- 1设计模式-组合模式_组合设计模式菜鸟
- 2Windows系统安装onlyoffice_windows安装only office
- 3Flask项目快速部署_flask部署到服务器
- 4深入理解Linux内核-磁盘IO-I/0体系结构和设备驱动程序
- 5Win10内置Ubuntu重启Docker服务_win10重启docker服务
- 6拜占庭容错共识(PBFT)
- 7数智赋能内涝治理,四信城市排水防涝解决方案保障城市安全运行
- 8Github authenticator登录问题_github-recovery-codes
- 9深入学习Java:关于List下标越界源码分析_removeall 避免数组下标越界
- 10编写测试用例标准_测试用例设计要求连贯性
java中用rabbitmq_RabbitMQ在java中基础使用
赞
踩
RabbitMQ相关术语:
1.Broker:简单来说就是消息队列服务器实体。
2.Exchange:消息交换机,它指定消息按什么规则,路由到哪个队列。
3.Queue:消息队列载体,每个消息都会被投入到一个或多个队列。
4.Binding:绑定,它的作用就是把exchange和queue按照路由规则绑定起来。
5.Routing Key:路由关键字,exchange根据这个关键字进行消息投递。
6.vhost:虚拟主机,一个broker里可以开设多个vhost,用作不同用户的权限分离。
7.producer:消息生产者,就是投递消息的程序。
8.consumer:消息消费者,就是接受消息的程序。
9.channel:消息通道,在客户端的每个连接里,可建立多个channel,每个channel代表一个会话任务。
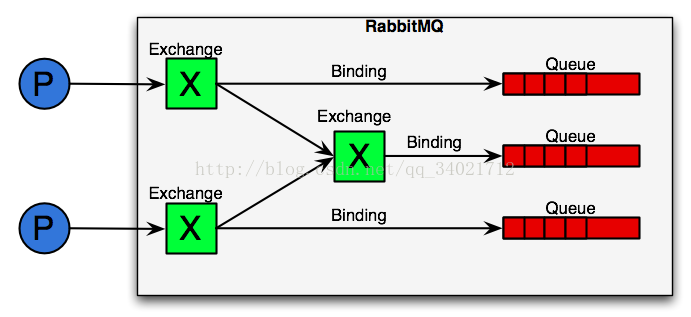
RabbitMQ常用发布订阅模式的运行流程:
AMQP模型中,消息在producer中产生,发送到MQ的exchange上,exchange根据配置的路由方式发到相应的Queue上,Queue又将消息发送给consumer,消息从queue到consumer有push和pull两种方式。 消息队列的使用过程大概如下:
1.客户端连接到消息队列服务器,打开一个channel。
2.客户端声明一个exchange,并设置相关属性。
3.客户端声明一个queue,并设置相关属性。
4.客户端使用routing key,在exchange和queue之间建立好绑定关系。
5.客户端投递消息到exchange。
RabbitMQ教程:
引入maven依赖:
com.rabbitmq
amqp-client
3.6.5
1.hello world!
