- 1Zookeeper集群部署
- 2基于单片机仓库智能巡检车的设计_仓库火灾检测智能车
- 3搭建个人博客-hexo+github详细完整步骤_hebox github 搭建
- 42020华为海思的实习生面试记录(雨人)
- 5【退役贴】再见了ACM,再会了算法竞赛_acm就是算法
- 6torch, cuda, 单机多卡与DDP分布式_单机单卡修改ddp
- 7在Anaconda环境下安装多个Python版本并安装相应的包_anaconda安装不同版本python
- 8顺序表_顺序表的地址计算
- 9【软考软件评测师】2013综合知识历年真题_负载压力测试不用发现不用负载场景下的速度变慢、内存泄露等问题
- 10Flask+Celery异步任务中共用上下文(g)_如何在celery异步任务中引入 flask的应用上下文
linux /proc/net/tcp 文件分析_seq_operations
赞
踩
/proc/net/tcp文件提供了tcp的连接信息,是由net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c中的tcp4_seq_show()实现信息打印的
本文内容来源于 linux官方文档proc_net_tcp.txt
1. 官方文档解释
proc_net_tcp.txt介绍了/proc/net/tcp和/proc/net/tcp6接口。这些接口展示了tcp的连接信息。
展示的信息中,首先是listening TCP sockets,接着是established TCP sockets。
在linux中执行cat /proc/net/tcp,输出结果如图1:
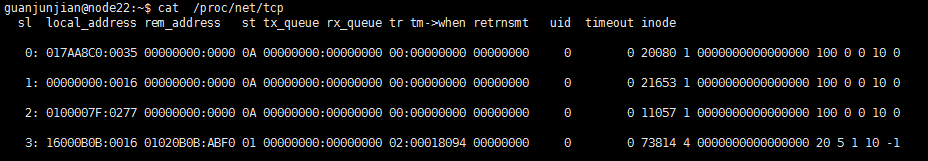
文档中对其中每个字段的解释如下(由于长度原因,分为3个部分):
part1:
- 46: 010310AC:9C4C 030310AC:1770 01
- | | | | | |--> connection state(套接字状态)
- | | | | |------> remote TCP port number(远端端口,主机字节序)
- | | | |-------------> remote IPv4 address(远端IP,网络字节序)
- | | |--------------------> local TCP port number(本地端口,主机字节序)
- | |---------------------------> local IPv4 address(本地IP,网络字节序)
- |----------------------------------> number of entry
connection state(套接字状态),不同的数值代表不同的状态,参照如下:
- TCP_ESTABLISHED:1 TCP_SYN_SENT:2
- TCP_SYN_RECV:3 TCP_FIN_WAIT1:4
- TCP_FIN_WAIT2:5 TCP_TIME_WAIT:6
- TCP_CLOSE:7 TCP_CLOSE_WAIT:8
- TCP_LAST_ACL:9 TCP_LISTEN:10
- TCP_CLOSING:11
part2:
- 00000150:00000000 01:00000019 00000000
- | | | | |--> number of unrecovered RTO timeouts(超时重传次数)
- | | | |----------> number of jiffies until timer expires(超时时间,单位是jiffies)
- | | |----------------> timer_active (定时器类型,see below)
- | |----------------------> receive-queue(根据状态不同有不同表示,see below)
- |-------------------------------> transmit-queue(发送队列中数据长度)
receive-queue,当状态是ESTABLISHED,表示接收队列中数据长度;状态是LISTEN,表示已经完成连接队列的长度。
timer_active:
- 0 no timer is pending //没有启动定时器
- 1 retransmit-timer is pending //重传定时器
- 2 another timer (e.g. delayed ack or keepalive) is pending //连接定时器、FIN_WAIT_2定时器或TCP保活定时器
- 3 this is a socket in TIME_WAIT state. Not all fields will contain data (or even exist) //TIME_WAIT定时器
- 4 zero window probe timer is pending //持续定时器
part3:
- 1000 0 54165785 4 cd1e6040 25 4 27 3 -1
- | | | | | | | | | |--> slow start size threshold,
- or -1 if the threshold is >=0xFFFF
- | | | | | | | | | (如果慢启动阈值大于等于0xFFFF则显示-1,否则表示慢启动阈值)
- | | | | | | | | |
- | | | | | | | | |----> sending congestion window(当前拥塞窗口大小)
- | | | | | | | |-------> (ack.quick<<1)|ack.pingpong
- (快速确认数和是否启用的标志位的或运算结果)
- | | | | | | |---------> Predicted tick of soft clock (delayed ACK control data)
- (用来计算延时确认的估值)
- | | | | | |
- | | | | | |------------> retransmit timeout()(RTO,单位是clock_t)
- | | | | |------------------> location of socket in memory(socket实例的地址)
- | | | |-----------------------> socket reference count(socket结构体的引用数)
- | | |-----------------------------> inode(套接字对应的inode)
- | |----------------------------------> unanswered 0-window probes(see below)
- |---------------------------------------------> uid(用户id)

