热门标签
热门文章
- 1【Docker】通过Dockerfile构建Redis镜像,java堆和栈的区别面试题
- 2python 判断类属性(方法)是否存在_python 判断属性是否存在
- 3解决el-dialog弹出时,页面抖动,右侧会缩小的问题_vue3中当点击弹窗的时候,原来的页面宽度右侧会缩小一点是什么原因
- 4Redis搭建及使用
- 5javaEE002.03 js的三种嵌入方式_js 方法嵌入方法
- 6通过智能反射面进行安全的无线通信_secure wireless communication via intelligent refl
- 7阿里云云原生一体化数仓 — 湖仓一体新能力解读_阿里云湖仓一体
- 8MySQL运维实战(2.4) SSL认证在MySQL中的应用
- 9PMP项目管理项目中的文件_项目管理相关文件
- 10SimpleNet: A Simple Network for Image Anomaly Detection and Localization CVPR2023
当前位置: article > 正文
动态规划法在扫地机器人中的实战应用(基于动作值函数的策略迭代 python 附源码)_自制扫地机器人编程和代码
作者:Gausst松鼠会 | 2024-05-12 18:10:06
赞
踩
自制扫地机器人编程和代码
需要源码或觉得有帮助请点赞关注收藏后评论区留下QQ邮箱或者私信博主
与基于状态值函数的策略迭代不同,基于动作值函数的策略迭代是在当前策略下用另一个式子进行评估。
关于条件描述和环境搭建可以参考我这篇博客扫地机器人简介
算法步骤如下

下面通过基于动作值函数的策略迭代算法应用于确定环境的扫地机器人任务中,经过多轮迭代后,得到下图中动作值函数和策略迭代的更新过程
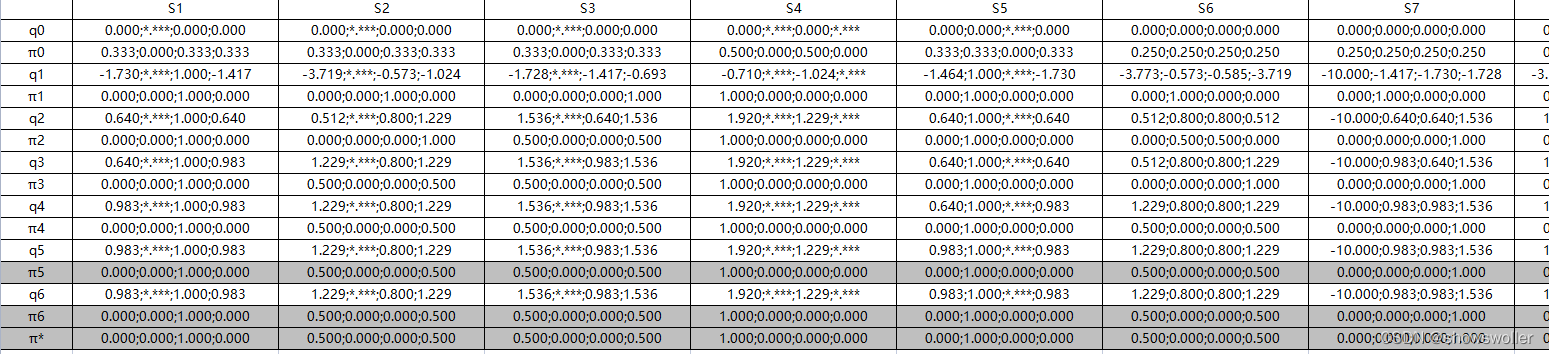
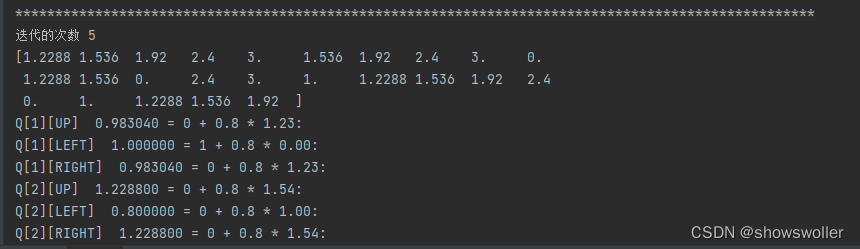
代码运行结果如下 经过五次迭代逐渐收敛
部分代码如下
- # 代11-例4.7-基于动作值函数的确定环境扫地机器人任务策略迭代
- import numpy as np
- world_h = 5
- world_w = 5
- length = world_h * world_w
- gamma = 0.8
- state = [i for i in range(length)] # 状态(编号)
- action = ['n', 's', 'w', 'e'] # 动作名称
- ds_action = {'n': -world_w, 'e': 1, 's': world_w, 'w': -1}
- value = [0 for i in range(length)] # 初始化状态值函数,均为0. [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
- policy = np.zeros([length, len(action)])
- suqe=[20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, 1, 2, 3,4]
-
-
-
-
- # 定义奖励
- def reward(s):
- if s == 20: # 到充电站
- return 1
- elif s == 12: # 到陷阱中
- return -10
- elif s == 9: # 到垃圾处
- return 3
- else:
- return 0 # 其他
- # in表示0是[*,*,*]中的一个
-
-
- def getAction(a):
- if a == 'n':
- return 0
- elif a == 'e':
- return 3
- elif a == 's':
- return 1
- elif a == 'w':
- return 2
-
-
- # 在s状态下执行动作a,返回下一状态(编号)
- def next_states(s, a):
- # 越过边界时pass
- if (s < world_w and a == 'n') \
- or (s % world_w == 0 and a == 'w') \
- or (s > length - world_w - 1 and a == 's') \
- or ((s + 1) % world_w == 0 and a == 'e'): # (s % (world_w - 1) == 0 and a == 'e' and s != 0)
- next_state = s # 表现为next_state不变
- else:
- next_state = s + ds_action[a] # 进入下一个状态
- return next_state
-
-
- # 在s状态下执行动作,返回所有可能的下一状态(编号)list
- def getsuccessor(s):
- successor = []
- for a in action: # 遍历四个动作
- if s == next_states(s, a):
- continue
- else:
- # print("状态s=%s,动作a=%s"%(s,a))
- next = next_states(s, a) # 得到下一个状态(编号)
- successor.append(next) # 以list保存当前状态s下执行四个动作的下一状态
- # print(len(successor))
- return successor
-
- def initPolicy():
- for s in range(length):
- for a in action:
- if next_states(s, a) == s:
- continue
- newAction = getAction(a)
- policy[s][newAction] = 1 / len(getsuccessor(s))
- # print(policy)
- def Caculate_Q(s, V, num, discount_factor=0.8):
- """
- Returns:
- A vector of length env.nA containing the expected value of each action.
