- 1Android开发之 permission动态权限获取_android import android.manifest
- 2jmeter安装教程与新手入门
- 3Redis搭建及使用
- 4leetcode 160. 相交链表 python_leetcode 相交链表超时
- 5面经八股汇总_bert八股
- 6数据结构入门7-2(散列表)_设散列表的长度为100
- 7【容器化】Oceanbase镜像构建及使用_obclient容器镜像
- 8Zookeeper笔记_zookeeper observer
- 9【计算机毕业设计】基于微信小程序的心理健康测试系统_微信小程序形式,实现特定群体心理健康状态测试、分析并设计干预交友等小功能
- 10在CentOS 7中安装kafka详细步骤_cent os安装kafka systemd
Hadoop的MapReduce使用_hadoop mapreduce使用
赞
踩

一、MapReduce框架结构
一个完整的mapreduce程序在分布式运行时有三类实例进程:
1、MRAppMaster:负责整个程序的过程调度及状态协调
2、MapTask:负责map阶段的整个数据处理流程
3、ReduceTask:负责reduce阶段的整个数据处理流程
二、MapReduce 编程规范及示例编写
2.1 编程规范
1、写一个类(MyMapper),继承hadoop框架的Mapper类,这个类就是map任务。我们只需要重写这个类的map方法(目的就是定义怎么检查每个组的作业)
2、写一个类(MyReducer),继承hadoop框架的Reducer类,这个类就是reduce任务。我们只需要重写这个类的reduce方法(目的就是定义怎么汇总那么多map任务的输出)
3、写一个普通的类(例如Demo),在Dem类中,创建一个Job对象,这个对象用于对MyMapper类和MyReducer类的配对,还用于配置MyMapper类的输出结果类型、输入数据来源。还用于配置MyReducer类的输出结果类型,输出结果目的地等等。
2.2 WordCount示例编写
需求:在一堆给定的文本文件中统计输出每一个单词出现的总次数
- public class Demo1_wordcount {
-
- private static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>{
- IntWritable v = new IntWritable(1);
- protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- String[] arr = value.toString().split("\\s+");
- for (String item : arr) {
- value.set(item);
- context.write(value, v);
- }
- }
- }
-
- private static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>{
- IntWritable v = new IntWritable();
- @Override
- protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> value, Context context)throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- int count = 0;
- Iterator<IntWritable> it = value.iterator();
- while(it.hasNext()){
- IntWritable next = it.next();
- count += next.get();
- }
- v.set(count);
- context.write(key, v);
- }
- }
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- Job job = Job.getInstance();
- //指定当前程序所在的jar包
- job.setJarByClass(WordCountDemo01.class);
-
- //指定使用哪个Mapper类
- job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
- //指定使用哪个Reducer类
- job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
-
- //指定mapper的输出类型
- job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
-
- //指定reducer的输出类型
- job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
-
- //指定数据来源
- FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
- //FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/in"));
- //指定目的地
- FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
- //FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/out"));
-
- //提交任务
- //job.submit();看不到日志的,不用它
- boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
- System.exit(b ? 0 : 1);
- }
- }

三、MapReduce 程序运行模式
3.1 本地运行模式
什么也不写,直接在工具上运行,默认就是本地运行模式。
前提:在windows中,解压好windows版本的hadoop,并且要配置好环境变量
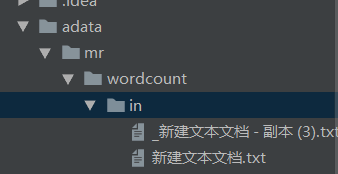
- FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/in"));
- FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/out"));
3.2 集群运行模式
1、注意修改数据来源是hdfs集群的路径、目的地也是集群中的路径
- FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
- FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
2、对包含mr程序的项目打包,并且指定mainclass是谁(主方法所在的类就是mainclass)
- <plugin>
- <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
- <artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
- <version>2.4</version>
- <configuration>
- <archive>
- <manifest>
- <addClasspath>true</addClasspath>
- <classpathPrefix>lib/</classpathPrefix>
- <mainClass>com.hadoop.Demo1_wordcount</mainClass>
- </manifest>
- </archive>
- </configuration>
- </plugin>
3、把打好的jar包,上传到linux系统中
4、hdfs集群中要提前创建好数据来源,并且hdfs、yarn集群先启动
start-all.sh5、hadoop jar hadoop-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar /wc/in /wc/out
这里的/wc/in会传输到args[0],/wc/out会传输到args[1]中
6、查看yarn集群界面:http://node1:8088

