热门标签
热门文章
- 1Django进阶:DRF(Django REST framework)_django drf
- 2ETH等提出思维图(GoT)超越思维链(CoT): 用LLMs解决复杂问题!
- 3计算机学院毕业生祝福,暖心的毕业祝愿赠言
- 4「屏蔽更新」 Mac如何屏蔽系统更新_mac屏蔽更新
- 5flink学习之sql-client之踩坑记录_org.apache.flink.table.catalog.exceptions.cataloge
- 6设计模式-解释器模式(Interpreter)_设计模式 解释器模式
- 7Qt lnk1158 无法运行rc.exe 解决_qtlnk1158: 无法运行“rc.exe”
- 8Java爬虫(七)-- httpClient进阶: https 和 证书认证(讲故事篇)
- 9大数据Hadoop之——EFAK和Confluent KSQL简单使用(kafka listeners 和 advertised.listeners)
- 10边缘计算采集网关解决方案:为企业提供高效、灵活的数据处理方案-天拓四方
当前位置: article > 正文
(6)文本挖掘(三)——文本特征TFIDF权重计算及文本向量空间VSM表示_tf-idf vsm
作者:Gausst松鼠会 | 2024-06-16 05:35:38
赞
踩
tf-idf vsm
建立文本数据数学描述的过程分为三个步骤:文本预处理、建立向量空间模型和优化文本向量。文本预处理主要采用分词、停用词过滤等技术将原始的文本字符串转化为词条串或者特点的符号串。文本预处理之后,每一个文本的词条串被进一步转换为一个文本向量,向量的每一维对应一个词条,其值反映的是这个词条与这个文本之间的相似度。相似度有很多不同的计算方法,所以优化文本向量就是采用最为合适的计算方法来规范化文本向量,使其能更好地应用于文本分类和文本聚类等方面。
TFIDF算法
TF-IDF使得一个单词能尽量与文本在语义上相关。TF-IDF算法的实现步骤:

经过试验发现,用TFIDF/max(TFIDF)的方法效果是最好的,具体代码如下:
import java.io.File;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 经过试验发现,用TFIDF/max(TFIDF)的方法效果是最好的
* @author Angela
*/
public class TFIDF {
private Map<String,Integer> TF;//文本词频集
private Map<String,Double> IDF;//特征-逆文档频率集
/**
* 构造方法,初始化TF和IDF
*/
public TFIDF(Map<String,Integer> TF,Map<String,Double> IDF){
this.TF=TF;
this.IDF=IDF;
}
/**
* 计算文本特征集的tf-idf权值
* @return filePath文件的特征-TFIDF集
*/
public Map<String,Double> getTFIDF(){
Map<String,Double> tfidf=new HashMap<String,Double>();
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> me: TF.entrySet()){
String f=me.getKey();
double weight=me.getValue()*IDF.get(f);
tfidf.put(f, weight);
}
return tfidf;
}
/**
* 计算文本特征集的对数tf-idf权值
* @return filePath文件的特征-TFIDF集
*/
public Map<String,Double> getLogTFIDF(){
Map<String,Double> tfidf=new HashMap<String,Double>();
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> me: TF.entrySet()){
String f=me.getKey();
double tf=1+Math.log(me.getValue());
double weight=tf*IDF.get(f);
tfidf.put(f, weight);
}
return tfidf;
}
/**
* 进行规一化,每一个特征除以这篇文本TFIDF值之和,构成新的TFIDF集
* @return filePath文件的特征-标准化TFIDF集
*/
public Map<String,Double> getNormalTFIDF(){
Map<String,Double> tfidf=new HashMap<String,Double>();
Map<String,Double> weight=getTFIDF();
double sum=MathUtil.calSum(weight);//计算TFIDF总和
for(Map.Entry<String, Double> me: weight.entrySet()){
String f=me.getKey();
double w=me.getValue()/sum;
tfidf.put(f, w);
}
return MapUtil.descend(tfidf);
}
/**
* 进行标准化,每一个特征除以这篇文本中最大的TFIDF值,构成新的TFIDF集
* @return filePath文件的特征-标准化TFIDF集
*/
public Map<String,Double> getStandardTFIDF(){
Map<String,Double> tfidf=new HashMap<String,Double>();
Map<String,Double> weight=getTFIDF();
Map<String,Double> temp=MapUtil.descend(weight);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> set = temp.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,Double>> it = set.iterator();
double max=0;
if(it.hasNext()){
max=it.next().getValue();
}
for(Map.Entry<String, Double> me: weight.entrySet()){
String f=me.getKey();
double w=me.getValue()/max;
tfidf.put(f, w);
}
return MapUtil.descend(tfidf);
}
/**
* 保存文本的TFIDF结果
* @param tf 文本的TF集
* @param idf IDF集
* @param savePath 保存路径
*/
public static void saveTFIDF(Map<String,Integer> tf,
Map<String,Double> idf,String savePath){
TFIDF tfidf=new TFIDF(tf,idf);
Map<String,Double> weight=tfidf.getStandardTFIDF();
Writer.saveMap(weight, savePath);
}
/**
* 保存TFIDF结果
* @param filePath 文本集的TF集路径
* @param idfPath IDF路径
* @param tarPath 保存路径
*/
public static void saveTFIDF(String TFPath,String IDFPath,String tarPath){
File tar=new File(tarPath);
