字段
我们对字段已经有了好的起点,我们在 HelloWorldQuery 中有两个字段:hello 和 world。他们都是单值字段。
现在我们可以扩展应用来支持复杂类型。例如,我们想象一下,我们在创建库存 Inventory 系统,我们从创建 Item 类型开始。
- public class Item
- {
- public string Barcode { get; set; }
-
- public string Title { get; set; }
-
- public decimal SellingPrice { get; set; }
- }
但是,我们不能直接查询这个类型,因为它不是 GraphQL 对象类型。也就是 ObjectGraphType。
为了使它可以通过 GraphQL 查询,我们需要从 ObjectGraphType 派生一个新的类型。
另外主要注意的是 ObjectGraphType 使用泛型类型。如你所猜中的,我们将 Item 作为泛型参数传递。
- public class ItemType : ObjectGraphType<Item>
- {
- public ItemType()
- {
- Field(i => i.Barcode);
- Field(i => i.Title);
- Field(i => i.SellingPrice);
- }
- }
需要注意两件事。
首先,我们不在字段中定义类型。它们将自动由库获取,比如 .net 的字符串类型将自动处理为 StringGraphType。
其次,我们使用 Lambda 表达式来映射属性,以及字段的名称等等。
属性映射的概念对于熟悉 DTOs/ViewModels 的开发者很容易理解。所以,我们并没有进行额外的类型创建工作。
然后,我们需要在 Query 对象的根注册 ItemType 。
- public HelloWorldQuery()
- {
- ...
- ...
-
- Field<ItemType>(
- "item",
- resolve: context =>
- {
- return new Item {
- Barcode = "123",
- Title = "Headphone",
- SellingPrice = 12.99M
- };
- }
- );
- }
此时,在试图查询 item 字段的时候,我们将会返回一个硬编码的 Item 实例。我们可以如下运行应用并测试。
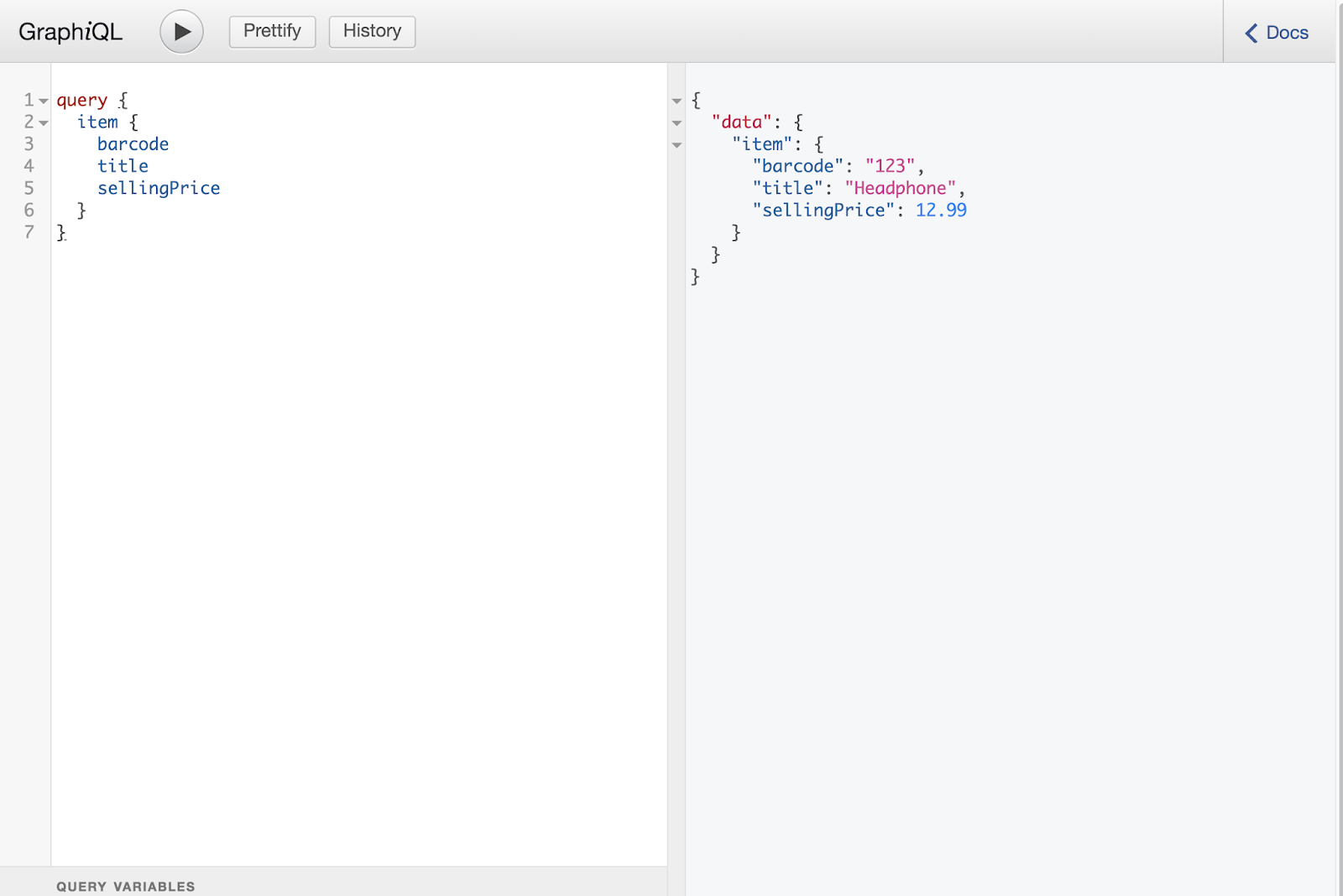
参数
使用硬编码的实例总是不爽的,为什么不引入一个提供项目列表的数据源呢?
- public class DataSource
- {
- public IList<Item> Items
- {
- get;
- set;
- }
-
- public DataSource()
- {
- Items = new List<Item>(){
- new Item { Barcode= "123", Title="Headphone", SellingPrice=50},
- new Item { Barcode= "456", Title="Keyboard", SellingPrice= 40},
- new Item { Barcode= "789", Title="Monitor", SellingPrice= 100}
- };
- }
-
- public Item GetItemByBarcode(string barcode)
- {
- return Items.First(i => i.Barcode.Equals(barcode));
- }
- }
除了 Items 集合之外,我们还需要一个方法通过 barcode 字符串参数来返回匹配的单个项目。
太棒了!我们现在可以为查询提供一个参数,我们需要将 item 这个 GraphQL 字段调整一下。
- Field<ItemType>(
- "item",
- arguments: new QueryArguments(new QueryArgument<StringGraphType> { Name = "barcode" }),
- resolve: context =>
- {
- var barcode = context.GetArgument<string>("barcode");
- return new DataSource().GetItemByBarcode(barcode);
- }
- );
这里可以有一系列参数;有些可以是必须的,有些可以是可选的。我们依次指定单个的参数,它的类型应该是 QueryArgument<T>。Name 表示参数的名称。
现在,我们可以在 GraphiQL 中构建一个查询,如下所示:
- query {
- item (barcode: "123") {
- title
- selling price
- }
- }
此时,barcode 是可选的,所以,如果您的查询如下所示,
- query {
- item {
- title
- sellingPrice
- }
- }
将会得到如下的错误
Error trying to resolve item.
我们没有加入任何的保护代码,所以这很正常。为了确保用户提供了参数,我们可以将参数设置为非空,如下所示:
QueryArgument<NonNullGraphType<StringGraphType>> { Name = "barcode" }
现在,如果您没有提供参数,将会收到如下的错误信息。
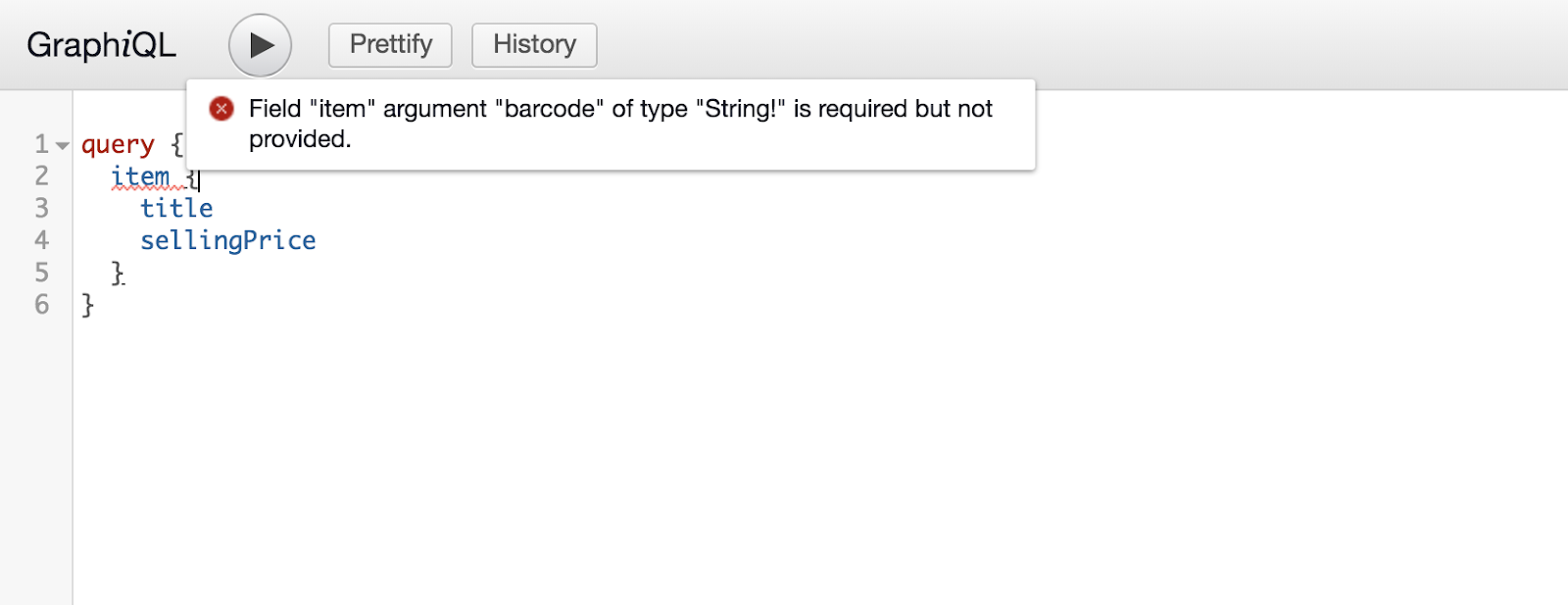
变量
现在,是让参数自己动态化的时候了。我们不希望在改变参数值的时候,重新构建整个查询,对不对?
这就是变量的用途。但是,首先,我们需要确保我们的 GraphQL 中间件接受变量。回到 GraphQLRequest 类,并添加 Variables 属性。
- public class GraphQLRequest
- {
- public string Query { get; set; }
- public JObject Variables { get; set; }
- }
然后,在中间件的 InvodeAsync 方法中找到 _executor.ExecuteAsync 方法,做如下修改:
- var result = await _executor.ExecuteAsync(doc =>
- {
- doc.Schema = _schema;
- doc.Query = request.Query;
-
- doc.Inputs = request.Variables.ToInputs();
-
- }).ConfigureAwait(false);
好了,现在我们的查询可以接受变量了。运行应用,并编写如下的查询:
- query($barcode: String!){
- item(barcode: $barcode){
- title
- sellingPrice
- }
- }
变量定义以字符 $ 开头,然后是变量的类型。
由于我们的 barcode 是非空的,这里我们需要确保该变量非空,注意,我们在 String 之后使用了 ! 。
我们需要在 Query Variables 面板中如下配置变量。




