基于SpringBoot的大学生心理健康管理系统的设计与实现
赞
踩
目录
前言
传统信息的管理大部分依赖于管理人员的手工登记与管理,然而,随着近些年信息技术的迅猛发展,让许多比较老套的信息管理模式进行了更新迭代,试卷信息因为其管理内容繁杂,管理数量繁多导致手工进行处理不能满足广大用户的需求,因此就应运而生出相应的大学生心理健康管理系统。
本大学生心理健康管理系统分为管理员还有用户两个权限,管理员可以管理用户的基本信息内容,可以管理通知信息以及通知的租赁信息,能够与用户进行相互交流等操作,用户可以查看试卷信息,可以查看通知以及查看管理员回复信息等操作。
该大学生心理健康管理系统采用的是WEB应用程序开发中最受欢迎的B/S三层结构模式,使用占用空间小但功能齐全的MySQL数据库进行数据的存储操作,系统开发技术使用到了JSP技术。该大学生心理健康管理系统能够解决许多传统手工操作的难题,比如数据查询耽误时间长,数据管理步骤繁琐等问题。总的来说,大学生心理健康管理系统性能稳定,功能较全,投入运行使用性价比很高。
一、技术栈
末尾获取源码
SpringBoot+Vue+JS+ jQuery+Ajax...
二、系统功能介绍
管理员功能模块的实现
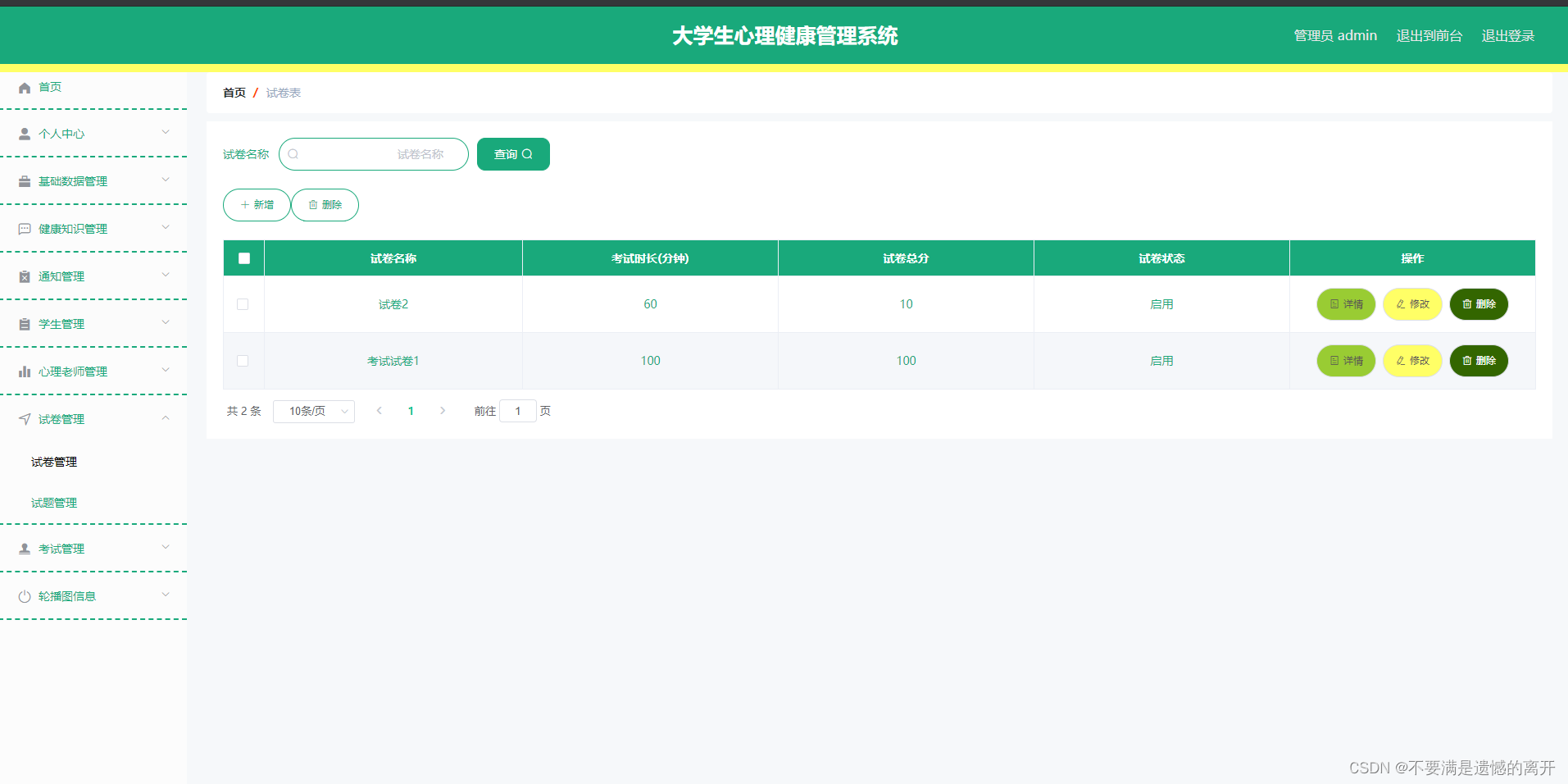
试卷列表
此页面提供给管理员的功能有:查看试卷、新增试卷、修改试卷、删除试卷等。
通知信息管理
管理员可以对前台的注册用户的基本信息进行管理,可以设置注册用户的账号为冻结或者是在用状态,管理员也能选择很多个已经失效的注册用户的信息进行批量删除操作。
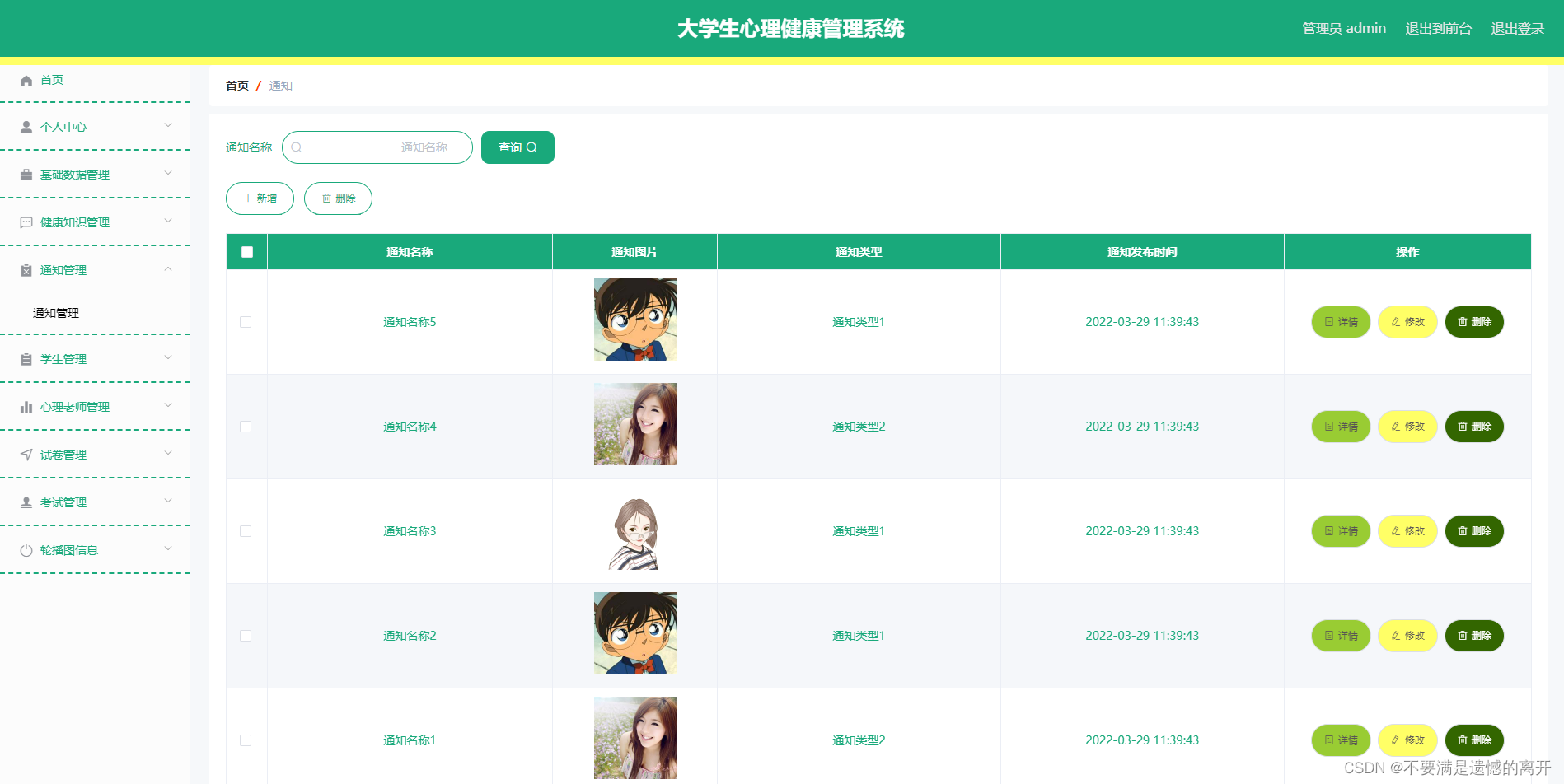
通知类型管理
通知类型管理页面显示所有通知类型,在此页面既可以让管理员添加新的通知信息类型,也能对已有的通知类型信息执行编辑更新,失效的通知类型信息也能让管理员快速删除。下图就是通知类型管理页面。

三、核心代码
1、登录模块
-
- package com.controller;
-
-
- import java.util.Arrays;
- import java.util.Calendar;
- import java.util.Date;
- import java.util.Map;
-
- import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
-
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
-
- import com.annotation.IgnoreAuth;
- import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.EntityWrapper;
- import com.entity.TokenEntity;
- import com.entity.UserEntity;
- import com.service.TokenService;
- import com.service.UserService;
- import com.utils.CommonUtil;
- import com.utils.MD5Util;
- import com.utils.MPUtil;
- import com.utils.PageUtils;
- import com.utils.R;
- import com.utils.ValidatorUtils;
-
- /**
- * 登录相关
- */
- @RequestMapping("users")
- @RestController
- public class UserController{
-
- @Autowired
- private UserService userService;
-
- @Autowired
- private TokenService tokenService;
-
- /**
- * 登录
- */
- @IgnoreAuth
- @PostMapping(value = "/login")
- public R login(String username, String password, String captcha, HttpServletRequest request) {
- UserEntity user = userService.selectOne(new EntityWrapper<UserEntity>().eq("username", username));
- if(user==null || !user.getPassword().equals(password)) {
- return R.error("账号或密码不正确");
- }
- String token = tokenService.generateToken(user.getId(),username, "users", user.getRole());
- return R.ok().put("token", token);