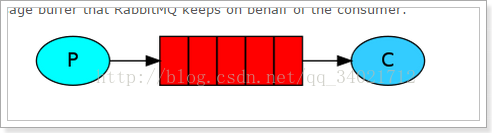
生产者:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_helloworld;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
/**
* helloworld
* @author
*/
public class Producer {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 从连接中创建通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/*
* 声明(创建)队列
* 参数1:队列名称
* 参数2:为true时server重启队列不会消失
* 参数3:队列是否是独占的,如果为true只能被一个connection使用,其他连接建立时会抛出异常
* 参数4:队列不再使用时是否自动删除(没有连接,并且没有未处理的消息)
* 参数5:建立队列时的其他参数
*/
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 消息内容
String message = "Hello World!";
/*
* 向server发布一条消息
* 参数1:exchange名字,若为空则使用默认的exchange
* 参数2:routing key
* 参数3:其他的属性
* 参数4:消息体
* RabbitMQ默认有一个exchange,叫default exchange,它用一个空字符串表示,它是direct exchange类型,
* 任何发往这个exchange的消息都会被路由到routing key的名字对应的队列上,如果没有对应的队列,则消息会被丢弃
*/
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println(" [生产者] Sent '" + message + "'");
//关闭通道和连接
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_helloworld;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
public class Consumer {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 从连接中创建通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列(如果你已经明确的知道有这个队列,那么下面这句代码可以注释掉,如果不注释掉的话,也可以理解为消费者必须监听一个队列,如果没有就创建一个)
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
/*
* 监听队列
* 参数1:队列名称
* 参数2:是否发送ack包,不发送ack消息会持续在服务端保存,直到收到ack。 可以通过channel.basicAck手动回复ack
* 参数3:消费者
*/
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, true, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [消费者] Received '" + message + "'");
}
}
}
2.Work模式
Work普通模式
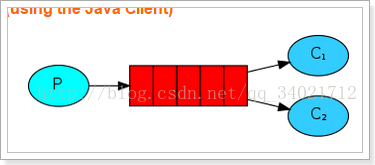
生产者:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_work;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
/**
* work模式
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public class Producer {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_work";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
// 消息内容
String message = "" + i;
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println(" [生产者] Sent '" + message + "'");
//发送的消息间隔越来越长
Thread.sleep(i * 10);
}
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者1:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_work;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
public class Consumer1 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_work";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者(能者多劳模式)
//channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
/*
* 监听队列,不自动返回ack包,下面手动返回
* 如果不回复,消息不会在服务器删除
*/
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [消费者1] Received '" + message + "'");
//休眠
Thread.sleep(10);
// 手动返回ack包确认状态
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
//channel.basicReject(); channel.basicNack(); //可以通过这两个函数拒绝消息,可以指定消息在服务器删除还是继续投递给其他消费者
}
}
}
消费者2:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_work;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
public class Consumer2 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_work";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者(能者多劳模式)
//channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成状态
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [消费者2] Received '" + message + "'");
// 休眠1秒
Thread.sleep(1000);
//反馈消息的消费状态
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}
测试结果:
1、消费者1和消费者2获取到的消息内容是不同的,同一个消息只能被一个消费者获取。
2、消费者1和消费者2获取到的消息的数量是相同的,一个是奇数一个是偶数。
其实,这样是不合理的,应该是消费者1要比消费者2获取到的消息多才对。
Work的能者多劳模式
需要将上面两个消费者的channel.basicQos(1);这行代码的注释打开,再次执行会发现,休眠时间短的消费者执行的任务多
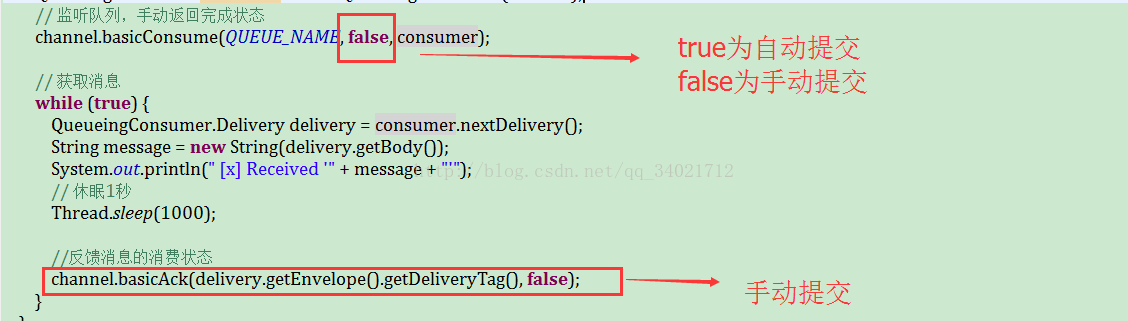
消息的确认
在以上的代码中,已经给出了注释,如何使用自动确认和手动确认,消费者从队列中获取消息,服务端如何知道消息已经被消费呢?
