热门标签
热门文章
- 1已解决EROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in. your SOL syntax. check the manual that corresponds to yo_you have an error in your sol syntax; check the ma
- 2Hadoop学习日记-HDFS分布式文件存储系统整体概述_namenode和datanode分布式存储
- 3阿里云Big Data - |分层| ODS& DWD& DWS& ADS| 行为数仓_dws表 data
- 4一文读懂非关系型数据库(NoSQL)
- 5百度安全多篇议题入选Blackhat Asia以硬技术发现“芯”问题
- 6Locust性能测试教程_locust 性能测试
- 7Linux 常用命令与教程_/sbin:/usr/sbin:/usr/local/sbin:/root/bin:/usr/loc
- 8论文阅读:(AAAI 2019)M2det: A single-shot object detector based on multi-level feature pyramid network_a detector based on dl
- 9LCD1602命令代码整合
- 10基于JAVA高考志愿辅助填报系统
当前位置: article > 正文
A*算法 C++简单实现走迷宫_迷宫问题a*算法
作者:IT小白 | 2024-05-02 21:29:45
赞
踩
迷宫问题a*算法
A*算法是一种启发式搜索算法,通常用于在图或者网络中找到从起始节点到目标节点的最短路径。A*算法在维持最小堆(或优先队列)的基础上,通过估算从起始节点到目标节点的代价(启发函数)来指导搜索过程。该算法同时考虑了实际路径成本(已经走过的路径长度)和启发函数的估计值,以选择下一步最有希望的路径。
基本原理和步骤
-
节点表示: 将搜索的图或网络表示为一系列节点,每个节点代表一个位置。
-
代价估计: 对每个节点计算两个值:已走过路径的实际成本(g值)和从当前节点到目标节点的估计成本(h值)。
-
总成本计算: 计算总成本f值,即已走过路径的实际成本加上估计成本。
-
节点扩展: 从开放列表(未完全探索的节点)中选择f值最小的节点进行扩展,将其相邻节点加入开放列表。
-
目标检查: 如果目标节点被加入开放列表,算法结束;否则,重复步骤 3 到步骤 5。
核心思想
A算法的核心思想是维护一个开放列表,其中包含待探索的节点。每次选择开放列表中f值(g值 + h值)最小的节点进行扩展。通过使用启发函数估计目标节点的距离,A算法能够更聪明地选择下一步的移动方向,以减少搜索空间,提高搜索效率。
示例代码
走迷宫
- #include <iostream>
- #include <vector>
- #include <queue>
- #include <cmath>
-
- using namespace std;
-
- // 定义节点结构体
- struct Node {
- int x, y; // 节点在网格中的坐标
- int g; // 从起点到该节点的实际代价
- int h; // 从该节点到目标的估计代价
- int f; // f = g + h,综合考虑实际代价和启发式代价
-
- bool operator<(const Node& other) const {
- return f > other.f;
- }
- };
-
- // 定义A*算法函数
- vector<pair<int, int>> AStar(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, pair<int, int> start, pair<int, int> goal) {
- // 定义移动方向,上下左右和对角线
- const int dx[] = { -1, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, 1, 1 };
- const int dy[] = { 0, 1, 0, -1, -1, 1, -1, 1 };
-
- int rows = grid.size();
- int cols = grid[0].size();
-
- // 创建二维数组来存储每个节点的父节点坐标
- vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> parent(rows, vector<pair<int, int>>(cols, { -1, -1 }));
-
- // 创建二维数组来存储每个节点的g值
- vector<vector<int>> g(rows, vector<int>(cols, INT_MAX));
-
- // 创建优先队列来存储待探索的节点
- priority_queue<Node> pq;
-
- // 初始化起点
- Node startNode = { start.first, start.second, 0, 0, 0 };
- pq.push(startNode);
- g[start.first][start.second] = 0;
-
- // A*算法主循环
- while (!pq.empty()) {
- // 取出当前f值最小的节点
- Node current = pq.top();
- pq.pop();
-
- // 到达目标节点,构建路径并返回