四、序列化
4.1 Writable 序列化接口
- public class FlowBean implements Writable {
-
- private long upflow; //上行流量
- private long downflow; //下行流量
-
- public long getUpflow() {
- return upflow;
- }
-
- public void setUpflow(long upflow) {
- this.upflow = upflow;
- }
-
- public long getDownflow() {
- return downflow;
- }
-
- public void setDownflow(long downflow) {
- this.downflow = downflow;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
- //先序列化upflow
- out.writeLong(this.upflow);
- //再序列化downflow
- out.writeLong(this.downflow);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
- //第一次调用readLong方法,其实是read到了upflow,因为序列化的时候,是先序列化upflow的
- this.upflow = in.readLong();
- this.downflow = in.readLong();
- }
-
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return this.upflow + "\t" + this.downflow + "\t" + (this.upflow + this.downflow);
- }
- }

4.2 流量汇总
- public class Demo02_FlowSum {
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- Job job = Job.getInstance();
- job.setJarByClass(Demo02_FlowSum.class);
-
- job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- job.setMapOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
-
- job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class);
-
- job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
- job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
-
- FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/in"));
- FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/out1"));
-
- System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
- }
-
- public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, FlowBean> {
-
- private Text k = new Text();
- private FlowBean v = new FlowBean();
-
- @Override
- protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- String[] arr = value.toString().split("\\s+");
- v.setUpflow(Integer.parseInt(arr[arr.length - 3]));
- v.setDownflow(Integer.parseInt(arr[arr.length - 2]));
- k.set(arr[1]);
- context.write(k, v);
- }
- }
-
- public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, FlowBean, Text, FlowBean> {
- private FlowBean flowBean = new FlowBean();
- @Override
- protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<FlowBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- flowBean.setUpflow(0);
- flowBean.setDownflow(0);
- for (FlowBean value : values) {
- flowBean.setUpflow(value.getUpflow() + flowBean.getUpflow());
- flowBean.setDownflow(value.getDownflow() + flowBean.getDownflow());
- }
- context.write(key, flowBean);
- }
- }
- }

五、自定义排序
5.1 需求
在得出统计每一个用户(手机号)所耗费的总上行流量、下行流量,总流量结果的基础之上再加一个需求:将统计结果按照总流量倒序排序。
5.2 排序代码实现
- public class FlowBean1 implements WritableComparable<FlowBean1> {
-
- private String phone;
- private int upflow; //上行流量
- private int downflow; //下行流量
-
- public String getPhone() {
- return phone;
- }
-
- public void setPhone(String phone) {
- this.phone = phone;
- }
-
- public int getUpflow() {
- return upflow;
- }
-
- public void setUpflow(int upflow) {
- this.upflow = upflow;
- }
-
- public int getDownflow() {
- return downflow;
- }
-
- public void setDownflow(int downflow) {
- this.downflow = downflow;
- }
-
- @Override
- public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
- out.writeUTF(this.phone);
- //先序列化upflow
- out.writeInt(this.upflow);
- //再序列化downflow
- out.writeInt(this.downflow);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
- //第一次调用readLong方法,其实是read到了upflow,因为序列化的时候,是先序列化upflow的
- this.phone = in.readUTF();
- this.upflow = in.readInt();
- this.downflow = in.readInt();
- }
-
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return this.phone + "\t" + this.upflow + "\t" + this.downflow + "\t" + (this.upflow + this.downflow);
- }
-
- /*
- 1、按照总流量从大到小的顺序排序
- 2、总流量一样的情况,按照手机号的字典顺序来排序
- */
- @Override
- public int compareTo(FlowBean1 o) {
- int sum = this.upflow + this.downflow - o.upflow - o.downflow;
- if (sum != 0) {
- return -sum;
- }
- int num = this.phone.compareTo(o.phone);
- if (num != 0) {
- return -num;
- }
- return 111;
- }
- }