模式1:自动确认
只要消息从队列中获取,无论消费者获取到消息后是否成功消息,都认为是消息已经成功消费。
模式2:手动确认
消费者从队列中获取消息后,服务器会将该消息标记为不可用状态,等待消费者的反馈,如果消费者一直没有反馈,那么该消息将一直处于不可用状态。
如果选用自动确认,在消费者拿走消息执行过程中出现宕机时,消息可能就会丢失!!
3.订阅模式
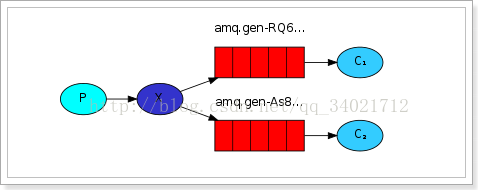
文章开头有发布订阅的流程介绍
生产者:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_pubsub;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
/**
* 订阅模式
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public class Producer {
//交换机的名称
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_fanout";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/*
* 声明exchange(交换机)
* 参数1:交换机名称
* 参数2:交换机类型
* 参数3:交换机持久性,如果为true则服务器重启时不会丢失
* 参数4:交换机在不被使用时是否删除
* 参数5:交换机的其他属性
*/
channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout",true,true,null);
// 消息内容
String message = "订阅消息";
channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, "", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println(" [生产者] Sent '" + message + "'");
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者1:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_pubsub;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
public class Consumer1 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_exchange_1";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_fanout";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
/*
* 绑定队列到交换机(这个交换机的名称一定要和上面的生产者交换机名称相同)
* 参数1:队列的名称
* 参数2:交换机的名称
* 参数3:Routing Key
*
*/
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [消费者1] Received '" + message + "'");
Thread.sleep(10);
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}
消费者2:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_pubsub;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
public class Consumer2 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_exchange_2";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_fanout";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [消费者2] Received '" + message + "'");
Thread.sleep(10);
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}
注意:消息发送到没有队列绑定的交换机时,消息将丢失,因为,交换机没有存储消息的能力,消息只能存在在队列中。
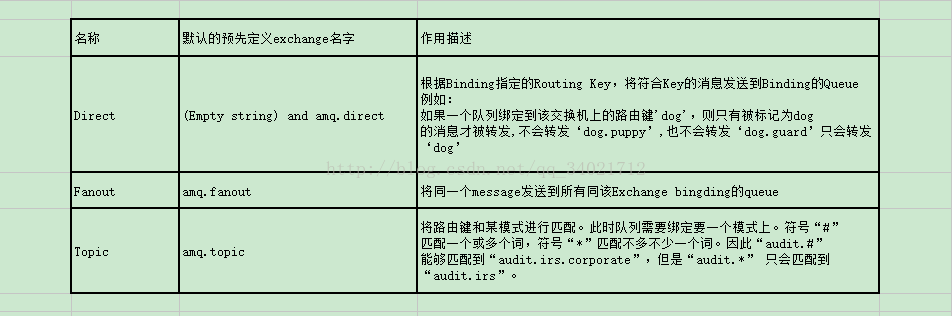
Exchange类型
Direct 、Fanout 、Topic 三种类型,RabbitMQ默认有一个exchange,叫default exchange,它用一个空字符串表示,它是direct exchange类型。
下面介绍的路由模式和通配符模式都是属于订阅模式,只不过加入了Routing Key(路由键,文章开头有介绍)。
3.1路由模式
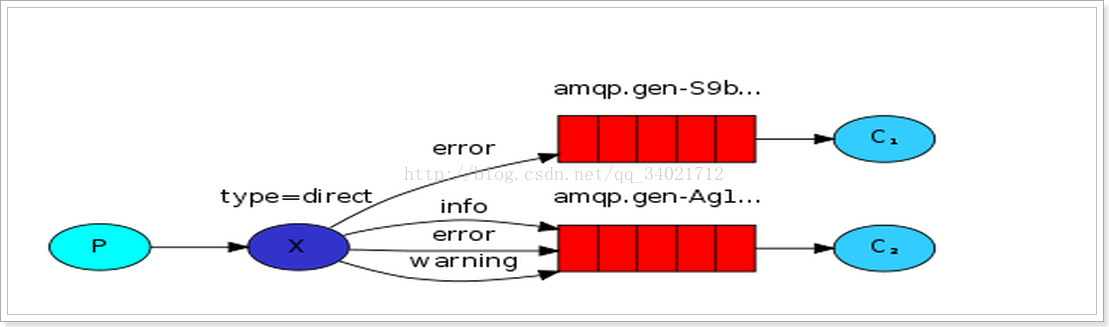
生产者:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_routing;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
/**
* 路由模式
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public class Producer {
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_direct";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明exchange
channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "direct");
// 消息内容
String message = "这是消息B";
channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, "B", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println(" [生产者] Sent '" + message + "'");
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者1:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_routing;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
public class Consumer1 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_direct_1";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_direct";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
