热门标签
热门文章
- 1javaScript之navigator 对象判断设备、客户端(微博、QQ、微信)、浏览器_js navigator远程客户端主机
- 2Android studio 打包生成jar包的流程详解_android studio 生成jar
- 3外包干了一个月,忘记Git怎么使用了...
- 4python按关键字爬取必应高清图片_基于关键词 搜索合适的图片
- 5uniapp左右菜单栏联动滚动代码_左右列表联动的网页代码
- 6如何将汇编语言转换为c语言,如何把汇编语言转换成C语言
- 7WASubContext.js?t=wechat&s=1670034424984&v=2.28.0:1 routeDone with a webviewId 1 that is not the cur
- 8docker-nginx配置及使用_docker nginx设置路由是
- 9Stream 流 获取list中对象的某个字段组成新的list_steam流取出一个字段组合成list
- 10设计模式:单例模式
当前位置: article > 正文
机器人自主导航程序分析_分析exploring_slam.py,理解如何实现自主导航的方法。
作者:不正经 | 2024-03-30 05:19:16
赞
踩
分析exploring_slam.py,理解如何实现自主导航的方法。
SLAM+自主导航
一、ROS中的导航框架

上图中,灰色的模块并不是必须的。
在ROS中,进行导航需要使用到的三个包是:
(1) move_base:根据参照的消息进行路径规划,使移动机器人到达指定的位置;
(2) gmapping:根据激光数据(或者深度数据模拟的激光数据)建立地图;
(3) amcl:根据已经有的地图进行定位。
二、ROS中的SLAM功能包
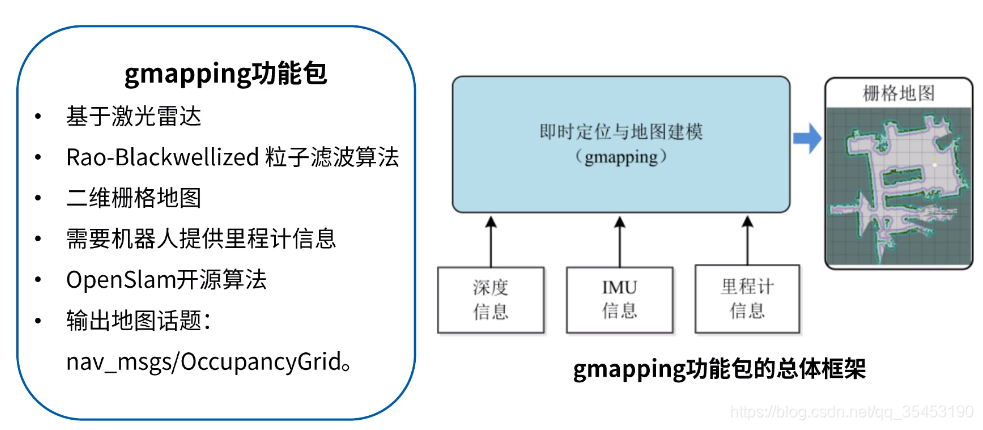
里程计作为移动机器人相对定位的有效传感器,为机器人提供了实时的位姿信息。移动机器人里程计模型决定于移动机器人结构和运动方式,即移动机器人运动学模型。针对双轮差动移动机器人平台,里程计的工作原理是根据安装在左右两个驱动轮电机上的光电编码器来检测车轮在一定时间内转过的弧度,进而推算机器人相对位姿的变化 。里程计由gazebo提供

三、基于雷达的自主导航
roslaunch mbot_gazebo mbot_laser_nav_gazebo.launch
roslaunch mbot_navigation exploring_slam_demo.launch
rosrun mbot_navigation exploring_slam.py
- 1
- 2
- 3
1、mbot_laser_nav_gazebo.launch
<launch> <!-- 设置launch文件的参数 --> <arg name="world_name" value="$(find mbot_gazebo)/worlds/cloister.world"/> <arg name="paused" default="false"/> <arg name="use_sim_time" default="true"/> <arg name="gui" default="true"/> <arg name="headless" default="false"/> <arg name="debug" default="false"/> <!-- 运行gazebo仿真环境 --> <include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch"> <arg name="world_name" value="$(arg world_name)" /> <arg name="debug" value="$(arg debug)" /> <arg name="gui" value="$(arg gui)" /> <arg name="paused" value="$(arg paused)"/> <arg name="use_sim_time" value="$(arg use_sim_time)"/> <arg name="headless" value="$(arg headless)"/> </include> <!-- 加载机器人模型描述参数 --> <param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro --inorder '$(find mbot_description)/urdf/mbot_with_laser_gazebo.xacro'" /> <!-- 运行joint_state_publisher节点,发布机器人的关节状态 --> <node name="joint_state_publisher" pkg="joint_state_publisher" type="joint_state_publisher" ></node> <!-- 运行robot_state_publisher节点,发布tf --> <node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" output="screen" > <param name="publish_frequency" type="double" value="50.0" /> </node> <!-- 在gazebo中加载机器人模型--> <node name="urdf_spawner" pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" respawn="false" output="screen" args="-urdf -model mbot -param robot_description"/> </launch>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
2、exploring_slam_demo.launch
<launch>
<include file="$(find mbot_navigation)/launch/gmapping.launch"/>
<!-- 运行move_base节点 -->
<include file="$(find mbot_navigation)/launch/move_base.launch" />
<!-- 运行rviz -->
<node pkg="rviz" type="rviz" name="rviz" args="-d $(find mbot_navigation)/rviz/nav.rviz"/>
</launch>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
3、exploring_slam.py
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import roslib; import rospy import actionlib from actionlib_msgs.msg import * from geometry_msgs.msg import Pose, PoseWithCovarianceStamped, Point, Quaternion, Twist from move_base_msgs.msg import MoveBaseAction, MoveBaseGoal from random import sample from math import pow, sqrt class NavTest(): def __init__(self): rospy.init_node('exploring_random', anonymous=True) rospy.on_shutdown(self.shutdown) # 在每个目标位置暂停的时间 (单位:s) self.rest_time = rospy.get_param("~rest_time", 2) # 是否仿真? self.fake_test = rospy.get_param("~fake_test", True) # 到达目标的状态 goal_states = ['PENDING', 'ACTIVE', 'PREEMPTED', 'SUCCEEDED', 'ABORTED', 'REJECTED', 'PREEMPTING', 'RECALLING', 'RECALLED', 'LOST'] # 设置目标点的位置 # 在rviz中点击 2D Nav Goal 按键,然后单击地图中一点 # 在终端中就会看到该点的坐标信息 locations = dict() locations['1'] = Pose(Point(4.589, -0.376, 