- """
- Q = np.zeros((length, 4))
- Q[:][:] = -100
- for a in action: # 遍历能走的动作
- # for prob, next_state, reward, done in env.P[s][a]:
- # Q[s][a] += prob * (reward + discount_factor * V[next_state]) # 计算当前状态s下的动作值函数列表 [q1,q2,q3,q4]
- next_state = next_states(s, a)
- if next_state == s: # 碰壁
- continue
- rewards = reward(next_state)
- numberA = getAction(a)
- if s == 12:
- Q[s][numberA] = rewards + discount_factor * V[s]
- else:
- Q[s][numberA] = rewards + discount_factor * V[next_state]
- action_name1 = ""
- if (numberA == 0):
- action_name1 = "UP"
- if (numberA == 1):
- action_name1 = "DOWN"
- if (numberA == 2):
- action_name1 = "LEFT"
- if (numberA == 3):
- action_name1 = "RIGHT"
-
- print("Q[%s][%s] %f = %s + 0.8 * %.2f:" % (num, action_name1, Q[s][numberA], rewards, V[next_state]))
- return Q
-
- def max_index(lst_int):#最大值索引函数
- index = []
- max_n = max(lst_int)
- for i in range(len(lst_int)):
- if lst_int[i] == max_n:
- index.append(i)
- return index #返回一个列表
-
- def list_not_equal(old,new):#判断list是否相等
- listequal=False
-
- for i in range(0,4):
- if old[i]!=new[i]:
- listequal=True
- break
- return listequal
- def policy_eval(theta=0.0001):
- V = np.zeros(length) # 初始化状态值函数列表
- iter = 0
-
- while True:
- k = -1
- delta = 0 # 定义最大差值,判断是否有进行更新
- for s in suqe: # 遍历所有状态 [0~25]
- k += 1
- if s in [9, 20, 12]: # 若当前状态为吸入状态,则直接pass不做操作
- continue
- v = 0 # 针对每个状态值函数进行计算
- # print("第%d 的状态" % (k), end="")
- for a in action:
- newAction = getAction(a)
- next_state = next_states(s, a)
- rewards = reward(next_state)
- if next_state == 12:
- v += policy[s][newAction] * (rewards + gamma * V[s])
- else:
- v += policy[s][newAction] * (rewards + gamma * V[next_state])
-
-
- delta = max(delta, np.abs(v - V[s])) # 更新差值
- V[s] = v # 存储(更新)每个状态下的状态值函数,即伪代码中的 v <- V(s)
- value = np.array(V).reshape(world_h, world_w)
- iter += 1
-
- if delta < theta: # 策略评估的迭代次数不能太多,否则状态值函数的数值会越来越大(即使算法仍然在收敛)
- break
- return V # 一轮迭代结束后,状态值函数暂时固定
-
-
- def policy_improvement(V, policy): # 策略改进
- """
- Returns:
- policy: the optimal policy, a matrix of shape [S, A] where each state s contains a valid probability distribution over actions.
- V: the value function for the optimal policy.
- """
- k = -1
- policy_stable = True # Will be set to false if we make any changes to the policy
- for s in [20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4]:
- if s in [9, 20, 12]:
- k += 1
- continue;
- k += 1
-
- [i]
- return V, policy_stable
-
- def Policy_Iterration_byQ():
- initPolicy()
- k = 1
- while True: # Evaluate the current policy
- print("迭代的次数",k)
- Q = policy_eval()
- print(Q)
- Q,policy_stable = policy_improvement(Q,policy)
- print("*" * 100)
- k+=1
- if policy_stable: # # If the policy is stable we've found an optimal policy. Return it
- return policy, Q
- Policy_Iterration_byQ()

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/Gausst松鼠会/article/detail/560116
推荐阅读
相关标签