/*
* 绑定队列到交换机
* 参数1:队列的名称
* 参数2:交换机的名称
* 参数3:routingKey
*/
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "A");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [消费者1] Received '" + message + "'");
Thread.sleep(10);
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}
消费者2:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_routing;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
public class Consumer2 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_direct_2";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_direct";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "B");
//如果想让消费者2同时接受routingKey为A 和为B的消息,只要在下面在此添加一个Bing就可以了
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "A");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [消费者2] Received '" + message + "'");
Thread.sleep(10);
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}
3.2通配符模式
将路由键和某模式进行匹配。此时队列需要绑定要一个模式上。符号“#”匹配一个或多个词,符号“*”只能匹配一个词。因此“audit.#”能够匹配到“audit.irs”和“audit.irs.corporate”,但是“audit.*” 只会匹配到“audit.irs”。
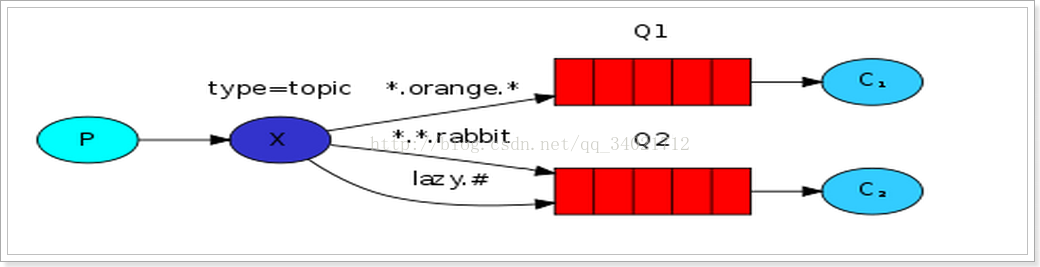
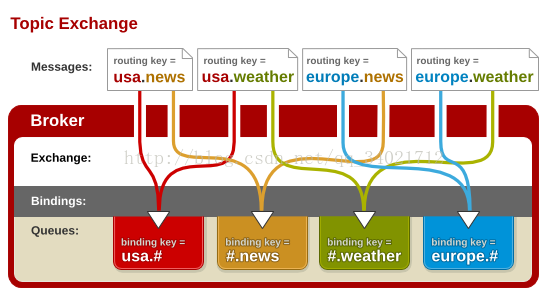
生产者:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_topic;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
/**
* 通配模式
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public class Producer {
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_topic";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明exchange
channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic");
// 消息内容 模拟 有人购物下订单
String message = "新增订单:id=101";
channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, "order.insert", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println(" [生产者] Sent '" + message + "'");
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
消费者1:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_topic;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
public class Consumer1 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_topic_1";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_topic";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "order.#");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [财务系统] Received '" + message + "'");
Thread.sleep(10);
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}
消费者2:
package com.rabbitmq.test.T_topic;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
import com.rabbitmq.test.util.ConnectionUtil;
public class Consumer2 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_topic_2";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_topic";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "order.insert");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
QueueingConsumer consumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, consumer);
// 获取消息
while (true) {
QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = consumer.nextDelivery();
String message = new String(delivery.getBody());
System.out.println(" [物流系统] Received '" + message + "'");
Thread.sleep(10);
channel.basicAck(delivery.getEnvelope().getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
}
}
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/qq_34021712/article/details/72567801


