热门标签
热门文章
- 1微信小程序之网易云音乐(五)- 排行详情页、歌单详情页、播放器组件开发_微信小程序歌曲榜单单个榜单制作
- 2spring源码解析之AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()方法刷新上下文过程_abstractwebapplicationrefreshcontext 未onapplicatio
- 3pytorch实战8:手把手教你基于pytorch实现ResNet(长文)_resnet代码pytorch
- 4C 语言 —— printf()_c打印输出语句
- 5PyCharm 连接 SQLSever_pycharm怎么连接sqlserver
- 6ES批量更新和如何添加新字段——LINUX_es更新多个字段
- 7vue事件中如何使用event对象?_vue中怎么使用event对象
- 8git 合并多次提交记录(commit)_git rebase devel
- 9Kafka简单总结_kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list
- 10C语言值传递与地址传递_为什么值传递不改变实参
当前位置: article > 正文
TransUnet官方代码测试自己的数据集(已训练完毕)_transunet测试
作者:Monodyee | 2024-02-15 10:59:44
赞
踩
transunet测试
***************************************************
码字不易,收藏之余,别忘了给我点个赞吧!
***************************************************
---------Start
首先参考上一篇的训练过程,这是测试过程,需要用到训练过程的权重。
1. TransUnet训练完毕之后,会生成权重文件(默认保存位置如下),snapshot_path为保存权重的路径。