unanswered 0-window probes:持续定时器或保活定时器周期性发送出去但未被确认的TCP段数目,在收到ACK之后清零
2. tcp4_seq_show()
tcp4_seq_show()函数位于net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c#L2306#L2329。
首先需要来认识一下struct seq_file,称为序列文件接口。在UNIX的世界里,文件是最普通的概念,所以用文件来作为内核和用户空间传递数据的接口也是再普通不过的事情,并且这样的接口对于shell也是相当友好的,方便管理员通过shell直接管理系统。由于伪文件系统proc文件系统在处理大数据结构(大于一页的数据)方面有比较大的局限性,使得在那种情况下进行编程特别别扭,很容易导致bug,所以序列文件接口被发明出来,它提供了更加友好的接口,以方便程序员。之所以选择序列文件接口这个名字,应该是因为它主要用来导出一条条的记录数据。 Seq_file的实现基于proc文件。使用Seq_file,用户必须抽象出一个链接对象,然后可以依次遍历这个链接对象。这个链接对象可以是链表,数组,哈希表等等。有两个重要的结构体:1.seq_operations:定义了start、next、show、stop四个操作函数;2.seq_file:该结构会在seq_open函数调用中分配,然后作为参数传递给每个seq_file的操作函数。Privat变量可以用来在各个操作函数之间传递参数
下面是代码:
- static int tcp4_seq_show(struct seq_file *seq, void *v)
- {
- struct tcp_iter_state *st;
- struct sock *sk = v;
- //set padding width
- seq_setwidth(seq, TMPSZ - 1);
- //SEQ_START_TOKEN:通常这个值传递给show的时候,show会打印表格头
- if (v == SEQ_START_TOKEN) {
- //向表头输入到seq中
- seq_puts(seq, " sl local_address rem_address st tx_queue "
- "rx_queue tr tm->when retrnsmt uid timeout "
- "inode");
- goto out;
- }
- //指向文件的私有数据,是特例化一个序列文件的方法
- st = seq->private;
- if (sk->sk_state == TCP_TIME_WAIT)
- get_timewait4_sock(v, seq, st->num);
- else if (sk->sk_state == TCP_NEW_SYN_RECV)
- get_openreq4(v, seq, st->num);
- else
- //下面分析
- get_tcp4_sock(v, seq, st->num);
- out:
- seq_pad(seq, '\n');
- return 0;
- }

接下来看get_tcp4_sock(),主要代码如下:
- static void get_tcp4_sock(struct sock *sk, struct seq_file *f, int i)
- {
- int timer_active;
- unsigned long timer_expires;
- const struct tcp_sock *tp = tcp_sk(sk);
- const struct inet_connection_sock *icsk = inet_csk(sk);
- const struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
- const struct fastopen_queue *fastopenq = &icsk->icsk_accept_queue.fastopenq;
- __be32 dest = inet->inet_daddr;
- __be32 src = inet->inet_rcv_saddr;
- //将一个16位数由网络字节顺序转换为主机字节顺序
- __u16 destp = ntohs(inet->inet_dport);
- __u16 srcp = ntohs(inet->inet_sport);
- int rx_queue;
- int state;
- //获取定时器类型(timer_active)和超时时间(timer_expires)
- if (icsk->icsk_pending == ICSK_TIME_RETRANS ||
- icsk->icsk_pending == ICSK_TIME_EARLY_RETRANS ||
- icsk->icsk_pending == ICSK_TIME_LOSS_PROBE) {
- timer_active = 1;
- timer_expires = icsk->icsk_timeout;
- } else if (icsk->icsk_pending == ICSK_TIME_PROBE0) {
- timer_active = 4;
- timer_expires = icsk->icsk_timeout;
- } else if (timer_pending(&sk->sk_timer)) {
- timer_active = 2;
- timer_expires = sk->sk_timer.expires;
- } else {
- timer_active = 0;
- timer_expires = jiffies;
- }
- //read sk->sk_state for lockless contexts
- state = sk_state_load(sk);
- //根据tcp的状态,获取receive-queue的值
- if (state == TCP_LISTEN)
- rx_queue = sk->sk_ack_backlog;
- else
- /* Because we don't lock the socket,
- * we might find a transient negative value.
- */
- rx_queue = max_t(int, tp->rcv_nxt - tp->copied_seq, 0);
- //将tcp的信息加入到f,即传入的seq_file中
- seq_printf(f, "%4d: %08X:%04X %08X:%04X %02X %08X:%08X %02X:%08lX "
- "%08X %5u %8d %lu %d %pK %lu %lu %u %u %d",
- i, src, srcp, dest, destp, state,
- tp->write_seq - tp->snd_una,
- rx_queue,
- timer_active,
- jiffies_delta_to_clock_t(timer_expires - jiffies),
- icsk->icsk_retransmits,
- from_kuid_munged(seq_user_ns(f), sock_i_uid(sk)),
- icsk->icsk_probes_out,
- sock_i_ino(sk),
- atomic_read(&sk->sk_refcnt), sk,
- jiffies_to_clock_t(icsk->icsk_rto),
- jiffies_to_clock_t(icsk->icsk_ack.ato),
- (icsk->icsk_ack.quick << 1) | icsk->icsk_ack.pingpong,
- tp->snd_cwnd,
- state == TCP_LISTEN ?
- fastopenq->max_qlen :
- (tcp_in_initial_slowstart(tp) ? -1 : tp->snd_ssthresh));
- }

