- 1解读Lawyer LLaMA,延申专业领域大模型微调:数据集构建,模型训练
- 2基于Java+SpringBoot+vue+element实现校园疫情防控系统详细设计和实现
- 3分享一个很实用的技巧:一两行Python代码完成的骚操作_python代码怎样两行显示
- 4Docker-高级篇(1)-Dockerfile(核心&构建Redis&构建JDK8)_dockerfile 打包 jdk jar mysql redis
- 5C++处理栅格数据
- 6❤️技术改变命运!中秋一天搞完私活,4K到手,分享下经验!确实有技术啥都不愁!❤️_全栈开发 拿4k
- 7E: Unable to locate package
- 8互联网找工作该选择大公司还是小公司
- 9NLP中的语言模型
- 10线性插值(Linear Interpolation):线性插值、双线性插值
人工智能-A*启发式搜索算法解决八数码问题 Python实现_基于python编程语言,利用任意一种搜索算法(盲目搜索,启发式搜索),解决“八数码”
赞
踩
一.问题描述
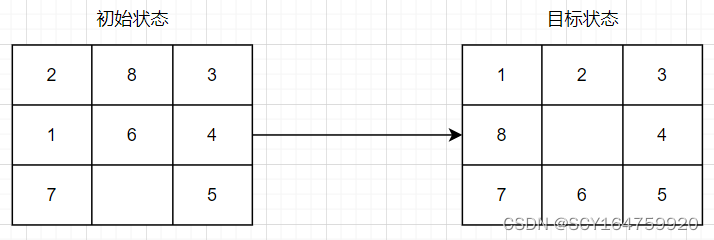
八数码问题也称为九宫问题。在 3×3 的棋盘,摆有八个棋子,每个棋子上标有 1 至 8 的某一数字,不同棋子上标的数字不相同。棋盘上还有一个空格(以数字 0 来表示),与空 格相邻的棋子可以移到空格中。 要求解决的问题是:给出一个初始状态和一个目标状态,找出一种从初始转变成目标状态的移动棋子步数最少的移动步骤。
该问题可用A*启发式搜索算法求解。
A*算法的估价函数如下:
其中启发函数可选择w(n)和p(n)两种,本文以w(n)为例编写程序

二.算法实现【理论部分】
本文以如下情况为例进行分析:
1.对问题进行抽象
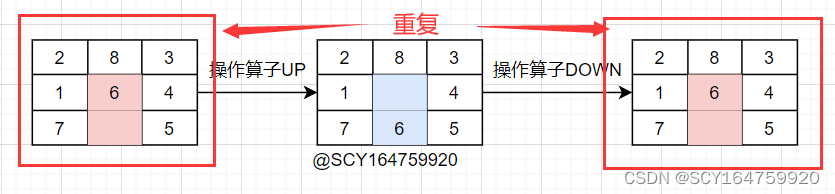
①.操作算子的选取
若着眼在数码上,则相应的操作算子就是数码的移动,可知共有4(方向)*8(码的个数)=32 种算子,设计起来较为复杂。
若着眼在空格上,则相应的操作算子就是空格的移动,在最理想的情况下【即空格在棋盘正中间时】,最多有4种算子【上移up,下移down,左移left,右移right】,设计较为简单。
综上所述,本程序选择着眼于空格,使用上下左右四种操作算子进行程序编写
②.数码移动过程的抽象
可将数码在3*3棋盘上的分布抽象为一维数组,这样每次空格的移动就等价于交换一维数组种两个元素的位置,如下图所示:
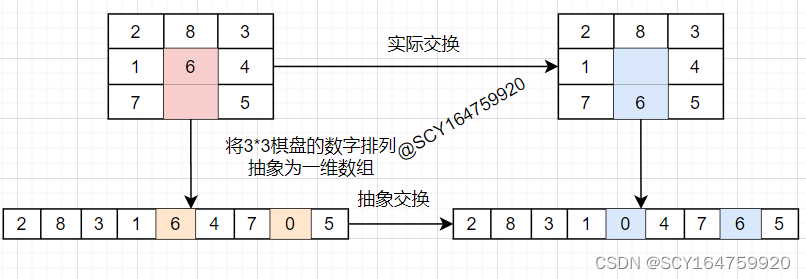
至此,数码的移动问题转换成了寻找两个待交换元素在数组中的下标并交换的问题
2.实际执行过程
①.搜索树
✅2023/12/17修正:
下图搜索树中的A(4)应该修改为A(6)
因为此时序列中共有:
2,8,3,1,6,4,(0),7,5 六个元素(标红)不在【目标位置】
1,2,3,8,(0),4,7,6,5(目标序列)
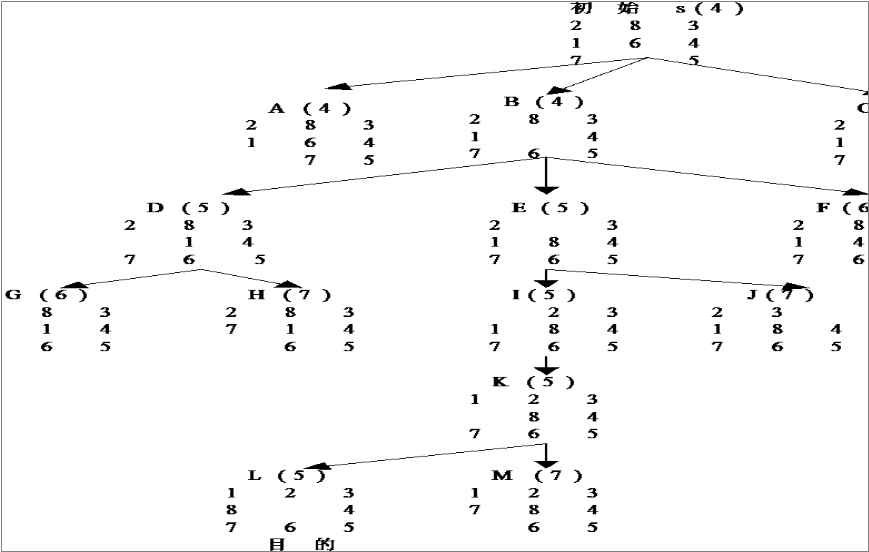
由上图的搜索树可知:
树上的任意一个节点应该包含如下信息:
·该节点在树中的深度
·该节点的估价函数值 f(n)
· 该节点的数码序列【抽象为一维数组】
②.open表和closed表
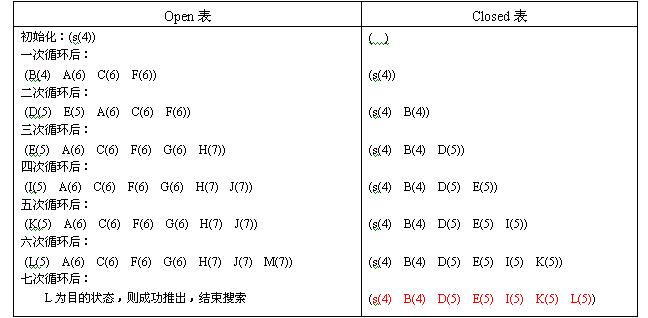
由上表可知:
open表中存放的是按估价函数值排序的节点,closed表存放的是每次从循环从open表中取出的第一个节点,直到取出节点的数码序列等于最终的数码序列,算法结束。
3.无解的情况
首先明确: 八数码问题是存在无解的情况的,在编写程序时,首先就需要判断初始序列和目标序列之间的变换是否是有解的,若将无解的两个序列执行算法,算法将陷入死循环
两个状态有无解的判断,由两个序列的逆序数奇偶性决定,若两序列的逆序数同为奇数或同为偶数,则两序列的变换有解,否则无解。
何为逆序数? 如何求逆序数? 看这篇文章,这里不多赘述 逆序数文章
4.操作算子的选择
①.边界条件 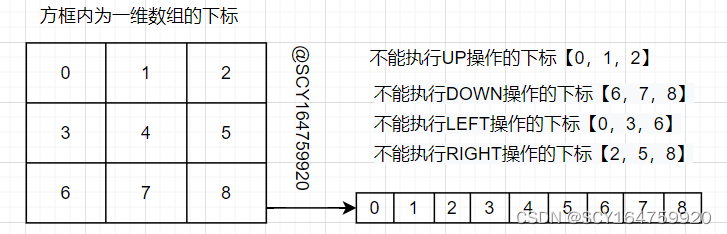
②.防止死循环
前一次执行UP操作,下一次迭代时应该禁用DOWN操作
前一次执行LEFT操作,下一次迭代应该禁用RIGHT操作 ,
反之亦然,目的是为了避免出现死循环
具体示例如下图:
总之,操作算子的选择在不考虑②中的约束条件时,其选取是的结果是十分固定的,例如0位置只能选择DOWN和RIGHT,5位置只能选择LEFT,UP和DOWN。在实际程序中可根据元素在数组中的位置+约束条件得到此次可选择的操作算子。
