- 1安装 flash_attn 时 ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘torch‘ 错误解决
- 2关于AndroidStudio Gradle 7.0版本及以上引用第三方库出现的问题_gradle无法访问其他模块的类
- 3和monkey的相处日记_monkey 设置权重
- 4linux驱动-内存分配_linux vmap 在哪个文件
- 5【沐风老师】3DMAX地板生成器插件FloorGenerator使用教程
- 6各个方法的不同和优缺点
- 7wps重复上一步快捷键_键盘上 F1~F12 的作用,你知道吗?
- 8Java编程技巧之单元测试用例编写流程_java单元测试用例怎么写
- 9JAVA程序员就业真的很难吗?_java真的很难找工作吗
- 10微信小程序 图书馆自习室座位预约管理系统设计与实现(源码+文档)_基于微信小程序的图书馆座位预约系统
人工智能 | ShowMeAI资讯日报 #2022.06.04_torch-ngp
赞
踩

ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架

工具库:Textnets - 基于网络的文本分析库
tags:[文本分析,网络化]
‘Textnets: text analysis with networks - Text analysis with networks.’ by John Boy
GitHub:http://github.com/jboynyc/textnets
工具库:NNSVS - 面向研究的神经网络歌唱合成库
tags:[音频合成,歌曲合成]
‘NNSVS - Neural network-based singing voice synthesis library for research’ by Ryuichi Yamamoto
GitHub:http://github.com/r9y9/nnsvs
工具库:PettingZoo - Python多智能体强化学习库
tags:[强化学习,多智能体,python]
‘PettingZoo - Gym for multi-agent reinforcement learning’
GitHub:http://github.com/Farama-Foundation/PettingZoo
工具库:PyTorch Metric Learning - PyTorch深度度量学习库
tags:[Pytorch,度量学习]
‘PyTorch Metric Learning - The easiest way to use deep metric learning in your application. Modular, flexible, and extensible. Written in PyTorch.’ by Kevin Musgrave
GitHub:http://github.com/KevinMusgrave/pytorch-metric-learning


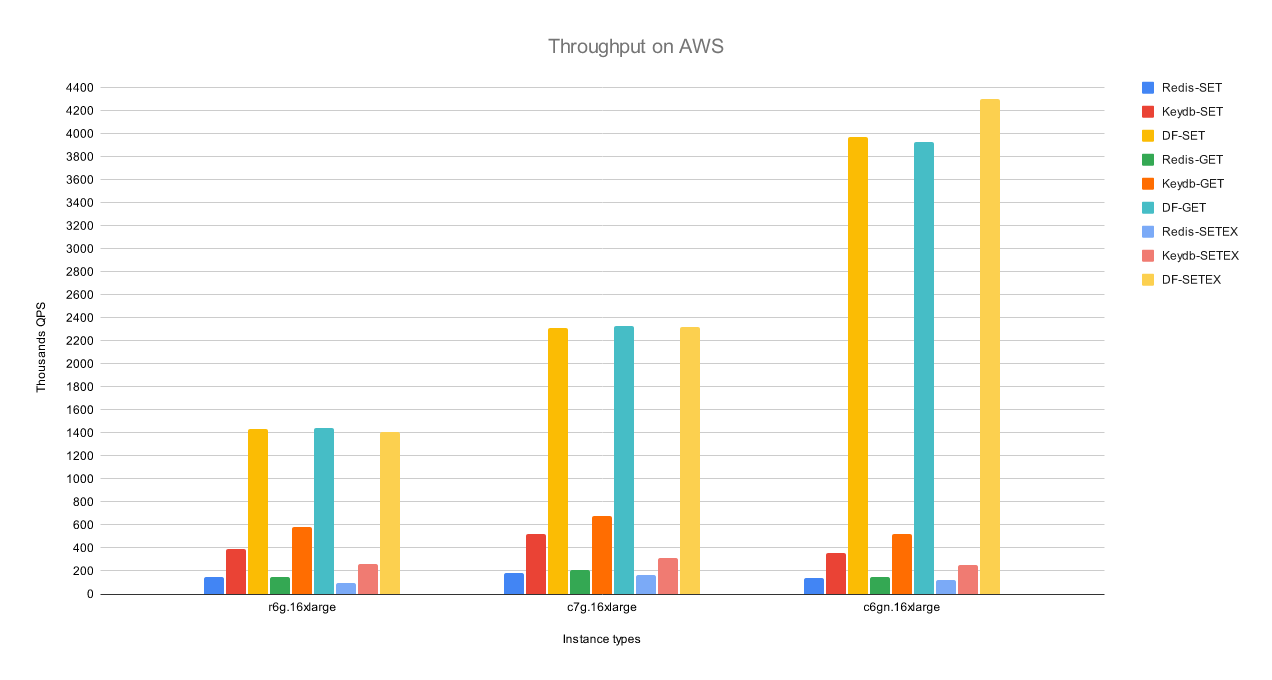
工具:dragonfly数据库工具
tags:[数据库,nosql,高性能数据库]
@作者介绍:Redis和Memcached的现代替代品,其性能可以达到Redis的 25倍,并且在单个实例上支持数百万QPS
‘dragonfly - A modern replacement for Redis and Memcached’
GitHub:http://github.com/dragonflydb/dragonfly
工具:datasette - 用于探索和发布数据的开源多功能工具
tags:[数据探索,数据分析,数据呈现]
‘datasette - An open source multi-tool for exploring and publishing data’ by Simon Willison
GitHub:http://github.com/simonw/datasette

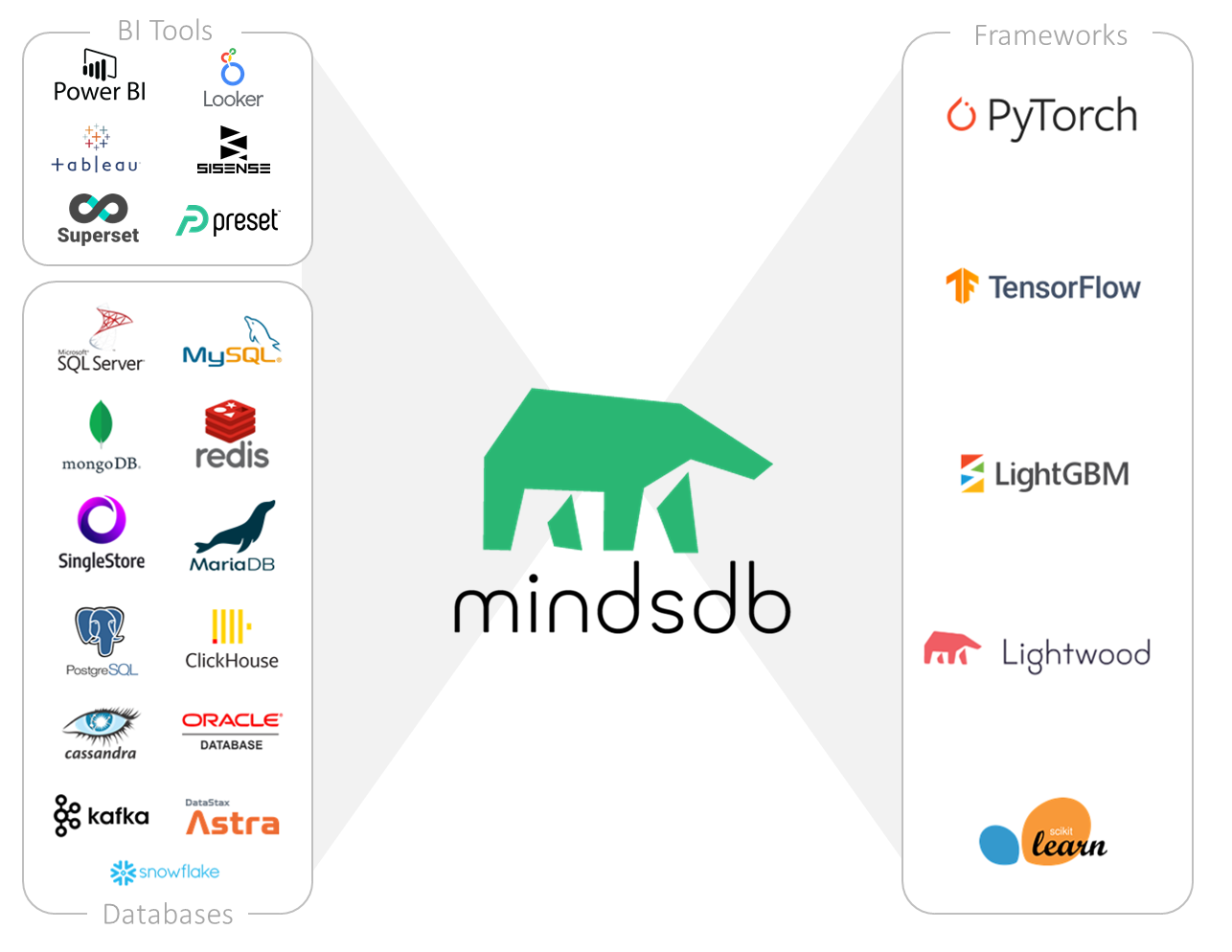
工具平台:MindsDB - 用SQL在数据库里做机器学习预测
tags:[SQL,机器学习]
‘MindsDB - In-Database Machine Learning’
GitHub:http://github.com/mindsdb/mindsdb
工具库:DoWhy - 端到端因果推理库
tags:[因果推理,端到端]
‘DoWhy - a Python library for causal inference that supports explicit modeling and testing of causal assumptions’ by PyWhy
GitHub:http://github.com/py-why/dowhy

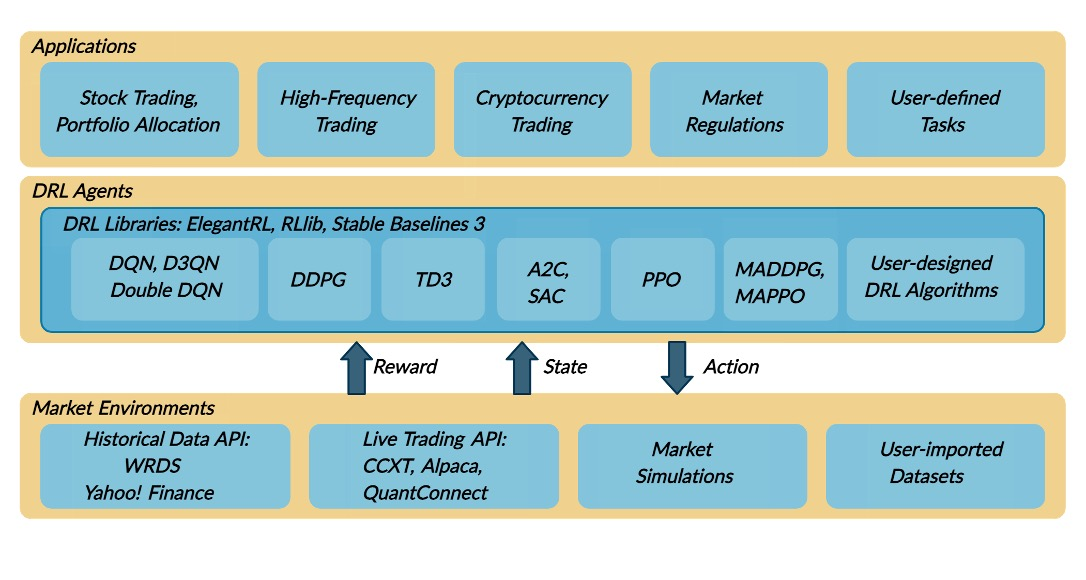
工具库:FinRL - 量化金融自动化股票交易深度强化学习库
tags:[量化,金融,交易,深度学习,强化学习]
‘FinRL: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Library for Automated Stock Trading in Quantitative Finance’ by AI4Finance-LLC
GitHub:http://github.com/AI4Finance-Foundation/FinRL

