- 1一个月看大流星概率91%,半个月是多少?_一个月概率是90 半个月
- 2使用ffmpeg 提取视频关键帧_利用ffmpeg提取视频中的任意关键帧
- 3深入解读 Axios 拦截器:全面了解它的工作原理和实际应用_axios拦截器原理及应用
- 4【Android】之【常用布局】_android常用布局
- 5Android studio | Unused import statement_android studio unused import
- 6Ubuntu 20.04 与22.04 内网apt源搭建_ubuntu20.04apt源
- 7目标检测标注文件yolov5(txt)格式转coco(json)格式详解及代码实现_txt转coco
- 8Go Modules( vgo ) 的介绍与使用以及Go Module Proxy_vgo golang
- 9PostgreSQL如何查询表大小_postgre 查看某张表占内存
- 10RocketMQ(15)——RocketMQ控制台
基于yolov5的目标检测和双目测距_yolov5 双目测距
赞
踩
目录
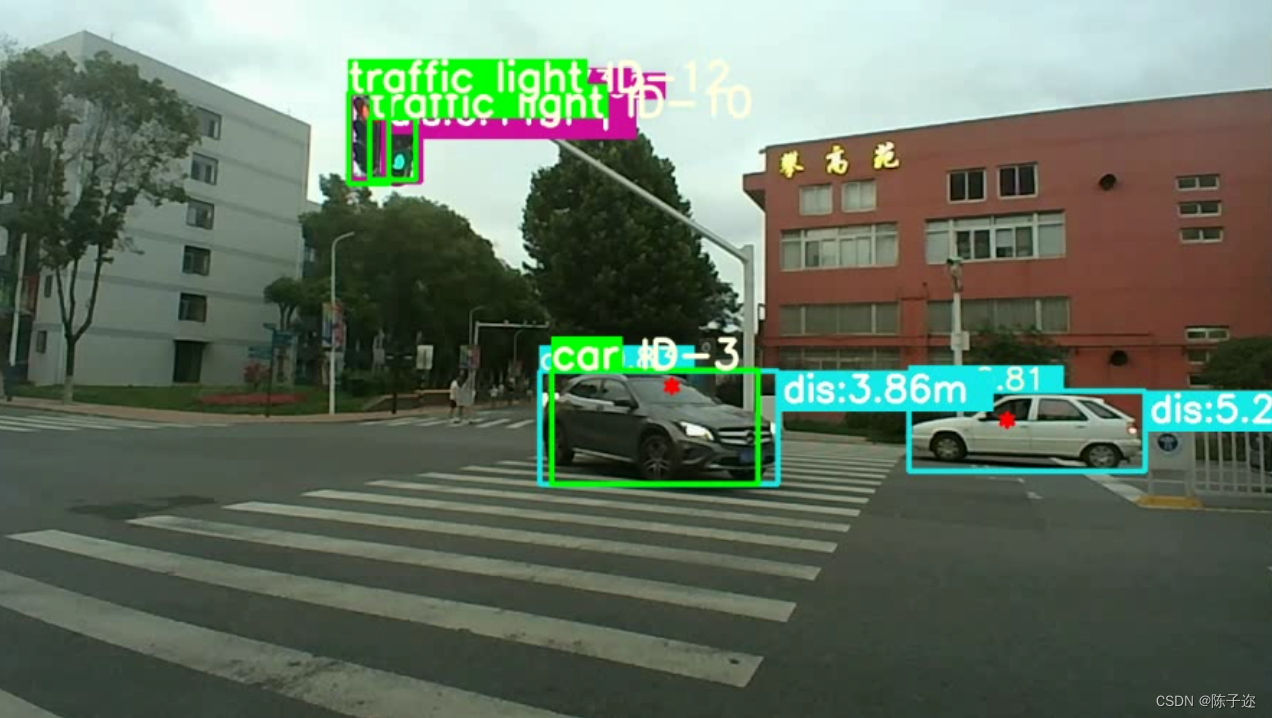
效果展示

一.简介
1.双目视觉
双目视觉是通过两个摄像机同时拍摄同一场景,通过计算两幅图像的差异来获取深度信息的一种计算机视觉技术。在双目视觉中,两个摄像机的成像位置和角度是预先确定的,它们之间的距离被称为基线,通过计算两个相机拍摄的图像中对应像素点的视差,可以计算出每个像素点的深度。
双目视觉的主要优势在于其可以通过将两个视角的信息进行比较,来消除图像中的噪声和误差,从而获得更准确的深度信息。此外,在近距离测量和物体检测等领域中都有广泛的应用。
双目视觉的基本流程包括以下几个步骤:
-
相机标定:确定相机的内外参数,包括焦距、畸变系数、旋转和平移矩阵等,以及两个摄像机之间的基线长度和相对位置关系。
-
图像获取:使用两个摄像机同时拍摄同一个场景,获取两幅图像。
-
特征提取:从两幅图像中提取特征点或者特征区域,例如SIFT或SURF算法,生成特征点集合。
-
特征匹配:通过比较两个图像中的特征点集合,找出相同的特征,建立对应关系。
-
视差计算:根据特征点间的视差大小,结合相机标定参数,计算出每个像素点的深度值。
-
深度图生成:将深度信息转换为灰度图像,生成深度图。
虽然双目视觉技术能够提供准确的深度信息,并可以运用在机器人导航、三维重建等领域,但是该技术还面临一些挑战,例如光照变化、遮挡和反射等问题,这些问题可能会影响特征提取和匹配,从而影响深度信息的准确性。
2 YOLOv5
YOLOv5是一种目标检测算法,由美国加州大学伯克利分校的研究团队开发。与其前身YOLOv4相比,YOLOv5在速度和检测精度方面有了非常显著的提升。
YOLOv5的全称是You Only Look Once version 5,意为“你只需要看一次”即可完成目标检测任务。它采用深度神经网络架构,在单张图像上进行物体检测,可以同时检测出多个物体,并得到它们的位置、类别和置信度等信息,具有高效、准确的特点。
YOLOv5的主要优势包括:
1. 高速度:相较于其前身YOLOv4,YOLOv5平均检测速度提高了65%,同时还具有更小的模型尺寸和更少的计算量。
2. 高检测精度:通过采用新的网络架构和数据增强技术,YOLOv5在检测精度方面取得了突破性的进展。
3. 简单易用:相对于其他目标检测算法,YOLOv5的代码量较小,易于实现和调试,能够应用于多种不同的应用场景。
目前,YOLOv5已经被广泛应用于自动驾驶、智能安防、工业自动化等领域,在实时物体检测和跟踪任务中具有广泛的应用前景。
二.双目准备
原理参考:双目标定之张正友标定法数学原理详解matlab版-CSDN博客
棋盘格图片自提
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1W31fTtr6db8qgTevulWeMA
提取码:ybca
二.双目准备
1双目矫正
打开Matlab 上方的工具栏APP,找到图像处理和计算机视觉下的Stereo Camera Calibration工具,打开并将分割后的图片导入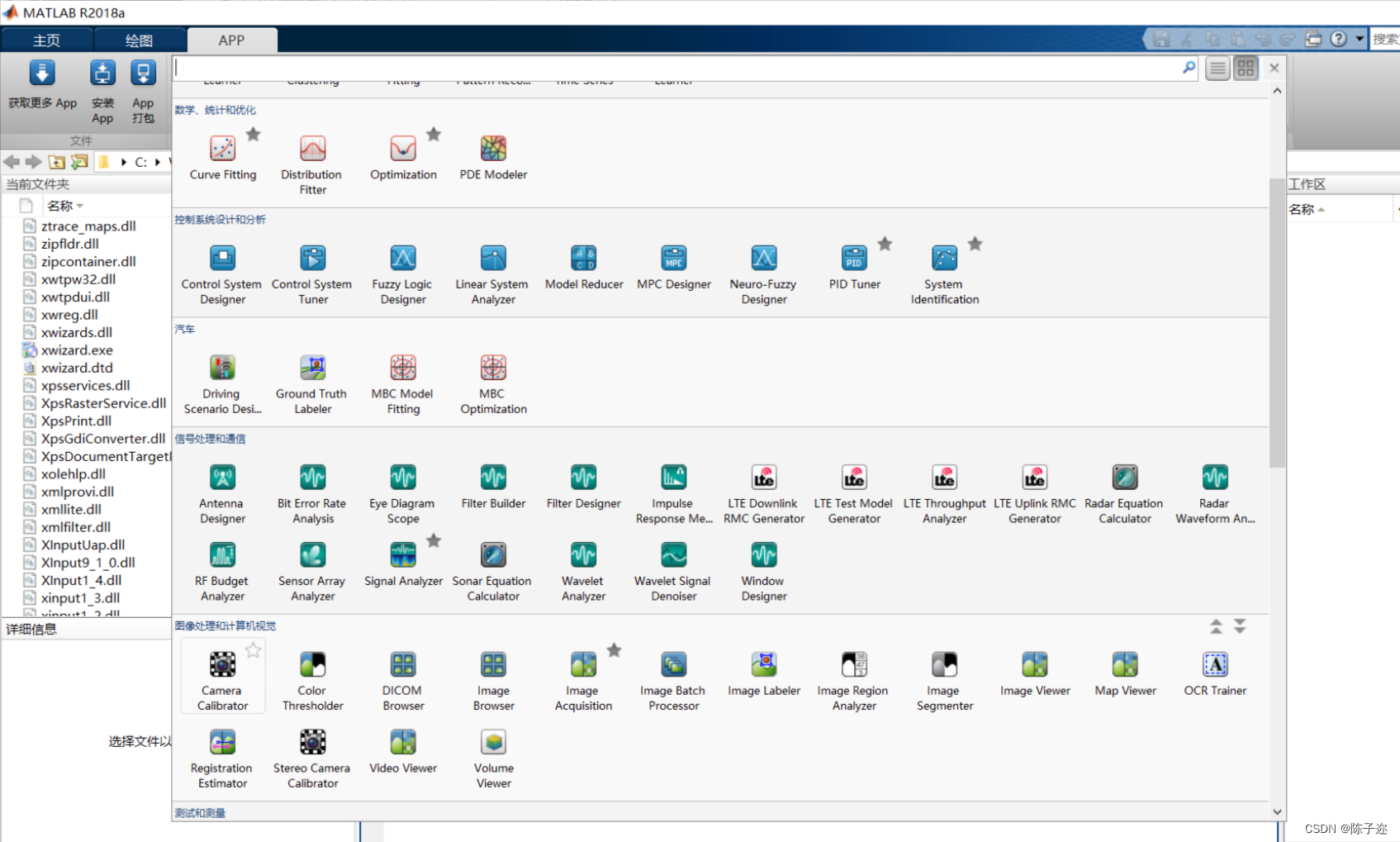

设置参数,对于一般的相机选择2 Coefficients选项即可,对于大视场相机则选择3 Coefficients选项。拉线删除误差较大的画面:

获取参数
在matlab控制台分别输入 stereoParams.CameraParameters1.IntrinsicMatrix 和stereoParams.CameraParameters2.IntrinsicMatrix 获得左右相机的参数,下边填写时请注意进行矩阵的转置
为了获取左相机的畸变系数:[k1, k2, p1, p2, k3],我们需要分别输入stereoParams.CameraParameters1.RadialDistortion 和 stereoParams.CameraParameters1.TangentialDistortion
