String s) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); int len = s.length(); int[] nums = new int[27]; for(int i = 0; i < len;i++){ nums[s.charAt(i) - 'a'] = i; } int right = 0; int left = 0; for(int i = 0;i < len;i++){ right = Math.max(right, nums[s.charAt(i) - 'a']); if(i == right){ res.add(right - left + 1); left = right + 1; } } return res; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
进
行
一
个
分
割
56. 合并区间
class Solution { public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) { Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0],b[0])); LinkedList<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>(); que.add(intervals[0]); for(int i = 1;i < intervals.length;i++){ if(intervals[i][0] <= que.getLast()[1]){ int start = que.getLast()[0]; int end = Math.max(intervals[i][1], que.getLast()[1]); que.removeLast(); que.add(new int[]{start, end}); } else{ que.add(intervals[i]); } } return que.toArray(new int[que.size()][]); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
进
行
一
个
分
割
738.单调递增的数字
从前向后遍历的话,遇到strNum[i - 1] > strNum[i]的情况,让strNum[i - 1]减一,但此时如果strNum[i - 1]减一了,可能又小于strNum[i - 2]。
数字:332,从前向后遍历的话,那么就把变成了329,此时2又小于了第一位的3了,真正的结果应该是299。
那么从后向前遍历,就可以重复利用上次比较得出的结果了,从后向前遍历332的数值变化为:332 -> 329 -> 299
class Solution { public int monotoneIncreasingDigits(int n) { char[] str = Integer.toString(n).toCharArray(); // flag用来标记赋值9从哪里开始 // 设置为这个默认值,为了防止第二个for循环在flag没有被赋值的情况下执行 int flag = str.length; for(int i = str.length - 1; i > 0; i--){ if(str[i-1] > str[i]){ flag = i; str[i-1]--; } } for (int i = flag; i < str.length; i++) { str[i] = '9'; } String strNum = String.valueOf(str); return Integer.parseInt(strNum); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
进
行
一
个
分
割
968.监控二叉树
我们要从下往上看,局部最优:让叶子节点的父节点安摄像头,所用摄像头最少,整体最优:全部摄像头数量所用最少!
对摄像头赋予不同的状态,用来判别是否该放摄像头。
递归中,总共有三种状态: 空节点是赋予有覆盖的状态,不然要对叶子结点进行布置摄像头,不符合最小。
1.左右孩子都是有覆盖的状态,父节点是无覆盖的状态
2.左右孩子有一个是无覆盖的状态,父节点必须放摄像头
3.左右孩子有一个是有摄像头的状态,父节点是有覆盖
class Solution { int result; public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) { int num = traversal(root); if(num == 0) result++; return result; } public int traversal(TreeNode root){ //0无覆盖,1有摄像头,2有覆盖 if(root == null) return 2; int left = traversal(root.left); int right = traversal(root.right); if(left == 2 && right == 2) return 0; if(left == 0 || right == 0) { result++; return 1; } if(left == 1 || right == 1 ) return 2; return -1; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23