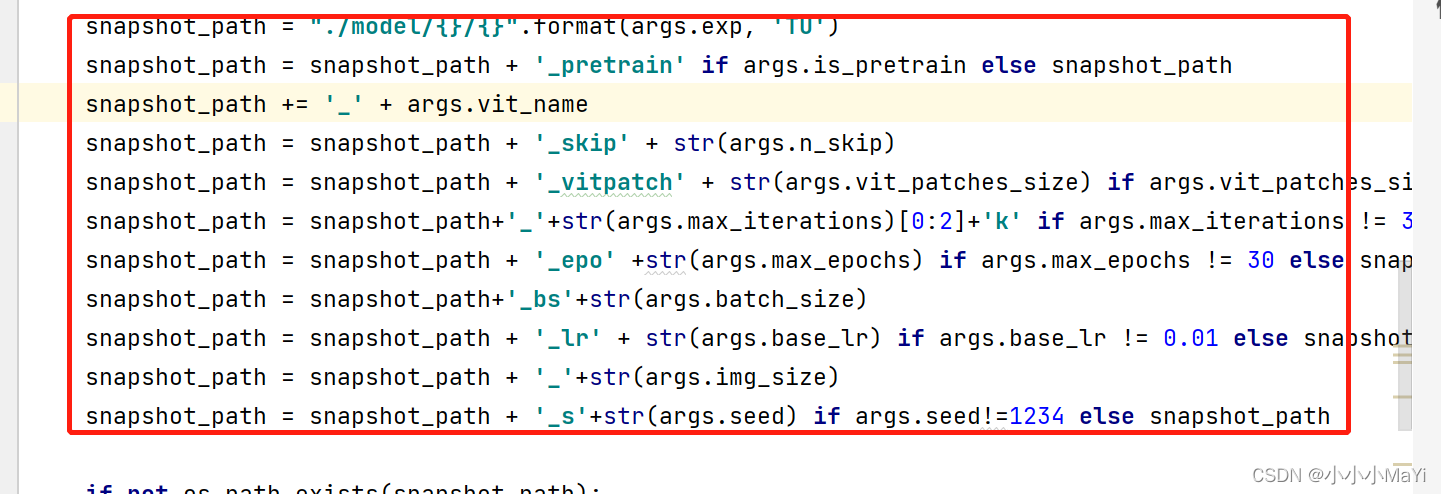
权重文件
2. 修改test.py文件
调整数据集路径。
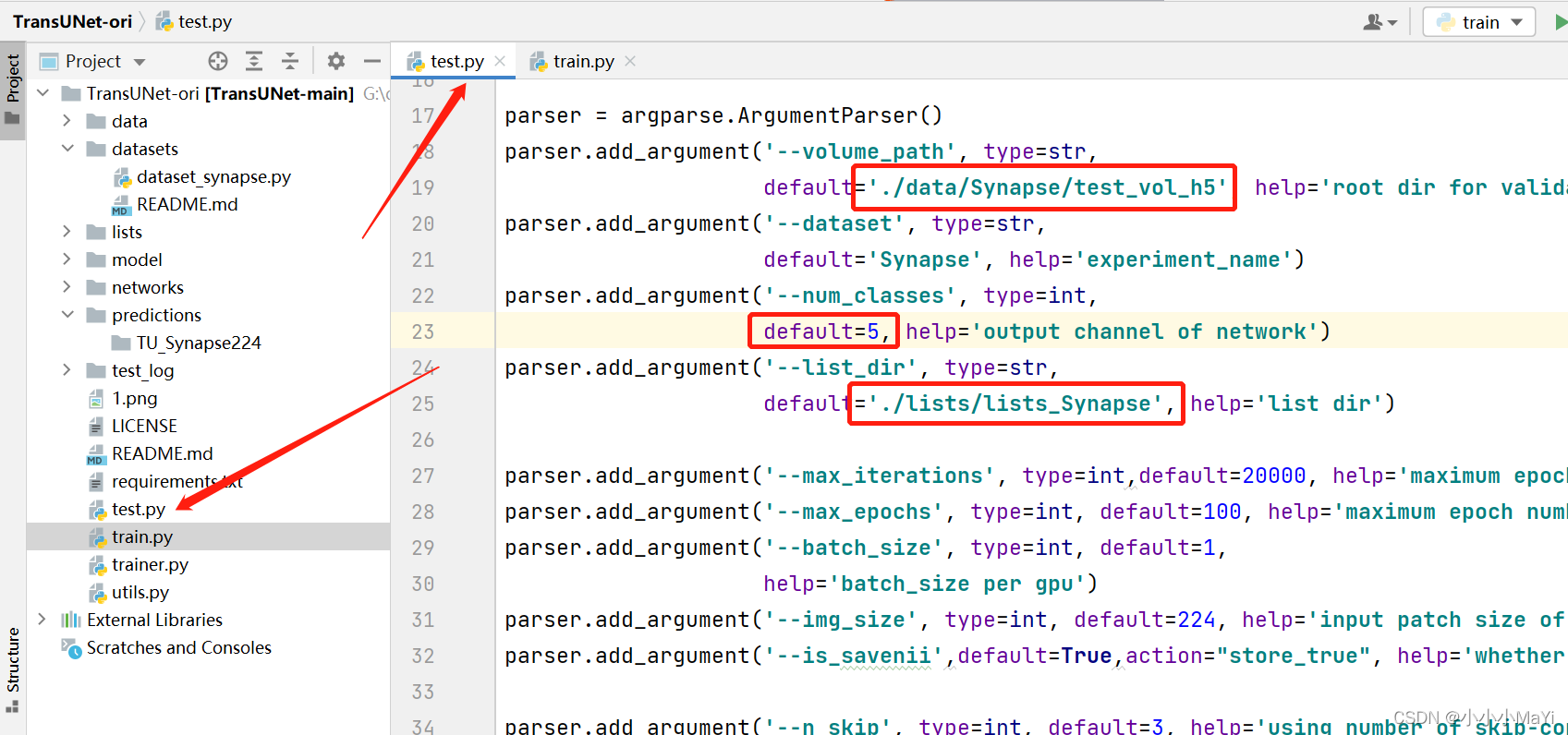
训练和测试时的图像设置相同大小,并设置主干模型的名称同训练时一致。
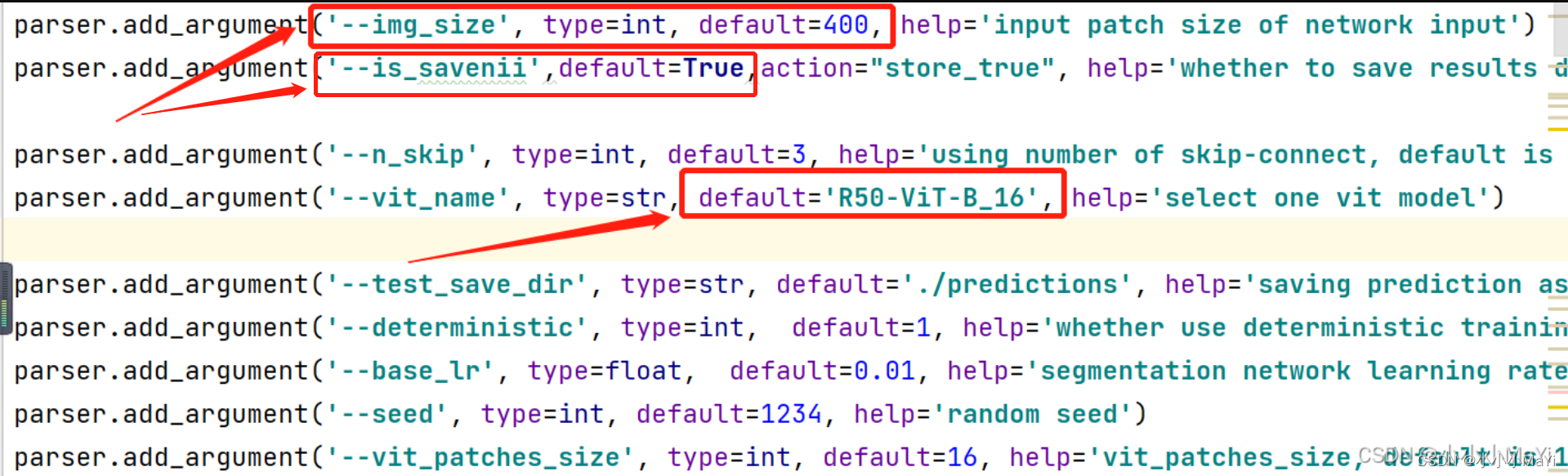
配置数据集相关信息。
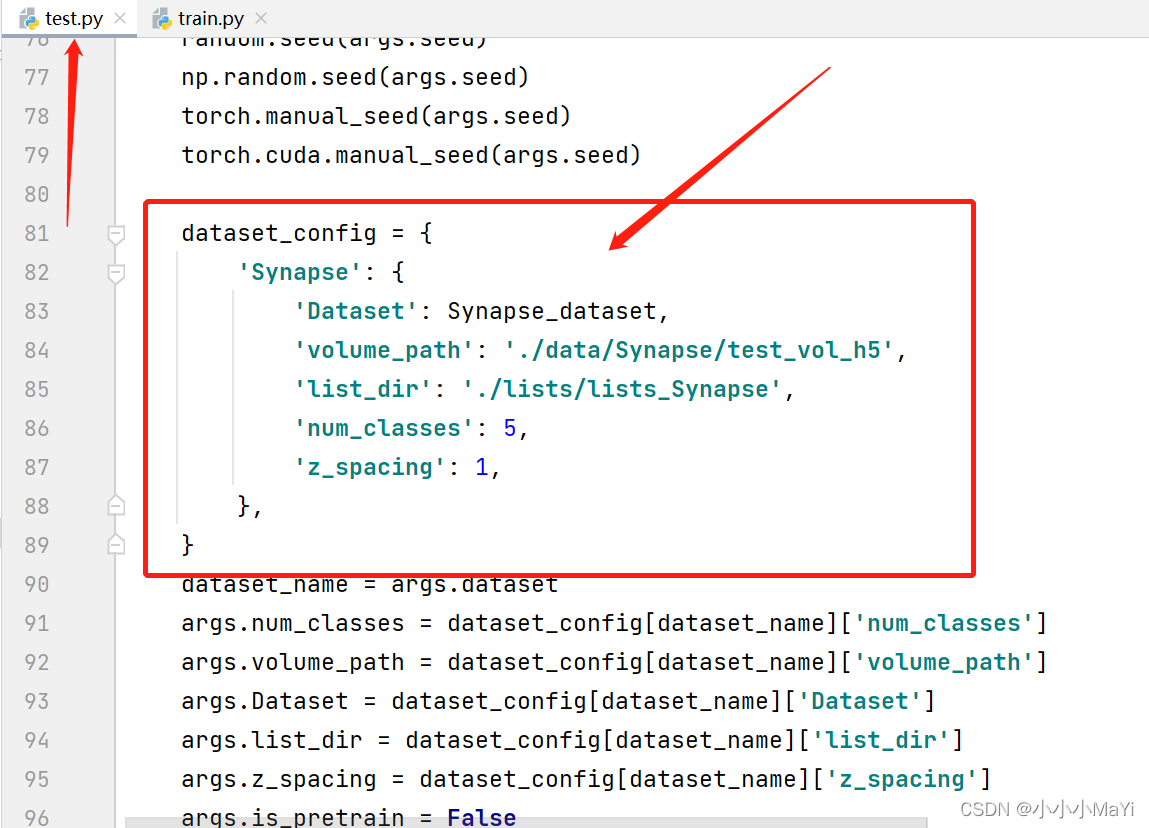
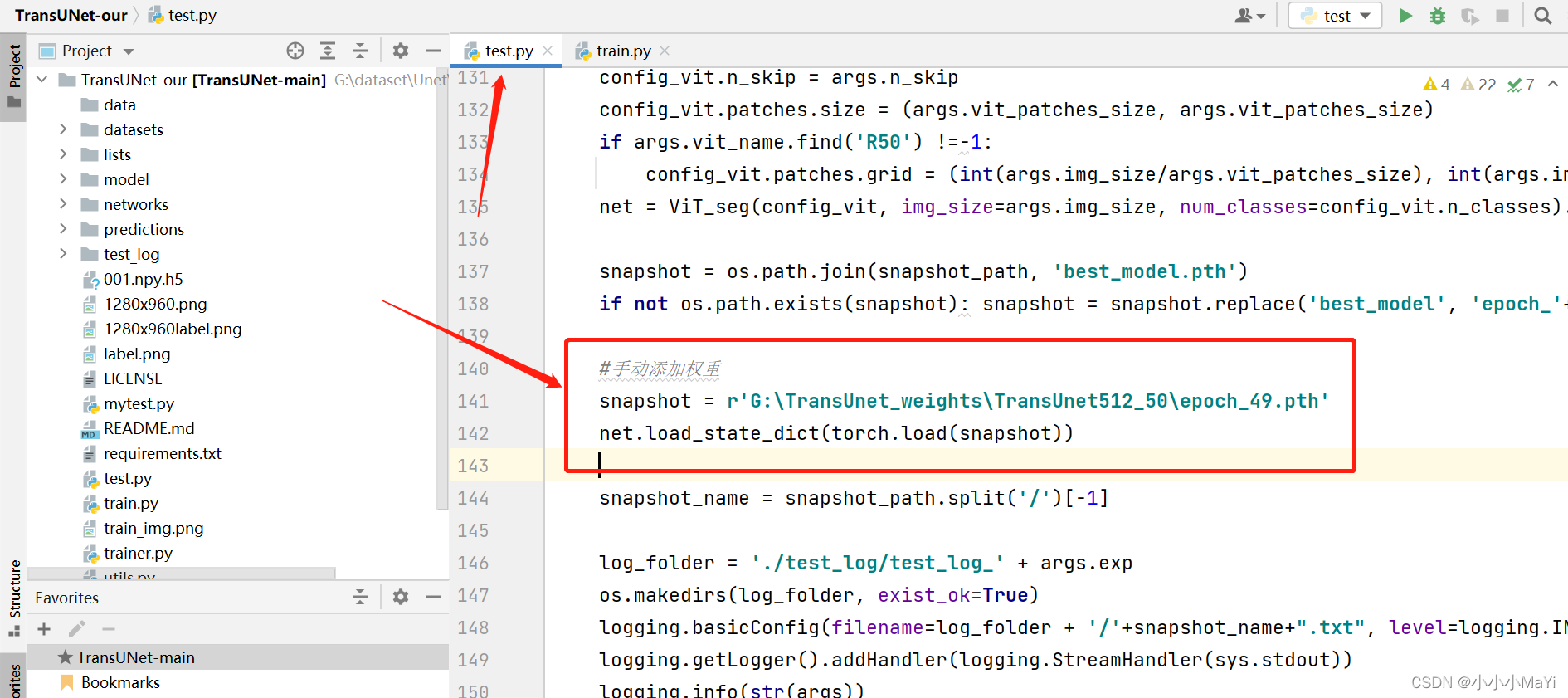
手动添加权重。
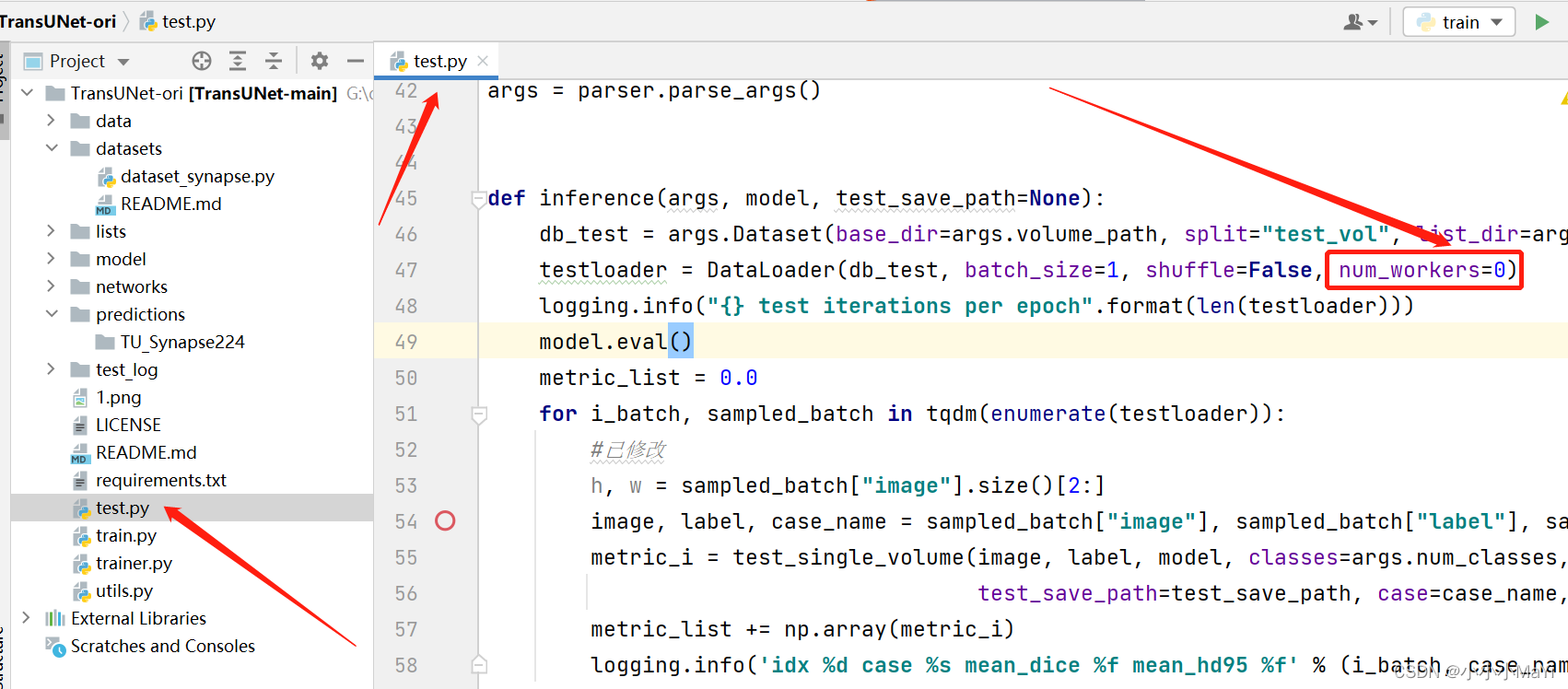
3. 设置DataLoader
设置DataLoader中参数num_workers=0。
4. 修改utils.py文件
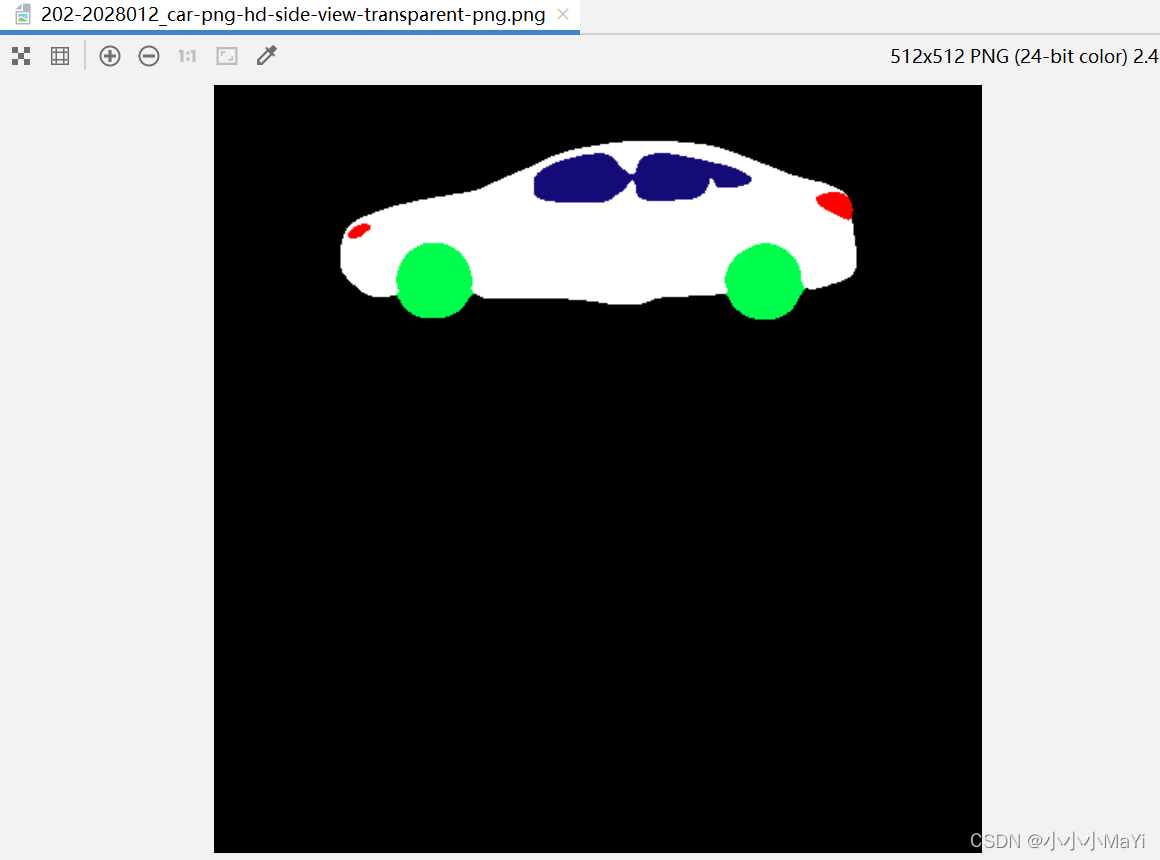
