- 1AI神经网络原理与Python实战:41. 图像数据处理与分析方法_ai对图片数据分析
- 2Keras——用Keras搭建RNN回归循环神经网络_# 搭建rnn神经网络模型 model =
- 3Fastgpt配合chatglm+m3e或ollama+m3e搭建个人知识库_fastgpt 接入 llama3
- 4网络攻防--网络防御技术
- 5java面试_javaweb张三转账给李四
- 6【OpenGL学习】texture_opengl texture函数详解
- 7RocketMQ 一个topic 多个消费者只有一个消费的问题_rocketmq多个消费者怎么配置
- 8工作总结
- 9node.js+uni计算机毕设项目音乐播放微信小程序LW(程序+小程序+LW)_音乐播放微信小程序运行环境
- 10从零教你实现一个物流管理系统[附源码]_物流管理系统的实现
13.Kafka系列之Stream核心原理(二)_kafkastream多线程多进程
赞
踩
Kafka Streams simplifies application development by building on the Kafka producer and consumer libraries and leveraging the native capabilities of Kafka to offer data parallelism, distributed coordination, fault tolerance, and operational simplicity. In this section, we describe how Kafka Streams works underneath the covers
Kafka Streams 通过构建在 Kafka 生产者和消费者库上并利用 Kafka 的本机功能来提供数据并行性、分布式协调、容错和操作简单性,从而简化了应用程序开发。在本节中,我们将描述 Kafka Streams 在幕后是如何工作的
The picture below shows the anatomy of an application that uses the Kafka Streams library. Let’s walk through some details
下图显示了使用 Kafka Streams 库的应用程序的剖析。让我们来看看一些细节
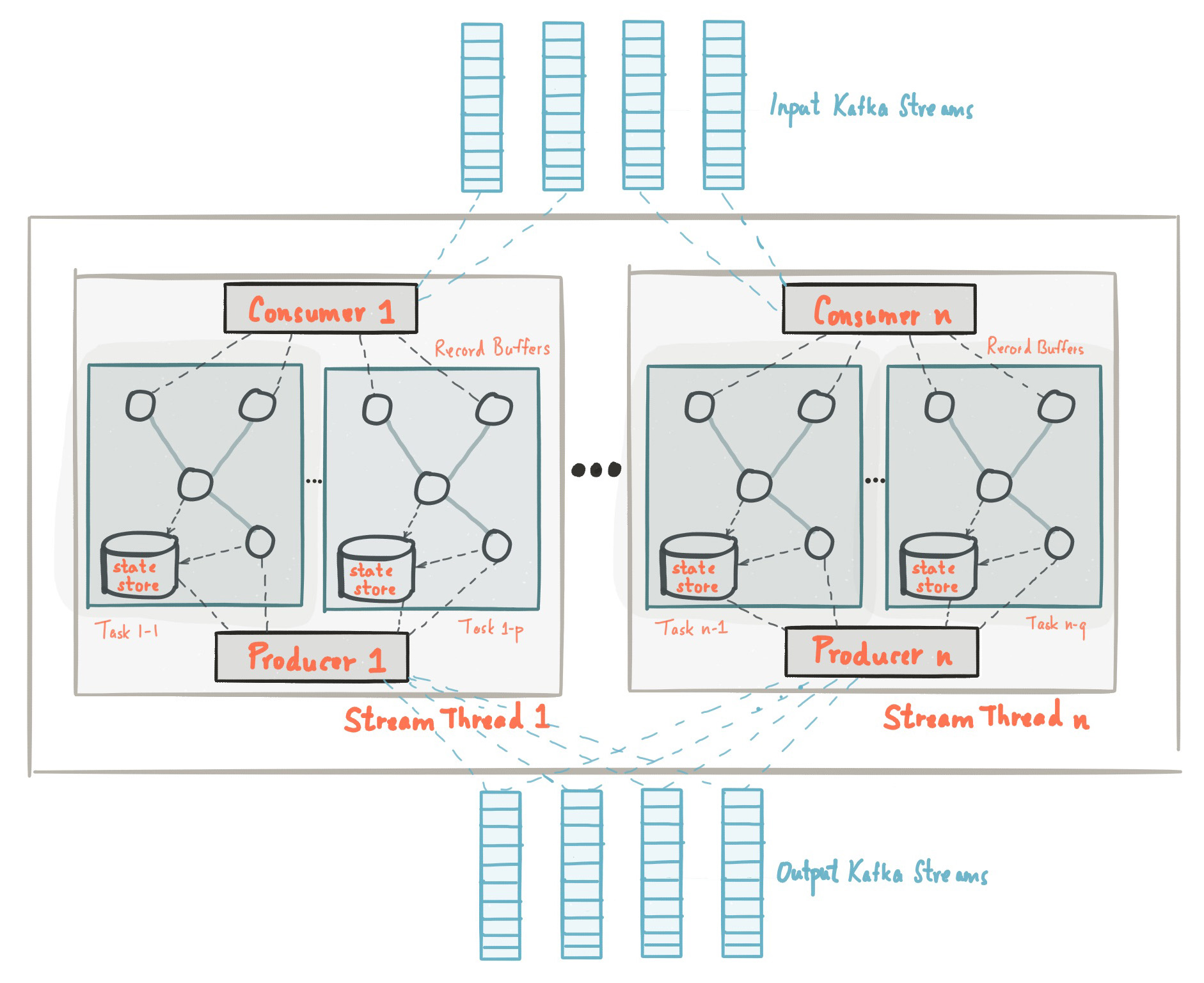
Stream Partitions and Tasks流分区和任务
The messaging layer of Kafka partitions data for storing and transporting it. Kafka Streams partitions data for processing it. In both cases, this partitioning is what enables data locality, elasticity, scalability, high performance, and fault tolerance. Kafka Streams uses the concepts of partitions and tasks as logical units of its parallelism model based on Kafka topic partitions. There are close links between Kafka Streams and Kafka in the context of parallelism:
Kafka 的消息传递层对数据进行分区以存储和传输数据。Kafka Streams 对数据进行分区以进行处理。在这两种情况下,这种分区都是实现数据局部性、弹性、可扩展性、高性能和容错的原因。Kafka Streams 使用分区和任务的概念作为其基于 Kafka 主题分区的并行模型的逻辑单元。在并行性方面,Kafka Streams 和 Kafka 之间有着密切的联系:
-
Each stream partition is a totally ordered sequence of data records and maps to a Kafka topic partition.
每个流分区都是一个完全有序的数据记录序列,并映射到一个 Kafka主题分区 -