3. /proc/net/tcp的创建
tcp4_proc_init_net()
/proc/net/tcp的初始化函数为tcp4_proc_init_net(),位于net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c#L2348#L2350。
- static int __net_init tcp4_proc_init_net(struct net *net)
- {
- return tcp_proc_register(net, &tcp4_seq_afinfo);
- }
-
首先来看一下tcp4_seq_afinfo
- static struct tcp_seq_afinfo tcp4_seq_afinfo = {
- .name = "tcp",
- .family = AF_INET,
- .seq_fops = &tcp_afinfo_seq_fops,
- .seq_ops = {
- .show = tcp4_seq_show,
- },
- };
可以看到name="tcp",也就是一会要创建的文件名字是tcp。.seq_ops.show=tcp4_seq_show()应该是cat /proc/net/tcp时会调用的函数。
tcp4_proc_init_net()–>tcp_proc_register()
接下来看 tcp_proc_register()
- int tcp_proc_register(struct net *net, struct tcp_seq_afinfo *afinfo)
- {
- int rc = 0;
- //proc目录结构体,定义位于fs/proc/internal.h
- struct proc_dir_entry *p;
- //赋值afinfo,也就是tcp4_seq_afinfo的seq_operations
- afinfo->seq_ops.start = tcp_seq_start;
- afinfo->seq_ops.next = tcp_seq_next;
- afinfo->seq_ops.stop = tcp_seq_stop;
- //下面接着分析
- p = proc_create_data(afinfo->name, S_IRUGO, net->proc_net,
- afinfo->seq_fops, afinfo);
- if (!p)
- rc = -ENOMEM;
- return rc;
- }

tcp4_proc_init_net()–>tcp_proc_register()–>proc_create_data()
下面接着看proc_create_data()
- /*
- * @name: afinfo->name,即"tcp",你要建立的文件名
- * @mode: 读写权限,是一个八进制,传入的是S_IRUGO,即(S_IRUSR|S_IRGRP|S_IROTH)=00444
- * @parent: 指的应该是"/pro/net/"目录
- * @proc_fops: 传入的是afinfo->seq_fops,所以应该是tcp_afinfo_seq_fops
- * @data: 传入的是afinfo,即tcp4_seq_afinfo
- */
- struct proc_dir_entry *proc_create_data(const char *name, umode_t mode,
- struct proc_dir_entry *parent,
- const struct file_operations *proc_fops,
- void *data)
- {
- struct proc_dir_entry *pde;
- //00444 & 00170000 == 0,所以mode==170444
- if ((mode & S_IFMT) == 0)
- mode |= S_IFREG;
- //S_ISREG(170444)==(((170444) & S_IFMT) == S_IFREG)==(((00170444) & 00170000) == 0100000)==(170000==100000)==false
- //??
- if (!S_ISREG(mode)) {
- WARN_ON(1); /* use proc_mkdir() */
- return NULL;
- }
- BUG_ON(proc_fops == NULL);
- //170444 & 7777 == 444,所以mode==170444
- if ((mode & S_IALLUGO) == 0)
- mode |= S_IRUGO;
- //获得一个初始化了的proc_dir_entry结构体,下面继续分析
- pde = __proc_create(&parent, name, mode, 1);
- if (!pde)
- goto out;
- //pde->proc_fops==tcp_afinfo_seq_fops
- pde->proc_fops = proc_fops;
- //pde->data==tcp4_seq_afinfo
- pde->data = data;
- pde->proc_iops = &proc_file_inode_operations;
- //下面接着分析proc_register()
- if (proc_register(parent, pde) < 0)
- goto out_free;
- return pde;
- out_free:
- kfree(pde);
- out:
- return NULL;
- }
-
- }