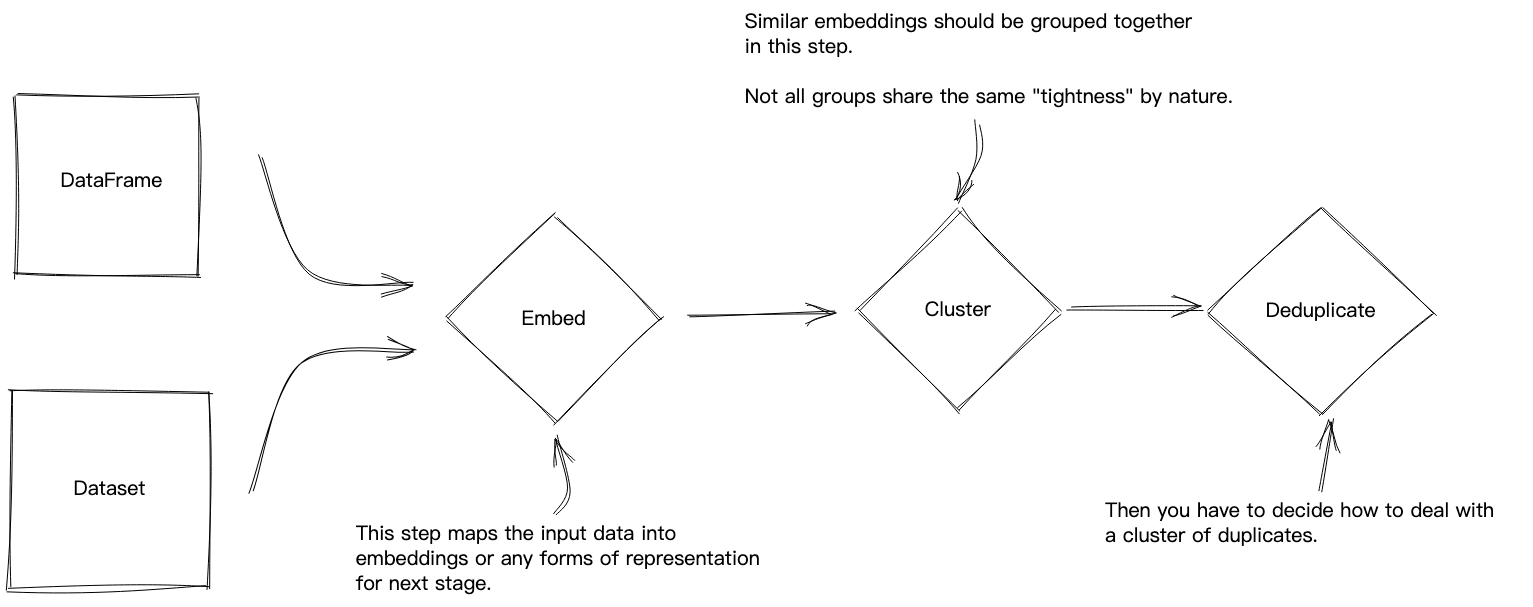
工具:text-dedup - 一站式文本去重工具
tags:[文本处理,去重]
‘text-dedup - All-in-one text de-duplication’ by Chenghao MOU
GitHub:http://github.com/ChenghaoMou/text-dedup
框架:Torch-RecHub - 易用的Lighting Pytorch推荐系统框架
tags:[推荐系统,框架,pytorch]
‘Torch-RecHub - A Lighting Pytorch Framework for Recommendation System, Easy-to-use and Easy-to-extend.’ by Mincai Lai
GitHub:http://github.com/morningsky/Torch-RecHub

2.项目&代码

项目:Kaggle Happywhale比赛第1名解决方案
‘1st Place Solution of Kaggle Happywhale Competition’ by Taiki Yamaguchi
比赛地址:<https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/happy-whale-and-dolphin/overview
GitHub:http://github.com/tyamaguchi17/kaggle-happywhale-1st-place-solution-charmq
3.博文&分享

教程:ACL 2022 Tutorial Slides 非自回归序列生成
tags:[ACL,教程,非自回归,序列生成]
‘Non-Autoregressive Sequence Generation’
GitHub:http://github.com/NAR-tutorial/acl2022
方案:Hugging Face Transformer模块企业级CPU/GPU推理服务器高效部署方案
tags:[**Transformer,部署]
‘Hugging Face Transformer submillisecond inference️ and deployment to production - Efficient, scalable and enterprise-grade CPU/GPU inference server for Hugging Face transformer models’ by Lefebvre Dalloz Services
GitHub:https://els-rd.github.io/transformer-deploy/
4.数据&资源

数据集:StreamingQA问答数据集
tags:[QA,问答,数据集]
‘StreamingQA’ by DeepMind
GitHub:http://github.com/deepmind/streamingqa
资源列表:深度学习蛋白质设计文献列表
tags:[蛋白质,深度学习,资料列表]
‘List of papers about Proteins Design using Deep Learning - List of papers about Proteins Design using Deep Learning’ by Sean Peldom Zhang
GitHub:http://github.com/Peldom/papers_for_protein_design_using_DL
资源列表:增量学习/持续学习/终生学习相关文献资源集
tags:[增量学习,持续学习,终生学习,资源列表]
‘Best Incremental Learning - An Incremental Learning, Continual Learning, and Life-Long Learning Repository’ by Vision-Intelligence-and-Robots-Group
GitHub:http://github.com/Vision-Intelligence-and-Robots-Group/Best-Incremental-Learning
资源列表:可信图神经网络资源列表
tags:[图神经网络,神经网络,资源列表]
‘Awesome Resources on Trustworthy Graph Neural Networks’ by He Zhang
GitHub:http://github.com/Radical3-HeZhang/Awesome-Trustworthy-GNNs
5.研究&论文

可以点击这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
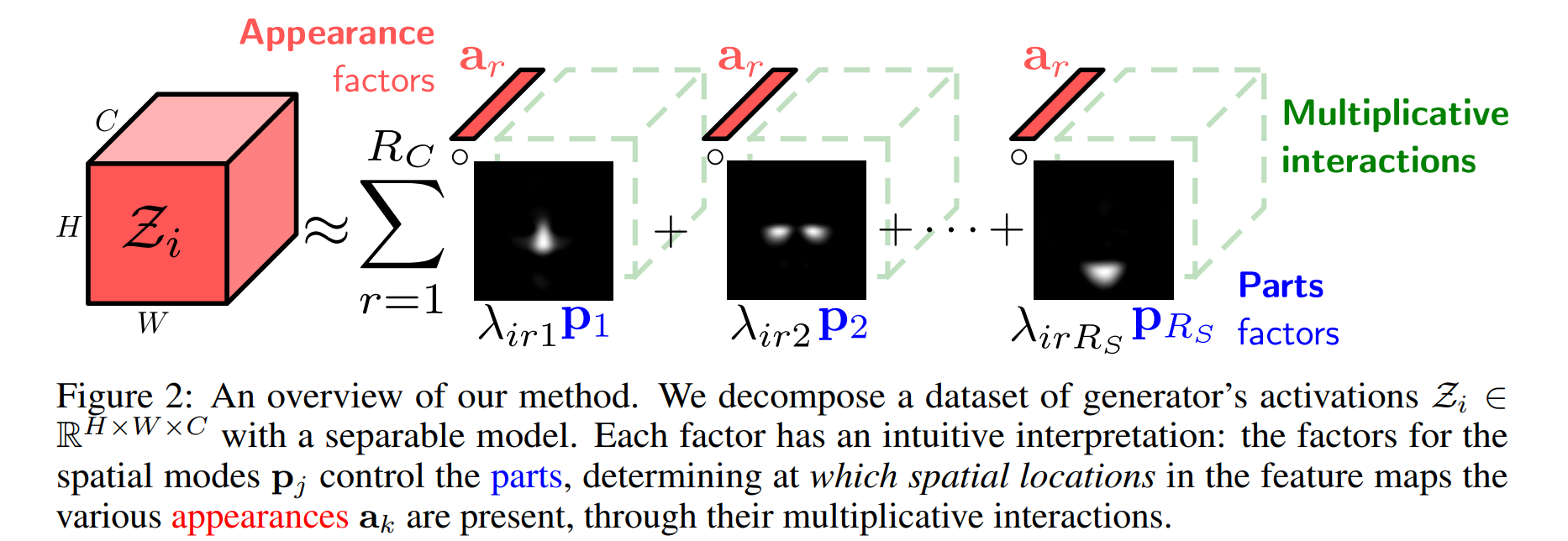
论文:PandA: Unsupervised Learning of Parts and Appearances in the Feature Maps of GANs
论文标题:PandA: Unsupervised Learning of Parts and Appearances in the Feature Maps of GANs
论文时间:31 May 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:无监督学习,生成对抗网络,模型理解
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00048
代码实现:https://github.com/james-oldfield/panda
论文作者:James Oldfield, Christos Tzelepis, Yannis Panagakis, Mihalis A. Nicolaou, Ioannis Patras
论文简介:Recent advances in the understanding of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have led to remarkable progress in visual editing and synthesis tasks, capitalizing on the rich semantics that are embedded in the latent spaces of pre-trained GANs. / 最近在对生成对抗网络 (GAN) 的理解方面取得了进展,利用嵌入在预训练 GAN 潜在空间中的丰富语义,在视觉编辑和合成任务方面取得了显着进展。
论文摘要:Recent advances in the understanding of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have led to remarkable progress in visual editing and synthesis tasks, capitalizing on the rich semantics that are embedded in the latent spaces of pre-trained GANs. However, existing methods are often tailored to specific GAN architectures and are limited to either discovering global semantic directions that do not facilitate localized control, or require some form of supervision through manually provided regions or segmentation masks. In this light, we present an architecture-agnostic approach that jointly discovers factors representing spatial parts and their appearances in an entirely unsupervised fashion. These factors are obtained by applying a semi-nonnegative tensor factorization on the feature maps, which in turn enables context-aware local image editing with pixel-level control. In addition, we show that the discovered appearance factors correspond to saliency maps that localize concepts of interest, without using any labels. Experiments on a wide range of GAN architectures and datasets show that, in comparison to the state of the art, our method is far more efficient in terms of training time and, most importantly, provides much more accurate localized control. Our code is available at https://github.com/james-oldfield/PandA .
最近在对生成对抗网络 (GAN) 的理解方面取得了进展,利用嵌入在预训练 GAN 潜在空间中的丰富语义,在视觉编辑和合成任务方面取得了显着进展。然而,现有的方法通常是针对特定的 GAN 架构量身定制的,并且仅限于发现不利于局部控制的全局语义方向,或者需要通过手动提供的区域或分割掩码进行某种形式的监督。有鉴于此,我们提出了一种与架构无关的方法,该方法以完全无监督的方式共同发现代表空间部分及其外观的因素。这些因子是通过在特征图上应用半非负张量分解来获得的,这反过来又可以通过像素级控制实现上下文感知的局部图像编辑。此外,我们展示了发现的外观因素对应于显著图(Saliency Map),这些显著图(Saliency Map)可以定位感兴趣的概念,而不使用任何标签。在广泛的 GAN 架构和数据集上进行的实验表明,与现有技术相比,我们的方法在训练时间方面效率更高,最重要的是,提供了更准确的局部控制。我们的代码可在 https://github.com/james-oldfield/PandA 获得。