分别输入 stereoParams.RotationOfCamera2 和 stereoParams 来获取双目的旋转矩阵和平移矩阵
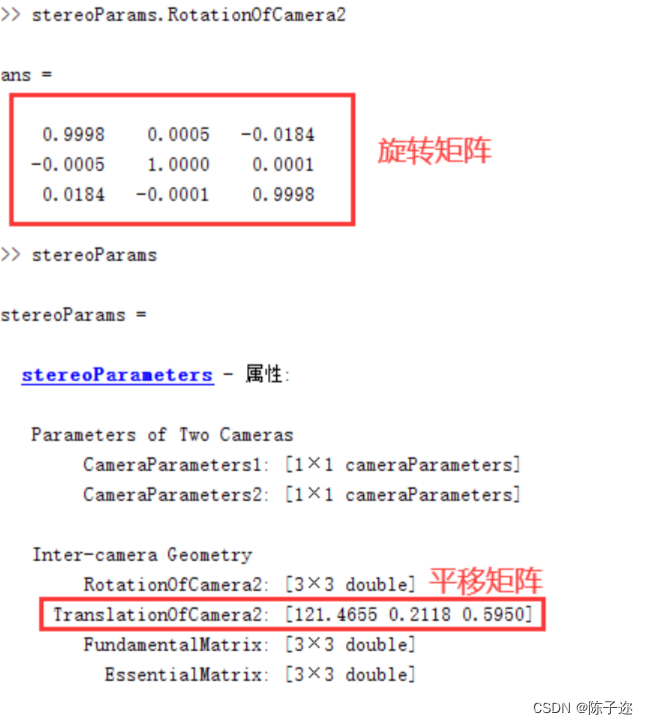
将以上参数填写进stereoconfig.py文件里,注意转置
- import numpy as np
-
- # 双目相机参数
- class stereoCamera(object):
- def __init__(self):
- # 左相机内参
- self.cam_matrix_left = np.array([ [479.6018, -0.0769, 652.6060],
- [ 0, 478.0229, 352.3870],
- [ 0, 0, 1]
- ])
- # 右相机内参
- self.cam_matrix_right = np.array([ [489.9354, 0.2789, 641.6219],
- [ 0, 487.9356, 354.5612],
- [ 0, 0, 1]
- ])
-
- # 左右相机畸变系数:[k1, k2, p1, p2, k3]
- self.distortion_l = np.array([[-0.0791, 0.0309, -0.0009, -0.0004, -0.0091]])
- self.distortion_r = np.array([[-0.1153, 0.1021, -0.0011, -0.0005, -0.0459]])
-
- # 旋转矩阵
- self.R = np.array([ [1.0000, 0.0005, -0.0184],
- [-0.0005, 1.0000, 0.0001],
- [ 0.0184, -0.0001, 1.0000]
- ])
- # 平移矩阵
- self.T = np.array([[121.4655], [0.2118], [0.5950]])
- # 焦距
- self.focal_length = 749.402 # 默认值,一般取立体校正后的重投影矩阵Q中的 Q[2,3]
- # 基线距离
- self.baseline = 121.4655 # 单位:mm, 为平移向量的第一个参数(取绝对值)
2.测距部分代码和函数
- import sys
- import cv2
- import numpy as np
- import stereoconfig
-
-
- # 预处理
- def preprocess(img1, img2):
- # 彩色图->灰度图
- if (img1.ndim == 3): # 判断是否为三维数组
- img1 = cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 通过OpenCV加载的图像通道顺序是BGR
- if (img2.ndim == 3):
- img2 = cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
-
- # 直方图均衡
- img1 = cv2.equalizeHist(img1)
- img2 = cv2.equalizeHist(img2)
-
- return img1, img2
-
-
- # 消除畸变
- def undistortion(image, camera_matrix, dist_coeff):
- undistortion_image = cv2.undistort(image, camera_matrix, dist_coeff)
-
- return undistortion_image
-
-
- # 获取畸变校正和立体校正的映射变换矩阵、重投影矩阵
- # @param:config是一个类,存储着双目标定的参数:config = stereoconfig.stereoCamera()
- def getRectifyTransform(height, width, config):
- # 读取内参和外参
- left_K = config.cam_matrix_left
- right_K = config.cam_matrix_right
- left_distortion = config.distortion_l
- right_distortion = config.distortion_r
- R = config.R
- T = config.T
-
- # 计算校正变换
- R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, roi1, roi2 = cv2.stereoRectify(left_K, left_distortion, right_K, right_distortion,