5.数据结构的设计
经过如上分析可知,要实现算法,关键要设计出搜索树中每个节点的数据结构,本次设计的结构如下:
- class statusObject:
- def __init__(self):
- # 当前状态的序列
- self.array = []
- # 当前状态的估价函数值
- self.Fn = 0
- # cameFrom表示该状态由上一步由何种operation得到
- # 目的是为了过滤 【死循环】
- # 0表示初始无状态 1表示up 2表示down 3表示left 4表示right
- self.cameFrom = 0
- # 第一次生成该节点时在图中的深度 计算估价函数使用
- self.Dn = 0
- # 该节点的父亲节点,用于最终溯源最终解
- self.Father = statusObject
三.算法实现【代码部分】
1.流程图:
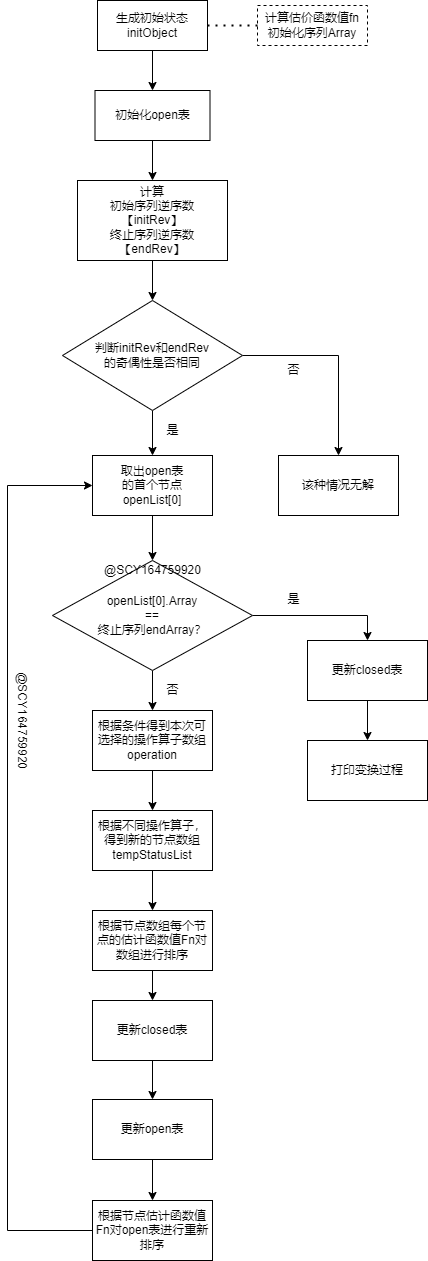
2.程序源码
程序使用了numpy包,运行前请自行安装
另外在调试过程中使用了很多print语句查看结果,现已注释,若不需要请自行删除
- import operator
- import sys
-
- import numpy as np
-
-
- class statusObject:
- def __init__(self):
- # 当前状态的序列
- self.array = []
- # 当前状态的估价函数值
- self.Fn = 0
- # cameFrom表示该状态由上一步由何种operation得到
- # 目的是为了过滤 【死循环】
- # 0表示初始无状态 1表示up 2表示down 3表示left 4表示right
- self.cameFrom = 0
- # 第一次生成该节点时在图中的深度 计算估价函数使用
- self.Dn = 0
- self.Father = statusObject
-
-
- def selectOperation(i, cameFrom):
- # @SCY164759920
- # 根据下标和cameFromReverse来选择返回可选择的操作
- selectd = []
- if (i >= 3 and i <= 8 and cameFrom != 2): # up操作
- selectd.append(1)
- if (i >= 0 and i <= 5 and cameFrom != 1): # down操作
- selectd.append(2)
- if (i == 1 or i == 2 or i == 4 or i == 5 or i == 7 or i == 8): # left操作
- if (cameFrom != 4):
- selectd.append(3)
- if (i == 0 or i == 1 or i == 3 or i == 4 or i == 6 or i == 7): # right操作
- if (cameFrom != 3):
- selectd.append(4)
- return selectd
-
-
- def up(i):
- return i - 3
-
-
- def down(i):
- return i + 3
-
-
- def left(i):
- return i - 1
-
-
- def right(i):
- return i + 1
-
- def setArrayByOperation(oldIndex, array, operation):
- # i为操作下标
- # 根据operation生成新状态
- if (operation == 1): # up
- newIndex = up(oldIndex) # 得到交换的下标
- if (operation == 2): # down
- newIndex = down(oldIndex)
- if (operation == 3): # left
- newIndex = left(oldIndex)
- if (operation == 4): # right
- newIndex = right(oldIndex)
- # 对调元素的值
- temp = array[newIndex]
- array[newIndex] = array[oldIndex]
- array[oldIndex] = temp
- return array
-
-
- def countNotInPosition(current, end): # 判断不在最终位置的元素个数
