- 1鸿蒙之通过Java引用资源ID给Text控件四周添加图片不变形、不拉伸_鸿蒙开发text 多行文本的第一行 插入一个图片
- 2人工智能多模态方向学习笔记-SHOW AND TELL算法_show and tell 模型实现
- 3Qat++,轻量级开源C++ Web框架_oat++
- 4【深度学习 | Transformer】Transformers 教程:pipeline一键预测_from transformers import pipeline
- 5机器学习之分层聚类中的概念聚类(Conceptual Clustering)
- 6matex2怎么升级鸿蒙,Mate X2怎么升级鸿蒙系统 Mate X2升级鸿蒙系统步骤教程
- 7这个“1句话生成视频”AI爆火:支持中文输入,分辨率达到480×480,清华&智源出品...
- 8MATLAB APP 设计:APP 登录界面的设计_matlab app登入界面设计
- 9chatgpt赋能python:Python程序并行的优势和挑战
- 10零基础学习Python?它的就业方向你都了解吗?_python物联网开发学习方向
Google Test简述_googletest
赞
踩
Google Test简述
Google Test 是由 Google 推出的 C++ 测试框架,具有稳定、跨平台、快速等特点,能够为 C++ 开发人员提供有效的单元测试和集成测试工具。Google Test 支持 Linux、macOS 和 Windows 操作系统,同时支持 gcc、clang 和 MSVC 等多种编译器和构建系统。Google Test 还提供了大量的失败信息,方便开发人员排查问题。
特点
- 跨平台
- 不止单元测试
- 稳定并且可重复
- 提供足够的失败信息
- 快速
- 线程安全
支持的平台,编译器和构建系统
平台
- Linux
- macOS
- Windows
编译器
- gcc 5.0+
- clang 5.0+
- MSVC 2015+
macOS users: Xcode 9.3+ provides clang 5.0+.
构建系统
- Bazel
- CMake
1.最简单的使用方法-cmake通过联网编译
注意此方法必须要联网的,因为是cmake直接从github上面拉取了googletest项目。