论文:Fractional ridge regression: a fast, interpretable reparameterization of ridge regression
论文标题:Fractional ridge regression: a fast, interpretable reparameterization of ridge regression
论文时间:7 May 2020
所属领域:nan
对应任务:nan
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.03220
代码实现:https://github.com/danielhanchen/hyperlearn , https://github.com/nrdg/fracridge
论文作者:Ariel Rokem, Kendrick Kay
论文简介:Ridge regression (RR) is a regularization technique that penalizes the L2-norm of the coefficients in linear regression./岭回归 (RR) 是一种正则化技术,用于惩罚线性回归中系数的 L2 范数。
论文摘要:Ridge regression (RR) is a regularization technique that penalizes the L2-norm of the coefficients in linear regression. One of the challenges of using RR is the need to set a hyperparameter (α) that controls the amount of regularization. Cross-validation is typically used to select the best α from a set of candidates. However, efficient and appropriate selection of α can be challenging, particularly where large amounts of data are analyzed. Because the selected α depends on the scale of the data and predictors, it is not straightforwardly interpretable. Here, we propose to reparameterize RR in terms of the ratio γ between the L2-norms of the regularized and unregularized coefficients. This approach, called fractional RR (FRR), has several benefits: the solutions obtained for different γ are guaranteed to vary, guarding against wasted calculations, and automatically span the relevant range of regularization, avoiding the need for arduous manual exploration. We provide an algorithm to solve FRR, as well as open-source software implementations in Python and MATLAB (https://github.com/nrdg/fracridge). We show that the proposed method is fast and scalable for large-scale data problems, and delivers results that are straightforward to interpret and compare across models and datasets.
岭回归 (RR) 是一种正则化技术,用于惩罚线性回归中系数的 L2 范数。使用它的挑战之一是需要设置一个控制正则化量的超参数 (α)。交叉验证通常用于从一组候选者中选择最佳 α。然而,有效和适当地选择 α 可能具有挑战性,尤其是在分析大量数据的情况下。因为选择的 α 取决于数据和预测变量的规模,所以不能直接解释。在这里,我们建议根据正则化和非正则化系数的 L2 范数之间的比率 γ 重新参数化 RR。这种称为分数 RR (FRR) 的方法有几个好处:保证针对不同 γ 获得的解决方案是变化的,防止计算浪费,并自动跨越相关的正则化范围,避免了繁重的手动探索的需要。我们提供了解决 FRR 的算法,以及 Python 和 MATLAB 中的开源软件实现 (https://github.com/nrdg/fracridge)。我们表明,所提出的方法对于大规模数据问题是快速且可扩展的,并且提供的结果可以直接解释和跨模型和数据集进行比较。


