热门标签
热门文章
- 1linux配置yum源_linux yum源
- 2国密算法介绍
- 3yolo可视化——loss、Avg IOU、P-R、mAP、Recall (没有xml文件的情况)_yolo评估指标box loss200
- 4RNN和LSTM详解_lstm 分类 损失函数
- 5SQL 入门及常用实例_sql实例
- 6SQL Server 2012 安装配置图文详解_sql2012安装教程图解
- 7无root权限安装git-lfs(linux版)_linux git lfs
- 8gepc 增强数据的加载 patch enhance_.stack(patches)
- 9基于java的企业员工信息管理系统,ssm+jsp,mysql数据库,员工+管理员,完美运行,有ppt,有一万五千字论文_员工管理系统计算机毕业论文一万五千字
- 10Adb windows脚本_adb 脚本宏
当前位置: article > 正文
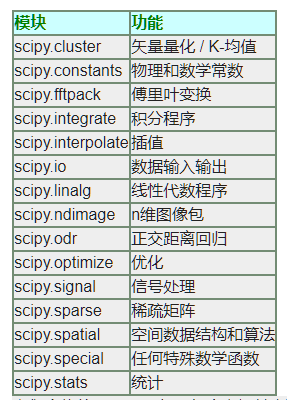
Scipy简介_scipy的主要功能
作者:Gausst松鼠会 | 2024-04-14 21:16:12
赞
踩
scipy的主要功能
Scipy简介
- Scipy依赖于Numpy
- Scipy包含的功能:最优化、线性代数、积分、插值、拟合、特殊函数、快速傅里叶变换、信号处理、图像处理、常微分方程求解器等
- 应用场景:Scipy是高端科学计算工具包,用于数学、科学、工程学等领域
- Scipy由一些特定功能的子模块组成:
图片消噪处理
- scipy.fftpack模块用来计算快速傅里叶变换
速度比传统傅里叶变换更快,是对之前算法的改进
图片是二维数据,注意使用fftpack的二维转变方法
from scipy.fftpack import fft2, ifft2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline import numpy as np #读取照片数据 moon = plt.imread('moonlanding.png') ==> array([[ 0.04705882, 0. , 0.23921569, ..., 0. , 0.00392157, 0.53333336], [ 0. , 0. , 0.67843139, ..., 0.10196079, 0.29019609, 0. ], [ 0.72156864, 0.10980392, 0.60392159, ..., 0. , 0.21568628, 1. ], ..., [ 0.00392157, 0. , 1. , ..., 1. , 1. , 0.95686275], [ 0. , 0. , 0.15686275, ..., 0. , 0. , 0.35294119], [ 1. , 0.52156866, 0.04705882, ..., 0. , 0. , 1. ]], dtype=float32 #数据形式 moon.shape ==> (474, 630) #展示图片 plt.imshow(moon, cmap='gray') #cmap 指定RGB的Z值,如果是三维数组则忽略cmap值 # 可选择的颜色映射参数为:Accent, Accent_r, Blues, Blues_r, BrBG, BrBG_r, BuGn, BuGn_r, BuPu, BuPu_r, CMRmap, CMRmap_r, Dark2, Dark2_r, GnBu, GnBu_r, Greens, Greens_r, Greys, Greys_r, OrRd, OrRd_r, Oranges, Oranges_r, PRGn, PRGn_r, Paired, Paired_r, Pastel1, Pastel1_r, Pastel2, Pastel2_r, PiYG, PiYG_r, PuBu, PuBuGn, PuBuGn_r, PuBu_r, PuOr, PuOr_r, PuRd, PuRd_r, Purples, Purples_r, RdBu, RdBu_r, RdGy, RdGy_r, RdPu, RdPu_r, RdYlBu, RdYlBu_r, RdYlGn, RdYlGn_r, Reds, Reds_r, Set1, Set1_r, Set2, Set2_r, Set3, Set3_r, Spectral, Spectral_r, Vega10, Vega10_r, Vega20, Vega20_r, Vega20b, Vega20b_r, Vega20c, Vega20c_r, Wistia, Wistia_r, YlGn, YlGnBu, YlGnBu_r, YlGn_r, YlOrBr, YlOrBr_r, YlOrRd, YlOrRd_r, afmhot, afmhot_r, autumn, autumn_r, binary, binary_r, bone, bone_r, brg, brg_r, bwr, bwr_r, cool, cool_r, coolwarm, coolwarm_r, copper, copper_r, cubehelix, cubehelix_r, flag, flag_r, gist_earth, gist_earth_r, gist_gray, gist_gray_r, gist_heat, gist_heat_r, gist_ncar, gist_ncar_r, gist_rainbow, gist_rainbow_r, gist_stern, gist_stern_r, gist_yarg, gist_yarg_r, gnuplot, gnuplot2, gnuplot2_r, gnuplot_r, gray, gray_r, hot, hot_r, hsv, hsv_r, inferno, inferno_r, jet, jet_r, magma, magma_r, nipy_spectral, nipy_spectral_r, ocean, ocean_r, pink, pink_r, plasma, plasma_r, prism, prism_r, rainbow, rainbow_r, seismic, seismic_r, spectral, spectral_r, spring, spring_r, summer, summer_r, tab10, tab10_r, tab20, tab20_r, tab20b, tab20b_r, tab20c, tab20c_r, terrain, terrain_r, viridis, viridis_r, winter, winter_r # 傅里叶变换消噪 # 把时域空间转换到频域空间 f_moon = fft2(moon) #关键步骤,过滤条件必须写好 # 在频域空间对高幅度的波进行过滤 f_moon[f_moon>3e2] = 0 # 把频域空间转回到时域空间 if_moon = np.real(ifft2(f_moon)) #展示 plt.imshow(if_moon, cmap="gray")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 图片灰度处理
用二维数组展示的图片,没有RGB三原色,只有一个灰度值
# 利用数组随机数生成一个图片
data = np.random.randint(0,255,size=(1000,1000,3))
# astype 用来转换数组中数据的类型
plt.imshow(data.astype(np.uint8))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5