替换utils.py中的test_single_volume函数,原网络输出的是0,1,2,3,4像素的图片,分别代表5个类别,直接显示均呈黑色。对此,我们通过像素调整,使每个类别呈现不同的颜色。
def test_single_volume(image, label, net, classes, patch_size=[256, 256], test_save_path=None, case=None, z_spacing=1): image, label = image.squeeze(0).cpu().detach().numpy(), label.squeeze(0).cpu().detach().numpy() _,x, y = image.shape if x != patch_size[0] or y != patch_size[1]: #缩放图像符合网络输入 image = zoom(image, (1,patch_size[0] / x, patch_size[1] / y), order=3) input = torch.from_numpy(image).unsqueeze(0).float().cuda() net.eval() with torch.no_grad(): out = torch.argmax(torch.softmax(net(input), dim=1), dim=1).squeeze(0) out = out.cpu().detach().numpy() if x != patch_size[0] or y != patch_size[1]: #缩放图像至原始大小 prediction = zoom(out, (x / patch_size[0], y / patch_size[1]), order=0) else: prediction = out metric_list = [] for i in range(1, classes): metric_list.append(calculate_metric_percase(prediction == i, label == i)) if test_save_path is not None: a1 = copy.deepcopy(prediction) a2 = copy.deepcopy(prediction) a3 = copy.deepcopy(prediction) a1[a1 == 1] = 255 a1[a1 == 2] = 0 a1[a1 == 3] = 255 a1[a1 == 4] = 20 a2[a2 == 1] = 255 a2[a2 == 2] = 255 a2[a2 == 3] = 0 a2[a2 == 4] = 10 a3[a3 == 1] = 255 a3[a3 == 2] = 77 a3[a3 == 3] = 0 a3[a3 == 4] = 120 a1 = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(a1)).convert('L') a2 = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(a2)).convert('L') a3 = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(a3)).convert('L') prediction = Image.merge('RGB', [a1, a2, a3]) prediction.save(test_save_path+'/'+case+'.png') return metric_list
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
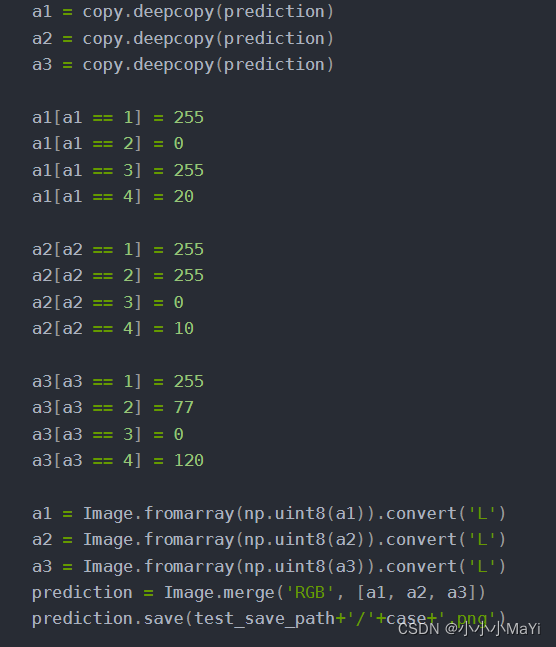
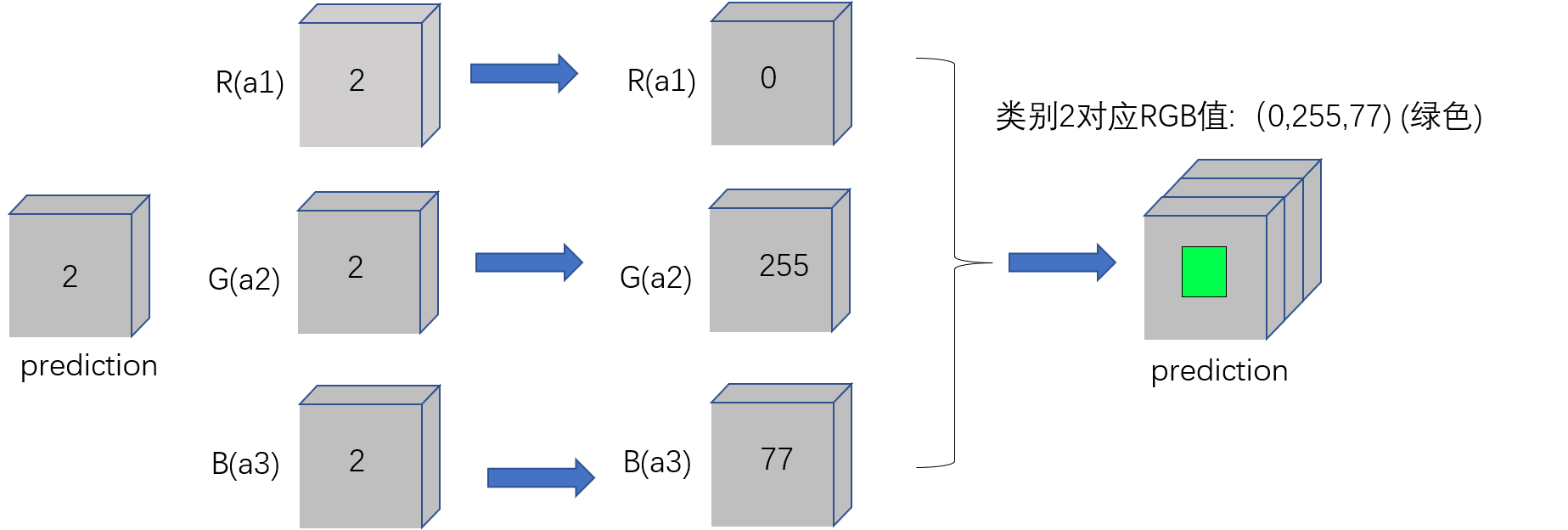