我是在mac os上测试的,其他平台大同小异
首先,我们需要创建一个名为 hello_test.cc 的文件,并在其中添加以下代码:
#include <gtest/gtest.h>
// Demonstrate some basic assertions.
TEST(HelloTest, BasicAssertions) {
// Expect two strings not to be equal.
EXPECT_STRNE("hello", "world");
// Expect equality.
EXPECT_EQ(7 * 6, 42);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
然后,我们需要创建一个名为 CMakeLists.txt 的文件,并在其中添加以下代码:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.14) project(my_project) # GoogleTest requires at least C++14 set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14) include(FetchContent) FetchContent_Declare( googletest GIT_REPOSITORY https://github.com/google/googletest.git GIT_TAG release-1.12.1 ) # For Windows: Prevent overriding the parent project's compiler/linker settings set(gtest_force_shared_crt ON CACHE BOOL "" FORCE) FetchContent_MakeAvailable(googletest) enable_testing() add_executable( hello_test hello_test.cc ) target_link_libraries( hello_test GTest::gtest_main ) include(GoogleTest) gtest_discover_tests(hello_test)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
然后在当前目录执行以下命令,进行 CMake 的配置:
cmake -S . -B build
- 1
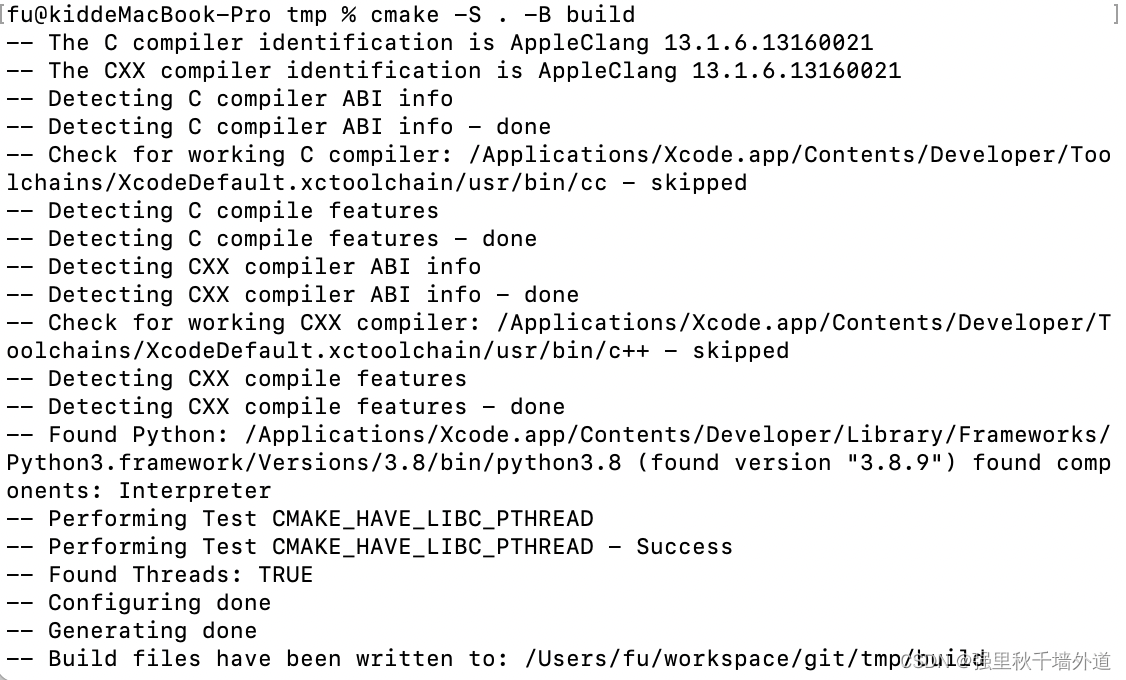
执行以上命令后,会在当前目录下创建一个名为 build 的文件夹,其中包含了 CMake 生成的 Makefile 和其他必要的文件。
接下来,我们需要执行以下命令,进行编译和链接:
cmake --build build
这一步会生成可执行文件
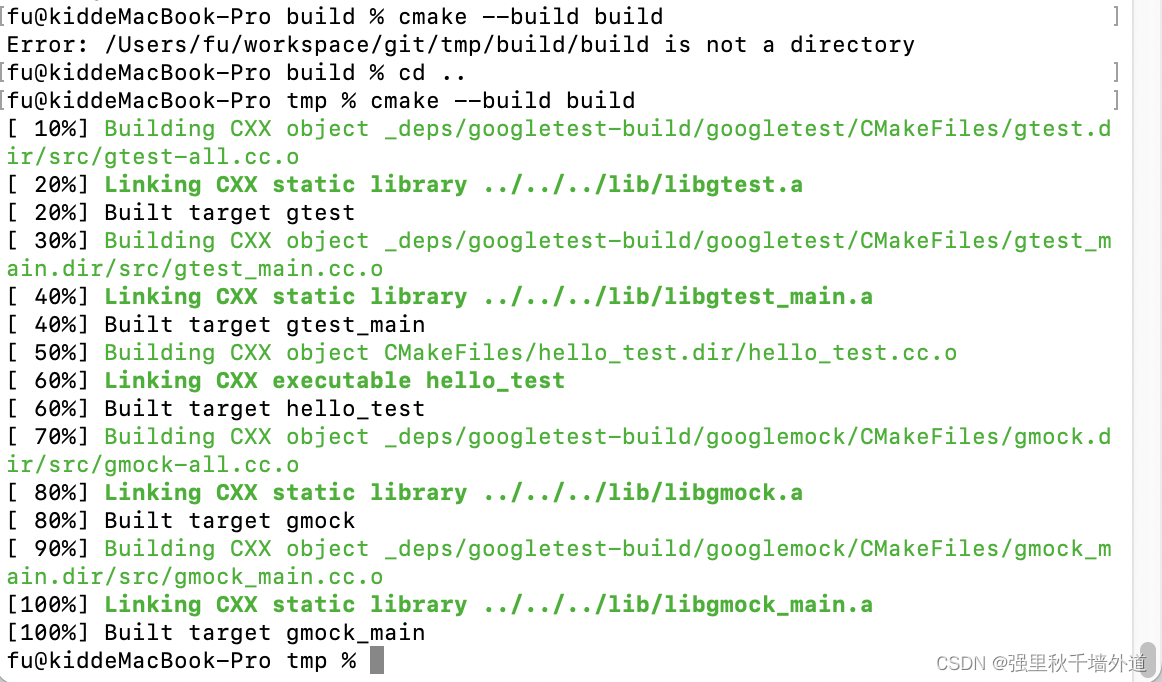
最后,我们需要执行以下命令,执行测试:
cd build && ctest
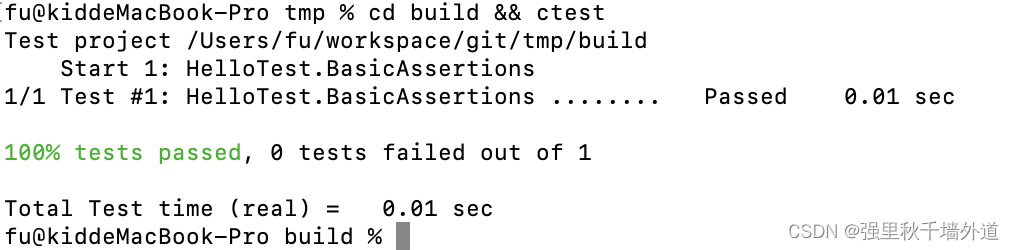
到这里已经搭建了一个很简单的googletest程序
从这里可以学会cmake的搭建一个应用的步骤
cmake -S . -B build # 搭建项目到build目录
cmake --build build # 编译链接为二进制程序
cd build #然后可以执行程序了
- 1
- 2
- 3
2.源代码编译
Google Test不是一个header-only的库,所以需要编译,同时确保头文件在包含目录中。
本文讲诉使用cmake构建Google Test,如果没有下载源代码需要下载。
Google Test使用cmake构建,cmake是现代许多C/C++项目的构建器,掌握了是很有好处的,cmake相当于对MakeFile的封装,其实底层还是调用的gcc/g++等编译器。
使用cmake编译:
git clone https://github.com/google/googletest.git -b release-1.10.0 #拉取源代码
cd googletest # 进入源代码目录
mkdir build # 创建 build 目录
cd build # 进入 build 目录
cmake .. # 生成构建文件
make # 编译生成库文件