A data record in the stream maps to a Kafka message from that topic.
流中的数据记录映射到来自该主题的 Kafka消息 -
The keys of data records determine the partitioning of data in both Kafka and Kafka Streams, i.e., how data is routed to specific partitions within topics.
数据记录的键决定了 Kafka 和 Kafka Streams 中数据的分区,即数据如何路由到主题内的特定分区
An application’s processor topology is scaled by breaking it into multiple tasks. More specifically, Kafka Streams creates a fixed number of tasks based on the input stream partitions for the application, with each task assigned a list of partitions from the input streams (i.e., Kafka topics). The assignment of partitions to tasks never changes so that each task is a fixed unit of parallelism of the application. Tasks can then instantiate their own processor topology based on the assigned partitions; they also maintain a buffer for each of its assigned partitions and process messages one-at-a-time from these record buffers. As a result stream tasks can be processed independently and in parallel without manual intervention.
应用程序的处理器拓扑通过将其分解为多个任务来扩展。更具体地说,Kafka Streams 根据应用程序的输入流分区创建固定数量的任务,每个任务分配一个来自输入流的分区列表(即 Kafka 主题)。分配给任务的分区永远不会改变,因此每个任务都是应用程序并行度的固定单元。然后,任务可以根据分配的分区实例化自己的处理器拓扑;它们还为其分配的每个分区维护一个缓冲区,并一次处理来自这些记录缓冲区的消息。因此,流任务可以独立并行处理,无需人工干预
Slightly simplified, the maximum parallelism at which your application may run is bounded by the maximum number of stream tasks, which itself is determined by maximum number of partitions of the input topic(s) the application is reading from. For example, if your input topic has 5 partitions, then you can run up to 5 applications instances. These instances will collaboratively process the topic’s data. If you run a larger number of app instances than partitions of the input topic, the “excess” app instances will launch but remain idle; however, if one of the busy instances goes down, one of the idle instances will resume the former’s work.