- (width, height), R, T, alpha=0)
-
- map1x, map1y = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(left_K, left_distortion, R1, P1, (width, height), cv2.CV_32FC1)
- map2x, map2y = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(right_K, right_distortion, R2, P2, (width, height), cv2.CV_32FC1)
-
- return map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y, Q
-
-
- # 畸变校正和立体校正
- def rectifyImage(image1, image2, map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y):
- rectifyed_img1 = cv2.remap(image1, map1x, map1y, cv2.INTER_AREA)
- rectifyed_img2 = cv2.remap(image2, map2x, map2y, cv2.INTER_AREA)
-
- return rectifyed_img1, rectifyed_img2
-
-
- # 立体校正检验----画线
- def draw_line(image1, image2):
- # 建立输出图像
- height = max(image1.shape[0], image2.shape[0])
- width = image1.shape[1] + image2.shape[1]
-
- output = np.zeros((height, width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
- output[0:image1.shape[0], 0:image1.shape[1]] = image1
- output[0:image2.shape[0], image1.shape[1]:] = image2
-
- # 绘制等间距平行线
- line_interval = 50 # 直线间隔:50
- for k in range(height // line_interval):
- cv2.line(output, (0, line_interval * (k + 1)), (2 * width, line_interval * (k + 1)), (0, 255, 0), thickness=2,
- lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
-
- return output
-
-
- # 视差计算
- def stereoMatchSGBM(left_image, right_image, down_scale=False):
- # SGBM匹配参数设置
- if left_image.ndim == 2:
- img_channels = 1
- else:
- img_channels = 3
- blockSize = 3
- paraml = {'minDisparity': 0,
- 'numDisparities': 64,
- 'blockSize': blockSize,
- 'P1': 8 * img_channels * blockSize ** 2,
- 'P2': 32 * img_channels * blockSize ** 2,
- 'disp12MaxDiff': 1,
- 'preFilterCap': 63,
- 'uniquenessRatio': 15,
- 'speckleWindowSize': 100,
- 'speckleRange': 1,
- 'mode': cv2.STEREO_SGBM_MODE_SGBM_3WAY
- }
-
- # 构建SGBM对象
- left_matcher = cv2.StereoSGBM_create(**paraml)
- paramr = paraml
- paramr['minDisparity'] = -paraml['numDisparities']
- right_matcher = cv2.StereoSGBM_create(**paramr)
-
- # 计算视差图
- size = (left_image.shape[1], left_image.shape[0])
- if down_scale == False:
- disparity_left = left_matcher.compute(left_image, right_image)
- disparity_right = right_matcher.compute(right_image, left_image)
- else:
- left_image_down = cv2.pyrDown(left_image)
- right_image_down = cv2.pyrDown(right_image)
- factor = left_image.shape[1] / left_image_down.shape[1]
-
- disparity_left_half = left_matcher.compute(left_image_down, right_image_down)
- disparity_right_half = right_matcher.compute(right_image_down, left_image_down)
- disparity_left = cv2.resize(disparity_left_half, size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
- disparity_right = cv2.resize(disparity_right_half, size, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
- disparity_left = factor * disparity_left
- disparity_right = factor * disparity_right
-
- # 真实视差(因为SGBM算法得到的视差是×16的)
- trueDisp_left = disparity_left.astype(np.float32) / 16.
- trueDisp_right = disparity_right.astype(np.float32) / 16.
-
- return trueDisp_left, trueDisp_right
-
-
- def getDepthMapWithQ(disparityMap: np.ndarray, Q: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
- points_3d = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disparityMap, Q) # points_3d 是一个三维的数组,前面两个是宽和高,第三维是一个(x,y,z)的坐标
- points = points_3d[:, :, 0:3]
-
- depthMap = points_3d[:, :, 2] # 索引三维数组的最后一维,就是深度信息
- reset_index = np.where(np.logical_or(depthMap < 0.0, depthMap > 65535.0))
- depthMap[reset_index] = 0
-
- return depthMap.astype(np.float32)
-
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- # 读取图片
- cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
- cap.set(3, 1280)
- cap.set(4, 480) # 打开并设置摄像头
-
- while True:
- ret, frame = cap.read()
- iml = frame[0:480, 0:640]
- imr = frame[0:480, 640:1280] # 分割双目图像
-
-
- if (iml is None) or (imr is None):
- print("Error: Images are empty, please check your image's path!")
- sys.exit(0)
- height, width = iml.shape[0:2] # 对图像进行切片操作,前面两位是高和宽
-
- iml_, imr_ = preprocess(iml, imr) # 预处理,一般可以削弱光照不均的影响,不做也可以
-
- # 读取相机内参和外参
- # 使用之前先将标定得到的内外参数填写到stereoconfig.py中的StereoCamera类中
- config = stereoconfig.stereoCamera()
- # print(config.cam_matrix_left)
-
- # 立体校正