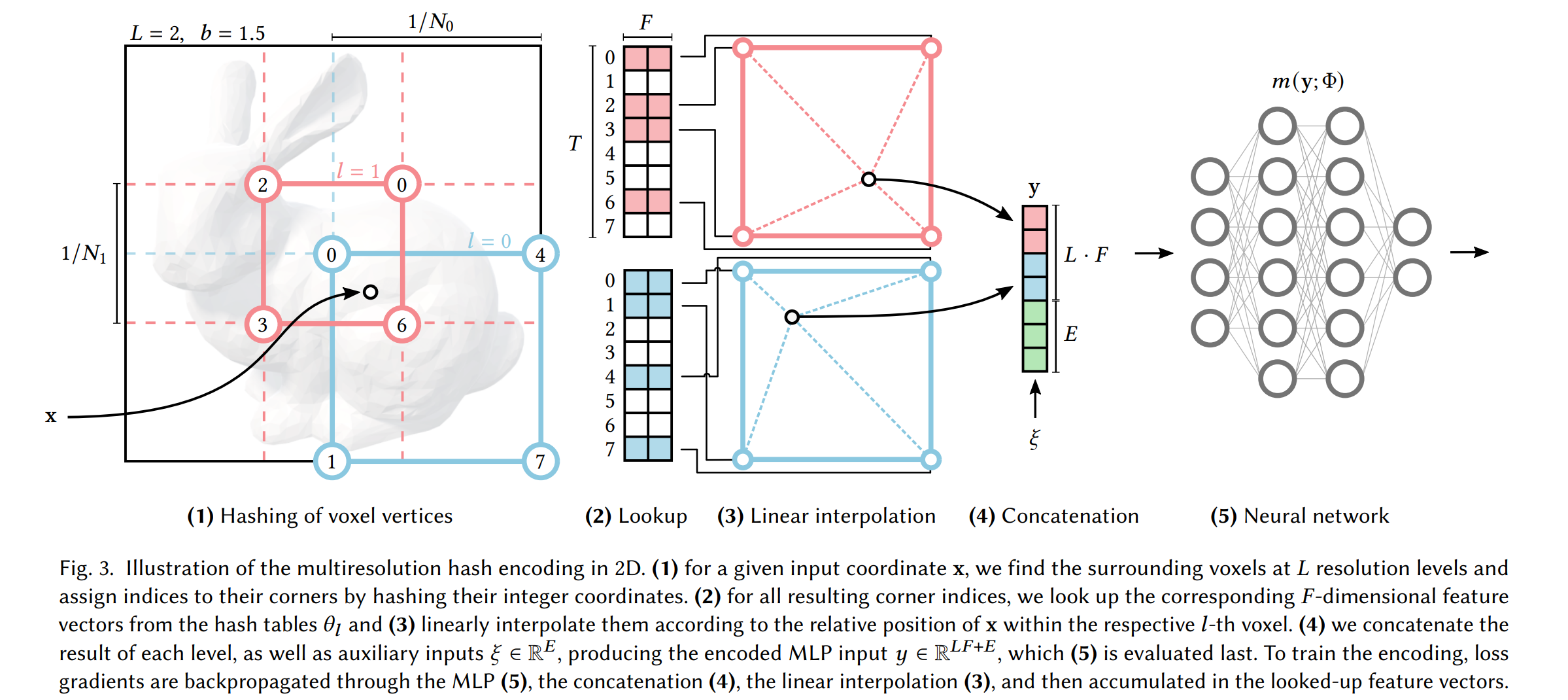
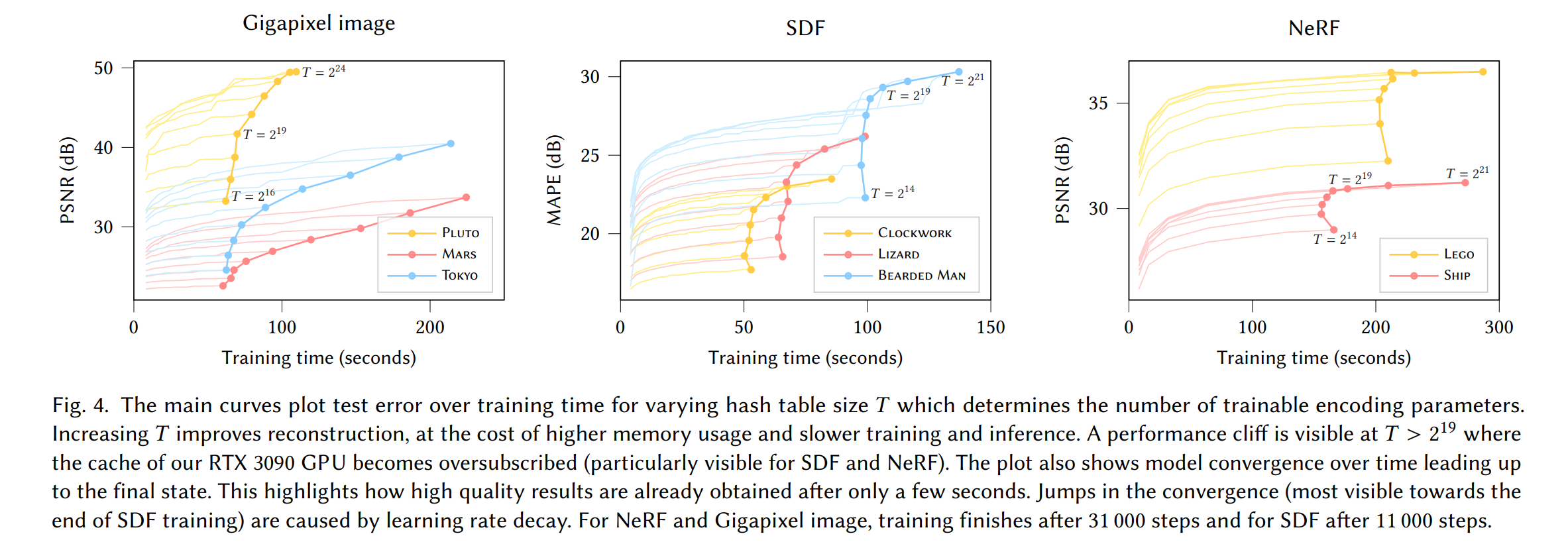
论文:Instant Neural Graphics Primitives with a Multiresolution Hash Encoding
论文标题:Instant Neural Graphics Primitives with a Multiresolution Hash Encoding
论文时间:16 Jan 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉
对应任务:3D Reconstruction,3D Shape Reconstruction,Neural Radiance Caching,Neural Rendering,Novel View Synthesis,3D重建,3D形状重建,神经辐射缓存,神经渲染,新视图合成,
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.05989
代码实现:https://github.com/nvlabs/instant-ngp , https://github.com/nvlabs/tiny-cuda-nn , https://github.com/ashawkey/torch-ngp , https://github.com/yashbhalgat/HashNeRF-pytorch , https://github.com/Jittor/JNeRF
论文作者:Thomas Müller, Alex Evans, Christoph Schied, Alexander Keller
论文简介:Neural graphics primitives, parameterized by fully connected neural networks, can be costly to train and evaluate. / 由完全连接神经网络参数化的神经图形基元,训练和评估的成本可能很高。
论文摘要:Neural graphics primitives, parameterized by fully connected neural networks, can be costly to train and evaluate. We reduce this cost with a versatile new input encoding that permits the use of a smaller network without sacrificing quality, thus significantly reducing the number of floating point and memory access operations: a small neural network is augmented by a multiresolution hash table of trainable feature vectors whose values are optimized through stochastic gradient descent. The multiresolution structure allows the network to disambiguate hash collisions, making for a simple architecture that is trivial to parallelize on modern GPUs. We leverage this parallelism by implementing the whole system using fully-fused CUDA kernels with a focus on minimizing wasted bandwidth and compute operations. We achieve a combined speedup of several orders of magnitude, enabling training of high-quality neural graphics primitives in a matter of seconds, and rendering in tens of milliseconds at a resolution of 1920×1080.
由全连接神经网络参数化的神经图形基元的训练和评估成本可能很高。我们通过一种通用的新输入编码来降低成本,该编码允许在不牺牲质量的情况下使用更小的网络,从而显着减少浮点和内存访问操作的数量:一个小型神经网络由可训练特征向量的多分辨率哈希表增强其值通过随机梯度下降优化。多分辨率结构允许网络消除哈希冲突的歧义,从而形成一个简单的架构,在现代 GPU 上并行化是效果不明显的。我们通过使用完全融合的 CUDA 内核实现整个系统来利用这种并行性,重点是最大限度地减少浪费的带宽和计算操作。我们实现了几个数量级的综合加速,能够在几秒钟内训练高质量的神经图形基元,并在几十毫秒内以 1920×1080 的分辨率进行渲染。
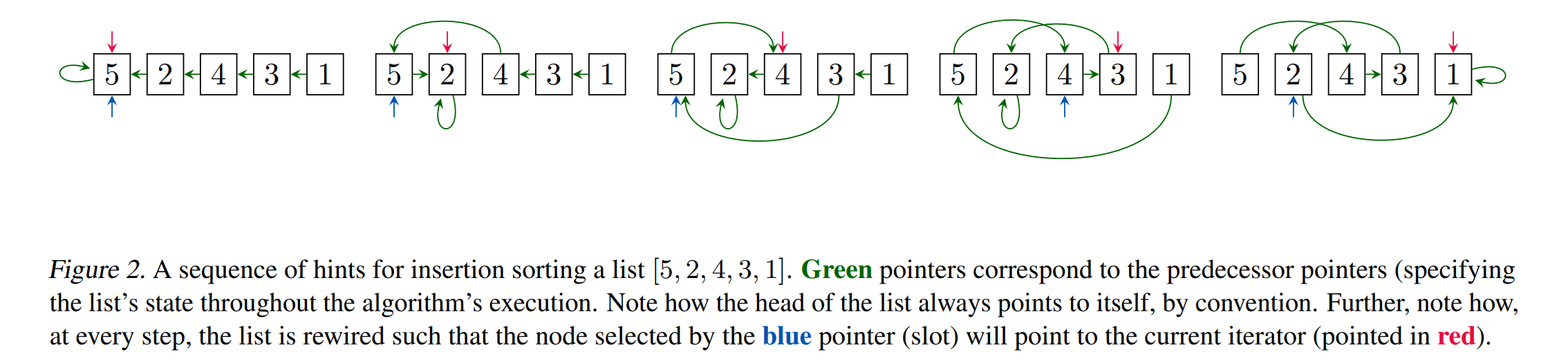
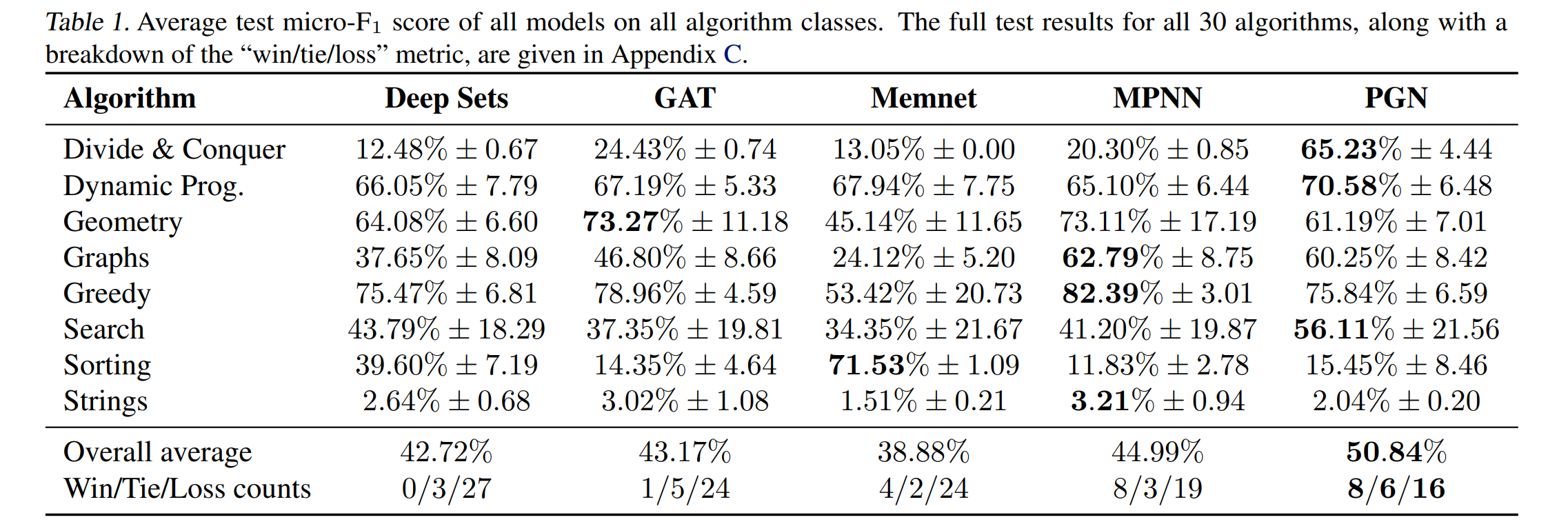
论文:The CLRS Algorithmic Reasoning Benchmark
论文标题:The CLRS Algorithmic Reasoning Benchmark
论文时间:31 May 2022
所属领域:Computer Code
对应任务:Learning to Execute
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.15659
代码实现:https://github.com/deepmind/clrs
论文作者:Petar Veličković, Adrià Puigdomènech Badia, David Budden, Razvan Pascanu, Andrea Banino, Misha Dashevskiy, Raia Hadsell, Charles Blundell
论文简介:Learning representations of algorithms is an emerging area of machine learning, seeking to bridge concepts from neural networks with classical algorithms./算法的学习表示是机器学习的一个新兴领域,旨在将神经网络的概念与经典算法联系起来。
论文摘要:Learning representations of algorithms is an emerging area of machine learning, seeking to bridge concepts from neural networks with classical algorithms. Several important works have investigated whether neural networks can effectively reason like algorithms, typically by learning to execute them. The common trend in the area, however, is to generate targeted kinds of algorithmic data to evaluate specific hypotheses, making results hard to transfer across publications, and increasing the barrier of entry. To consolidate progress and work towards unified evaluation, we propose the CLRS Algorithmic Reasoning Benchmark, covering classical algorithms from the Introduction to Algorithms textbook. Our benchmark spans a variety of algorithmic reasoning procedures, including sorting, searching, dynamic programming, graph algorithms, string algorithms and geometric algorithms. We perform extensive experiments to demonstrate how several popular algorithmic reasoning baselines perform on these tasks, and consequently, highlight links to several open challenges. Our library is readily available at https://github.com/deepmind/clrs .
算法的学习表示是机器学习的一个新兴领域,旨在将神经网络中的概念与经典算法联系起来。一些重要的工作已经研究了神经网络是否可以像算法一样有效地推理,通常是通过学习执行它们。然而,该领域的共同趋势是生成有针对性的算法数据来评估特定假设,这使得结果难以跨出版物转移,并增加了进入门槛。为了巩固进展并努力实现统一评估,我们提出了 CLRS 算法推理基准,涵盖了《算法导论》教科书中的经典算法。我们的基准测试涵盖各种算法推理过程,包括排序、搜索、动态规划、图算法、字符串算法和几何算法。我们进行了广泛的实验,以展示几种流行的算法推理基线如何在这些任务上执行,并因此突出显示与几个开放挑战的链接。我们的库可在 https://github.com/deepmind/clrs 上轻松获得。
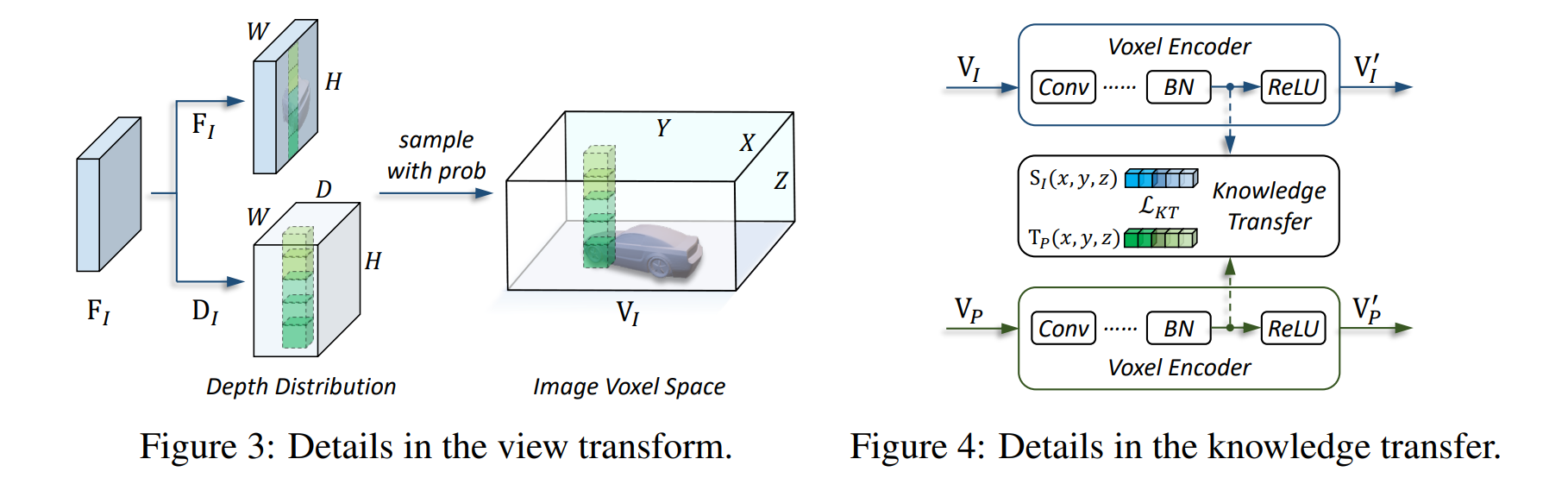
论文:Unifying Voxel-based Representation with Transformer for 3D Object Detection
论文标题:Unifying Voxel-based Representation with Transformer for 3D Object Detection
论文时间:1 Jun 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉
对应任务:3D Object Detection,Object Detection,Transfer Learning,3D物体检测,物体检测,迁移学习
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00630
代码实现:https://github.com/dvlab-research/uvtr
论文作者:Yanwei Li, Yilun Chen, Xiaojuan Qi, Zeming Li, Jian Sun, Jiaya Jia
论文简介:To this end, the modality-specific space is first designed to represent different inputs in the voxel feature space. / 为此,首先设计模态特定空间来表示体素特征空间中的不同输入。
论文摘要:In this work, we present a unified framework for multi-modality 3D object detection, named UVTR. The proposed method aims to unify multi-modality representations in the voxel space for accurate and robust single- or cross-modality 3D detection. To this end, the modality-specific space is first designed to represent different inputs in the voxel feature space. Different from previous work, our approach preserves the voxel space without height compression to alleviate semantic ambiguity and enable spatial interactions. Benefit from the unified manner, cross-modality interaction is then proposed to make full use of inherent properties from different sensors, including knowledge transfer and modality fusion. In this way, geometry-aware expressions in point clouds and context-rich features in images are well utilized for better performance and robustness. The transformer decoder is applied to efficiently sample features from the unified space with learnable positions, which facilitates object-level interactions. In general, UVTR presents an early attempt to represent different modalities in a unified framework. It surpasses previous work in single- and multi-modality entries and achieves leading performance in the nuScenes test set with 69.7%, 55.1%, and 71.1% NDS for LiDAR, camera, and multi-modality inputs, respectively. Code is made available at https://github.com/dvlab-research/UVTR .
在这项工作中,我们提出了一个用于多模态 3D 对象检测的统一框架,名为 UVTR。所提出的方法旨在统一体素空间中的多模态表示,以实现准确和鲁棒的单模态或跨模态 3D 检测。为此,首先设计模态特定空间来表示体素特征空间中的不同输入。与以前的工作不同,我们的方法在没有高度压缩的情况下保留了体素空间,以减轻语义歧义并实现空间交互。受益于统一的方式,然后提出了跨模态交互以充分利用来自不同传感器的固有属性,包括知识转移和模态融合。通过这种方式,点云中的几何感知表达式和图像中的上下文丰富的特征被很好地利用,以获得更好的性能和鲁棒性。转换器解码器用于有效地从具有可学习位置的统一空间中采样特征,这有助于对象级交互。一般来说,UVTR 提出了在统一框架中表示不同模式的早期尝试。它超越了之前在单模态和多模态输入方面的工作,并在 nuScenes 测试集中取得了领先的性能,LiDAR、相机和多模态输入的 NDS 分别为 69.7%、55.1% 和 71.1%。代码可在 https://github.com/dvlab-research/UVTR 获得。