0.000), Quaternion(0.000, 0.000, -0.447, 0.894)) locations['2'] = Pose(Point(4.231, -6.050, 0.000), Quaternion(0.000, 0.000, -0.847, 0.532)) locations['3'] = Pose(Point(-0.674, -5.244, 0.000), Quaternion(0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 1.000)) locations['4'] = Pose(Point(-5.543, -4.779, 0.000), Quaternion(0.000, 0.000, 0.645, 0.764)) locations['5'] = Pose(Point(-4.701, -0.590, 0.000), Quaternion(0.000, 0.000, 0.340, 0.940)) locations['6'] = Pose(Point(2.924, 0.018, 0.000), Quaternion(0.000, 0.000, 0.000, 1.000)) # 发布控制机器人的消息 self.cmd_vel_pub = rospy.Publisher('cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size=5) # 订阅move_base服务器的消息 self.move_base = actionlib.SimpleActionClient("move_base", MoveBaseAction) rospy.loginfo("Waiting for move_base action server...") # 60s等待时间限制 self.move_base.wait_for_server(rospy.Duration(60)) rospy.loginfo("Connected to move base server") # 保存机器人的在rviz中的初始位置 initial_pose = PoseWithCovarianceStamped() # 保存成功率、运行时间、和距离的变量 n_locations = len(locations) n_goals = 0 n_successes = 0 i = n_locations distance_traveled = 0 start_time = rospy.Time.now() running_time = 0 location = "" last_location = "" # 确保有初始位置 while initial_pose.header.stamp == "": rospy.sleep(1) rospy.loginfo("Starting navigation test") # 开始主循环,随机导航 while not rospy.is_shutdown(): # 如果已经走完了所有点,再重新开始排序 if i == n_locations: i = 0 sequence = sample(locations, n_locations) # 如果最后一个点和第一个点相同,则跳过 if sequence[0] == last_location: i = 1 # 在当前的排序中获取下一个目标点 location = sequence[i] # 跟踪行驶距离 # 使用更新的初始位置 if initial_pose.header.stamp == "": distance = sqrt(pow(locations[location].position.x - locations[last_location].position.x, 2) + pow(locations[location].position.y - locations[last_location].position.y, 2)) else: rospy.loginfo("Updating current pose.") distance = sqrt(pow(locations[location].position.x - initial_pose.pose.pose.position.x, 2) + pow(locations[location].position.y - initial_pose.pose.pose.position.y, 2)) initial_pose.header.stamp = "" # 存储上一次的位置,计算距离 last_location = location # 计数器加1 i += 1 n_goals += 1 # 设定下一个目标点 self.goal = MoveBaseGoal() self.goal.target_pose.pose = locations[location] self.goal.target_pose.header.frame_id = 'map' self.goal.target_pose.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now() # 让用户知道下一个位置 rospy.loginfo("Going to: " + str(location)) # 向下一个位置进发 self.move_base.send_goal(self.goal) # 五分钟时间限制 finished_within_time = self.move_base.wait_for_result(rospy.Duration(300)) # 查看是否成功到达 if not finished_within_time: self.move_base.cancel_goal() rospy.loginfo("Timed out achieving goal") else: state = self.move_base.get_state() if state == GoalStatus.SUCCEEDED: rospy.loginfo("Goal succeeded!") n_successes += 1 distance_traveled += distance rospy.loginfo("State:" + str(state)) else: rospy.loginfo("Goal failed with error code: " + str(goal_states[state])) # 运行所用时间 running_time = rospy.Time.now() - start_time running_time = running_time.secs / 60.0 # 输出本次导航的所有信息 rospy.loginfo("Success so far: " + str(n_successes) + "/" + str(n_goals) + " = " + str(100 * n_successes/n_goals) + "%") rospy.loginfo("Running time: " + str(trunc(running_time, 1)) + " min Distance: " + str(trunc(distance_traveled, 1)) + " m") rospy.sleep(self.rest_time) def update_initial_pose(self, initial_pose): self.initial_pose = initial_pose def shutdown(self): rospy.loginfo("Stopping the robot...") self.move_base.cancel_goal() rospy.sleep(2) self.cmd_vel_pub.publish(Twist()) rospy.sleep(1) def trunc(f, n): slen = len('%.*f' % (n, f)) return float(str(f)[:slen]) if __name__ == '__main__': try: NavTest() rospy.spin() except rospy.ROSInterruptException: rospy.loginfo("Exploring SLAM finished.")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
转载https://class.guyuehome.com/detail/p_5ee871cc4674f_R75Aafau/6
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/不正经/article/detail/339261
推荐阅读
相关标签