看完了proc_create_data(),下面再分别看__proc_create()和proc_register()
tcp4_proc_init_net()–>tcp_proc_register()–>proc_create_data()–>__proc_create()
首先来看__proc_create(),分析如下:
- /*
- * @ parent:指的应该是"/pro/net/"目录
- * @ name: "tcp"
- * @ mode: 170444
- * @ nlink: 1
- */
- static struct proc_dir_entry *__proc_create(struct proc_dir_entry **parent,
- const char *name,
- umode_t mode,
- nlink_t nlink)
- {
- struct proc_dir_entry *ent = NULL;
- const char *fn;
- /*
- * "quick string" -- eases parameter passing, but more importantly
- * saves "metadata" about the string (ie length and the hash).
- * /
- struct qstr qstr;
- //fn=tcp
- if (xlate_proc_name(name, parent, &fn) != 0)
- goto out;
- qstr.name = fn;
- qstr.len = strlen(fn);
- //对文件名字的长度进行检验
- if (qstr.len == 0 || qstr.len >= 256) {
- WARN(1, "name len %u\n", qstr.len);
- return NULL;
- }
- if (*parent == &proc_root && name_to_int(&qstr) != ~0U) {
- WARN(1, "create '/proc/%s' by hand\n", qstr.name);
- return NULL;
- }
- if (is_empty_pde(*parent)) {
- WARN(1, "attempt to add to permanently empty directory");
- return NULL;
- }
- //分配内存空间,由于proc_dir_entry结构体的name为char name[],所以这里要为proc_dir_entry加上名字的长度
- ent = kzalloc(sizeof(struct proc_dir_entry) + qstr.len + 1, GFP_KERNEL);
- if (!ent)
- goto out;
- //给ent的name赋值
- memcpy(ent->name, fn, qstr.len + 1);
- ent->namelen = qstr.len;
- ent->mode = mode;
- ent->nlink = nlink;
- ent->subdir = RB_ROOT;
- atomic_set(&ent->count, 1);
- spin_lock_init(&ent->pde_unload_lock);
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&ent->pde_openers);
- proc_set_user(ent, (*parent)->uid, (*parent)->gid);
- out:
- return ent;
- }

tcp4_proc_init_net()–>tcp_proc_register()–>proc_create_data()–>proc_register()
接着是proc_register(),分析如下:
- /**
- * @ dir: 传入的是parent,即"/proc/net"
- * @ dp: 传入的是pde,即name为"tcp"的proc_dir_entry
- */
- static int proc_register(struct proc_dir_entry * dir, struct proc_dir_entry * dp)
- {
- int ret;
- //Return an inode number
- ret = proc_alloc_inum(&dp->low_ino);
- if (ret)
- return ret;
- write_lock(&proc_subdir_lock);
- dp->parent = dir;
- //将新创建的文件添加到其父目录的红黑树中
- if (pde_subdir_insert(dir, dp) == false) {
- WARN(1, "proc_dir_entry '%s/%s' already registered\n",
- dir->name, dp->name);
- write_unlock(&proc_subdir_lock);
- proc_free_inum(dp->low_ino);
- return -EEXIST;
- }
- write_unlock(&proc_subdir_lock);
- return 0;
- }

到这里结束tcp4_proc_init_net()的分析,可以看到,这里就是将一个name为”tcp”的proc_dir_entry加入到了"/proc/net/"这个目录下,而再详细看这个name为”tcp”的proc_dir_entry,如下:
- struct proc_dir_entry {
- unsigned int low_ino; //inode number
- umode_t mode; //
- nlink_t nlink; // 1
- kuid_t uid;
- kgid_t gid;
- loff_t size;
- const struct inode_operations *proc_iops; //proc_file_inode_operations
- const struct file_operations *proc_fops; //tcp_afinfo_seq_fops
- struct proc_dir_entry *parent; // "/proc/net/"
- struct rb_root subdir;
- struct rb_node subdir_node;
- void *data; //tcp4_seq_afinfo
- atomic_t count; /* use count */
- atomic_t in_use; /* number of callers into module in progress; */
- /* negative -> it's going away RSN */
- struct completion *pde_unload_completion;
- struct list_head pde_openers; /* who did ->open, but not ->release */
- spinlock_t pde_unload_lock; /* proc_fops checks and pde_users bumps */
- u8 namelen;
- char name[]; //"tcp"
- };

