- 1虚拟机(VirtualBox)新手安装指南_虚拟机安装教程
- 2区块链技术_目前七块连接的技术正确理什么阶
- 3Text2sql的一些技巧_text2sql prompt
- 4ssl忽略证书 SSLHandshakeException:PKIX path building failed ——java client
- 5网络安全学习路线+自学笔记(超详细) 自学网络安全看这一篇就够了_网络安全的学习路线从哪儿开始
- 6LeetCode-热题100:416. 分割等和子集
- 7深入Java自动化探针技术的原理和实践_java 探针
- 8Home Assistant入门1-3:在树莓派Raspbian官方系统的Python中安装Home Assistant_卸载hass
- 9重新安装VSCode后,按住Ctrl(or Command) 点击鼠标左键不跳转问题_vscode command+鼠标左键无法跳转,需要安装什么插件
- 102023年11-12月可以参加的数学建模竞赛汇总来啦~_2023小美赛
华为 在ESPN中配置单区域MSTP_华为espn
赞
踩
MSTP(Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol)是一种网络通信协议,它用于在以太网交换机上实现多个冗余链路的冗余路径选择。MSTP允许在一个网络中存在多个覆盖网络拓扑结构的Spanning Tree实例,从而提高网络的可靠性和容错性。
在单区域MSTP中,整个网络被划分为一个区域,该区域内运行MSTP协议,而不涉及不同区域之间的通信。单区域MSTP适用于小型和中型网络,其中只有一个MSTP区域。
在单区域MSTP中,交换机使用MSTP协议来计算生成树,选择最佳的路径进行数据转发。MSTP使用BPDU(Bridge Protocol Data Units)进行交换机之间的协商和通信,以选择生成树的根节点和最佳路径。
通过使用MSTP,单区域网络可以实现冗余路径选择和环路消除,确保网络的稳定性和高可靠性。它可以自动检测和切换到备用链路,以确保网络的连通性,并在网络出现故障时提供快速恢复。
总之,单区域MSTP是一种用于实现冗余路径选择和提高网络可靠性的协议,在小型和中型网络中使用。它通过选择最佳的生成树路径来优化数据转发,并提供快速的故障恢复能力。
要配置单区域MSTP,需要按照以下步骤进行操作:
-
为交换机配置MSTP协议:在交换机上启用单区域MSTP功能,使用命令将其配置为MSTP模式。
-
配置MSTP根桥:在单区域MSTP中,必须指定一个交换机作为根交换机。根交换机是生成树的起点,它负责将数据转发到网络中的其他交换机。通常,您可以通过配置交换机的优先级和MAC地址来指定根桥。
-
配置MSTP端口:通过为交换机上的每个端口设置路径成本和端口优先级,将端口分配给MSTP实例。这些配置将确定生成树中每个端口的状态和优先级。
-
配置MSTP实例:在单个MSTP区域中,可以配置多个MSTP实例。每个实例使用不同的VLAN范围,并有其自己的生成树。在单区域MSTP中,您只需要创建一个MSTP实例。
1.MSTP技术特点
MSTP,即Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol,多重生成树协议,是Spanning Tree Protocol(STP)的改进版,它支持网络中使用多条生成树,并根据用户需求限制生成树间的路径,保证不同 VLAN 之间的 L2 网络互不干扰。MSTP将多个VLAN映射到一棵生成树上,允许在拓扑不变的情况下使用多条路径,提高了网络的可用性和带宽利用率。同时MSTP也支持快速收敛和自动恢复,保证网络的可靠性。
2.MSTP的优缺点
优点:
- 高可用性:采用多生成树技术,提高网络的容错能力,保证网络可靠性及可用性。
- 灵活性:支持将多个VLAN映射到一颗生成树中,支持多路径转发,更加灵活,可以根据业务需求任意设置生成树。
- 带宽利用率高:MSTP在保证冗余的情况下,可以使用多条链路增大了带宽利用率。
缺点:
- 较复杂:相较于普通的单生成树协议,多重生成树需要复杂的配置和维护,但凭借其优越的特点,已经被广泛地应用到企业网络、数据中心网络或ISP运营商的核心接入层等部分。
实验部分:
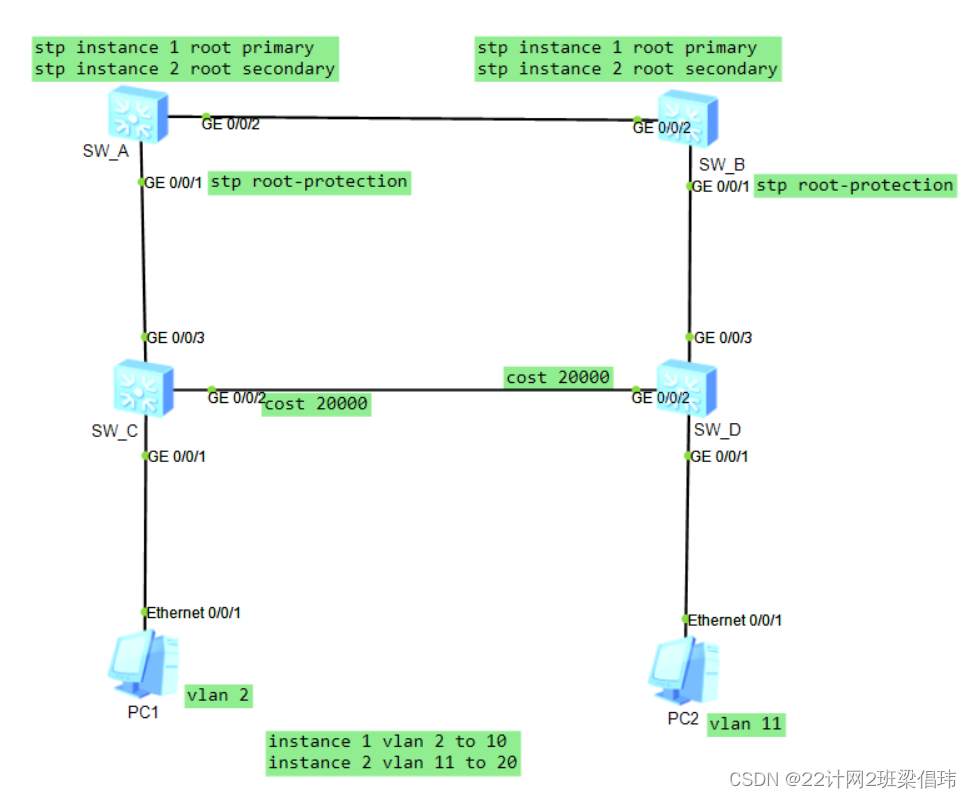
配置MSTP功能SW_A
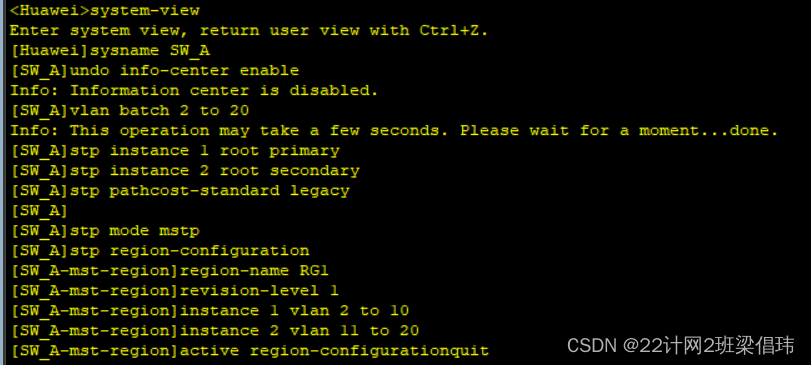
- system-view
- sysname SW_A
- undo info-center enable
-
- vlan batch 2 to 20
-
- stp instance 1 root primary
- stp instance 2 root secondary
- stp pathcost-standard legacy
-
- stp mode mstp
- stp region-configuration
- region-name RG1
- revision-level 1
- instance 1 vlan 2 to 10
- instance 2 vlan 11 to 20
- active region-configurationquit
- quit
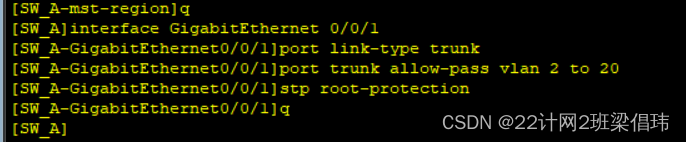
-
- interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1
- port link-type trunk
- port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20
- stp root-protection
-
-
- interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2
- port link-type trunk
- port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20
- stp root-protection
- quit
-
- quit
- sa
- y

SW-B
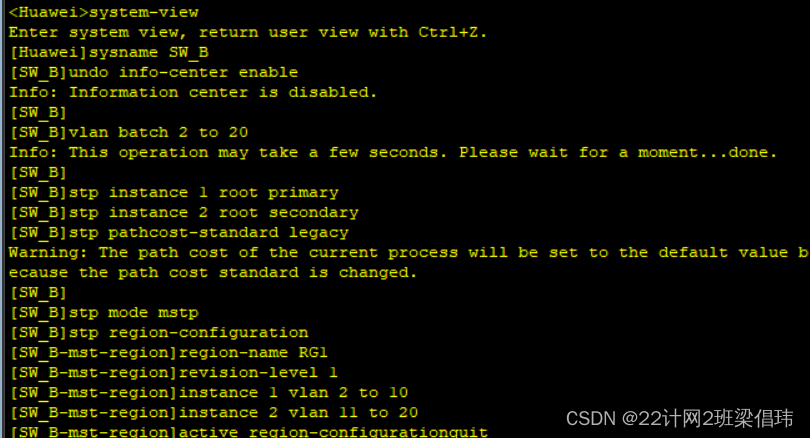
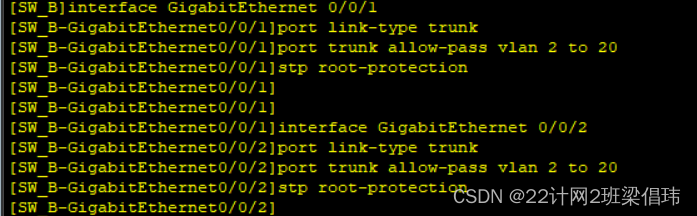
- system-view
- sysname SW_B
