热门标签
热门文章
- 1NL2SQL技术方案系列(5):金融领域NL2SQL技术方案以及行业案例实战讲解3--非LLM技术方案
- 2Umi + React + Ant Design Pro + TS 项目搭建_react+ts+umi+antd项目搭建
- 3求助,为什么navicat查询结果不能分页_navicat 没有分页
- 4Java超简单全套入门基础笔记(学不会你打我)_java学习笔记 java自学笔记 mashibin.cn
- 5【正点原子Linux连载】 第三十三章 Linux CAN驱动实验 摘自【正点原子】ATK-DLRK3568嵌入式Linux驱动开发指南
- 62021-05-28_statcpclient_unvarnishtest
- 7利用问心一言插件实现思维导图的制作_文心一言怎么画研究框架图
- 8Java并发编程-无锁CAS与Unsafe类及其并发包Atomic_cas unsafe 类的作用
- 9uniapp/vue3中使用rsa加密来传输密码,引入问题解决_vue3 rsa加密
- 10Wireguard各主流平台的配置教程_隧道无法启动 请确保您已连接到互联网
当前位置: article > 正文
12 Python 与 MySQL 数据库交互(含案例实战2:把金融数据存入数据库中)_python 连接金融数据库
作者:Gausst松鼠会 | 2024-04-16 18:20:24
赞
踩
python 连接金融数据库
Python 与 MySQL 数据库交互
安装PyMySQL
在本专栏的 11 MySQL数据库我们进行了操作说明。
通过pip命令安装pymysql数据库。
用Python连接数据库
import pymysql
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3308, user='root', password='', database='pachong', charset='utf8')
- 1
- 2
参数说明:
- host代表MySQL服务器地址,localhost代表本地地址,也可以写成127.0.0.1的本机IP地址形式。
- port代表端口,默认为3306,我这里是3308。
- user代表MySQL数据库的用户名。
- password代表密码。
- database代表要连接的数据库名称。
- charset代表编码方式。
用Python存储数据到数据库
插入数据的SQL语句:
INSERT INTO `test` (`company`, `title`, `href`, `date`, `source`)
VALUES('阿里巴巴', '标题2', '链接2', '日期2', '来源2')
- 1
- 2
在Python进行数据曾删改减得首先引入一个会话指针cursor,然后调用SQL语句:
cur = db.cursor() # 获取会话指针
- 1
为了让代码更简洁:
sql = 'INSERT INTO test (company, title, href, date, source) VALUES(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s)'
- 1
%s为占位符,,每一个%s代表一个字符,之后可以传入相应的数据。
再通过如下代码传入%s中:
cur.execute(sql, (company, title, href, date, source)) # 执行SQL语句
db.commit() # 固定写法,作用为提交修改
- 1
- 2
最后关闭会话指针和数据库的连接:
cur.close() # 关闭会话
db.close() # 关闭数据库连接
- 1
- 2
代码汇总:
# 先预定义变量 company = '阿里巴巴' title = '测试标题' href = '测试链接' source = '测试来源' date = '测试日期' # 连接数据库 import pymysql db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3308, user='root', password='', database='pachong', charset='utf8') # 插入数据 cur = db.cursor() # 获取会话指针 sql = 'INSERT INTO test (company, title, href, date, source) VALUES(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s)' cur.execute(sql, (company, title, href, date, source)) # 执行SQL语句 db.commit() # 固定写法,作用为提交修改 cur.close() # 关闭会话 db.close() # 关闭数据库连接
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
输出结果:

补充知识:占位符
%s为字符串类型的占位符,只能字符串类型的才能进入
%d为整数类型的占位符
%f为小数类型的占位符
用Python在数据库中查找并提取数据
在SQL语句中是:
SELECT * FROM `test` WHERE `company` LIKE '阿里巴巴'
- 1
Python语句:
# 连接数据库
import pymysql
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3308, user='root', password='', database='pachong', charset='utf8')
company = '阿里巴巴'
# 插入数据
cur = db.cursor() # 获取会话指针
sql = 'SELECT * FROM test WHERE company = %s'
cur.execute(sql, company) # 执行SQL语句
data = cur.fetchall() # 提取数据赋值给data
print(data)
db.commit() # 固定写法,作用为提交修改
cur.close() # 关闭会话
db.close() # 关闭数据库连接
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
输出:
((‘阿里巴巴’, ‘测试标题’, ‘测试链接’, ‘测试日期’, ‘测试来源’))
可以发现为元组的形势,那么我们进行处理
for i in range(len(data)):
print(data[i])
- 1
- 2
输出为:
(‘阿里巴巴’, ‘测试标题’, ‘测试链接’, ‘测试日期’, ‘测试来源’)
如果再往里取可以写成:
for i in range(len(data)):
print(data[i][0])
- 1
- 2
输出为:
阿里巴巴
如果筛选条件为多个,那么只需改为:
sql = 'SELECT * FROM test WHERE company = %s AND title = %s'
cur.execute(sql, (company, title)) # 执行SQL语句
- 1
- 2
用Python从数据库中删除数据
SQL中:
DELETE FROM `test` WHERE `company` = '百度'
- 1
Python中:
# 连接数据库
import pymysql
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3308, user='root', password='', database='pachong', charset='utf8')
company = '百度'
# 插入数据
cur = db.cursor() # 获取会话指针
sql = 'DELETE FROM test WHERE company = %s'