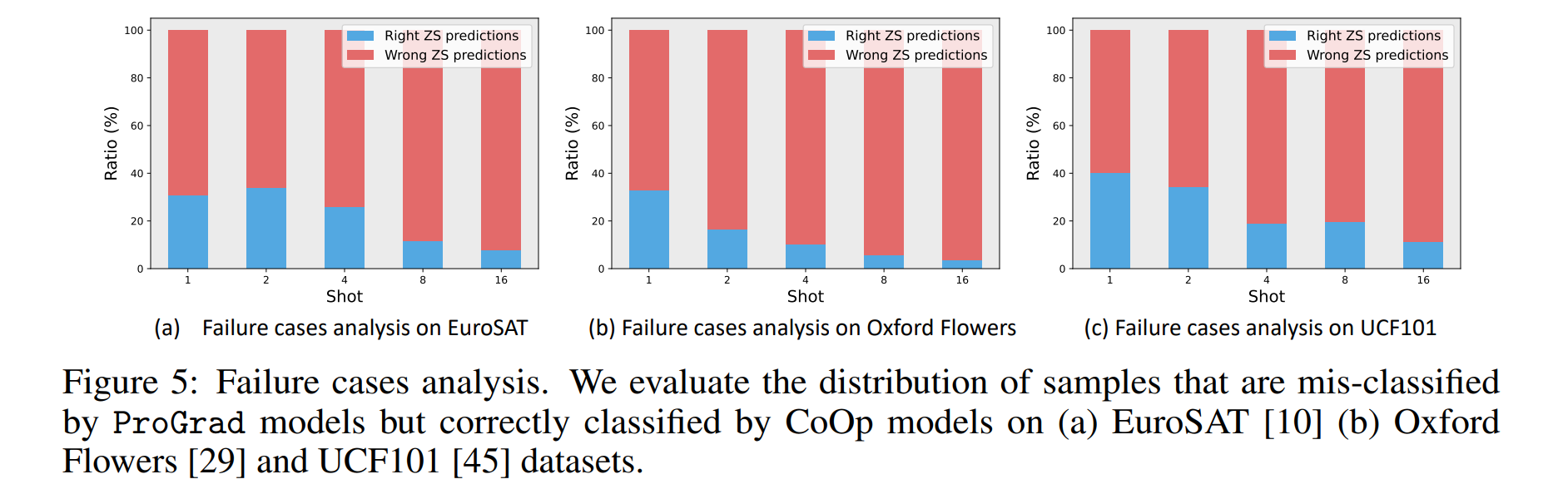
论文:Prompt-aligned Gradient for Prompt Tuning
论文标题:Prompt-aligned Gradient for Prompt Tuning
论文时间:30 May 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉,自然语言处理
对应任务:Data Augmentation/数据增强
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14865
代码实现:https://github.com/beierzhu/prompt-align
论文作者:Beier Zhu, Yulei Niu, Yucheng Han, Yue Wu, Hanwang Zhang
论文简介:Thanks to the large pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP, we can craft a zero-shot classifier by “prompt”, e. g., the confidence score of an image being “[CLASS]” can be obtained by using the VLM provided similarity measure between the image and the prompt sentence “a photo of a [CLASS]”. / 感谢像 CLIP 这样的大型预训练视觉语言模型 (VLM),我们可以通过“提示”来制作零样本分类器,例如。 g. 可以使用 VLM 提供的图像与提示句“a photo of a [CLASS]”之间的相似性度量来获得图像为“[CLASS]”的置信度分数。 /
论文摘要:Thanks to the large pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP, we can craft a zero-shot classifier by “prompt”, e.g., the confidence score of an image being “[CLASS]” can be obtained by using the VLM provided similarity measure between the image and the prompt sentence “a photo of a [CLASS]”. Therefore, prompt shows a great potential for fast adaptation of VLMs to downstream tasks if we fine-tune the prompt-based similarity measure. However, we find a common failure that improper fine-tuning may not only undermine the prompt’s inherent prediction for the task-related classes, but also for other classes in the VLM vocabulary. Existing methods still address this problem by using traditional anti-overfitting techniques such as early stopping and data augmentation, which lack a principled solution specific to prompt. We present Prompt-aligned Gradient, dubbed ProGrad, to prevent prompt tuning from forgetting the the general knowledge learned from VLMs. In particular, ProGrad only updates the prompt whose gradient is aligned (or non-conflicting) to the “general direction”, which is represented as the gradient of the KL loss of the pre-defined prompt prediction. Extensive experiments demonstrate the stronger few-shot generalization ability of ProGrad over state-of-the-art prompt tuning methods. Codes are available at https://github.com/BeierZhu/Prompt-align .
感谢像 CLIP 这样的大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLM),我们可以通过“prompt/提示”来制作零样本分类器,例如,可以获得图像为“[CLASS]”的置信度分数通过使用 VLM 提供的图像与提示句“a photo of a [CLASS]”之间的相似性度量。因此,如果我们微调基于提示的相似性度量,提示显示了 VLM 快速适应下游任务的巨大潜力。然而,我们发现一个常见的错误是,不正确的微调不仅会破坏提示对任务相关类的固有预测,而且还会破坏 VLM 词汇表中的其他类。现有的方法仍然通过使用early stopping早停止和数据增强等传统的抗过拟合技术来解决这个问题,这些技术缺乏针对提示的原则性解决方案。我们提出 Prompt-aligned Gradient,称为 ProGrad,以防止快速调整忘记从 VLM 学到的一般知识。特别是,ProGrad 仅将梯度对齐(或不冲突)的提示更新为“大方向”,表示为预定义提示预测的 KL 损失的梯度。大量的实验证明了 ProGrad 的小样本泛化能力优于最先进的快速调整方法。代码可在 https://github.com/BeierZhu/Prompt-align 获得。