- if (current.x == goal.first && current.y == goal.second) {
- vector<pair<int, int>> path;
- while (current.x != -1 && current.y != -1) {
- path.push_back({ current.x, current.y });
- current = { parent[current.x][current.y].first, parent[current.x][current.y].second };
- }
- reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
- return path;
- }
-
- // 探索当前节点的邻居
- for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
- int nx = current.x + dx[i];
- int ny = current.y + dy[i];
-
- // 检查邻居是否在网格内且不是障碍物
- if (nx >= 0 && nx < rows && ny >= 0 && ny < cols && grid[nx][ny] != 1) {
- int new_g = current.g + 1;
-
- // 如果新的g值更小,更新节点信息
- if (new_g < g[nx][ny]) {
- g[nx][ny] = new_g;
- int h = abs(nx - goal.first) + abs(ny - goal.second); // 曼哈顿距离作为启发式函数
- int f = new_g + h;
-
- // 将邻居节点加入优先队列
- pq.push({ nx, ny, new_g, h, f });
- parent[nx][ny] = { current.x, current.y };
- }
- }
- }
- }
-
- // 如果队列为空,说明没有找到路径
- return {};
- }
-
- // 打印路径的函数
- void printPath(const vector<pair<int, int>>& path) {
- for (const auto& point : path) {
- cout << "(" << point.first << ", " << point.second << ") ";
- }
- cout<<endl;
- }
-
- void printPathAndMap(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, const vector<pair<int, int>>& path) {
- // 复制一份原始地图,用于标记路径
- vector<vector<int>> mapWithPaths = grid;
-
- // 在地图上标记路径
- for (const auto& point : path) {
- mapWithPaths[point.first][point.second] = -1;
- }
-
- // 打印地图
- for (const auto& row : mapWithPaths) {
- for (int cell : row) {
- if (cell == 0) {
- cout << "0 "; // 0表示可走路径
- }
- else if (cell == 1) {
- cout << "1 "; // 1表示障碍物
- }
- else if (cell == -1) {
- cout << "* "; // -1表示路径
- }
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
- }
-
- int main() {
- //地图网格,0表示可走路径,1表示障碍物
- vector<vector<int>> grid = {
- {0, 0, 0, 0, 0,0},
- {0, 1, 1, 0, 0,1},
- {0, 0, 0, 1, 0,1},
- {0, 1, 0, 1, 0,0},
- {0, 0, 0, 0, 0,1},
- {0, 1, 1, 0, 1,0}
- };
-
- pair<int, int> start = { 0, 0 };
- pair<int, int> goal = { 5, 5 };
-
- vector<pair<int, int>> path = AStar(grid, start, goal);
-
- // 输出路径
- printPath(path);
-
- printPathAndMap(grid, path);
-
- return 0;
- }

运行结果:
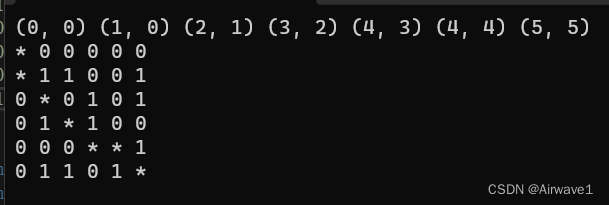
在A*算法主循环中,要不断从优先队列中取出f值最小的节点进行探索。如果当前节点是目标节点,就通过父节点链追溯回起点,构建路径并返回。否则,将当前节点的邻居加入优先队列进行进一步探索。
关键的步骤包括:
- 初始化起点并将其加入优先队列。
- 在主循环中,反复从优先队列中取出节点,探索其邻居,并更新节点信息。
- 如果找到目标节点,通过父节点链构建路径并返回。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/IT小白/article/detail/526206
推荐阅读
相关标签


