- 1Installed Build Tools revision 31.0.0 is corrupted. Remove and install again using the SDK Manager
- 2升级鸿蒙系统后游戏数据会没吗,华为手机升级鸿蒙系统会清空数据吗
- 3【基础知识】extern 和 extern “C“详解_extern "c
- 4AndroidStudio的安装配置&&注意要点_android studio no windows desktop project configur
- 5android与mysql连接不上去_android – 通过LAN连接到mySQL数据库,而不使用网络服务器...
- 6最小二乘_最小二乘法范数
- 7AspectJ入门(一)
- 8埃森哲大中华区战略与咨询董事总经理陈继东:业务全面重塑,“人”要如何重塑?_埃森哲中国咨询公司董事长
- 9鸿蒙学习2-1,手机USB连接电脑实现本地模拟器功能_鸿蒙使用手机作为模拟器
- 1045个值得收藏的 CSS 形状_css长方形弯曲
K8S环境下配置SpringBoot健康检查(活性探针)_springboot 启用 liveness 和 readiness 探针
赞
踩
主要是通过
K8S的健康检查探针,对SpringBoot应用进行运行健康监控,检测pod是否存活,从而对pod进行重启之类的操作
k8s 探针配置:
kubernetes提供了三种探针(支持exec、tcp和http方式)来探测容器的状态:
LivenessProbe:容器存活性检查,用于判断容器是否健康,告诉 kubelet 一个容器什么时候处于不健康的状态。如果 LivenessProbe 探针探测到容器不健康,则 kubelet 将删除该容器,并根据容器的重启策略做相应的处理。如果一个容器不包含 LivenessProbe 探针,那么 kubelet 认为该容器的 LivenessProbe 探针返回的值永远是 Success;
ReadinessProbe:容器就绪性检查,用于判断容器是否启动完成且准备接收请求。如果ReadinessProbe探针探测到失败,Endpoint Controller 将从 Service 的 Endpoint 中删除包含该容器所在 Pod 的 IP 地址的Endpoint条目。如果容器不提供就绪态探针,则默认状态为 Success。
StartupProbe: 容器启动检查,指示容器中的应用是否已经启动。如果提供了启动探针,则所有其他探针都会被禁用,直到此探针成功为止。如果启动探测失败,kubelet 将杀死容器,而容器依其重启策略进行重启。 如果容器没有提供启动探测,则默认状态为 Success。
三种探针共有配置:
Probe有如下配置字段,可以使用这些字段精确的控制存活和就绪检测的行为:
initialDelaySeconds:容器启动后要等待多少秒后存活和就绪探测器才被初始化,默认是 0 秒,最小值是 0。
periodSeconds:执行探测的时间间隔(单位是秒)。默认是 10 秒。最小值是 1。
timeoutSeconds:探测的超时后等待多少秒。默认值是 1 秒。最小值是 1。
successThreshold:探测器在失败后,被视为成功的最小连续成功数。默认值是 1。 存活和启动探测的这个值必须是 1。最小值是 1。
failureThreshold:当探测失败时,Kubernetes 的重试次数。 存活探测情况下的放弃就意味着重新启动容器。 就绪探测情况下的放弃 Pod 会被打上未就绪的标签。默认值是 3。最小值是 1。
说明:
在 Kubernetes 1.20 版本之前,exec 探针会忽略 timeoutSeconds:探针会无限期地 持续运行,甚至可能超过所配置的限期,直到返回结果为止。这一缺陷在 Kubernetes v1.20 版本中得到修复。
具体配置如下
推荐使用SpringBoot版本在2.3.2版本以上,这样才好的支持开启应用探针功能,所以先检查项目的版本号
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
再引入pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
在yml文件中加入以下配置
server: port: 8080 shutdown: graceful # 默认为IMMEDIATE,表示立即关机;GRACEFUL表示优雅关机 servlet: context-path: /test spring: lifecycle: timeout-per-shutdown-phase: 30s # 停机过程超时时长设置30s,超过30s,直接停机 application: name: test management: # 开启shutdown和health端点 endpoint: health: probes: enabled: true health: livenessstate: enabled: true readynessstate: enabled: true
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
在k8s部署文件中加入以下配置
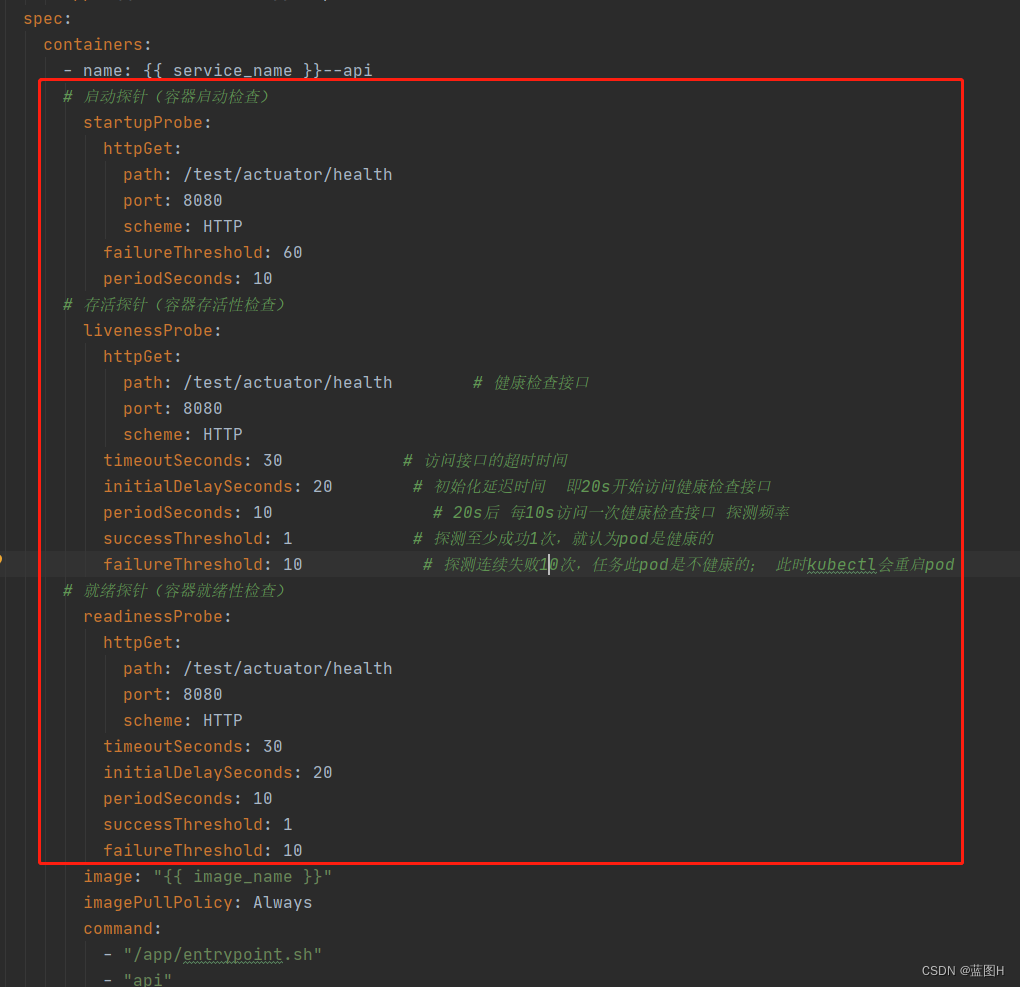
--- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: {{ service_name }}--api spec: selector: matchLabels: app: {{ service_name }}--api replicas: {{ replicas }} # Pod副本数 strategy: type: RollingUpdate # 滚动更新策略 rollingUpdate: maxSurge: 25% maxUnavailable: 25% template: metadata: name: {{ service_name }}--api labels: app: {{ service_name }}--api spec: containers: - name: {{ service_name }}--api # 启动探针(容器启动检查) startupProbe: httpGet: path: /test/actuator/health port: 8080 scheme: HTTP failureThreshold: 60 periodSeconds: 10 # 存活探针(容器存活性检查) livenessProbe: httpGet: path: /test/actuator/health # 健康检查接口 port: 8080 scheme: HTTP timeoutSeconds: 30 # 访问接口的超时时间 initialDelaySeconds: 20 # 初始化延迟时间 即20s开始访问健康检查接口 periodSeconds: 10 # 20s后 每10s访问一次健康检查接口 探测频率 successThreshold: 1 # 探测至少成功1次,就认为pod是健康的 failureThreshold: 10 # 探测连续失败10次,任务此pod是不健康的; 此时kubectl会重启pod # 就绪探针(容器就绪性检查) readinessProbe: httpGet: path: /test/actuator/health port: 8080 scheme: HTTP timeoutSeconds: 30 initialDelaySeconds: 20 periodSeconds: 10 successThreshold: 1 failureThreshold: 10 image: "{{ image_name }}" imagePullPolicy: Always command: - "/app/entrypoint.sh" - "api" volumeMounts: - name: config-envs mountPath: /etc/config/envs readOnly: true - name: secret-mysql-config mountPath: /etc/secrets/mysql/config readOnly: true - name: secret-redis-config mountPath: /etc/secrets/redis/config readOnly: true - name: secret-storage-sa mountPath: /etc/secrets/storage/sa readOnly: true - name: secret-storage-config mountPath: /etc/secrets/storage/config readOnly: true resources: # 容器资源管理 limits: # 资源限制(监控使用情况) cpu: "{{ cpu_limits }}" memory: "{{ memory_limits }}" requests: # 最小可用资源(灵活调度) cpu: "{{ cpu_requests }}" memory: "{{ memory_requests }}" nodeSelector: {{ k8s_priority_node_pool }} affinity: # 设置调度策略,采取多主机/多可用区部署 podAntiAffinity: preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: - weight: 100 podAffinityTerm: labelSelector: matchExpressions: - key: app operator: In values: - {{ service_name }}--api topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname" volumes: - name: config-envs configMap: name: {{ service_name }}--config--envs - name: secret-mysql-config secret: secretName: {{ service_name }}--config--mysql - name: secret-redis-config secret: secretName: {{ service_name }}--config--redis - name: secret-storage-sa secret: secretName: {{ service_name }}--sa--storage - name: secret-storage-config secret: secretName: {{ service_name }}--config--storage
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
后续使用问题
更新:
用了一段时间后,在某一次服务器资源不够后,导致服务全部停止,然后多个pod陷入无限重启状态。原因是多个pod一直在探测是否有成功启动的pod,然后导致先后批次的pod都在等待对方启动完成,后面发现是重启的时间设置的不合理导致的。后续有时间专门出一篇文章细说一下。