- map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y, Q = getRectifyTransform(height, width, config) # 获取用于畸变校正和立体校正的映射矩阵以及用于计算像素空间坐标的重投影矩阵
- iml_rectified, imr_rectified = rectifyImage(iml, imr, map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y)
- # print(Q)
-
- # 绘制等间距平行线,检查立体校正的效果
- line = draw_line(iml_rectified, imr_rectified)
- cv2.imwrite('check_rectification.png', line)
-
- # 立体匹配
- disp, _ = stereoMatchSGBM(iml_rectified, imr_rectified, False) # 这里传入的是经立体校正的图像
-
- cv2.imwrite('disaprity.png', disp * 4)
-
- # fx = config.cam_matrix_left[0, 0]
- # fy = fx
- # cx = config.cam_matrix_left[0, 2]
- # cy = config.cam_matrix_left[1, 2]
-
- # print(fx, fy, cx, cy)
-
- # 计算像素点的3D坐标(左相机坐标系下)
- points_3d = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disp, Q) # 参数中的Q就是由getRectifyTransform()函数得到的重投影矩阵
-
-
-
- # 设置想要检测的像素点坐标(x,y)
- x = 120
- y = 360
- cv2.circle(iml, (x, y), 5, (0, 0, 255), -1)
-
- # x1 = points_3d[y, x] # 索引 (y, x) 对应的是三维坐标 (x1, y1, z1)
- # print(x1)
-
- print('x:', points_3d[int(y), int(x), 0], 'y:', points_3d[int(y), int(x), 1], 'z:',
- points_3d[int(y), int(x), 2]) # 得出像素点的三维坐标,单位mm
- print('distance:', (points_3d[int(y), int(x), 0] ** 2 + points_3d[int(y), int(x), 1] ** 2 + points_3d[
- int(y), int(x), 2] ** 2) ** 0.5) # 计算距离,单位mm
-
-
- cv2.namedWindow("disparity", 0)
- cv2.imshow("disparity", iml)
- # cv2.setMouseCallback("disparity", onMouse, 0)
-
-
- # 等待用户按键,如果按下 'q' 键或者 Esc 键,则退出循环
- c = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
- if c == 27 or c == ord('q'):
- break
-
- # 释放视频对象并关闭窗口
- cap.release()
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()
三.yolov5部分代码代码展示
- # 读取相机内参和外参
- config = stereoconfig_040_2.stereoCamera()
-
- # 立体校正
- map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y, Q = getRectifyTransform(720, 1280, config) # 获取用于畸变校正和立体校正的映射矩阵以及用于计算像素空间坐标的重投影矩阵
-
- for path, img, im0s, vid_cap in dataset:
- img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)
- img = img.half() if half else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
- img /= 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
- if img.ndimension() == 3:
- img = img.unsqueeze(0)
-
- # Inference
- t1 = time_synchronized()
