- import os
- import torch
- import torch.nn as nn
- import torch.nn.functional as F
- import torchvision
- from torchvision import transforms
- from torchvision.utils import save_image
-
- # 配置GPU或CPU设置
- device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
-
- # 创建目录
- # Create a directory if not exists
- sample_dir = 'samples'
- if not os.path.exists(sample_dir):
- os.makedirs(sample_dir)
-
- # 超参数设置
- # Hyper-parameters
- image_size = 784
- h_dim = 400
- z_dim = 20
- num_epochs = 15
- batch_size = 128
- learning_rate = 1e-3
-
- # 获取数据集
- # MNIST dataset
- dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root='./data',
- train=True,
- transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
- download=True)
-
- # 数据加载,按照batch_size大小加载,并随机打乱
- data_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=dataset,
- batch_size=batch_size,
- shuffle=True)
-
- # 定义VAE类
- # VAE model
- class VAE(nn.Module):
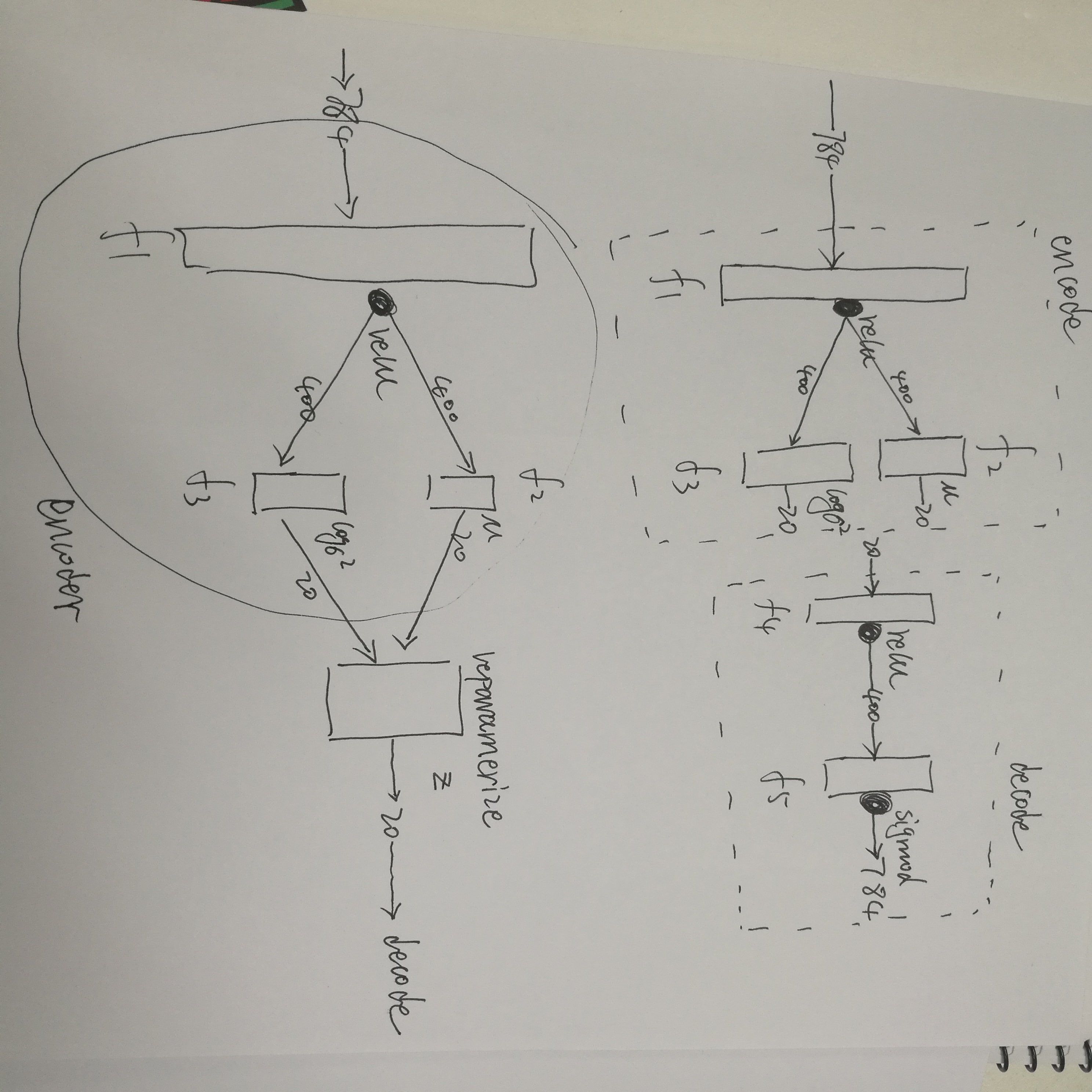
- def __init__(self, image_size=784, h_dim=400, z_dim=20):
- super(VAE, self).__init__()
- self.fc1 = nn.Linear(image_size, h_dim)
- self.fc2 = nn.Linear(h_dim, z_dim)
- self.fc3 = nn.Linear(h_dim, z_dim)
- self.fc4 = nn.Linear(z_dim, h_dim)
- self.fc5 = nn.Linear(h_dim, image_size)
-
- # 编码 学习高斯分布均值与方差
- def encode(self, x):
- h = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
- return self.fc2(h), self.fc3(h)
-
- # 将高斯分布均值与方差参数重表示,生成隐变量z 若x~N(mu, var*var)分布,则(x-mu)/var=z~N(0, 1)分布
- def reparameterize(self, mu, log_var):
- std = torch.exp(log_var / 2)
- eps = torch.randn_like(std)
- return mu + eps * std
- # 解码隐变量z
- def decode(self, z):
- h = F.relu(self.fc4(z))
- return F.sigmoid(self.fc5(h))
-
- # 计算重构值和隐变量z的分布参数
- def forward(self, x):
- mu, log_var = self.encode(x)# 从原始样本x中学习隐变量z的分布,即学习服从高斯分布均值与方差
- z = self.reparameterize(mu, log_var)# 将高斯分布均值与方差参数重表示,生成隐变量z
- x_reconst = self.decode(z)# 解码隐变量z,生成重构x’
- return x_reconst, mu, log_var# 返回重构值和隐变量的分布参数
-
- # 构造VAE实例对象
- model = VAE().to(device)
- print(model)
- # VAE( (fc1): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=400, bias=True)