**方便小伙伴理解这部分代码,特意做了个图,a1,a2,a3分别代表RGB三个通道,开始它们的值通过deepcopy函数直接赋值,故三者的值都是一样的。
这里拿类别1举例:a1[a12]=0代表R通道中输出结果为2的赋值0,
a2[a22]=255代表G通道中输出结果为2的赋值255,
a3[a3==2]=77代表B通道中输出结果为2的赋值77,(0,255,77)对应就是绿色,类别2就是绿色(轮子)。
然后通过Image.merge(‘RGB’, [a1, a2, a3])函数合并三个通道,此时prediction就成了三通道彩色图。
至此,设置完毕,右键run运行。
5. 测试结束
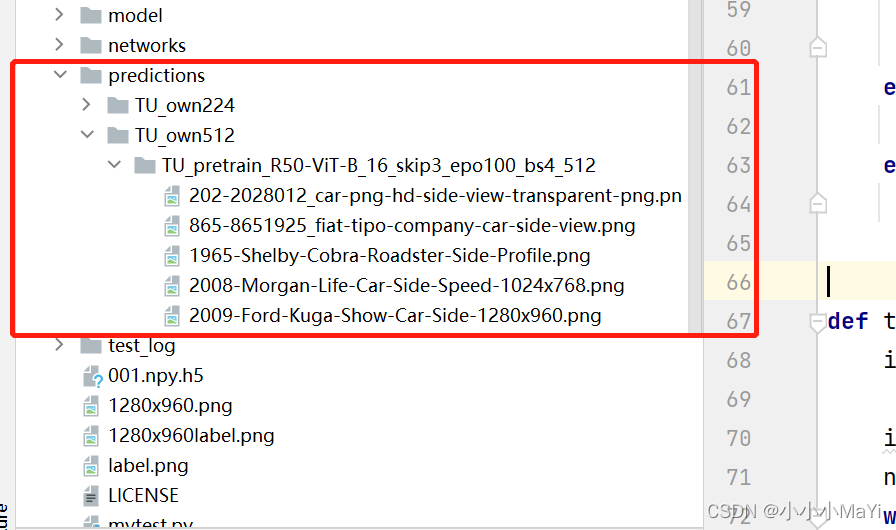
测试结束后,会在根目录下生成predictions文件夹,文件夹的内容如下。

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/Monodyee/article/detail/83906
推荐阅读
相关标签