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
如果接着输入如下代码,就可以直接在build目录生成库了,-S是source的缩写代表源码路径,-B是build的缩写,代表生成路径
cmake -S . -B build
- 1
如果要编译为动态库,则
cmake -DGTEST_CREATE_SHARED_LIBRARY=1 -S . -B build
- 1
或者进入build打开sln文件即可用IDE编译。
库文件生成在build/lib目录下面,默认为静态库。头文件在googletest/include目录下面。
我这里是使用Xcode打开,
点击这个按钮就生成了文件
可以看到库文件已经生成
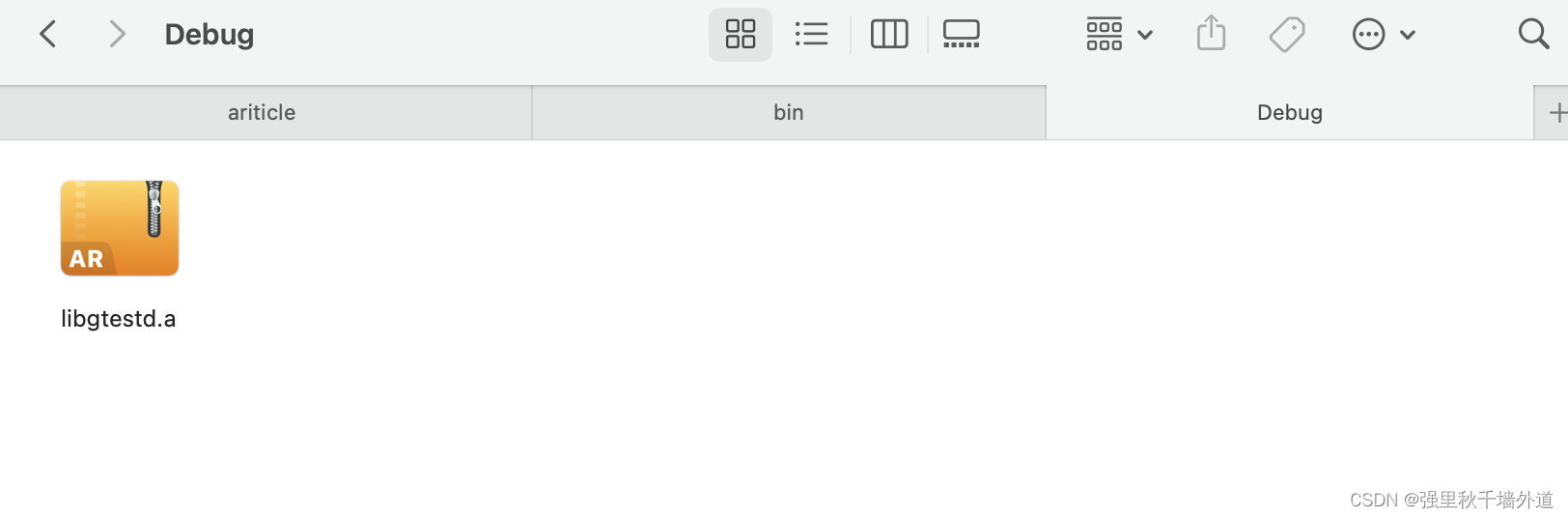
生成了库和头文件之后,就可以使用googletest了,windows平台下类似操作,使用Visual Studio生成项目文件,然后去目录中找到对应的头文件与库文件,最后将要测试的项目来编译就行了。
3. VS2019新建项目
还有一种windows上可以用的,在vs2019,我发现googletest是默认的项目模板之一,所以直接使用Visual Studio2019新建一个Google Test项目。如下图
测试代码示例
现有如下文件
sample1.h
#ifndef GOOGLETEST_SAMPLES_SAMPLE1_H_
#define GOOGLETEST_SAMPLES_SAMPLE1_H_
// Returns n! (the factorial of n). For negative n, n! is defined to be 1.
int Factorial(int n);
#endif // GOOGLETEST_SAMPLES_SAMPLE1_H_
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
sample2.cpp
#include "sample1.h"
// Returns n! (the factorial of n). For negative n, n! is defined to be 1.
int Factorial(int n) {
int result = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
result *= i;
}
return result;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
sample1_unittest.cpp
// Step 1. Include necessary header files such that the stuff your // test logic needs is declared. // // Don't forget gtest.h, which declares the testing framework. #include <limits.h> #include "sample1.h" #include "gtest/gtest.h" namespace { // Step 2. Use the TEST macro to define your tests. // // TEST has two parameters: the test case name and the test name. // After using the macro, you should define your test logic between a // pair of braces. You can use a bunch of macros to indicate the // success or failure of a test. EXPECT_TRUE and EXPECT_EQ are // examples of such macros. For a complete list, see gtest.h. // // <TechnicalDetails> // // In Google Test, tests are grouped into test cases. This is how we // keep test code organized. You should put logically related tests // into the same test case. // // The test case name and the test name should both be valid C++ // identifiers. And you should not use underscore (_) in the names. // // Google Test guarantees that each test you define is run exactly // once, but it makes no guarantee on the order the tests are // executed. Therefore, you should write your tests in such a way // that their results don't depend on their order. // // </TechnicalDetails> // Tests Factorial(). // Tests factorial of negative numbers. TEST(FactorialTest, Negative) { // This test is named "Negative", and belongs to the "FactorialTest" // test case. EXPECT_EQ(1, Factorial(-5)); EXPECT_EQ(1, Factorial(-1)); EXPECT_GT(Factorial(-10), 0); // <TechnicalDetails> // // EXPECT_EQ(expected, actual) is the same as // // EXPECT_TRUE((expected) == (actual)) // // except that it will print both the expected value and the actual // value when the assertion fails. This is very helpful for // debugging. Therefore in this case EXPECT_EQ is preferred. // // On the other hand, EXPECT_TRUE accepts any Boolean expression, // and is thus more general. // // </TechnicalDetails> } // Tests factorial of 0. TEST(FactorialTest, Zero) { EXPECT_EQ(1, Factorial(0)); } // Tests factorial of positive numbers. TEST(FactorialTest, Positive) { EXPECT_EQ(1, Factorial(1)); EXPECT_EQ(2, Factorial(2)); EXPECT_EQ(6, Factorial(3)); EXPECT_EQ(40320, Factorial(8)); } // Step 3. Call RUN_ALL_TESTS() in main(). // // We do this by linking in src/gtest_main.cc file, which consists of // a main() function which calls RUN_ALL_TESTS() for us. // // This runs all the tests you've defined, prints the result, and // returns 0 if successful, or 1 otherwise. // // Did you notice that we didn't register the tests? The // RUN_ALL_TESTS() macro magically knows about all the tests we // defined. Isn't this convenient?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
Assertions 宏详解
Googletest 断言就是宏。通过断言测试一个函数或者类的行为。
出现错误时,googletest会打印源文件、代码行数和错误信息。
结果只有三种,分别是成功,非致命错误,致命错误,即success, nonfatal failure, fatal failure。非致命错误不会终止当前函数,致命错误会终止测试程序并且退出,也就是说接下来的测试就不会运行了。
一般使用EXPECT_*,这样可以跑完整个测试程序。
宏的格式有两种:
| 宏 | 产生效果 |
|---|---|
| ASSERT_* | 致命错误 |
| EXPECT_* | 非致命错误 |
一般来说,EXPECT_*用得更多,因为可显示的错误信息不止一个。除非某条件不成立,程序就无法运行时,就使用ASSERT__*。
使用<<运算符来打印错误信息,示例:
ASSERT_EQ(x.size(), y.size()) << "Vectors x and y are of unequal length";
for (int i = 0; i < x.size(); ++i) {
EXPECT_EQ(x[i], y[i]) << "Vectors x and y differ at index " << i;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Basic Assertions
最基础的真假条件判断
| Fatal assertion | Nonfatal assertion | Verifies |
|---|---|---|
ASSERT_TRUE(condition); | EXPECT_TRUE(condition); | condition is true |
ASSERT_FALSE(condition); | EXPECT_FALSE(condition); | condition is false |
Binary Comparison
判断两个值
| Fatal assertion | Nonfatal assertion | Verifies |
|---|---|---|
ASSERT_EQ(val1, val2); | EXPECT_EQ(val1, val2); | val1 == val2 |
ASSERT_NE(val1, val2); | EXPECT_NE(val1, val2); | val1 != val2 |
ASSERT_LT(val1, val2); | EXPECT_LT(val1, val2); | val1 < val2 |
ASSERT_LE(val1, val2); | EXPECT_LE(val1, val2); | val1 <= val2 |
ASSERT_GT(val1, val2); | EXPECT_GT(val1, val2); | val1 > val2 |
ASSERT_GE(val1, val2); | EXPECT_GE(val1, val2); | val1 >= val2 |
其实有一个更简单的方式,使用vcpkg,vcpkg是微软出的C++库管理器,非常好用。基本上流行的开源的库都有。
如何使用vcpkg在我的一篇文章中有,googletest使用vcpkg编译