- jpg图像和png图像的区别
- jpg图像 3个0-255之间的uint8类型整数来表示颜色
- png图像 3个0-1之间的float32类型小数来表示颜色
back = plt.imread('back.jpg')
back.shape ==> (506, 900, 3)
back.dtype ==>dtype('uint8')
back.max(), back.min() ==>(255, 0)
#取最大值或最小值
back.max(axis=2).shape
plt.imshow(back.max(axis=2))
#取平均值
plt.imshow(back.mean(axis=2))
#用点乘积引入权重
weight = np.array([0.3,0.4,0.3])
plt.imshow(np.dot(back, weight), cmap="gray")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
原照片

处理后

高数积分
- 使用 数值积分,求解圆周率
# 使用scipy.integrate进行积分,调用quad()方法 #定义圆函数 f = lambda x : (1-x**2)**0.5 #对积分区间切分 x = np.linspace(-1,1,100) y = f(x) #定义图像大小 plt.figure(figsize=(4,4)) #使图像横轴纵轴比例一致 plt.axis("equal") #指定x、y的值域区间 plt.plot(x, y) plt.plot(x, -y) # 求不规则图形的面积 from scipy.integrate import quad area, err = quad(f, a, b) 得到面积和误差==> (1.5707963267948986, 1.0002356720661965e-09) #用s/r^2得到圆周率 area*2/1**2 ==>3.141592653589797
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21

Scipy文件输入/输出
scipy.io
import scipy.io as io
- 1
随机生成数组,使用scipy中的io.savemat()保存
文件格式是.mat,标准的二进制文件
import scipy.io as scio
使用io.savemat()保存图片,数据必须用字典格式
#scio.savemat(file_name, mdict, appendmat=True, format='5', long_field_names=False, do_compression=False, oned_as='row')
scio.savemat('back.mat',{"data":back})
使用io.loadmat()读取数据
# scio.loadmat(file_name, mdict=None, appendmat=True, **kwargs)
scio.loadmat('back.mat')["data"]
#展示数据
plt.imshow(scio.loadmat('back.mat')["data"])
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12