稍微简化一下,您的应用程序可以运行的最大并行度受最大流任务数的限制,而最大流任务数本身由应用程序正在读取的输入主题的最大分区数决定。例如,如果您的输入主题有 5 个分区,那么您最多可以运行 5 个应用程序实例。这些实例将协作处理主题的数据。如果您运行的应用程序实例数量多于输入主题的分区数量,“多余”的应用程序实例将启动但保持空闲状态;但是,如果其中一个繁忙的实例出现故障,其中一个空闲的实例将恢复前者的工作
It is important to understand that Kafka Streams is not a resource manager, but a library that “runs” anywhere its stream processing application runs. Multiple instances of the application are executed either on the same machine, or spread across multiple machines and tasks can be distributed automatically by the library to those running application instances. The assignment of partitions to tasks never changes; if an application instance fails, all its assigned tasks will be automatically restarted on other instances and continue to consume from the same stream partitions.
重要的是要了解 Kafka Streams 不是资源管理器,而是一个在其流处理应用程序运行的任何地方“运行”的库。应用程序的多个实例要么在同一台机器上执行,要么分布在多台机器上,任务可以由库自动分发给那些正在运行的应用程序实例。分配给任务的分区永远不会改变;如果应用程序实例失败,所有分配给它的任务将在其他实例上自动重新启动,并继续使用相同的流分区
NOTE: Topic partitions are assigned to tasks, and tasks are assigned to all threads over all instances, in a best-effort attempt to trade off load-balancing and stickiness of stateful tasks. For this assignment, Kafka Streams uses the StreamsPartitionAssignor class and doesn’t let you change to a different assignor. If you try to use a different assignor, Kafka Streams ignores it.
注意:主题分区分配给任务,任务分配给所有实例上的所有线程,尽最大努力权衡负载平衡和有状态任务的粘性。对于此分配,Kafka Streams 使用 StreamsPartitionAssignor 类,并且不允许您更改为不同的分配器。如果您尝试使用不同的分配器,Kafka Streams 会忽略它
The following diagram shows two tasks each assigned with one partition of the input streams
下图显示了两个任务,每个任务分配了一个输入流分区
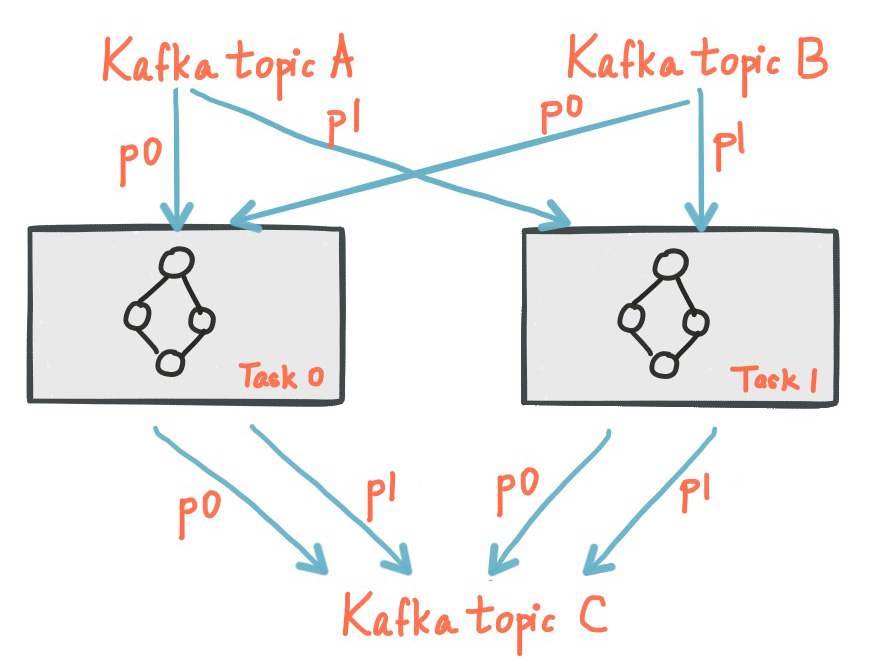
Threading Model线程模型