4. cat /proc/net/tcp
分析cat命令,目的是了解cat的时候,调用了哪些proc_dir_entry的函数。cat源码,位于src/cat.c。如 cat 命令不使用任何格式参数, 如 -v, -t. 那么就调用simple_cat来完成操作。所以我们这里主要分析simple_cat。
首先看看在cat.c主函数中,对simple_cat()的调用。
- int
- main (int argc, char **argv)
- {
- //需要打开的文件的名字,即"/proc/net/tcp"
- infile = argv[argind];
- //得到打开的文件的文件描述符
- input_desc = open (infile, file_open_mode);
- ...
- /**
- *ptr_align是一个辅助函数. 因为IO操作一次读取一页,
- *ptr_align是使得缓冲数组的起始地址为也大小的整数倍, 以增加IO的效率.
- */
- ok &= simple_cat (ptr_align (inbuf, page_size), insize);
- ...
- }
下面来分析simple_cat():
- static bool
- simple_cat (
- /* Pointer to the buffer, used by reads and writes. */
- char *buf,
-
- /* Number of characters preferably read or written by each read and write
- call. */
- size_t bufsize)
- {
- /* Actual number of characters read, and therefore written. */
- size_t n_read;
- /* Loop until the end of the file. */
- while (true)
- {
- /* Read a block of input. */
- /* 普通的read可能被信号中断 */
- n_read = safe_read (input_desc, buf, bufsize);
- if (n_read == SAFE_READ_ERROR)
- {
- error (0, errno, "%s", infile);
- return false;
- }
- /* End of this file? */
- if (n_read == 0)
- return true;
- /* Write this block out. */
- {
- /* The following is ok, since we know that 0 < n_read. */
- size_t n = n_read;
-
- /* Read up to COUNT bytes at BUF from descriptor FD, retrying if interrupted.
- *Return the actual number of bytes read, zero for EOF, or SAFE_READ_ERROR
- *upon error.
- * full_write 和 safe_read都调用的是 safe_rw, 用宏实现的,
- * 查看 safe_write.c 就可以发现其实现的关键.
- *
- */
- if (full_write (STDOUT_FILENO, buf, n) != n)
- error (EXIT_FAILURE, errno, _("write error"));
- }
- }
-
- }

从n_read = safe_read (input_desc, buf, bufsize);可以知道,safe_read()根据文件描述符input_desc获得文件信息,并将文件内容复制到buf中。所以,接下来继续看safe_read()。 在lib/safe-read.h中可以找到safe_read(),再看lib/safe-read.c,有# define safe_rw safe_read,所以safe_read()是由safe_rw()函数实现的,该函数的实现就定义在lib/safe-read.c中,代码分析如下:
- /* Read(write) up to COUNT bytes at BUF from(to) descriptor FD, retrying if
- * interrupted. Return the actual number of bytes read(written), zero for EOF,
- * or SAFE_READ_ERROR(SAFE_WRITE_ERROR) upon error.
- * 原始的read()函数返回值是 ssize_t
- * @ fd: input_desc
- */
- size_t
- safe_rw (int fd, void const *buf, size_t count)
- {
- for (;;)
- {
- ssize_t result = rw (fd, buf, count);
-
- if (0 <= result)
- return result;
- else if (IS_EINTR (errno))
- continue;
- else if (errno == EINVAL && BUGGY_READ_MAXIMUM < count)
- count = BUGGY_READ_MAXIMUM;
- else
- return result;
- }
- }

接着到rw(),根据# define rw read可以知道,rw实际调用的是read,而在lib/unitsd.in.h中,有# define read rpl_read,最终在lib/read.c中找到rw()的实际实现rpl_read(),代码如下:
- ssize_t
- rpl_read (int fd, void *buf, size_t count)
- {
- ssize_t ret = read_nothrow (fd, buf, count);
- ...
- }
接着继续到read_nothrow(),代码如下:
- read_nothrow (int fd, void *buf, size_t count)
- {
- ...
- result = read (fd, buf, count);
- }
所以最终调用的是linux的read()。read函数在用户空间是由read系统调用实现的,由编译器编译成软中断int 0x80来进入内核空间,然后在中端门上进入函数SYSCALL_DEFINE3(read, unsigned int, fd, char __user *, buf, size_t, count),从而进入内核空间执行read操作。
5. SYSCALL_DEFINE3(read,…)
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(read,...)位于fs/read_write.c,主要代码如下:
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(read,…)
- SYSCALL_DEFINE3(read, unsigned int, fd, char __user *, buf, size_t, count)
- {
- //获得fd结构体,包括struct file指针
- struct fd f = fdget_pos(fd);
- ssize_t ret = -EBADF;
-
- if (f.file) {
- //获取光标位置
- loff_t pos = file_pos_read(f.file);
- //虚拟文件系统读,虚拟文件系统屏蔽了底层的各种文件系统的差异性,让上层应用程序可以忽略底层用的是哪种文件系统
- ret = vfs_read(f.file, buf, count, &pos);
- if (ret >= 0)
- file_pos_write(f.file, pos);
- fdput_pos(f);
- }
- return ret;
- }