- }
-
- /**
- * 注册
- */
- @IgnoreAuth
- @PostMapping(value = "/register")
- public R register(@RequestBody UserEntity user){
- // ValidatorUtils.validateEntity(user);
- if(userService.selectOne(new EntityWrapper<UserEntity>().eq("username", user.getUsername())) !=null) {
- return R.error("用户已存在");
- }
- userService.insert(user);
- return R.ok();
- }
-
- /**
- * 退出
- */
- @GetMapping(value = "logout")
- public R logout(HttpServletRequest request) {
- request.getSession().invalidate();
- return R.ok("退出成功");
- }
-
- /**
- * 密码重置
- */
- @IgnoreAuth
- @RequestMapping(value = "/resetPass")
- public R resetPass(String username, HttpServletRequest request){
- UserEntity user = userService.selectOne(new EntityWrapper<UserEntity>().eq("username", username));
- if(user==null) {
- return R.error("账号不存在");
- }
- user.setPassword("123456");
- userService.update(user,null);
- return R.ok("密码已重置为:123456");
- }
-
- /**
- * 列表
- */
- @RequestMapping("/page")
- public R page(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> params,UserEntity user){
- EntityWrapper<UserEntity> ew = new EntityWrapper<UserEntity>();
- PageUtils page = userService.queryPage(params, MPUtil.sort(MPUtil.between(MPUtil.allLike(ew, user), params), params));
- return R.ok().put("data", page);
- }
-
- /**
- * 列表
- */
- @RequestMapping("/list")
- public R list( UserEntity user){
- EntityWrapper<UserEntity> ew = new EntityWrapper<UserEntity>();
- ew.allEq(MPUtil.allEQMapPre( user, "user"));
- return R.ok().put("data", userService.selectListView(ew));
- }
-
- /**
- * 信息
- */
- @RequestMapping("/info/{id}")
- public R info(@PathVariable("id") String id){
- UserEntity user = userService.selectById(id);
- return R.ok().put("data", user);
- }
-
- /**
- * 获取用户的session用户信息
- */
- @RequestMapping("/session")
- public R getCurrUser(HttpServletRequest request){
- Long id = (Long)request.getSession().getAttribute("userId");
- UserEntity user = userService.selectById(id);
- return R.ok().put("data", user);
- }
-
- /**
- * 保存
- */
- @PostMapping("/save")
- public R save(@RequestBody UserEntity user){
- // ValidatorUtils.validateEntity(user);
- if(userService.selectOne(new EntityWrapper<UserEntity>().eq("username", user.getUsername())) !=null) {