Kafka Streams allows the user to configure the number of threads that the library can use to parallelize processing within an application instance. Each thread can execute one or more tasks with their processor topologies independently. For example, the following diagram shows one stream thread running two stream tasks
Kafka Streams 允许用户配置库可用于在应用程序实例中并行处理的线程数。每个线程都可以独立地使用其处理器拓扑执行一项或多项任务。例如,下图显示了一个流线程运行两个流任务
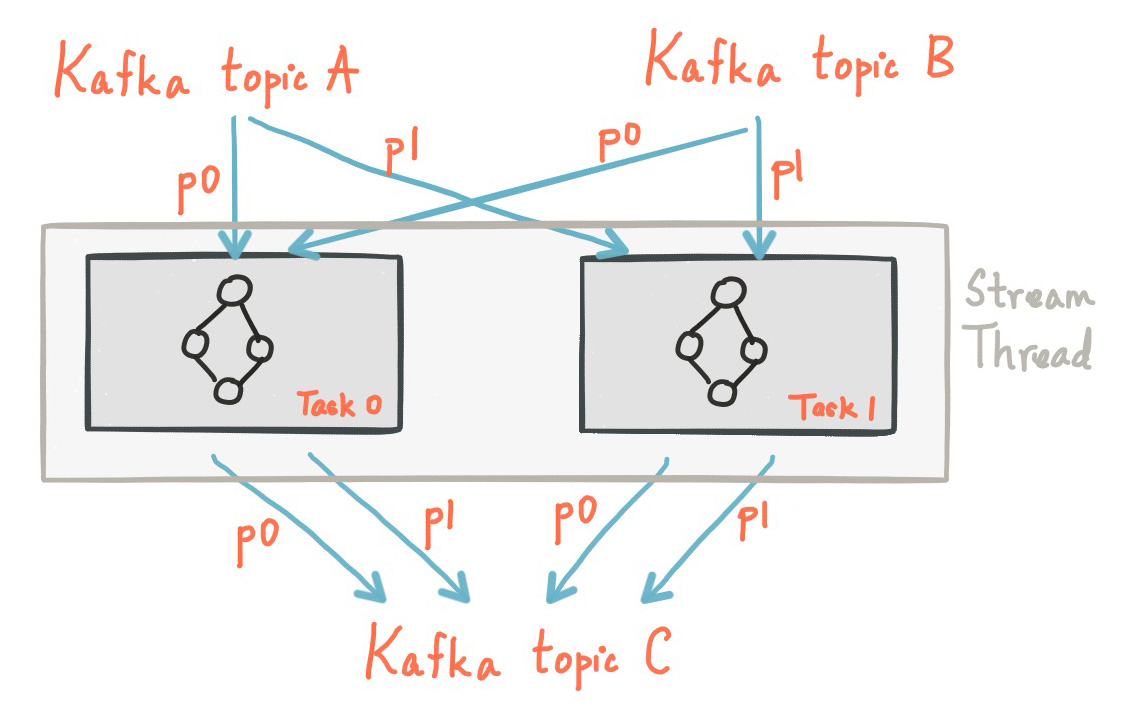
Starting more stream threads or more instances of the application merely amounts to replicating the topology and having it process a different subset of Kafka partitions, effectively parallelizing processing. It is worth noting that there is no shared state amongst the threads, so no inter-thread coordination is necessary. This makes it very simple to run topologies in parallel across the application instances and threads. The assignment of Kafka topic partitions amongst the various stream threads is transparently handled by Kafka Streams leveraging Kafka’s coordination functionality.
启动更多流线程或应用程序的更多实例仅相当于复制拓扑并让它处理 Kafka 分区的不同子集,从而有效地并行处理。值得注意的是,线程之间没有共享状态,因此不需要线程间协调。这使得跨应用程序实例和线程并行运行拓扑变得非常简单。Kafka Streams 利用Kafka 的协调功能透明地处理各种流线程之间的 Kafka 主题分区分配
As we described above, scaling your stream processing application with Kafka Streams is easy: you merely need to start additional instances of your application, and Kafka Streams takes care of distributing partitions amongst tasks that run in the application instances. You can start as many threads of the application as there are input Kafka topic partitions so that, across all running instances of an application, every thread (or rather, the tasks it runs) has at least one input partition to process.