接下来看vfs_read()。
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(read,…)–>vfs_read()
- ssize_t vfs_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
- {
- ssize_t ret;
- //3个if就是判断下接下来的操作是否能进行
- if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_READ))
- return -EBADF;
- if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_CAN_READ))
- return -EINVAL;
- if (unlikely(!access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, buf, count)))
- return -EFAULT;
- //对当前的位置和需要读取的字节数进行判断是否可行
- ret = rw_verify_area(READ, file, pos, count);
- if (!ret) {
- if (count > MAX_RW_COUNT)
- count = MAX_RW_COUNT;
- //下面接着看
- ret = __vfs_read(file, buf, count, pos);
- if (ret > 0) {
- fsnotify_access(file);
- add_rchar(current, ret);
- }
- inc_syscr(current);
- }
-
- return ret;
- }

接下去是__vfs_read()
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(read,…)–>vfs_read()–>__vfs_read()
- ssize_t __vfs_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count,
- loff_t *pos)
- {
- //判断文件是否有自己的读函数,如果有则调用自己的函数
- if (file->f_op->read)
- return file->f_op->read(file, buf, count, pos);
- else if (file->f_op->read_iter)
- return new_sync_read(file, buf, count, pos);
- else
- return -EINVAL;
- }
到这里,我们可以看到,如果读取的是proc_dir_entry的话,应该是调用的proc_dir_entry的proc_fops的read函数,接下来对其进行分析。
6. proc_dir_entry的读取
根据前文3.中对"tcp"这个proc_dir_entry的proc_fops为tcp_afinfo_seq_fops,我们来看看tcp_afinfo_seq_fops,位于net/ipv4/tcp_ipv4.c,结构体如下:
tcp_afinfo_seq_fops
- static const struct file_operations tcp_afinfo_seq_fops = {
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- .open = tcp_seq_open, //将文件与seq_file关联
- .read = seq_read,
- .llseek = seq_lseek,
- .release = seq_release_net
- };
6.1 tcp_seq_open
首先来看一下tcp_seq_open
tcp_afinfo_seq_fops–>tcp_seq_open
- int tcp_seq_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
- {
- //返回这个inode对应的proc_inode的proc_dir_entry的data,根据前文可知,这个data==tcp4_seq_afinfo
- struct tcp_seq_afinfo *afinfo = PDE_DATA(inode);
- struct tcp_iter_state *s;
- int err;
- //下面接着看
- err = seq_open_net(inode, file, &afinfo->seq_ops,
- sizeof(struct tcp_iter_state));
- if (err < 0)
- return err;
-
- s = ((struct seq_file *)file->private_data)->private;
- s->family = afinfo->family;
- s->last_pos = 0;
- return 0;
- }

来看seq_open_net()
tcp_afinfo_seq_fops–>tcp_seq_open–>seq_open_net()
- /**
- * @ ino: inode
- * @ f: file
- * @ ops: afinfo->seq_ops,这其中有.show、.start、.next、.stop函数
- * @ size: sizeof(struct tcp_iter_state)
- */
- int seq_open_net(struct inode *ino, struct file *f,
- const struct seq_operations *ops, int size)
- {
- struct net *net;
- struct seq_net_private *p;
- BUG_ON(size < sizeof(*p));
- //获取这个inode所在的网络命名空间
- net = get_proc_net(ino);
- if (net == NULL)
- return -ENXIO;
- //下面接着看
- p = __seq_open_private(f, ops, size);
- if (p == NULL) {
- put_net(net);
- return -ENOMEM;
- }
- #ifdef CONFIG_NET_NS
- p->net = net;
- #endif
- return 0;
- }

tcp_afinfo_seq_fops–>tcp_seq_open–>seq_open_net()–>__seq_open_private()
- void *__seq_open_private(struct file *f, const struct seq_operations *ops,
- int psize)
- {
- int rc;
- void *private;
- struct seq_file *seq;
- private = kzalloc(psize, GFP_KERNEL);
- if (private == NULL)
- goto out;
- //下面接着看,将file、seq_file、seq_ops关联起来
- rc = seq_open(f, ops);
- if (rc < 0)
- goto out_free;
- seq = f->private_data;
- seq->private = private;
- return private;
-
- out_free:
- kfree(private);
- out:
- return NULL;
- }

tcp_afinfo_seq_fops–>tcp_seq_open–>seq_open_net()–>__seq_open_private()–>seq_open()
- /**
- * seq_open - initialize sequential file
- * @file: file we initialize
- * @op: method table describing the sequence,afinfo->seq_ops,这其中有.show、.start、.next、.stop函数
- * seq_open将@file与@op联系起来
- * @op->start()设置迭代器iterator并返回第一个元素
- * @op->stop() shuts it down
- * @op->next() 返回下一个元素
- * @op->show() 将元素信息打印到buffer中
- */
- int seq_open(struct file *file, const struct seq_operations *op)
- struct seq_file *p;
- WARN_ON(file->private_data);
- p = kzalloc(sizeof(*p), GFP_KERNEL);
- ...
- file->private_data = p;
- mutex_init(&p->lock);
- //将afinfo->seq_ops赋值给seq_file
- p->op = op;
- p->file = file;
- ...
- }