- count = 0 # 统计个数
- current = np.array(current)
- end = np.array(end)
- for index, item in enumerate(current):
- if ((item != end[index]) and item != 0):
- count = count + 1
- return count
-
-
- def computedLengthtoEndArray(value, current, end): # 两元素的下标之差并去绝对值
- def getX(index): # 获取当前index在第几行
- if 0 <= index <= 2:
- return 0
- if 3 <= index <= 5:
- return 1
- if 6 <= index <= 8:
- return 2
-
- def getY(index): # 获取当前index在第几列
- if index % 3 == 0:
- return 0
- elif (index + 1) % 3 == 0:
- return 2
- else:
- return 1
-
- currentIndex = current.index(value) # 获取当前下标
- currentX = getX(currentIndex)
- currentY = getY(currentIndex)
- endIndex = end.index(value) # 获取终止下标
- endX = getX(endIndex)
- endY = getY(endIndex)
- length = abs(endX - currentX) + abs(endY - currentY)
- return length
-
- def countTotalLength(current, end):
- # 根据current和end计算current每个棋子与目标位置之间的距离和【除0】
- count = 0
- for item in current:
- if item != 0:
- count = count + computedLengthtoEndArray(item, current, end)
- return count
-
- def printArray(array): # 控制打印格式
- print(str(array[0:3]) + '\n' + str(array[3:6]) + '\n' + str(array[6:9]) + '\n')
-
- def getReverseNum(array): # 得到指定数组的逆序数 包括0
- count = 0
- for i in range(len(array)):
- for j in range(i + 1, len(array)):
- if array[i] > array[j]:
- count = count + 1
- return count
-
-
- openList = [] # open表 存放实例对象
- closedList = [] # closed表
- endArray = [1, 2, 3, 8, 0, 4, 7, 6, 5] # 最终状态
- countDn = 0 # 执行的次数
-
- initObject = statusObject() # 初始化状态
- # initObject.array = [2, 8, 3, 1, 6, 4, 7, 0, 5]
- initObject.array = [2, 8, 3, 1, 6, 4, 7, 0, 5]
- # initObject.array = [2, 1, 6, 4, 0, 8, 7, 5, 3]
- initObject.Fn = countDn + countNotInPosition(initObject.array, endArray)
- # initObject.Fn = countDn + countTotalLength(initObject.array, endArray)
- openList.append(initObject)
- zeroIndex = openList[0].array.index(0)
- # 先做逆序奇偶性判断 0位置不算
- initRev = getReverseNum(initObject.array) - zeroIndex # 起始序列的逆序数
- print("起始序列逆序数", initRev)