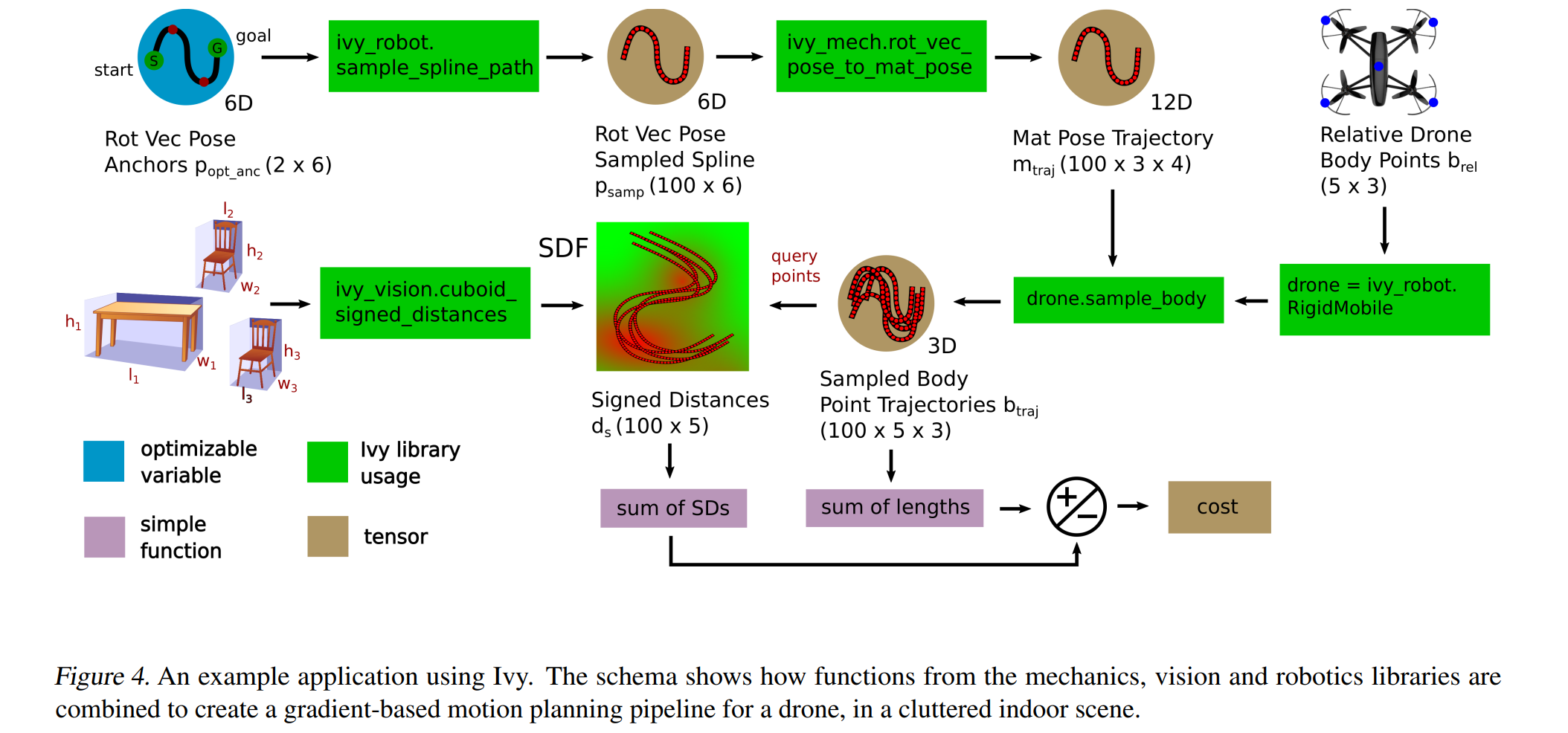
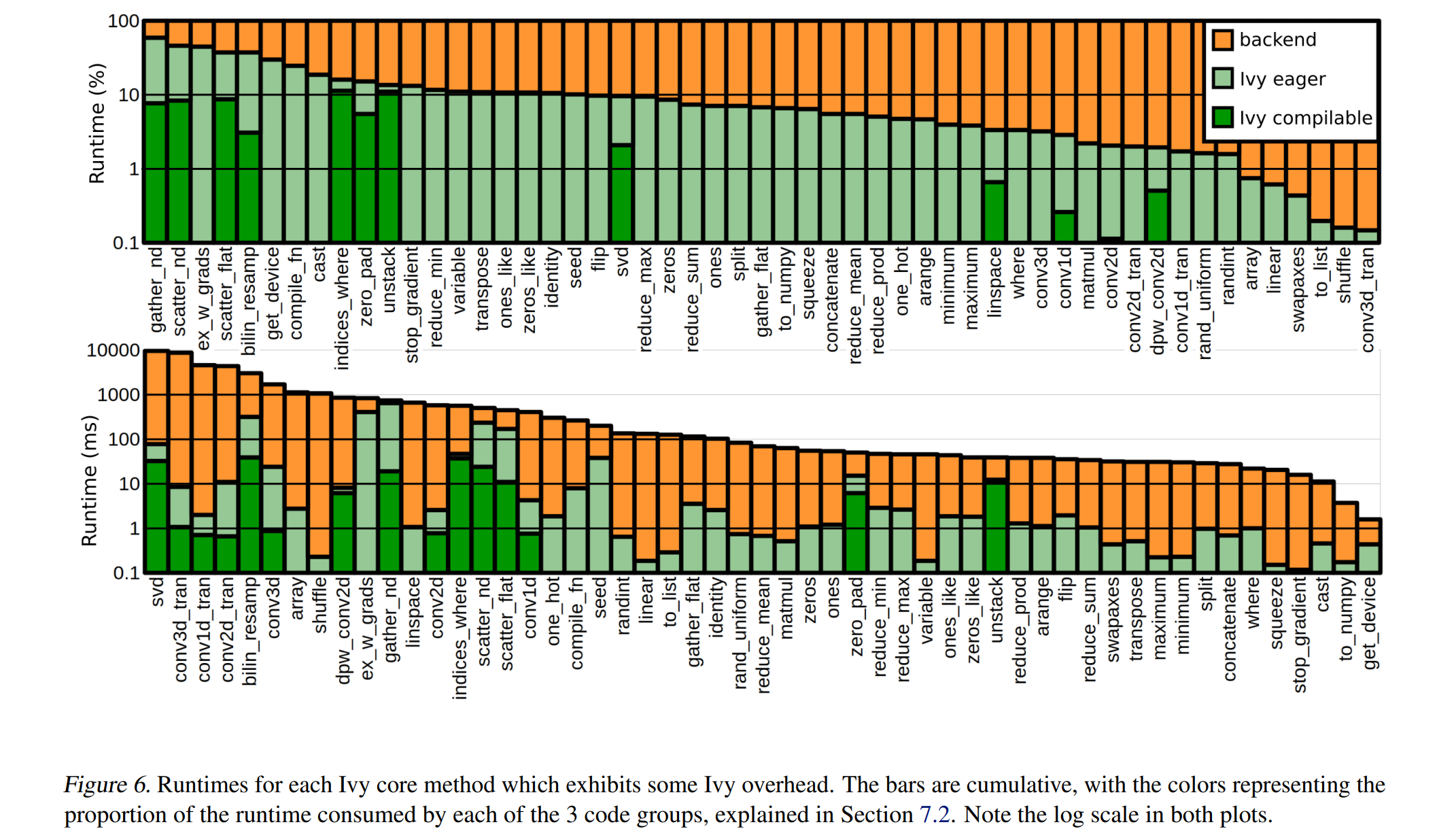
论文:Ivy: Templated Deep Learning for Inter-Framework Portability
论文标题:Ivy: Templated Deep Learning for Inter-Framework Portability
论文时间:4 Feb 2021
所属领域:nan
对应任务:
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.02886
代码实现:https://github.com/ivy-dl/ivy
论文作者:Daniel Lenton, Fabio Pardo, Fabian Falck, Stephen James, Ronald Clark
论文简介:We introduce Ivy, a templated Deep Learning (DL) framework which abstracts existing DL frameworks. / 我们介绍了 Ivy,一个模板化的深度学习 (DL) 框架,它抽象了现有的 DL 框架。
论文摘要:We introduce Ivy, a templated Deep Learning (DL) framework which abstracts existing DL frameworks. Ivy unifies the core functions of these frameworks to exhibit consistent call signatures, syntax and input-output behaviour. New high-level framework-agnostic functions and classes, which are usable alongside framework-specific code, can then be implemented as compositions of the unified low-level Ivy functions. Ivy currently supports TensorFlow, PyTorch, MXNet, Jax and NumPy. We also release four pure-Ivy libraries for mechanics, 3D vision, robotics, and differentiable environments. Through our evaluations, we show that Ivy can significantly reduce lines of code with a runtime overhead of less than 1% in most cases. We welcome developers to join the Ivy community by writing their own functions, layers and libraries in Ivy, maximizing their audience and helping to accelerate DL research through inter-framework codebases. More information can be found at https://ivy-dl.org .
我们介绍了 Ivy,一个模板化的深度学习(DL)框架,它抽象了现有的 DL 框架。 Ivy 统一了这些框架的核心功能,以展示一致的调用签名、语法和输入输出行为。新的与框架无关的高级函数和类可以与特定于框架的代码一起使用,然后可以作为统一的低级 Ivy 函数的组合来实现。 Ivy 目前支持 TensorFlow、PyTorch、MXNet、Jax 和 NumPy。我们还发布了四个用于力学、3D 视觉、机器人和可微环境的纯 Ivy 库。通过我们的评估,我们表明,在大多数情况下,Ivy 可以显着减少代码行数,运行时开销不到 1%。我们欢迎开发人员通过在 Ivy 中编写自己的函数、层和库来加入 Ivy 社区,最大限度地扩大他们的受众,并通过跨框架代码库帮助加速 DL 研究。更多信息可以在 https://ivy-dl.org 找到。
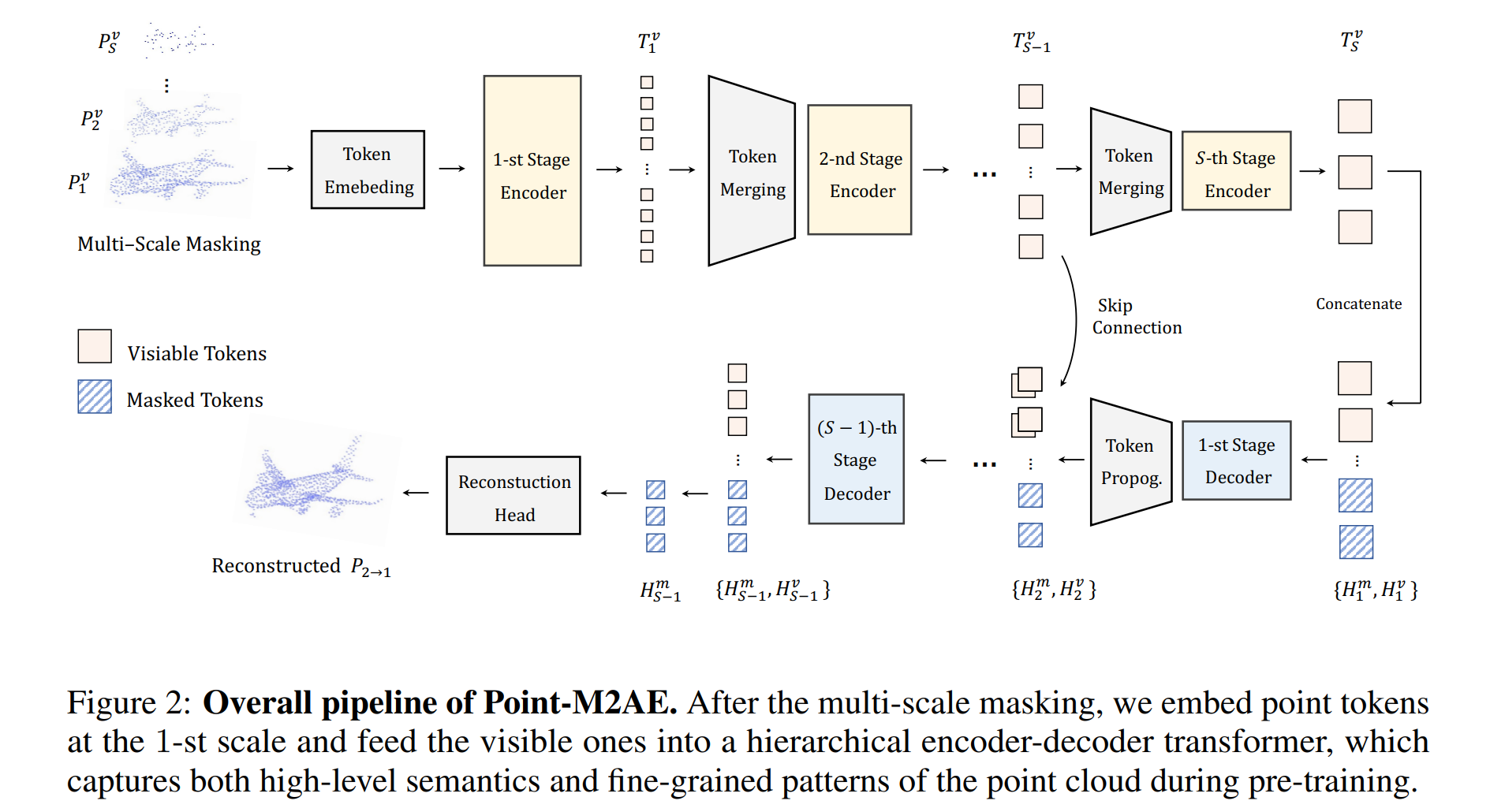
论文:Point-M2AE: Multi-scale Masked Autoencoders for Hierarchical Point Cloud Pre-training
论文标题:Point-M2AE: Multi-scale Masked Autoencoders for Hierarchical Point Cloud Pre-training
论文时间:28 May 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉
对应任务:3D Object Detection,Object Detection,Point Cloud Pre-training,Representation Learning,Self-Supervised Learning,3D物体检测,物体检测,点云预训练,表征学习,自监督学习
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14401
代码实现:https://github.com/zrrskywalker/point-m2ae
论文作者:Renrui Zhang, Ziyu Guo, Peng Gao, Rongyao Fang, Bin Zhao, Dong Wang, Yu Qiao, Hongsheng Li
论文简介:By fine-tuning on downstream tasks, Point-M2AE achieves 86. 43% accuracy on ScanObjectNN, +3. 36% to the second-best, and largely benefits the few-shot classification, part segmentation and 3D object detection with the hierarchical pre-training scheme. / 通过对下游任务的微调,Point-M2AE 在 ScanObjectNN 上达到 86. 43% 的准确率,+3.36% 的次优提升,并在很大程度上有利于使用分层预训练方案进行少样本分类、部分分割和 3D 对象检测。
论文摘要:Masked Autoencoders (MAE) have shown great potentials in self-supervised pre-training for language and 2D image transformers. However, it still remains an open question on how to exploit masked autoencoding for learning 3D representations of irregular point clouds. In this paper, we propose Point-M2AE, a strong Multi-scale MAE pre-training framework for hierarchical self-supervised learning of 3D point clouds. Unlike the standard transformer in MAE, we modify the encoder and decoder into pyramid architectures to progressively model spatial geometries and capture both fine-grained and high-level semantics of 3D shapes. For the encoder that downsamples point tokens by stages, we design a multi-scale masking strategy to generate consistent visible regions across scales, and adopt a local spatial self-attention mechanism to focus on neighboring patterns. By multi-scale token propagation, the lightweight decoder gradually upsamples point tokens with complementary skip connections from the encoder, which further promotes the reconstruction from a global-to-local perspective. Extensive experiments demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of Point-M2AE for 3D representation learning. With a frozen encoder after pre-training, Point-M2AE achieves 92.9% accuracy for linear SVM on ModelNet40, even surpassing some fully trained methods. By fine-tuning on downstream tasks, Point-M2AE achieves 86.43% accuracy on ScanObjectNN, +3.36% to the second-best, and largely benefits the few-shot classification, part segmentation and 3D object detection with the hierarchical pre-training scheme. Code will be available at https://github.com/ZrrSkywalker/Point-M2AE .
Masked Autoencoders (MAE) 在语言和 2D 图像转换器的自监督预训练中显示出巨大的潜力。然而,如何利用掩码自动编码来学习不规则点云的 3D 表示仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。在本文中,我们提出了 Point-M2AE,这是一个强大的多尺度 MAE 预训练框架,用于 3D 点云的分层自监督学习。与 MAE 中的标准转换器不同,我们将编码器和解码器修改为金字塔架构,以逐步建模空间几何形状并捕获 3D 形状的细粒度和高级语义。对于分阶段对点标记进行下采样的编码器,我们设计了一种多尺度掩蔽策略来生成跨尺度一致的可见区域,并采用局部空间自注意力机制来关注相邻模式。通过多尺度令牌传播,轻量级解码器逐渐对具有来自编码器的互补跳过连接的点令牌进行上采样,这进一步促进了从全局到局部的重构。大量实验证明了 Point-M2AE 在 3D 表示学习方面的最新性能。使用预训练后的冻结编码器,Point-M2AE 在 ModelNet40 上实现了 92.9% 的线性 SVM 准确率,甚至超过了一些经过充分训练的方法。通过对下游任务的微调,Point-M2AE 在 ScanObjectNN 上的准确率达到 86.43%,次优提高 3.36%,并且通过分层预训练方案在很大程度上有利于少样本分类、部分分割和 3D 对象检测。代码将在 https://github.com/ZrrSkywalker/Point-M2AE 上提供。