6.2 seq_read
接下来看seq_read()。
普通文件struct file的读取函数为seq_read,完成seq_file的读取过程,正常情况下分两次完成:
- 第一次执行执行seq_read时:start->show->next->show…->next->show->next->stop,此时返回内核自定义缓冲区所有内容,即copied !=0,所以会有第二次读取操作。
- 第二次执行seq_read时:由于此时内核自定义内容都返回,根据seq_file->index指示,所以执行start->stop,返回0,即copied=0,并退出seq_read操作。
整体来看,用户态调用一次读操作,seq_file流程为:该函数调用struct seq_operations结构体顺序为:start->show->next->show…->next->show->next->stop->start->stop来读取顺序文件。
tcp_afinfo_seq_fops–>tcp_seq_read
- ssize_t seq_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ppos)
- {
- //获取file的数据,由上文seq_open()可知,这里是一个seq_file,这个seq_file的op==afinfo->seq_ops
- struct seq_file *m = file->private_data;、
- size_t copied = 0;
- loff_t pos;
- size_t n;
- void *p;
- int err = 0;
- mutex_lock(&m->lock);
- m->version = file->f_version;
- /*
- * if request is to read from zero offset, reset iterator to first
- * record as it might have been already advanced by previous requests
- */
- if (*ppos == 0)
- m->index = 0;
- //如果用户已经读取内容和seq_file中不一致,要将seq_file部分内容丢弃
- if (unlikely(*ppos != m->read_pos)) {
- //如果是这样,首先通过seq_start,seq_show,seq_next,seq_show...seq_next,seq_show,seq_stop读取*pos大小内容到seq_file的buf中
- while ((err = traverse(m, *ppos)) == -EAGAIN)
- ;
- if (err) {
- /* With prejudice... */
- m->read_pos = 0;
- m->version = 0;
- m->index = 0;
- m->count = 0;
- goto Done;
- } else {
- //将起读点赋值给seq_file
- m->read_pos = *ppos;
- }
- }
- //如果第一次读取seq_file,申请4K大小空间
- if (!m->buf) {
- m->buf = seq_buf_alloc(m->size = PAGE_SIZE);
- if (!m->buf)
- goto Enomem;
- }
- /** if not empty - flush it first
- * 如果seq_file中已经有内容,可能在前面通过traverse考了部分内容
- */
- if (m->count) {
- n = min(m->count, size);
- //拷贝到用户态
- err = copy_to_user(buf, m->buf + m->from, n);
- if (err)
- goto Efault;
- m->count -= n;
- m->from += n;
- size -= n;
- buf += n;
- copied += n;
- /**
- * 如果正好通过seq_序列操作拷贝了count个字节,从下个位置开始拷贝
- * 不太清楚,traverse函数中,m->index已经增加过了,这里还要加?
- */
- if (!m->count) {
- m->from = 0;
- m->index++;
- }
- if (!size)
- goto Done;
- }
- /** we need at least one record in buffer
- * 假设该函数从这里开始执行,pos=0,当第二次执行时,pos =上次遍历的最后下标 + 1 >0,
- * 所以在start中,需要对pos非0特殊处理
- */
- pos = m->index;
- //p为seq_start返回的字符串指针,pos=0;
- p = m->op->start(m, &pos);
-
- while (1) {
- err = PTR_ERR(p);
- /**
- * 如果通过start或next遍历出错,即返回的p出错,则退出循环,
- * 一般情况下,在第二次seq_open时,通过start即出错[pos变化],退出循环
- */
- if (!p || IS_ERR(p))
- break;
- //将p所指的内容显示到seq_file结构的buf缓冲区中
- err = m->op->show(m, p);
- //如果通过show输出出错,退出循环,此时表明buf已经溢出
- if (err < 0)
- break;
- /**
- * 如果seq_show返回正常[即seq_file的buf未溢出,则返回0],
- * 此时将m->count设置为0,要将m->count设置为0
- */
- if (unlikely(err))
- m->count = 0;
- //一般情况下,m->count==0,所以该判定返回false,#define unlikely(x) __builtin_expect(!!(x), 0)用于分支预测,提高系统流水效率
- if (unlikely(!m->count)) {
- p = m->op->next(m, p, &pos);
- m->index = pos;
- continue;
- }
- //一般情况下,经过seq_start->seq_show到达这里[基本上是这一种情况],或者在err!=0 [即show出错] && m->count != 0时到达这里
- if (m->count < m->size)
- goto Fill;
- m->op->stop(m, p);
- kvfree(m->buf);
- m->count = 0;
- m->buf = seq_buf_alloc(m->size <<= 1);
- if (!m->buf)
- goto Enomem;
- m->version = 0;
- pos = m->index;
- p = m->op->start(m, &pos);
- }
- /**
- * 正常情况下,进入到这里,此时已经将所有的seq_file文件拷贝到buf中,
- * 且buf未溢出,这说明seq序列化操作返回的内容比较少,少于4KB
- */
- m->op->stop(m, p);
- m->count = 0;
- goto Done;
- Fill:
- //一般情况在上面的while循环中只经历了seq_start和seq_show函数,然后进入到这里,在这个循环里,执行下面循环
- while (m->count < size) {
- size_t offs = m->count;
- loff_t next = pos;
- p = m->op->next(m, p, &next);
- /**
- * 如果seq_file的buf未满: seq_next,seq_show,....seq_next->跳出
- * 如果seq_file的buf满了:则offs表示了未满前最大的读取量,此时p返回自定义结构内容的指针,
- * 但是后面show时候只能拷贝了该内容的一部分,导致m->cont == m->size判断成立,
- * 从而m->count回滚到本次拷贝前,后面的pos++表示下次从下一个开始拷贝
- */
- if (!p || IS_ERR(p)) {
- err = PTR_ERR(p);
- break;
- }
- err = m->op->show(m, p);
- //如果seq_file的buf满: seq_next,seq_show,....seq_next,seq_show->跳出
- if (seq_has_overflowed(m) || err) {
- m->count = offs;
- if (likely(err <= 0))
- break;
- }
- pos = next;
- }
- //最后执行seq_stop函数
- m->op->stop(m, p);
- n = min(m->count, size);
- //将最多size大小的内核缓冲区内容拷贝到用户态缓冲区buf中
- err = copy_to_user(buf, m->buf, n);
- if (err)
- goto Efault;
- copied += n;
- m->count -= n;
- //如果本次给用户态没拷贝完,比如seq_file中count=100,但是n=10,即拷贝了前10个,则下次从10位置开始拷贝,这种情况一般不会出现
- if (m->count)
- m->from = n;
- else //一般情况下,pos++,下次遍历时从next中的下一个开始,刚开始时,让seq_func遍历指针递减,但是每次以k退出后,下次继续从k递减,原来是这里++了,所以遍历最好让指针递增
- pos++;
- m->index = pos;
- Done:
- if (!copied)
- copied = err;
- else {
- *ppos += copied;
- m->read_pos += copied;
- }
- file->f_version = m->version;
- mutex_unlock(&m->lock);
- // 返回拷贝的字符数目,将copied个字符内容从seq_file的buf中拷贝到用户的buf中
- return copied;
- Enomem:
- err = -ENOMEM;
- goto Done;
- Efault:
- err = -EFAULT;
- goto Done;
- }