cur.execute(sql, company) # 执行SQL语句
db.commit() # 固定写法,作用为提交修改
cur.close() # 关闭会话
db.close() # 关闭数据库连接
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
输出:
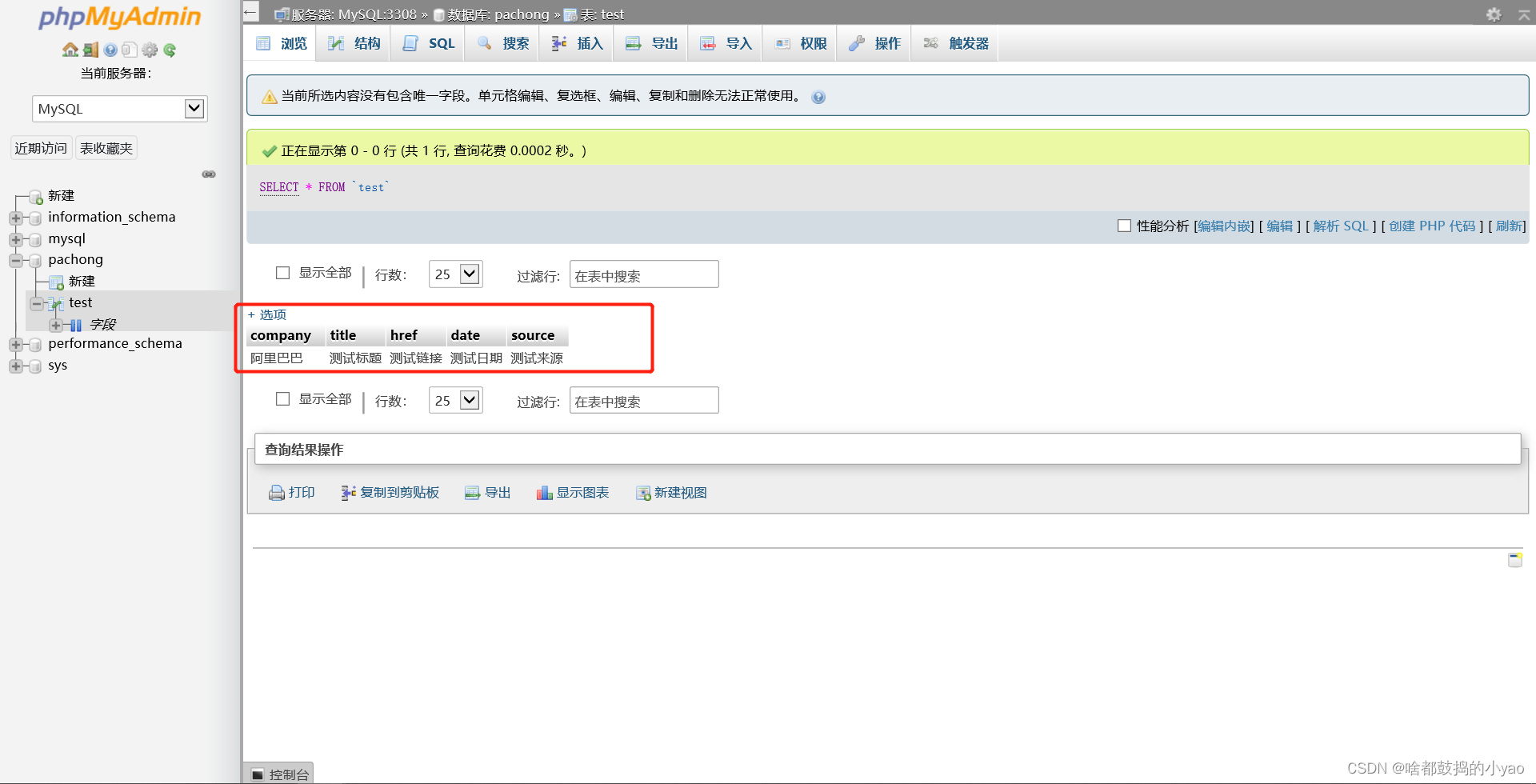
案例实战2:把数据存入数据库中
import requests import re import pymysql headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/69.0.3497.100 Safari/537.36'} def baidu(company): url = 'https://www.baidu.com/s?tn=news&rtt=1&bsst=1&cl=2&wd='+company res = requests.get(url, headers=headers).text p_href = '<h3 class="news-title_1YtI1 "><a href="(.*?)"' href = re.findall(p_href, res, re.S) # print(href) p_title = '<h3 class="news-title_1YtI1 ">.*?aria-label="标题:(.*?)"' title = re.findall(p_title, res, re.S) # print(title) p_date = '<span class="c-color-gray2 c-font-normal c-gap-right-xsmall".*?>(.*?)</span>' date = re.findall(p_date, res) # print(date) p_source = '<span class="c-color-gray".*?>(.*?)</span>' source = re.findall(p_source, res) # print(source) for i in range(len(title)): db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3308, user='root', password='', database='pachong', charset='utf8') # 插入数据 cur = db.cursor() # 获取会话指针 sql = 'INSERT INTO test (company, title, href, date, source) VALUES(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s)' cur.execute(sql, (company, title[i], href[i], date[i], source[i])) # 执行SQL语句 db.commit() # 固定写法,作用为提交修改 cur.close() # 关闭会话 db.close() # 关闭数据库连接 baidu('阿里巴巴')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
输出:
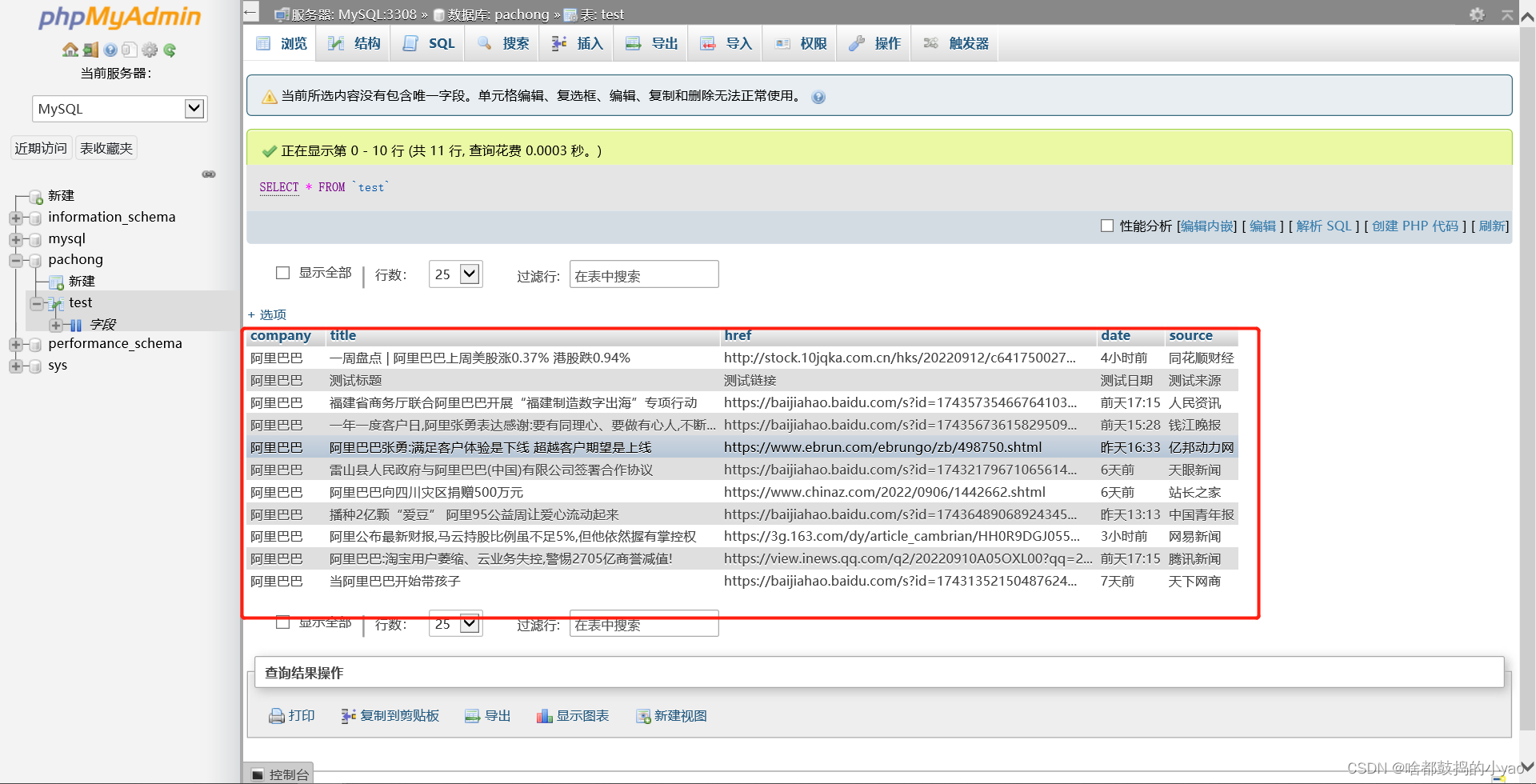
若想要爬取多家公司的信息,只需要加上一个循环:
companys = ['阿里巴巴', '百度', '腾讯', '京东']
for company in companys:
try:
baidu(company)
print(company+'成功')
except:
print(company+'失败')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/Gausst松鼠会/article/detail/435714
推荐阅读
相关标签