如上所述,使用 Kafka Streams 扩展流处理应用程序很容易:您只需启动应用程序的其他实例,Kafka Streams 负责在应用程序实例中运行的任务之间分配分区。您可以启动与输入 Kafka 主题分区一样多的应用程序线程,以便在应用程序的所有运行实例中,每个线程(或者更确切地说,它运行的任务)至少有一个输入分区要处理
As of Kafka 2.8 you can scale stream threads much in the same way you can scale your Kafka Stream clients. Simply add or remove stream threads and Kafka Streams will take care of redistributing the partitions. You may also add threads to replace stream threads that have died removing the need to restart clients to recover the number of thread running
从 Kafka 2.8 开始,您可以像扩展 Kafka Stream 客户端一样扩展流线程。只需添加或删除流线程,Kafka Streams 就会负责重新分配分区。您还可以添加线程来替换已死亡的流线程,从而无需重新启动客户端以恢复正在运行的线程数
Local State Stores本地状态存储
Kafka Streams provides so-called state stores, which can be used by stream processing applications to store and query data, which is an important capability when implementing stateful operations. The Kafka Streams DSL, for example, automatically creates and manages such state stores when you are calling stateful operators such as join() or aggregate(), or when you are windowing a stream.
Kafka Streams 提供了所谓的状态存储,流处理应用程序可以使用它来存储和查询数据,这是实现有状态操作时的重要能力。例如,Kafka Streams DSL 会在您调用有状态运算符,如join()或aggregate()或窗口化流时自动创建和管理此类状态存储
Every stream task in a Kafka Streams application may embed one or more local state stores that can be accessed via APIs to store and query data required for processing. Kafka Streams offers fault-tolerance and automatic recovery for such local state stores.
Kafka Streams 应用程序中的每个流任务都可以嵌入一个或多个可以通过 API 访问的本地状态存储,以存储和查询处理所需的数据。Kafka Streams 为此类本地状态存储提供容错和自动恢复
The following diagram shows two stream tasks with their dedicated local state stores.
下图显示了两个流任务及其专用的本地状态存储
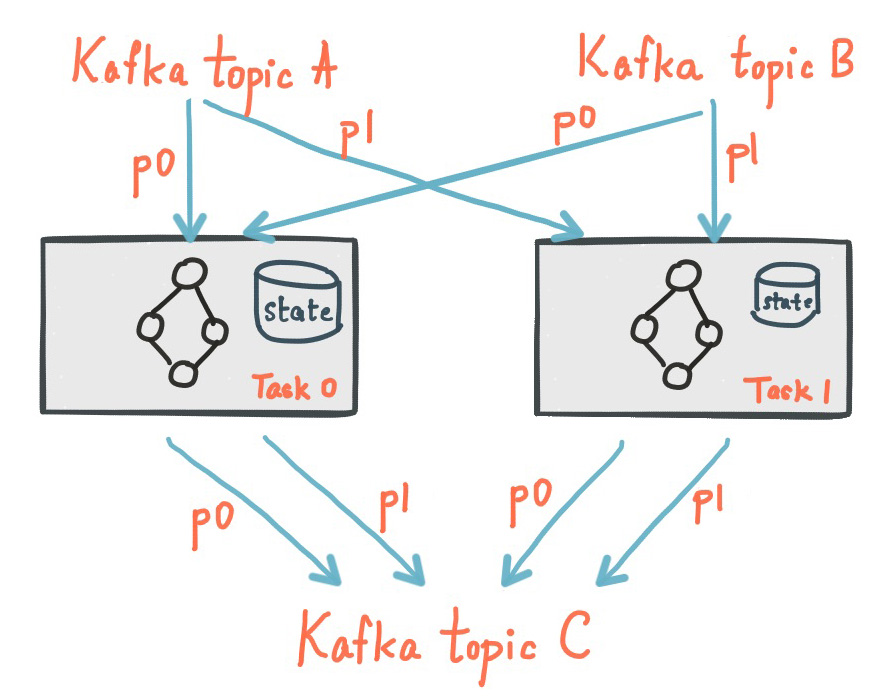
Fault Tolerance容错
Kafka Streams builds on fault-tolerance capabilities integrated natively within Kafka. Kafka partitions are highly available and replicated; so when stream data is persisted to Kafka it is available even if the application fails and needs to re-process it. Tasks in Kafka Streams leverage the fault-tolerance capability offered by the Kafka consumer client to handle failures. If a task runs on a machine that fails, Kafka Streams automatically restarts the task in one of the remaining running instances of the application
Kafka Streams 建立在 Kafka 中本地集成的容错功能之上。Kafka 分区是高可用和可复制的;因此,当流数据持久化到 Kafka 时,即使应用程序失败并需要重新处理它也是可用的。Kafka Streams 中的任务利用 Kafka 消费者客户端提供的容错功能来处理故障。如果任务在失败的机器上运行,Kafka Streams 会自动在应用程序的剩余运行实例之一中重新启动任务。