- pred = model(img, augment=opt.augment)[0]
-
- # Apply NMS
- pred = non_max_suppression(pred, opt.conf_thres, opt.iou_thres, classes=opt.classes, agnostic=opt.agnostic_nms)
- t2 = time_synchronized()
-
- # Apply Classifier
- if classify:
- pred = apply_classifier(pred, modelc, img, im0s)
-
-
-
- # Process detections
- for i, det in enumerate(pred): # detections per image
- if webcam: # batch_size >= 1
- p, s, im0, frame = path[i], '%g: ' % i, im0s[i].copy(), dataset.count
-
- else:
- p, s, im0, frame = path, '', im0s, getattr(dataset, 'frame', 0)
-
- ###############################
- #stereo code
- fps_set = 10 #setting the frame
- if(accel_frame % fps_set == 0):
- #t3 = time.time() # stereo time start 0.510s
- #string = ''
-
- #thread = threading.Thread(target = mythread,args = ((config,im0,map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y,Q)) )
-
- thread= MyThread(stereo_threading,args = (config,im0,map1x, map1y, map2x, map2y,Q))
- thread.start()
-
- #if(accel_frame % fps_set == 0):
- # thread.join()
- #points_3d = thread.get_result()
- print()
- print(threading.active_count()) #获取已激活的线程数
- print(threading.enumerate()) # see the thread list,查看所有线程信息,一个<_MainThread(...)> 带多个 <Thread(...)>
- print()
- print("############## Frame is %d !##################" %accel_frame)
-
-
-
- p = Path(p) # to Path
- if webcam:
- save_stream_path = str(save_stream_dir / "stream0.mp4") # save streams path
- else:
- save_path = str(save_dir / p.name) # img.jpg
- txt_path = str(save_dir / 'labels' / p.stem) + ('' if dataset.mode == 'image' else f'_{frame}') # img.txt
-
-
-
-
- s += '%gx%g ' % img.shape[2:] # print string
- #print("txt_path is %s"%txt_path)
- gn = torch.tensor(im0.shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]] # normalization gain whwh
-
- if len(det):
- # Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
- det[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
-
- # Print results
- for c in det[:, -1].unique():
- n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum() # detections per class
- s += f"{n} {names[int(c)]} {'s' * (n > 1)} , " # add to string
本项目不开源,需要的私聊 ,谢谢