- return R.error("用户已存在");
- }
- userService.insert(user);
- return R.ok();
- }
-
- /**
- * 修改
- */
- @RequestMapping("/update")
- public R update(@RequestBody UserEntity user){
- // ValidatorUtils.validateEntity(user);
- userService.updateById(user);//全部更新
- return R.ok();
- }
-
- /**
- * 删除
- */
- @RequestMapping("/delete")
- public R delete(@RequestBody Long[] ids){
- userService.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(ids));
- return R.ok();
- }
- }

2、文件上传模块
- package com.controller;
-
- import java.io.File;
- import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.util.Arrays;
- import java.util.Date;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.List;
- import java.util.Map;
- import java.util.Random;
- import java.util.UUID;
-
- import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
- import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
- import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
- import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
- import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
- import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
- import org.springframework.util.ResourceUtils;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
- import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
-
- import com.annotation.IgnoreAuth;
- import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.mapper.EntityWrapper;
- import com.entity.ConfigEntity;
- import com.entity.EIException;
- import com.service.ConfigService;
- import com.utils.R;
-
- /**
- * 上传文件映射表
- */
- @RestController
- @RequestMapping("file")
- @SuppressWarnings({"unchecked","rawtypes"})
- public class FileController{
- @Autowired
- private ConfigService configService;
- /**
- * 上传文件
- */
- @RequestMapping("/upload")
- public R upload(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file,String type) throws Exception {
- if (file.isEmpty()) {
- throw new EIException("上传文件不能为空");
- }
- String fileExt = file.getOriginalFilename().substring(file.getOriginalFilename().lastIndexOf(".")+1);
- File path = new File(ResourceUtils.getURL("classpath:static").getPath());