In addition, Kafka Streams makes sure that the local state stores are robust to failures, too. For each state store, it maintains a replicated changelog Kafka topic in which it tracks any state updates. These changelog topics are partitioned as well so that each local state store instance, and hence the task accessing the store, has its own dedicated changelog topic partition. Log compaction is enabled on the changelog topics so that old data can be purged safely to prevent the topics from growing indefinitely. If tasks run on a machine that fails and are restarted on another machine, Kafka Streams guarantees to restore their associated state stores to the content before the failure by replaying the corresponding changelog topics prior to resuming the processing on the newly started tasks. As a result, failure handling is completely transparent to the end user
此外,Kafka Streams 还确保本地状态存储对故障具有鲁棒性。对于每个状态存储,它维护一个复制的变更日志 Kafka 主题,在其中跟踪任何状态更新。这些变更日志主题也被分区,以便每个本地状态存储实例以及访问存储的任务都有自己专用的变更日志主题分区。 日志压缩在更改日志主题上启用,以便可以安全地清除旧数据以防止主题无限增长。如果任务在发生故障的机器上运行并在另一台机器上重新启动,Kafka Streams 保证通过在恢复处理新启动的任务之前重放相应的变更日志主题,将其关联的状态存储恢复到故障前的内容。因此,故障处理对最终用户是完全透明的。
Note that the cost of task (re)initialization typically depends primarily on the time for restoring the state by replaying the state stores’ associated changelog topics. To minimize this restoration time, users can configure their applications to have standby replicas of local states (i.e. fully replicated copies of the state). When a task migration happens, Kafka Streams will assign a task to an application instance where such a standby replica already exists in order to minimize the task (re)initialization cost. See num.standby.replicas in the Kafka Streams Configs section. Starting in 2.6, Kafka Streams will guarantee that a task is only ever assigned to an instance with a fully caught-up local copy of the state, if such an instance exists. Standby tasks will increase the likelihood that a caught-up instance exists in the case of a failure
请注意,任务(重新)初始化的成本通常主要取决于通过重放状态存储的相关变更日志主题来恢复状态的时间。为了最大限度地减少恢复时间,用户可以将他们的应用程序配置为具有本地状态的备用副本(即状态的完全复制副本)。当发生任务迁移时,Kafka Streams 会将任务分配给已经存在此类备用副本的应用程序实例,以最小化任务(重新)初始化成本。num.standby.replicas在Kafka Streams Configs中查看部分。从 2.6 开始,Kafka Streams 将保证任务只会分配给具有完全捕获状态本地副本的实例(如果存在这样的实例)。备用任务将增加在发生故障时存在被捕获实例的可能性。
You can also configure standby replicas with rack awareness. When configured, Kafka Streams will attempt to distribute a standby task on a different “rack” than the active one, thus having a faster recovery time when the rack of the active tasks fails. See rack.aware.assignment.tags
您还可以配置具有机架意识的备用副本。配置后,Kafka Streams 将尝试将备用任务分配到与活动任务不同的“机架”上,从而在活动任务的机架发生故障时具有更快的恢复时间.请参阅Kafka Streams 开发人员指南rack.aware.assignment.tags 部分