scipy.misc
- misc.imread()/imsave() 读写图片
from scipy import misc
#读取照片数据
#misc.imread(name, flatten=False, mode=None)
back = misc.imread('back.jpg')
#写入文件, misc.imsave(name, arr, format=None)
data = np.random.randint(0,255,size=(100,100,3))
# numpy series
data = data.astype(np.uint8)
misc.imsave('data.jpg', data)
#展示保存图片
plt.imshow(misc.imread('data.jpg'))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- misc的rotate、resize、imfilter操作
# 旋转图片 #1.读取照片数据(系统自带的照片),face = misc.face(gray=True) face = misc.face(gray=True) #2.展示 misc.imrotate(arr, angle, interp='bilinear') plt.imshow(misc.imrotate(face, angle=70)) # 改变照片大小,misc.imresize(arr, size, interp='bilinear', mode=None) #1.size使用0-1之间的小数,表示的是分数比 plt.imshow(misc.imresize(face, size=0.5)) #2.size使用整数,表示的是百分比 plt.imshow(misc.imresize(face, size=50)) #3.size使用元组,表示两个方向保留的像素点个数,取值是等间距取值 plt.imshow(misc.imresize(face, size=(30,60))) #滤镜 Signature: misc.imfilter(arr, ftype) # ftype的取值:'blur', 'contour', 'detail', 'edge_enhance', 'edge_enhance_more','emboss', 'find_edges', 'smooth', 'smooth_more', 'sharpen'. plt.imshow(misc.imfilter(face, "emboss"),cmap="gray")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
使用scipy.ndimage图片处理
使用scipy.misc.face(gray=True)获取图片,使用ndimage移动坐标、旋转图片、切割图片、缩放图片
from scipy import ndimage # 1.shift移动坐标 ''' ndimage.shift(input, shift, output=None, order=3, mode='constant', cval=0.0, prefilter=True) mode(移动图片后空余部分的填充方式) 可选参数 'constant', 'nearest', 'reflect', 'mirror' or 'wrap' shift 移动的范围,给定的数值是float则x,y移动相同距离,也可以给定一个列表 ''' plt.imshow(ndimage.shift(face,shift=200,mode="constant"), cmap="gray") plt.imshow(ndimage.shift(face,shift=[100,100],mode="mirror")) # rotate旋转图片 ''' ndimage.rotate(input, angle, axes=(1, 0), reshape=True, output=None, order=3, mode='constant', cval=0.0, prefilter=True) ''' plt.imshow(ndimage.rotate(face, angle=60)) # zoom缩放图片 ''' ndimage.zoom(input, zoom, output=None, order=3, mode='constant', cval=0.0, prefilter=True) zoom接受一个比例列表,表示不同的轴上的比值 ''' plt.imshow(ndimage.zoom(face,zoom=0.5)) plt.imshow(ndimage.zoom(face,zoom=[0.3,2]))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 图片进行过滤
添加噪声,对噪声图片使用ndimage中的高斯滤波、中值滤波、signal中维纳滤波进行处理
使图片变清楚
# 加载图片,使用灰色图片misc.face()添加噪声 moon = plt.imread('moonlanding.png') plt.imshow(moon, cmap="gray") #gaussian高斯滤波参数sigma:高斯核的标准偏差 ''' ndimage.gaussian_filter(input, sigma, order=0, output=None, mode='reflect', cval=0.0, truncate=4.0) ''' plt.imshow(ndimage.gaussian_filter(moon, sigma=0.8), cmap="gray") #median中值滤波 ''' ndimage.median_filter(input, size=None, footprint=None, output=None, mode='reflect', cval=0.0, origin=0) 参数size:给出在每个元素上从输入数组中取出的形状位置,定义过滤器功能的输入 ''' plt.imshow(ndimage.median_filter(moon, size=6), cmap="gray") #signal维纳滤波 ''' signal.wiener(im, mysize=None, noise=None) 参数mysize:滤镜尺寸的标量 ''' import scipy.signal as signal plt.imshow(signal.wiener(moon, mysize=6), cmap="gray")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
pandas绘图函数
Series和DataFrame都有一个用于生成各类图表的plot方法。默认情况下,它们所生成的是线形图
- matplotlib来绘制
- 格式: s.plot(kind=‘line’, ax=None, figsize=None, use_index=True, title=None, grid=None, legend=False, style=None, logx=False, logy=False, loglog=False, xticks=None, yticks=None, xlim=None, ylim=None, rot=None, fontsize=None, colormap=None, table=False, yerr=None, xerr=None, label=None, secondary_y=False, **kwds)
- 参数kind用来指定绘制图像类型:
- ‘line’ : line plot (default)
- ‘bar’ : vertical bar plot
- ‘barh’ : horizontal bar plot
- ‘hist’ : histogram
- ‘box’ : boxplot
- ‘kde’ : Kernel Density Estimation plot
- ‘density’ : same as ‘kde’
- ‘area’ : area plot
- ‘pie’ : pie plot
- 参数kind用来指定绘制图像类型:
# pandas整合的一些图形的绘制办法
# 绘图要先导入包
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 在当前文本编辑器中绘制图像
%matplotlib inline
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
线形图line
- 一般用于描述数据变化趋势
- 线型图最常用的横坐标就是时间
# data是要展示的数据 data = np.random.randint(0,100,size=(10)) # 横坐标 x = np.arange(10) # Series绘制的线性图是单条线, index作为横坐标, values作为展示的数据 s = Series(data=data, index=x) s.plot(kind="line") ==>图一 # DataFrame绘制多条线,每一列作为一条线绘制 df ==> A B 0 76 51 1 93 36 2 88 59 3 55 75 4 11 9 5 43 35 6 10 67 7 43 51 8 54 42 9 39 74 df.plot(kind="line") ==> 图二
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
图一

图二

柱状图bar
Series柱状图示例,kind = ‘bar’/‘barh’
- 一般用于数据间的横向比较
# 1.Series 数据
data = [10,16,19,18]
# 默认不支持汉语显示
x = ["tom","jack","lucy","mery"]
s = Series(data=data, index=x)
s.plot(kind="bar")
# 2.DataFrame数据
df = DataFrame({
"python":[89,78,99],
"C":[70,75,80],
"PHP":[11,15,10]
}, index=["tom","lucy","jack"])
df.plot(kind="bar")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
Series
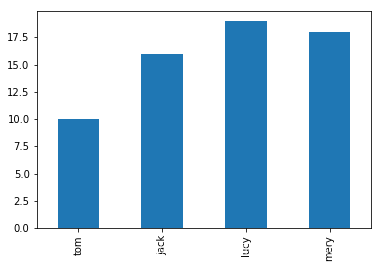
DataFrame

直方图hist
- 直方图是用来表示频率的图像
- 每一个柱子的高度,表示的是在该数据区间,数据出现的次数。 每一个柱子的宽度,表示的是数据区间,默认是10个柱子,把数据从最大值~最小值平均分成10个区间
- 参数bins可以设置直方图方柱的个数上限,越大柱宽越小,数据分组越细致
- 设置normed参数为True,可以把频数转换为概率
- kde图:核密度估计,用于弥补直方图由于参数bins设置的不合理导致的精度缺失问题
s = Series(data=np.random.randn(100))
# bins可能会导致直方图绘制不合理,所以一般会结合kde一起展示,但是要使用normed统一单位
# normed=True,柱高表示该区间数据出现的概率
s.plot(kind="hist", bins=8, normed=True)
s.plot(kind="kde")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

散点图scatter
- 散布图 散布图是观察两个一维数据数列之间的关系的有效方法,DataFrame对象可用
- 使用方法: 设置kind = ‘scatter’,给明标签columns
df = DataFrame(data={
"X":[1,3,5,7,9],
"Y":[3,6,8,9,0],
"M":[10,10,12,8,11],
})
# dataFrame对象绘制散点图与索引无关,一般就是查看某两列数据之间的对应关系
df.plot(kind="scatter",x="Y",y="M")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9

-
散布图矩阵,当有多个点时,两两点的关系
-
使用函数:pd.plotting.scatter_matrix(),
pd.plotting.scatter_matrix(frame, alpha=0.5, figsize=None, ax=None, grid=False, diagonal=‘hist’, marker=’.’, density_kwds=None, hist_kwds=None, range_padding=0.05, **kwds)
-
参数diagnol:设置对角线的图像类型
-
pd.plotting.scatter_matrix(df,diagonal="hist")
- 1

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/Gausst松鼠会/article/detail/424157?site
推荐阅读
相关标签