- if(!path.exists()) {
- path = new File("");
- }
- File upload = new File(path.getAbsolutePath(),"/upload/");
- if(!upload.exists()) {
- upload.mkdirs();
- }
- String fileName = new Date().getTime()+"."+fileExt;
- File dest = new File(upload.getAbsolutePath()+"/"+fileName);
- file.transferTo(dest);
- FileUtils.copyFile(dest, new File("C:\\Users\\Desktop\\jiadian\\springbootl7own\\src\\main\\resources\\static\\upload"+"/"+fileName));
- if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(type) && type.equals("1")) {
- ConfigEntity configEntity = configService.selectOne(new EntityWrapper<ConfigEntity>().eq("name", "faceFile"));
- if(configEntity==null) {
- configEntity = new ConfigEntity();
- configEntity.setName("faceFile");
- configEntity.setValue(fileName);
- } else {
- configEntity.setValue(fileName);
- }
- configService.insertOrUpdate(configEntity);
- }
- return R.ok().put("file", fileName);
- }
-
- /**
- * 下载文件
- */
- @IgnoreAuth
- @RequestMapping("/download")
- public ResponseEntity<byte[]> download(@RequestParam String fileName) {
- try {
- File path = new File(ResourceUtils.getURL("classpath:static").getPath());
- if(!path.exists()) {
- path = new File("");
- }
- File upload = new File(path.getAbsolutePath(),"/upload/");
- if(!upload.exists()) {
- upload.mkdirs();
- }
- File file = new File(upload.getAbsolutePath()+"/"+fileName);
- if(file.exists()){
- /*if(!fileService.canRead(file, SessionManager.getSessionUser())){
- getResponse().sendError(403);
- }*/
- HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
- headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM);
- headers.setContentDispositionFormData("attachment", fileName);
- return new ResponseEntity<byte[]>(FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(file),headers, HttpStatus.CREATED);
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return new ResponseEntity<byte[]>(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
- }
-
- }

3、代码封装
- package com.utils;
-
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.Map;
-
- /**
- * 返回数据
- */
- public class R extends HashMap<String, Object> {
- private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
-