if(!tar.exists()) tar.mkdir();
Map<String,Double> idf=Reader.toDoubleMap(IDFPath);//IDF
File file=new File(TFPath);
File[] labels=file.listFiles();//类别
for(File label: labels){
String labelpath=tarPath+File.separator+label.getName();
File labelPath=new File(labelpath);
if(!labelPath.exists()) labelPath.mkdir();
File[] texts=label.listFiles();//文本
for(File text: texts){
String savePath=labelpath+File.separator+text.getName();
Map<String,Integer> tf=Reader.toIntMap(text.getAbsolutePath());
saveTFIDF(tf,idf,savePath);
System.out.println("Saved "+savePath);
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
String TFPath="data\\r8trainTF";
String IDFPath="data\\r8trainIDF.txt";
String tarPath="data\\r8trainTFIDF3";
saveTFIDF(TFPath,IDFPath,tarPath);
}
}

- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
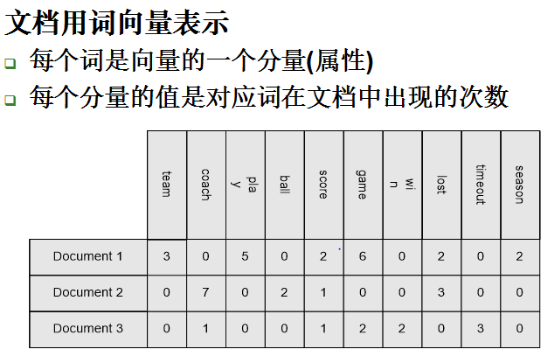
向量空间模型VSM
余弦相似度
文本与文本之间的相似度不能简单地用欧式距离来计算,更合理的计算方式是余弦相似度。
下面就是涉及这两个知识点的工具类。
MathUtil存放通用的计算公式方法
import java.util.Map;
/**
*
* @author Angela
*/
public class MathUtil {
/**
* 计算Map的键值之和
* @param map
* @return
*/
public static double calSum(Map<String,Double> map){
double sum=0;
for(Map.Entry<String,Double> me: map.entrySet()){
sum+=me.getValue();
}
return sum;
}
/**
* 计算两篇文本的相似度
* @param text1 文本1
* @param text2 文本2
* @return text1和text2的余弦相似度,值越大越相似
*/
public static double calSim(Map<String,Double> text1,
Map<String,Double> text2){
double sim=0;//相似度
double sum=0;//相同特征的权重相乘之和
double len1=0;//文本1的长度
double len2=0;//文本2的长度
for(Map.Entry<String,Double> me: text1.entrySet()){
String f=me.getKey();
double value=me.getValue();
if(text2.containsKey(f)){
sum+=value*text2.get(f);
}
len1+=value*value;
}
for(Map.Entry<String,Double> me: text2.entrySet()){
double value=me.getValue();
len2+=value*value;
}
sim=sum/(Math.sqrt(len1)*Math.sqrt(len2));
return sim;
}
}

- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
GetData获取DF、TFIDF即VSM、类别成员clusterMember、类别列表LabelList及由TFIDF构造的其它数据
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
*
* @author Angela
*/
public class GetData {
/**
* 根据TFIDF得到对应的DF集合
* 如果你的TFIDF集只是原始的一部分,就用这个方法来获取对应的DF集
* @param tfidf TFIDF集合
* @return
*/
public static Map<String,Integer> getDF(Map<String,Map<String,Double>> tfidf){
Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<String,Integer>();
for(Map.Entry<String,Map<String,Double>> me: tfidf.entrySet()){
Map<String,Double> text=me.getValue();
for(Map.Entry<String,Double> t: text.entrySet()){
String feature=t.getKey();
if(map.containsKey(feature)){
map.put(feature,map.get(feature)+1);
}else{
map.put(feature, 1);
}
}
}
return map;
}
/**
* 读取文本集,返回Map<类别+文件名,Map<特征,权重>>
* 当你进行特征选择后,得到特征子集,可以用这个方法
* 从文本集中构建新的VSM
* @param filePath TFIDF存放路径
* @param featureSet 特征集
* @return
*/
public static Map<String,Map<String,Double>> getTFIDF(String filePath,
Set<String> featureSet){
Map<String,Map<String,Double>> map=new HashMap<String,Map<String,Double>>();
File path=new File(filePath);
File[] files=path.listFiles();//类别
for(File file: files){
String label=file.getName();
File[] texts=file.listFiles();//文本
for(File text: texts){
Map<String,Double> tfidf=Reader.toDoubleMap(text.getAbsolutePath());
Map<String,Double> temp=new HashMap<String,Double>();
for(Map.Entry<String,Double> me: tfidf.entrySet()){
String feature=me.getKey();
if(featureSet.contains(feature)){
temp.put(feature,me.getValue());
}
}
map.put(label+File.separator+text.getName(), temp);
}
}
return map;
}
/**
* 根据特征集构建新的VSM,返回Map<类别+文件名,Map<特征,权重>>
* 当你进行特征选择后,得到特征子集,可以用这个方法
