- 1ROCK Pi N10(Rk3399Pro)开发记录 —— 基于Debian10系统的开发环境配置_rock pi系统
- 2【计算机毕业设计】115乐购游戏商城系统
- 3【Linux】anaconda安装
- 4探索Python中的强化学习:Q-learning_python q learning
- 523届春招结束_分享java岗面试心得_23届的java大专
- 62024年运维最新总结一下:运维工程师面试的经历及面试相关问题(1),【2024Linux运维最新学习路线
- 7【应用】【正则化】L1、L2正则化_l1正则化和l2正则化
- 8PDF Squeezer for Mac,让PDF压缩更高效
- 9IDEA下载Maven依赖包报错:Could not transfer artifact org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-parent:pom_idea could not transfer artifact org.springframewo
- 10Git详细安装教程(windows)_windows系统git安装教程(详解git安装过程) - 知乎
yolov5交互式界面 通用界面-yolo-pyqt-gui(通用界面制作+代码-V5.0-6.0版本)_yolov5界面
赞
踩
"YOLOv5交互式界面 - 通用界面-YOLO-PyQt-GUI" 它为YOLOv5的目标检测模型提供了一个用户友好的图形化操作界面。该项目通常基于Python的PyQt库构建,用于封装YOLOv5的功能,并将其转化为可视化工具,使得非专业开发人员也能便捷地使用YOLOv5进行图像或视频中目标的实时检测。
具体来说,该通用界面的主要功能可能包括:
1. 文件上传:用户可以直接在界面上加载图片或视频文件,无需通过命令行接口。
2. 实时预览:对接YOLOv5模型,实现实时视频流的人工智能目标检测,展示带有边界框和类别标签的结果。
3. 检测参数设置:允许用户自定义YOLOv5运行时的各种参数,如模型权重文件路径、输入尺寸、置信度阈值、非极大抑制阈值等。
4. 结果保存:用户可以保存检测结果,包括标注后的图片或者检测到的目标信息。
项目对YOLOv5模型应用的普及和推广有着重要作用,降低了使用者的技术门槛,让AI技术更加贴近实际应用场景,方便用户在无需深入理解YOLOv5内部原理的情况下,快速部署和使用目标检测功能。此GUI界面能适配YOLOv5在这两个主要版本间的更新变化。
yolo GUI OYQT界面——
YOLOv5-GUI是一款专为YOLOv5(包括版本5和版本6)目标检测算法设计开发的图形用户界面(GUI)工具,采用强大的Qt框架构建。该工具汲取了Javacr大神在UI设计与逻辑方面的精华理念,旨在为广大用户提供更为直观、便捷且高效的YOLOv5模型训练、测试和应用体验。
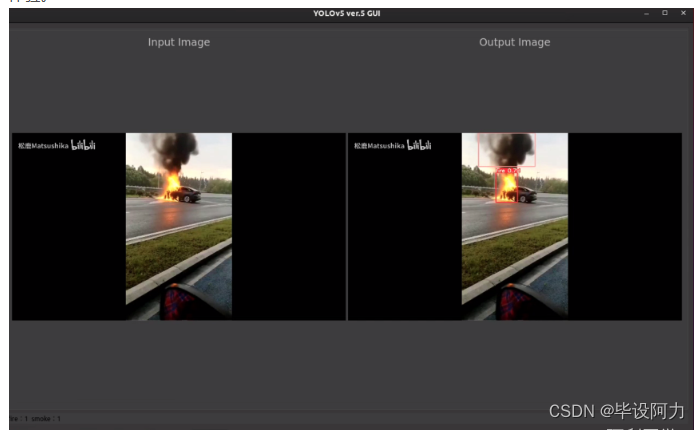
YOLOv5-GUI拥有深色和浅色两种主题风格供用户自由选择,满足不同场景下的视觉需求。深色模式有助于降低长时间使用电脑时的眼部疲劳,而浅色模式则适合在各种光照条件下保持清晰舒适的视觉效果。
此GUI工具集成了YOLOv5的核心功能,包括但不限于模型加载、参数配置、数据集管理、训练过程可视化监控、实时视频目标检测以及结果展示等环节。用户无需通过命令行操作,只需通过点击和拖拽等方式即可完成复杂的深度学习任务,极大降低了YOLOv5的使用门槛。
在实际应用中,YOLOv5-GUI能够帮助科研人员、开发者以及广大AI爱好者更高效地利用YOLOv5算法进行目标检测项目的研究与实践,无论是对已有的公开数据集进行模型训练优化,还是针对特定场景定制目标检测解决方案,都能轻松应对。
代码使用
切换到项目目录:
- bash
- cd [PyQt5-YOLOv5_V5/PyQt5-YOLOv5_V6]
接下来,安装所需的环境依赖:
- bash
- pip install -r requirements.txt
现在,你可以启动应用程序:
- bash
- python run.py
该GUI应用程序默认采用深色模式,但如果你想切换到浅色模式,只需在run.py文件中将main_ui_dark修改为main_ui_light即可。
这个GUI应用程序提供了许多功能和选项,可以帮助你使用YOLOv5更加方便和高效。你可以在界面上进行图像处理、对象检测等操作。另外,你也可以根据自己的需求对代码进行定制和扩展。
总的来说,这个项目为使用YOLOv5提供了一个直观和友好的界面,使得用户能够更轻松地利用这一强大的目标检测工具。希望你能享受使用这个GUI应用程序,并从中获得更多的收获和乐趣!