- public class Demo03_FlowSumSort {
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- Job job = Job.getInstance();
- job.setJarByClass(Demo03_FlowSumSort.class);
-
- job.setMapOutputKeyClass(FlowBean1.class);
- job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
-
- job.setOutputKeyClass(FlowBean1.class);
- job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
-
- job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
- job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
-
- FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/out1"));
- FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/out2"));
-
- System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
- }
-
- public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, FlowBean1, NullWritable> {
- private FlowBean1 bean = new FlowBean1();
- private NullWritable v = NullWritable.get();
- @Override
- protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- String[] arr = value.toString().split("\\s+");
- bean.setPhone(arr[0]);
- bean.setUpflow(Integer.parseInt(arr[1]));
- bean.setDownflow(Integer.parseInt(arr[2]));
- context.write(bean, v);
- }
- }
-
- public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<FlowBean1, NullWritable, FlowBean1, NullWritable> {
- private NullWritable v = NullWritable.get();
- @Override
- protected void reduce(FlowBean1 key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- context.write(key, v);
- }
- }
- }

六、自定义分区
6.1 需求
将流量汇总统计结果,按照手机归属地不同省份输出到不同文件中。
6.2 代码实现
- public class Demo04_Partitioner {
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- Job job = Job.getInstance();
- job.setJarByClass(Demo04_Partitioner.class);
-
- job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
-
- job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
-
- job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
- job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
- job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class);//设置使用自己的分区类
- job.setNumReduceTasks(3);//有几个分区,就设置几个reducetask
-
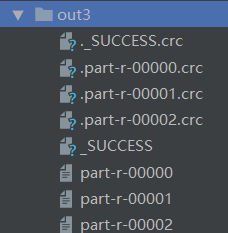
- FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/out2"));
- FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/out3"));
-
- System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
- }
-
-
- public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
- @Override
- protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- context.write(value, NullWritable.get());
- }
- }
-
- public static class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, NullWritable> {
- @Override
- public int getPartition(Text text, NullWritable nullWritable, int numPartitions) {
- String phone = text.toString().substring(0, 3);
- switch (phone) {
- case "134":
- case "135":
- case "136":
- return 0;
- case "137":
- case "138":
- return 1;
- }
- return 2;
- }
- }
-
- public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, NullWritable, Text, NullWritable> {
-
- private NullWritable v = NullWritable.get();
- @Override
- protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- context.write(key, v);
- }
- }
- }

七、combiner的使用
每一个 map 都可能会产生大量的本地输出,Combiner 的作用就是对 map 端的输出先做一次合并,以减少在 map 和 reduce 节点之间的数据传输量,以提高网络 IO 性能,是 MapReduce 的一种优化手段之一。
Combiner的父类,也是Reducer。使用时,可以公用MyReducer类,作为Combinner类 。注意:Combiner的输出类型,必须和Mapper的输出类型一致。
代码实现:
- public class Demo05_WordCount {
-
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- Job job = Job.getInstance();
-
- job.setCombinerClass(MyCombiner.class);
-
- //指定当前程序所在的jar包
- job.setJarByClass(Demo05_WordCount.class);
-
- //指定数据来源
- FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/in"));
-
- //指定目的地
- FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("adata/mr/wordcount/out4"));
-
- //指定使用哪个mapper类
- job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
-
- //指定使用哪个Reducer类
- job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
-
- //指定map方法的输出类型
- job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
-
- //指定reduce方法的输出类型
- job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
- job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
-
- //提交任务
- //job.submit();看不到日志的,不用
- boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
-
- //如果是0,就代表程序运行正常,正常退出虚拟机。非0就代表异常
- System.exit(b ? 0 : 443);
- }
-
-
- public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
- private IntWritable v = new IntWritable(1);
- private Text k = new Text();
- @Override
- protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- String[] arr = value.toString().split("\\s+");
- for (String str : arr) {
- k.set(str);
- context.write(k, v);
- }
- }
- }
-
- public static class MyCombiner extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
- private IntWritable v = new IntWritable();
- @Override
- protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- int count = 0;
- for (IntWritable value : values) {
- count += value.get();
- }
- v.set(count);
- context.write(key, v);
- }
- }
-
- public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
- @Override
- protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
- for (IntWritable value : values) {
- context.write(key, value);
- }
- }
- }
- }