- undo info-center enable
-
- vlan batch 2 to 20
-
- stp instance 1 root primary
- stp instance 2 root secondary
- stp pathcost-standard legacy
-
- stp mode mstp
- stp region-configuration
- region-name RG1
- revision-level 1
- instance 1 vlan 2 to 10
- instance 2 vlan 11 to 20
- active region-configurationquit
- quit
-
- interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1
- port link-type trunk
- port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20
- stp root-protection
-
-
- interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2
- port link-type trunk
- port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20
- stp root-protection
- quit
-
- quit
- sa
- y

SW_C
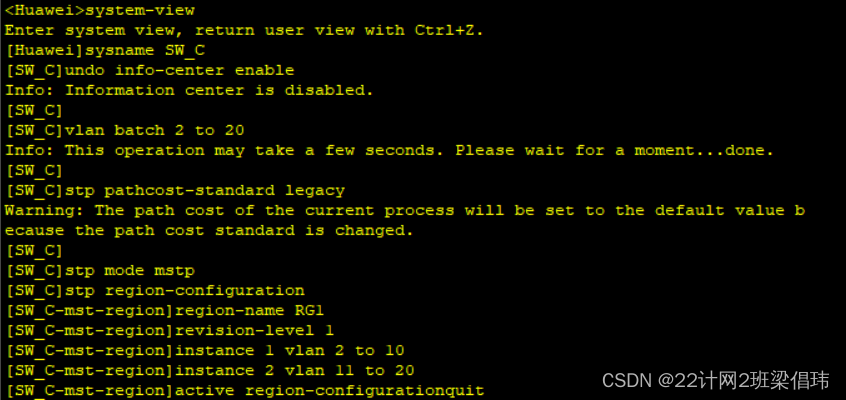
- system-view
- sysname SW_C
- undo info-center enable
-
- vlan batch 2 to 20
-
- stp pathcost-standard legacy
-
- stp mode mstp
- stp region-configuration
- region-name RG1
- revision-level 1
- instance 1 vlan 2 to 10
- instance 2 vlan 11 to 20
- active region-configurationquit
- quit
-
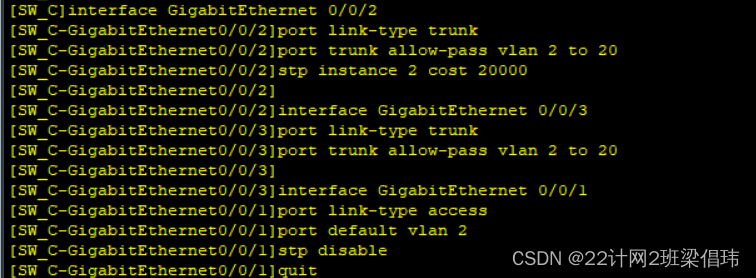
- interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2
- port link-type trunk
- port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20
- stp instance 2 cost 20000
-
- interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/3
- port link-type trunk
- port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20
-
- interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1
- port link-type access
- port default vlan 2
- stp disable
- quit
-
- quit
- sa
- y

SW_D
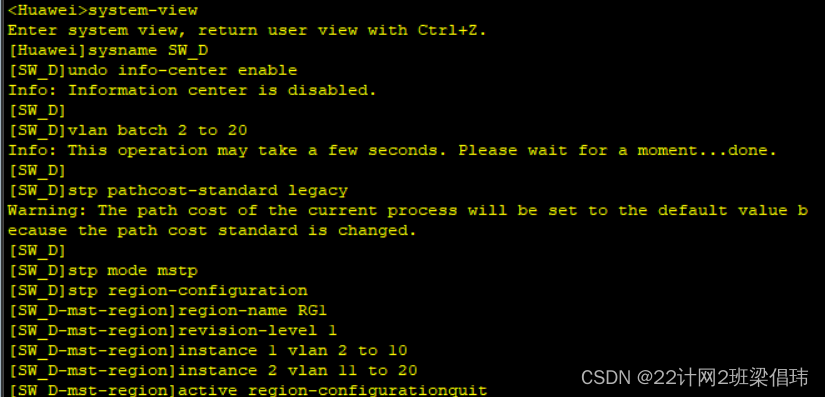
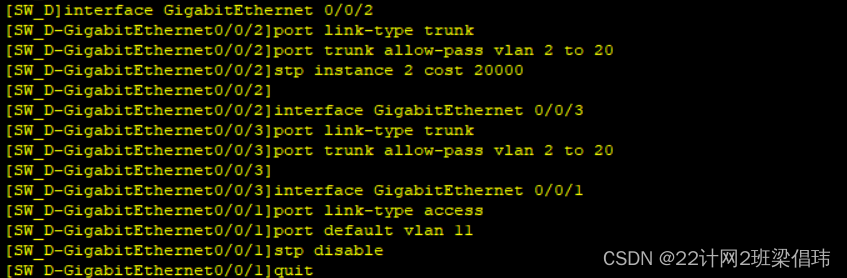
- system-view
- sysname SW_D
- undo info-center enable
-
- vlan batch 2 to 20
-
- stp pathcost-standard legacy
-
- stp mode mstp
- stp region-configuration
- region-name RG1
- revision-level 1
- instance 1 vlan 2 to 10
- instance 2 vlan 11 to 20
- active region-configurationquit
- q
-
- interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/2
- port link-type trunk
- port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20
- stp instance 2 cost 20000
-
- interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/3
- port link-type trunk
- port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 to 20
-
- interface GigabitEthernet 0/0/1
- port link-type access
- port default vlan 11
- stp disable
- quit
-
- q
- sa
- y

一定要多保存几遍 以免配置丢失!
本实验!
STP/RSTP/MSTP区别为:迁移不同、负载分担不同、字段利用不同。
一、迁移不同
1、STP:STP不能快速迁移,即使是在点对点链路或边缘端口,也必须等待时间延迟,网络才能收敛。
2、RSTP:RSTP可以快速迁移,却不能按vlan阻塞冗余链路。
3、MRSTP:MRSTP允许不同vlan的流量沿各自的路径分发,实现快速迁移不阻塞。
二、负载分担不同
1、STP:STP都采用了一棵STP tree,负载分担不可实现。
2、RSTP:RSTP都采用了一棵STP tree,负载分担不可实现。
3、MRSTP:MRSTP采用了每个VLAN一棵生成树,可以将多个VLAN的生成树映射为一个实例,实现负载分担。
三、字段利用不同
1、STP:STP对BPDU中type字段的利用,只使用了其中的两个位。
2、RSTP:RSTP对BPDU中type字段的利用,使用了所有的八个位。
3、MRSTP:MRSTP对BPDU中type字段的利用,使用了所有的八个位。
感谢观看!