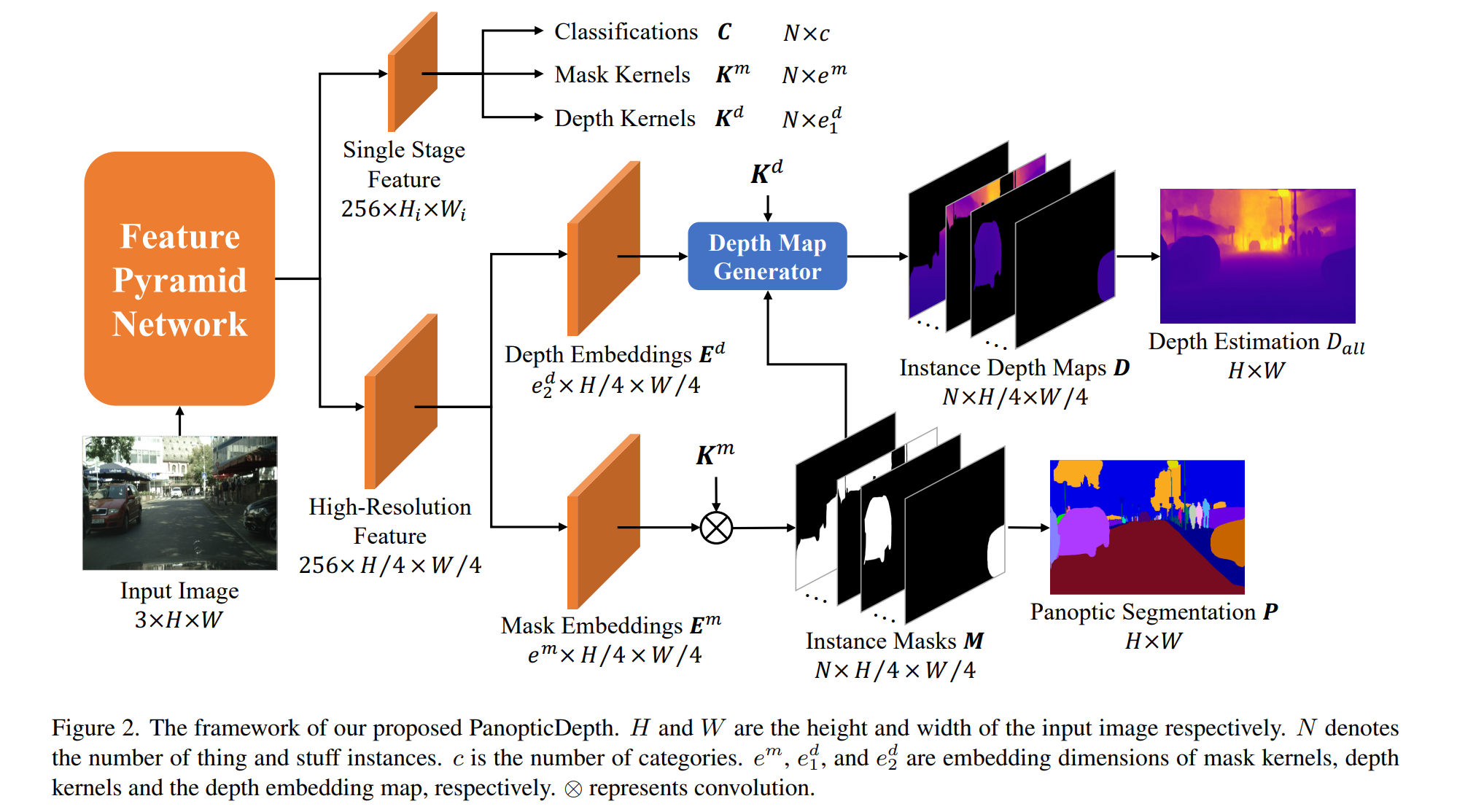
论文:PanopticDepth: A Unified Framework for Depth-aware Panoptic Segmentation
论文标题:PanopticDepth: A Unified Framework for Depth-aware Panoptic Segmentation
论文时间:1 Jun 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision/计算机视觉
对应任务:Depth Estimation,Panoptic Segmentation,深度估计,全景分割
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00468
代码实现:https://github.com/naiyugao/panopticdepth
论文作者:Naiyu Gao, Fei He, Jian Jia, Yanhu Shan, Haoyang Zhang, Xin Zhao, Kaiqi Huang
论文简介:To overcome these limitations, we propose a unified framework for the DPS task by applying a dynamic convolution technique to both the PS and depth prediction tasks. / 为了克服这些限制,我们通过将动态卷积技术应用于 PS 和深度预测任务,为 DPS 任务提出了一个统一的框架。
论文摘要:This paper presents a unified framework for depth-aware panoptic segmentation (DPS), which aims to reconstruct 3D scene with instance-level semantics from one single image. Prior works address this problem by simply adding a dense depth regression head to panoptic segmentation (PS) networks, resulting in two independent task branches. This neglects the mutually-beneficial relations between these two tasks, thus failing to exploit handy instance-level semantic cues to boost depth accuracy while also producing sub-optimal depth maps. To overcome these limitations, we propose a unified framework for the DPS task by applying a dynamic convolution technique to both the PS and depth prediction tasks. Specifically, instead of predicting depth for all pixels at a time, we generate instance-specific kernels to predict depth and segmentation masks for each instance. Moreover, leveraging the instance-wise depth estimation scheme, we add additional instance-level depth cues to assist with supervising the depth learning via a new depth loss. Extensive experiments on Cityscapes-DPS and SemKITTI-DPS show the effectiveness and promise of our method. We hope our unified solution to DPS can lead a new paradigm in this area. Code is available at https://github.com/NaiyuGao/PanopticDepth .
本文提出了一个统一的深度感知全景分割(DPS)框架,旨在从单个图像重建具有实例级语义的 3D 场景。先前的工作通过简单地将密集深度回归头添加到全景分割(PS)网络来解决这个问题,从而产生两个独立的任务分支。这忽略了这两个任务之间的互利关系,因此未能利用方便的实例级语义线索来提高深度准确性,同时也产生次优深度图。为了克服这些限制,我们通过将动态卷积技术应用于 PS 和深度预测任务,提出了 DPS 任务的统一框架。具体来说,我们不是一次预测所有像素的深度,而是生成特定于实例的内核来预测每个实例的深度和分割掩码。此外,利用实例深度估计方案,我们添加了额外的实例级深度提示,以通过新的深度损失来帮助监督深度学习。在 Cityscapes-DPS 和 SemKITTI-DPS 上的大量实验表明了我们方法的有效性和前景。我们希望我们对 DPS 的统一解决方案能够引领该领域的新范式。代码可在 https://github.com/NaiyuGao/PanopticDepth 获得。