- endRev = getReverseNum(endArray) - endArray.index(0) # 终止序列的逆序数
- print("终止序列逆序数", endRev)
- res = countTotalLength(initObject.array, endArray)
- # print("距离之和为", res)
- # @SCY164759920
- # 若两逆序数的奇偶性不同,则该情况无解
-
- if((initRev%2==0 and endRev%2==0) or (initRev%2!=0 and endRev%2!=0)):
- finalFlag = 0
- while(1):
- # 判断是否为end状态
- if(operator.eq(openList[0].array,endArray)):
- # 更新表,并退出
- deep = openList[0].Dn
- finalFlag = finalFlag +1
- closedList.append(openList[0])
- endList = []
- del openList[0]
- if(finalFlag == 1):
- father = closedList[-1].Father
- endList.append(endArray)
- print("最终状态为:")
- printArray(endArray)
- while(father.Dn >=1):
- endList.append(father.array)
- father = father.Father
- endList.append(initObject.array)
- print("【变换成功,共需要" + str(deep) +"次变换】")
- for item in reversed(endList):
- printArray(item)
- sys.exit()
- else:
- countDn = countDn + 1
- # 找到选中的状态0下标
- zeroIndex = openList[0].array.index(0)
- # 获得该位置可select的operation
- operation = selectOperation(zeroIndex, openList[0].cameFrom)
- # print("0的下标", zeroIndex)
- # print("cameFrom的值", openList[0].cameFrom)
- # print("可进行的操作",operation)
- # # print("深度",openList[0].Dn)
- # print("选中的数组:")
- # printArray(openList[0].array)
- # 根据可选择的操作算出对应的序列
- tempStatusList = []
- for opeNum in operation:
- # 根据操作码返回改变后的数组
- copyArray = openList[0].array.copy()
- newArray = setArrayByOperation(zeroIndex, copyArray, opeNum)
- newStatusObj = statusObject() # 构造新对象插入open表
- newStatusObj.array = newArray
- newStatusObj.Dn = openList[0].Dn + 1 # 更新dn 再计算fn
- newFn = newStatusObj.Dn + countNotInPosition(newArray, endArray)
- # newFn = newStatusObj.Dn + countTotalLength(newArray, endArray)
- newStatusObj.Fn = newFn
- newStatusObj.cameFrom = opeNum
- newStatusObj.Father = openList[0]
- tempStatusList.append(newStatusObj)
- # 将操作后的tempStatusList按Fn的大小排序
- tempStatusList.sort(key=lambda t: t.Fn)
- # 更新closed表
- closedList.append(openList[0])
- # 更新open表
- del openList[0]
- for item in tempStatusList:
- openList.append(item)
- # 根据Fn将open表进行排序
- openList.sort(key=lambda t: t.Fn)
- # print("第"+str(countDn) +"次的结果:")
- # print("open表")
- # for item in openList:
- # print("Fn" + str(item.Fn))
- # print("操作" + str(item.cameFrom))
- # print("深度"+str(item.Dn))
- # printArray(item.array)
- # @SCY164759920
- # print("closed表")
- # for item2 in closedList:
- # print("Fn" + str(item2.Fn))
- # print("操作" + str(item2.cameFrom))
- # print("深度" + str(item2.Dn))
- # printArray(item2.array)
- # print("==================分割线======================")
- else:
- print("该种情况无解")
2022.10.28 13:32更新:
经测试后发现,源代码的输出在某些情况下会BUG,现已修改,修改了原数据结构,在每个节点中添加了“Father”属性,用以存放每个节点的父亲节点。修改后,经测试已经能正常输出,若读者是在更新时间之后阅读本文,直接可忽略。
更新:
原程序的启发函数只提供了w(n)的方法,现更新p(n)的实现:
【p(n)即:节点n的每个棋子与目标位置之间的距离总和】
修改方法:
将源程序中两处计算Fn的函数进行替换 并添加两个计算函数
第一处
【原】:initObject.Fn = countDn + countNotInPosition(initObject.array, endArray)
【替换】:initObject.Fn = countDn + countTotalLength(initObject.array, endArray)
第二处:
【原】:newFn = newStatusObj.Dn + countNotInPosition(newArray, endArray)
【替换】:newFn = newStatusObj.Dn + countTotalLength(newArray, endArray)
添加两个计算函数:
- def computedLengthtoEndArray(value, current, end): # 两元素的下标之差并去绝对值
- def getX(index): # 获取当前index在第几行
- if 0 <= index <= 2:
- return 0
- if 3 <= index <= 5:
- return 1
- if 6 <= index <= 8:
- return 2
-
- def getY(index): # 获取当前index在第几列
- if index % 3 == 0:
- return 0
- elif (index + 1) % 3 == 0:
- return 2
- else:
- return 1
-
- currentIndex = current.index(value) # 获取当前下标
- currentX = getX(currentIndex)
- currentY = getY(currentIndex)
- endIndex = end.index(value) # 获取终止下标
- endX = getX(endIndex)
- endY = getY(endIndex)
- length = abs(endX - currentX) + abs(endY - currentY)
- return length
-
- def countTotalLength(current, end):
- # 根据current和end计算current每个棋子与目标位置之间的距离和【除0】
- count = 0
- for item in current:
- if item != 0:
- count = count + computedLengthtoEndArray(item, current, end)
- return count
分别运行启发函数取w(n)和p(n)发现,在本次选取的示例转换中:
取p(n)时转换过程共需要5步
取w(n)时转换过程共需要5步