* 从原始的VSM中构建新的VSM
* @param tfidf 原始的VSM
* @param featureSet 特征集
* @return
*/
public static Map<String,Map<String,Double>> getTFIDF(
Map<String,Map<String,Double>> tfidf,Set<String> featureSet){
Map<String,Map<String,Double>> map=new HashMap<String,Map<String,Double>>();
for(Map.Entry<String,Map<String,Double>> me: tfidf.entrySet()){
Map<String,Double> text=me.getValue();
Map<String,Double> temp=new HashMap<String,Double>();
for(Map.Entry<String,Double> t: text.entrySet()){
String feature=t.getKey();
if(featureSet.contains(feature)){
temp.put(feature,t.getValue());
}
}
map.put(me.getKey(), temp);
}
return map;
}
/**
* 根据TFIDF文本集和特征集构建
* Map<特征,Map<文本路径名,特征在该文本中的TFIDF值>>
* @param tfidf TFIDF文本集
* @param featureSet 特征集
* @return
*/
public static Map<String,Map<String,Double>> getTermIndex(
Map<String,Map<String,Double>> tfidf,Set<String> featureSet){
Map<String,Map<String,Double>> termIndex=
new HashMap<String,Map<String,Double>>();
for(String f: featureSet){//特征
//包含有特征f的所有文本及特征f在该文本中的权重
Map<String,Double> feature=new HashMap<String,Double>();
for(Map.Entry<String,Map<String,Double>> me: tfidf.entrySet()){
Map<String,Double> text=me.getValue();//文本
if(text.containsKey(f)){//如果文本包含特征f
//将文本的路径和特征f的值赋给feature
feature.put(me.getKey(), text.get(f));
}
}
//将特征及feature赋给termIndex
termIndex.put(f,feature);
}
return termIndex;
}
/**
* 根据文本特征集和特征集构建Map<特征,Set<文本路径名>>
* @param dataSet Map<文本,Set<特征>>
* @param featureSet 特征集
* @return
*/
public static Map<String,Set<String>> getFeatureIndex(
Map<String,Set<String>> dataSet,Set<String> featureSet){
Map<String,Set<String>> featureIndex=
new HashMap<String,Set<String>>();
for(String f: featureSet){//特征
Set<String> textSet=new HashSet<String>();
for(Map.Entry<String,Set<String>> me: dataSet.entrySet()){
String textPath=me.getKey();//文本路径
Set<String> feature=me.getValue();//文本的特征集
//如果文本包含特征f
if(feature.contains(f)){
textSet.add(textPath);
}
}
//将特征及文本集赋给termText
featureIndex.put(f,textSet);
}
return featureIndex;
}
/**
* 文本集的类别成员
* @param filePath
* @return
*/
public static Map<Integer,List<String>> getClusterMember(String filePath){
Map<Integer,List<String>> clusterMember=new HashMap<Integer,List<String>>();
File file=new File(filePath);
File[] labels=file.listFiles();
int labelNum=labels.length;
for(int i=0;i<labelNum;i++){
File[] texts=labels[i].listFiles();
String label=labels[i].getName();
List<String> member=new ArrayList<String>();
for(File text: texts){
member.add(label+File.separator+text.getName());
}
clusterMember.put(i, member);
}
return clusterMember;
}
/**
* 类别集
* @param filePath
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getLabelList(String filePath){
List<String> labelList=new ArrayList<String>();
File files=new File(filePath);
File[] file=files.listFiles();
for(File f: file){
labelList.add(f.getName());
}
return labelList;
}
/**
* 根据TFIDF集构造类别集
* @param TFIDF
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getLabelList(Map<String,Map<String,Double>> TFIDF){
Set<String> labels=new HashSet<String>();
for(Map.Entry<String,Map<String,Double>> me: TFIDF.entrySet()){
String path=me.getKey();
String label=path.substring(0,path.lastIndexOf(File.separator));
labels.add(label);
}
List<String> labelList=new ArrayList<String>(labels);
return labelList;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
因为文本数据量一般很大,而且VSM具有高维稀疏的特点,所以一般需要进行特征选择,来减少特征的数量。下一节,我将介绍几种特征选择方法。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/Gausst松鼠会/article/detail/725349
推荐阅读
相关标签