- public R() {
- put("code", 0);
- }
-
- public static R error() {
- return error(500, "未知异常,请联系管理员");
- }
-
- public static R error(String msg) {
- return error(500, msg);
- }
-
- public static R error(int code, String msg) {
- R r = new R();
- r.put("code", code);
- r.put("msg", msg);
- return r;
- }
-
- public static R ok(String msg) {
- R r = new R();
- r.put("msg", msg);
- return r;
- }
-
- public static R ok(Map<String, Object> map) {
- R r = new R();
- r.putAll(map);
- return r;
- }
-
- public static R ok() {
- return new R();
- }
-
- public R put(String key, Object value) {
- super.put(key, value);
- return this;
- }
- }

四、系统测试
程序软件一旦被开发完成之后,在真正投入日常生活中进行运行使用之前,是必须要经历测试这一个重要的操作环节,因为开发期间注重的是每个单独功能模块的开发,尽管每次开发完成一个单独功能模块时,会通过单元测试进行检验,检验合格才会让程序员继续开发下一个子功能模块,以此类推,当程序员完成所有的系统子功能模块的开发时,这个时候就需要引进系统测试,系统测试就是把所有的子功能模块集成到一起,构建成整个系统,在指定的运行环境下进行运行,主要就是测试系统的所有功能模块在一起是否良好运行,一旦程序软件通过了系统测试这一环节,就意味着它可以进行最终的验收测试了,这个测试步骤的操作用户是程序面向的客户或者是最终用户了。
软件测试
软件测试包括的对象有详细设计,开发出来的软件的运行环境,软件的需求以及软件的源代码内容等,软件测试也包括了五个要素,分别是软件的质量,技术,人员还有流程以及资源这几个要素。软件测试的目标包含了测试的覆盖率信息还有测试效率信息。一般来说,软件测试主要分成了单元测试,集成测试以及系统测试和验收测试这四个阶段的内容,下面将分别进行相关阐述。
单元测试:这个部分需要涉及到程序的代码方面的知识,这个操作环节是程序的开发者进行的,当程序开发者通过代码编写程序的子功能模块时,就会进行单元级别的测试,通常这个环节的测试也会被称作是白盒测试。
集成测试:这个步骤的前提是程序的所有功能模块都已完成开发,这个时候需要把程序所有的子功能模块集成到一起,形成一个完整的系统,此测试的主要目的就是检查这些功能模块集成在一起时的兼容性,也就是检测它们是否按照预期正常运行。
系统测试:当程序测试进入到这个环节时,就意味着程序测试工作已经进行到一半了,这个部分的测试也有另外一个名字,称作是黑盒测试,主要用于测试系统的功能是否按照预期进行运行。
验收测试:开发的程序已经通过了前面的单元测试,集成测试,以及系统测试环节时,就需要进行验收了,这个环节的操作用户就是程序面临的最终用户或者是客户。测试主要目的就是验证开发完成的程序是不是能够符合用户对其的期望,以及程序的所有功能是否符合用户的真正需求。
测试环境
大学生心理健康管理系统的测试选用的测试平台是IDEA平台环境,测试时首先需要用户打开MySQL数据库进行数据库文件的附加操作,然后打开IDEA,选择文件打开网站,把大学生心理健康管理系统的程序添加进入IDEA平台中,接着把文件部署到tomcat服务器里面,最后运行程序,这时用户可以操作系统里面的各个功能,看看程序有没有达到用户的要求。
测试用例
用户登录测试
用户登录需要的信息包含登录名称还有对应密码,输入数据信息都正确了才能进行系统访问处理。用户登录测试过程如表6.1所示:
用户登录测试表
| 测试目的 | 操作流程 | 测试用例 | 预测结果 | 测试结果 |
| 用户登录 | 填写用户名密码,点击首页登录按钮 | 错误填写用户名还有密码 | 登录失败 | 提示错误信息 |
| 正确填写用户名和密码 | 登录成功 | 登录成功 |
添加通知类别测试
管理员可以在添加通知类别界面输入通知类别名称信息,如果数据信息为空,系统会给出相应提示。只有所有的数据信息都合理输入,管理员才能完成通知类别的添加操作。测试数据见下表:
添加通知类别测试表
| 添加通知类别 | 类别名称为空 | 添加失败,提示请填写内容 | ||
| 合理填写类别名称 |
测试结果
经过此次对大学生心理健康管理系统的综合性测试,我们不难发现程序的功能并没有出现明显的逻辑性错误,用户在进行功能操作时,程序基本能根据用户操作情况给出相应的反馈。程序质量以及可靠性在系统的反复测试中都经过了严格检验,程序投入生活使用完全没有问题。