接下来,就来看start、show、next、stop这四个函数。由前文可知:
- static struct tcp_seq_afinfo tcp4_seq_afinfo = {
- .name = "tcp",
- .family = AF_INET,
- .seq_fops = &tcp_afinfo_seq_fops,
- .seq_ops = {
- .start = tcp_seq_start,
- .show = tcp4_seq_show,
- .next = tcp4_seq_next,
- .stop = tcp4_seq_stop,
- },
- };
6.2.1 tcp_seq_start()
- static void *tcp_seq_start(struct seq_file *seq, loff_t *pos)
- {
- struct tcp_iter_state *st = seq->private;
- void *rc;
- //如果来到了最后一位,暂且不看,先往下看
- if (*pos && *pos == st->last_pos) {
- rc = tcp_seek_last_pos(seq);
- if (rc)
- goto out;
- }
-
- st->state = TCP_SEQ_STATE_LISTENING;
- st->num = 0;
- st->bucket = 0;
- st->offset = 0;
- //如果pos为0,则返回SEQ_START_TOKEN,用于让show函数输出文件头
- //如果不是0,则调用tcp_get_idx(),下面接着看
- rc = *pos ? tcp_get_idx(seq, *pos - 1) : SEQ_START_TOKEN;
- }

tcp_seq_start()–>tcp_get_idx(seq, *pos - 1)
- static void *tcp_get_idx(struct seq_file *seq, loff_t pos)
- {
- void *rc;
- struct tcp_iter_state *st = seq->private;
- }
参考
- /proc/net/tcp中各项参数说明
- 序列文件(seq_file)接口
- seq_file工作机制实例
- proc net arp文件的创建
- Linux cat 命令源码剖析
- linux文件系统之读流程 SYSCALL_DEFINE3(read, xxx)
- proc_dir_entry结构
- linux下proc文件的读写(部分转载)
- seq_file文件的内核读取过程
- linux 读取proc文件之seq_file浅析1
- kernel module编程(八):读取proc文件之seq_file
- 走马观花: Linux 系统调用 open 七日游(一)