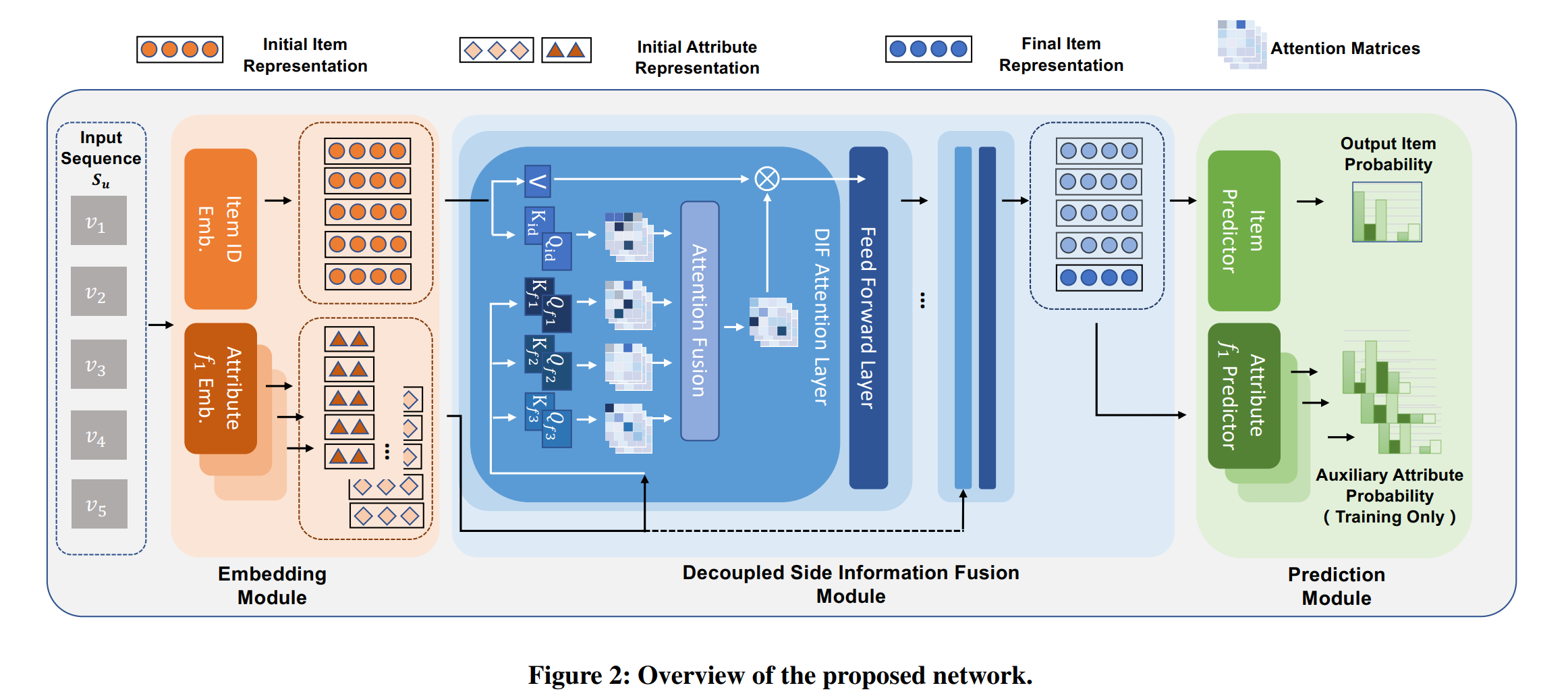
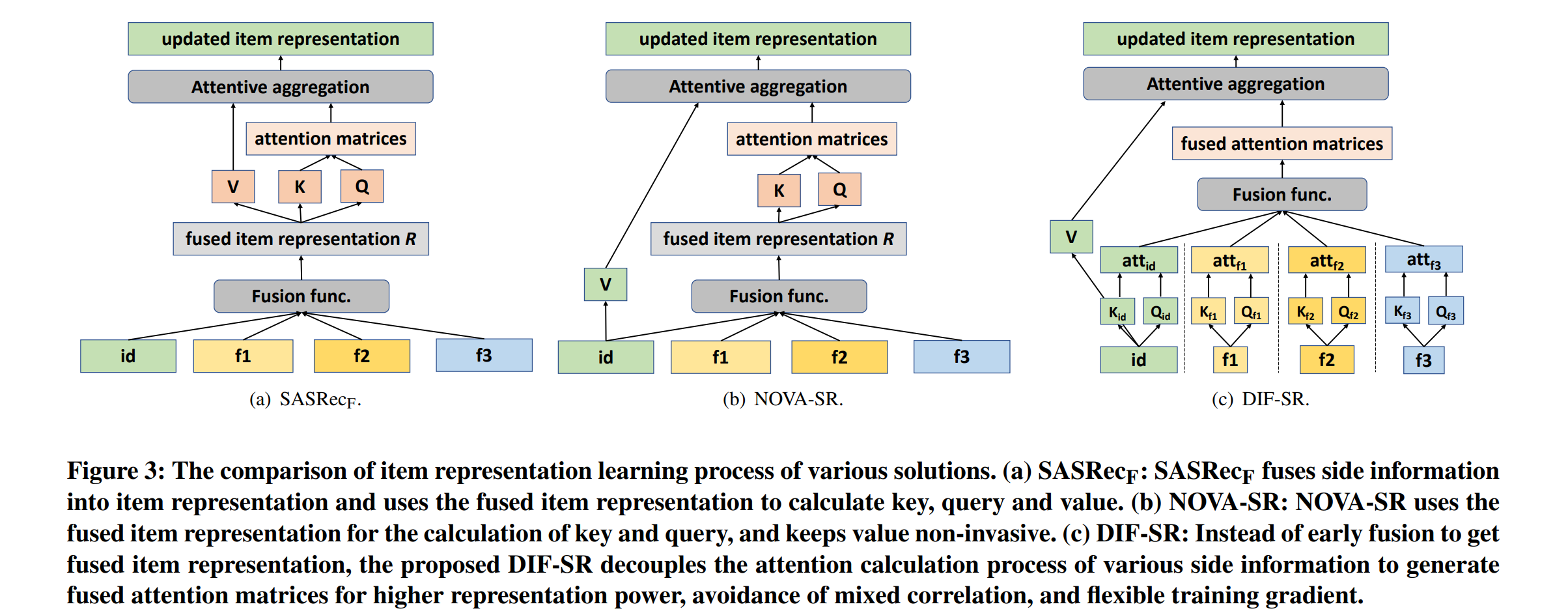
论文:Decoupled Side Information Fusion for Sequential Recommendation
论文标题:Decoupled Side Information Fusion for Sequential Recommendation
论文时间:23 Apr 2022
所属领域:推荐系统
对应任务:Representation Learning,Sequential Recommendation,表征学习,序列推荐
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.11046
代码实现:https://github.com/AIM-SE/DIF-SR
论文作者:Yueqi Xie, Peilin Zhou, Sunghun Kim
论文简介:Motivated by this, we propose Decoupled Side Information Fusion for Sequential Recommendation (DIF-SR), which moves the side information from the input to the attention layer and decouples the attention calculation of various side information and item representation. / 受此启发,我们提出了 Decoupled Side Information Fusion for Sequential Recommendation (DIF-SR),将辅助信息从输入移动到注意力层,将各种辅助信息和项目表示的注意力计算解耦。
论文摘要:Side information fusion for sequential recommendation (SR) aims to effectively leverage various side information to enhance the performance of next-item prediction. Most state-of-the-art methods build on self-attention networks and focus on exploring various solutions to integrate the item embedding and side information embeddings before the attention layer. However, our analysis shows that the early integration of various types of embeddings limits the expressiveness of attention matrices due to a rank bottleneck and constrains the flexibility of gradients. Also, it involves mixed correlations among the different heterogeneous information resources, which brings extra disturbance to attention calculation. Motivated by this, we propose Decoupled Side Information Fusion for Sequential Recommendation (DIF-SR), which moves the side information from the input to the attention layer and decouples the attention calculation of various side information and item representation. We theoretically and empirically show that the proposed solution allows higher-rank attention matrices and flexible gradients to enhance the modeling capacity of side information fusion. Also, auxiliary attribute predictors are proposed to further activate the beneficial interaction between side information and item representation learning. Extensive experiments on four real-world datasets demonstrate that our proposed solution stably outperforms state-of-the-art SR models. Further studies show that our proposed solution can be readily incorporated into current attention-based SR models and significantly boost performance. Our source code is available at https://github.com/AIM-SE/DIF-SR .
用于序列推荐(SR)的边信息融合旨在有效地利用各种边信息来提高下一项预测的性能。大多数最先进的方法都建立在自注意力网络之上,并专注于探索各种解决方案,以在注意力层之前集成项目嵌入和边信息嵌入。然而,我们的分析表明,由于秩瓶颈,各种嵌入的早期集成限制了注意力矩阵的表达能力,并限制了梯度的灵活性。此外,它涉及不同异构信息资源之间的混合相关性,给注意力计算带来了额外的干扰。受此启发,我们提出了序列推荐的解耦辅助信息融合(DIF-SR),它将辅助信息从输入移动到注意层,并将各种辅助信息和项目表示的注意力计算解耦。我们从理论上和经验上表明,所提出的解决方案允许更高等级的注意力矩阵和灵活的梯度来增强边信息融合的建模能力。此外,还提出了辅助属性预测器以进一步激活辅助信息和项目表示学习之间的有益交互。对四个真实世界数据集的广泛实验表明,我们提出的解决方案稳定地优于最先进的 SR 模型。进一步的研究表明,我们提出的解决方案可以很容易地融入当前基于注意力的 SR 模型并显着提高性能。我们的源代码可在 https://github.com/AIM-SE/DIF-SR 获得。
我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。