重要代码
- def run(self,
- imgsz=640, # inference size (pixels)
- iou_thres=0.45, # NMS IOU threshold
- max_det=1000, # maximum detections per image
- device='', # cuda device, i.e. 0 or 0,1,2,3 or cpu
- view_img=True, # show results
- save_txt=False, # save results to *.txt
- save_conf=False, # save confidences in --save-txt labels
- save_crop=False, # save cropped prediction boxes
- nosave=False, # do not save images/videos
- classes=None, # filter by class: --class 0, or --class 0 2 3
- agnostic_nms=False, # class-agnostic NMS
- augment=False, # augmented inference
- visualize=False, # visualize features
- update=False, # update all models
- project='runs/detect', # save results to project/name
- name='exp', # save results to project/name
- exist_ok=False, # existing project/name ok, do not increment
- line_thickness=3, # bounding box thickness (pixels)
- hide_labels=False, # hide labels
- hide_conf=False, # hide confidences
- half=False, # use FP16 half-precision inference
- dnn=False, # use OpenCV DNN for ONNX inference
- ):
-
- # Initialize
- device = select_device(device)
- half &= device.type != 'cpu' # half precision only supported on CUDA
-
- # Load model
- model = DetectMultiBackend(self.weights, device=device, dnn=dnn)
- num_params = 0
- for param in model.parameters():
- num_params += param.numel()
- stride, names, pt, jit, onnx, engine = model.stride, model.names, model.pt, model.jit, model.onnx, model.engine
- imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=stride) # check image size
- names = model.module.names if hasattr(model, 'module') else model.names # get class names
- if half:
- model.half() # to FP16
-
- # Dataloader
- if self.source.isnumeric():
- view_img = check_imshow()
- cudnn.benchmark = True # set True to speed up constant image size inference
- dataset = LoadStreams(self.source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride, auto=pt and not jit)
- bs = len(dataset) # batch_size
- else:
- dataset = LoadImages(self.source, img_size=imgsz, stride=stride, auto=pt and not jit)
- bs = 1 # batch_size
- vid_path, vid_writer = [None] * bs, [None] * bs
-
- # Run inference
- # model.warmup(imgsz=(1, 3, *imgsz), half=half) # warmup
- dt, seen = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], 0
- for path, im, im0s, self.vid_cap, s in dataset:
- statistic_dic = {name: 0 for name in names}
- t1 = time_sync()
- im = torch.from_numpy(im).to(device)
- im = im.half() if half else im.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
- im /= 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
- if len(im.shape) == 3:
- im = im[None] # expand for batch dim
- t2 = time_sync()
- dt[0] += t2 - t1
-
- # Inference
- pred = model(im, augment=augment)
- t3 = time_sync()
- dt[1] += t3 - t2
-
- # NMS
- pred = non_max_suppression(pred, self.conf_thres, iou_thres, classes, agnostic_nms, max_det=max_det)
- dt[2] += time_sync() - t3
-
- for i, det in enumerate(pred): # detections per image
- im0 = im0s.copy()
- annotator = Annotator(im0, line_width=line_thickness, example=str(names))
- if len(det):
- det[:, :4] = scale_coords(im.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
- for c in det[:, -1].unique():
- n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per class
- s += f"{n} {names[int(c)]}{'s' * (n > 1)}, " # add to string
-
- for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
- c = int(cls) # integer class
- statistic_dic[names[c]] += 1
- label = None if hide_labels else (names[c] if hide_conf else f'{names[c]} {conf:.2f}')
- annotator.box_label(xyxy, label, color=colors(c, True))
-
-
- time.sleep(1/40)
- # print(type(im0s))
- self.send_img.emit(im0)
- self.send_raw.emit(im0s if isinstance(im0s, np.ndarray) else im0s[0])
- self.send_statistic.emit(statistic_dic)