- # (fc2): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=20, bias=True)
- # (fc3): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=20, bias=True)
- # (fc4): Linear(in_features=20, out_features=400, bias=True)
- # (fc5): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=784, bias=True))
-
- # 选择优化器,并传入VAE模型参数和学习率
- optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
- #开始训练
- for epoch in range(num_epochs):
- for i, (x, _) in enumerate(data_loader):
- # 前向传播
- x = x.to(device).view(-1, image_size)# 将batch_size*1*28*28 ---->batch_size*image_size 其中,image_size=1*28*28=784
- x_reconst, mu, log_var = model(x)# 将batch_size*748的x输入模型进行前向传播计算,重构值和服从高斯分布的隐变量z的分布参数(均值和方差)
-
- # 计算重构损失和KL散度
- # Compute reconstruction loss and kl divergence
- # For KL divergence, see Appendix B in VAE paper or http://yunjey47.tistory.com/43
- # 重构损失
- reconst_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy(x_reconst, x, size_average=False)
- # KL散度
- kl_div = - 0.5 * torch.sum(1 + log_var - mu.pow(2) - log_var.exp())
-
- # 反向传播与优化
- # 计算误差(重构误差和KL散度值)
- loss = reconst_loss + kl_div
- # 清空上一步的残余更新参数值
- optimizer.zero_grad()
- # 误差反向传播, 计算参数更新值
- loss.backward()
- # 将参数更新值施加到VAE model的parameters上
- optimizer.step()
- # 每迭代一定步骤,打印结果值
- if (i + 1) % 10 == 0:
- print ("Epoch[{}/{}], Step [{}/{}], Reconst Loss: {:.4f}, KL Div: {:.4f}"
- .format(epoch + 1, num_epochs, i + 1, len(data_loader), reconst_loss.item(), kl_div.item()))
-
- with torch.no_grad():
- # Save the sampled images
- # 保存采样值
- # 生成随机数 z
- z = torch.randn(batch_size, z_dim).to(device)# z的大小为batch_size * z_dim = 128*20
- # 对随机数 z 进行解码decode输出
- out = model.decode(z).view(-1, 1, 28, 28)
- # 保存结果值
- save_image(out, os.path.join(sample_dir, 'sampled-{}.png'.format(epoch + 1)))
-
- # Save the reconstructed images
- # 保存重构值
- # 将batch_size*748的x输入模型进行前向传播计算,获取重构值out
- out, _, _ = model(x)
- # 将输入与输出拼接在一起输出保存 batch_size*1*28*(28+28)=batch_size*1*28*56
- x_concat = torch.cat([x.view(-1, 1, 28, 28), out.view(-1, 1, 28, 28)], dim=3)
- save_image(x_concat, os.path.join(sample_dir, 'reconst-{}.png'.format(epoch + 1)))
大概长这么个样子:
附上一张结果图:




