springboot整合redis_sessioncallback lettuce
赞
踩
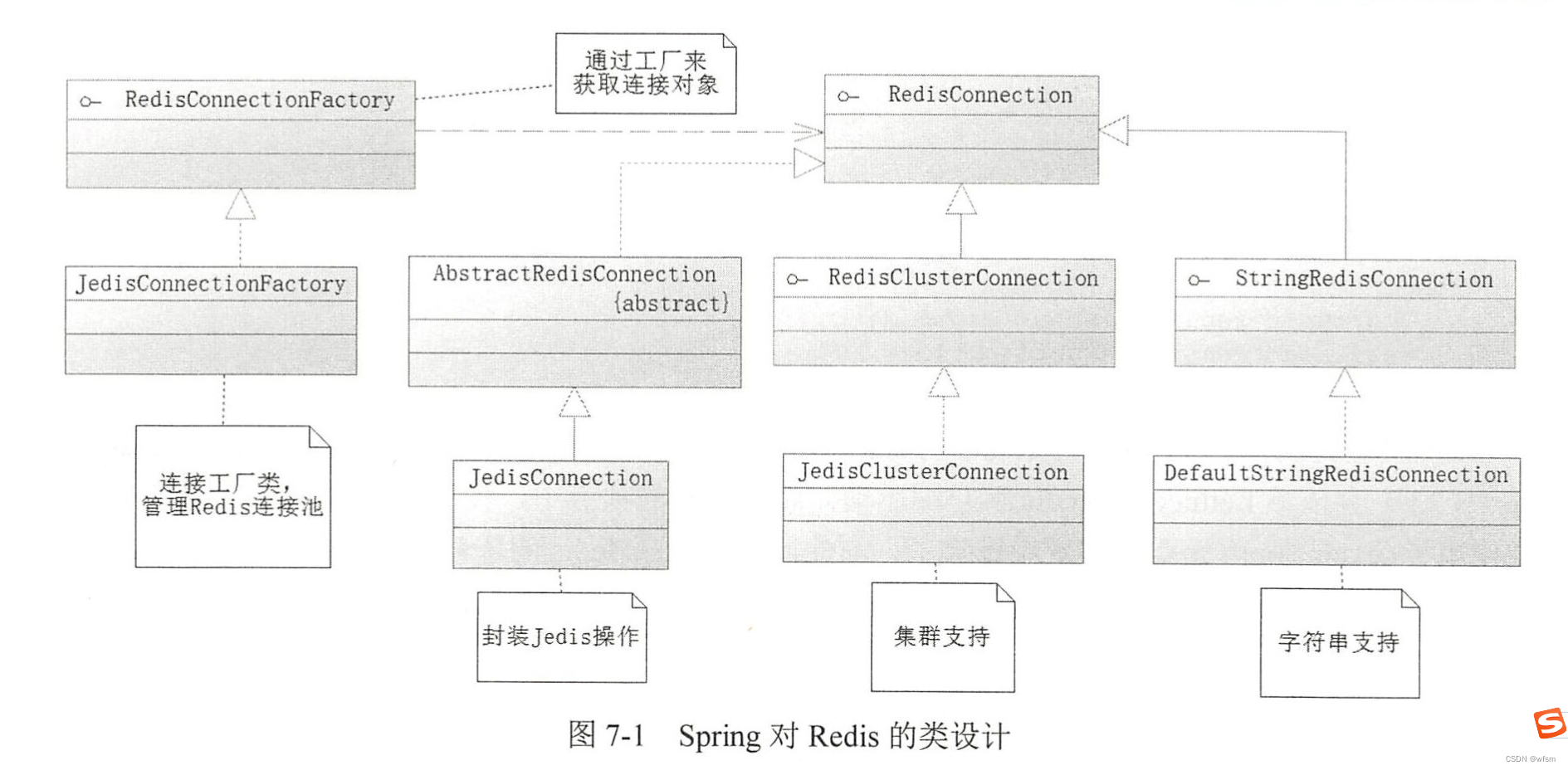
spring提供了 RedisConnectionFactory
RedisConnectionFactory : 生成 RedisConnection接口对象
RedisConnection : 是redis底层接口的封装,,,比如RedisConnection的实现类JedisConnection 去封装原有的Jedis
导包:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>io.lettuce:lettuce-core:5.3.5.RELEASE</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
创建自己的RedisConnectionFactory
@Bean public RedisConnectionFactory initRedisConnectionFactory(){ JedisPoolConfig poolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig(); // 最大空闲数 poolConfig.setMaxIdle(30); // 最大连接数 poolConfig.setMaxTotal(50); // 最大等待毫秒数 poolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(2000); // 创建jedis连接工厂 JedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new JedisConnectionFactory(poolConfig); // 获取redis单机配置 RedisStandaloneConfiguration redisConfig = connectionFactory.getStandaloneConfiguration(); connectionFactory.setHostName("114.132.51.96"); connectionFactory.setPassword("123"); connectionFactory.setPort( 6379); return connectionFactory; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
在使用一个连接的时候,,要先从RedisConnectionFactory中获取连接,,,在使用完成之后,,关闭它。。
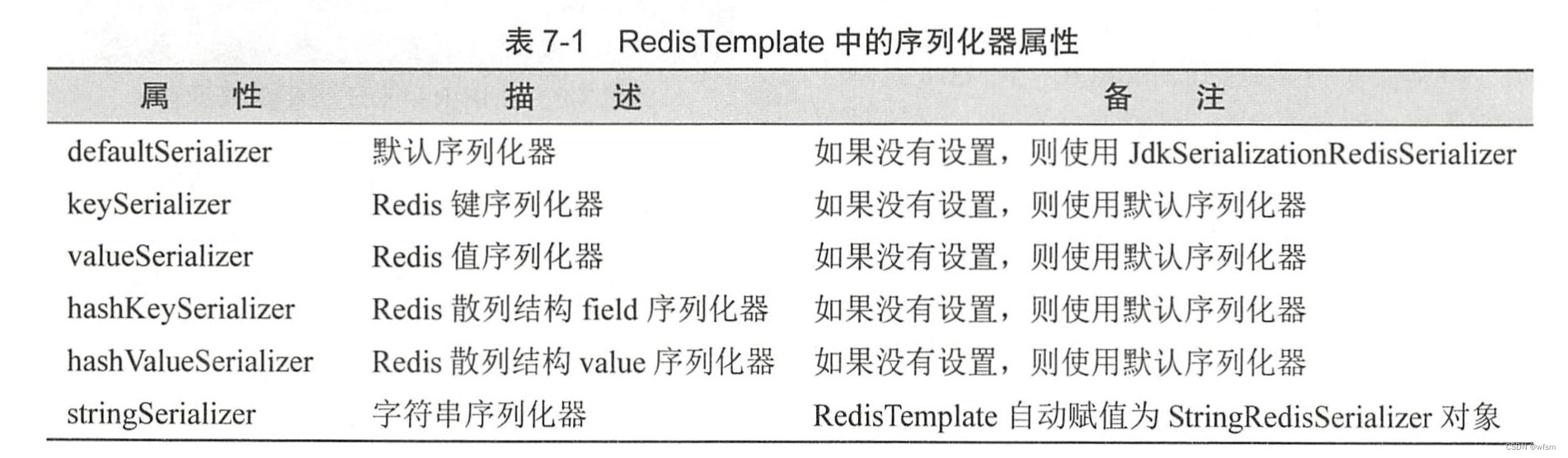
spring为了简化开发,提供了RedisTemplate
redis序列化器
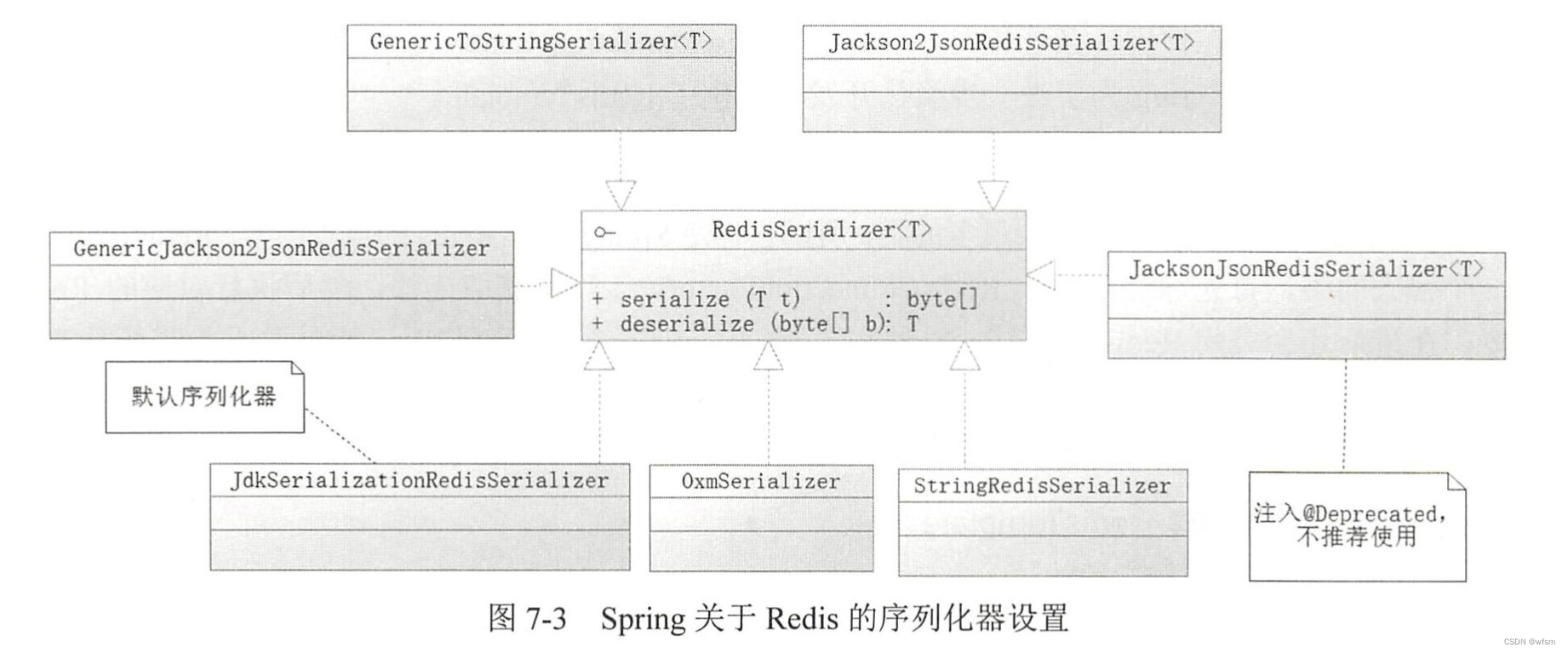
spring提供 RedisSerializer接口,,他有两个方法serialize,deserialize
默认使用JdkSerializationRedisSerializer 对对象进行序列化和反序列化
创建自己的RedisTemplate
// springboot 会默认注册 名为 redisTemplate 和 stringRedisTemplate的bean...这个name要覆盖redisTemplate
@Bean(name = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<Object,Object> initRedisTemplate(){
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
// RedisTemplate自动初始化StringRedisSerializer
RedisSerializer<String> stringSerializer = redisTemplate.getStringSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(stringSerializer);
// 设置连接工厂
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return redisTemplate;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
springboot中自己会注册 名字为 redisTemplate,和 stringRedisTemplate的bean
redis数据封装

如果需要连续操作一个 散列数据类型 或者 列表 多次,,可以使用BoundXXXOperations接口

RedisCallback和 SessionCallback
多个操作并不是在同一个redis连接下完成的,,有时候我们更加希望是在同一个连接中执行两个命令,,为了克服这个问题,spring提供了SessionCallback 和 RedisCallback
SessionCallback 和 RedisCallback 作用: 让RedisTemplate进行回调,,在同一条连接下执行多个redis命令
public void useRedisCallback(RedisTemplate redisTemplate){
redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback() {
@Override
public Object doInRedis(RedisConnection connection) throws DataAccessException {
connection.set("key1".getBytes(),"value1".getBytes());
return null;
}
});
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
public void useSessionCallback(RedisTemplate redisTemplate){
redisTemplate.execute(new SessionCallback() {
@Override
public Object execute(RedisOperations operations) throws DataAccessException {
operations.opsForValue().set("hehe","11");
System.out.println(operations.opsForValue().get("hehe"));
return null;
}
});
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
springboot使用redis
导包:
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
获取原生连接:
// 获取底层连接
Jedis jedis = (Jedis) stringRedisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().getNativeConnection();
jedis.decr("num");
- 1
- 2
- 3
hash
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("field1", "value1");
map.put("field2", "value2");
// 存入一个散列
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll("hash", map);
// 给hash新增一个字段
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put("hash", "username", "cc");
// 批量操作hash
BoundHashOperations<String, Object, Object> hashOps = stringRedisTemplate.boundHashOps("hash");
// 删除两个字段
hashOps.delete("field1", "field2");
// 删除一个字段
hashOps.put("age", "18");
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
list
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushAll("list1", "v2", "v3", "v4", "v5"); stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll("list2", "v1", "v2", "v3", "v4"); BoundListOperations<String, String> listOps = stringRedisTemplate.boundListOps("list2"); // 右边弹出一个 String result1 = listOps.rightPop(); System.out.println("result1 = " + result1); // 获取第几个元素,,,下标从0 开始计算 String result2 = listOps.index(1); System.out.println("result2 = " + result2); listOps.leftPush("sb"); // 链表长度 Long size = listOps.size(); // 取范围 List<String> range = listOps.range(0, 1); System.out.println("range = " + range);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
set
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("set1", "v1", "v2", "v3"); stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("set2", "v1", "v2", "v3"); BoundSetOperations<String, String> setOps = stringRedisTemplate.boundSetOps("set1"); setOps.add("v4", "v5"); setOps.remove("v1", "v2"); // 返回所有set Set<String> members = setOps.members(); System.out.println("members = " + members); // set 大小 Long size = setOps.size(); System.out.println("size = " + size); Set<String> intersect = setOps.intersect("set2"); System.out.println("intersect = " + intersect); // 求交集,,并用新集合 inter 保存 setOps.intersectAndStore("set2", "inter"); Set<String> diff = setOps.diff("set2"); System.out.println("diff = " + diff); setOps.diffAndStore("set2", "diff"); Set<String> union = setOps.union("set2"); setOps.unionAndStore("set2", "union");
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
zset
HashSet<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> typedTupleSet = new HashSet<>(); for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { double score = i * 0.1; DefaultTypedTuple<String> typedTuple = new DefaultTypedTuple<>("value" + i, score); typedTupleSet.add(typedTuple); } stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("zset1", typedTupleSet); BoundZSetOperations<String, String> zsetOps = stringRedisTemplate.boundZSetOps("zset1"); // 添加一个元素 zsetOps.add("sb", 0.3); Set<String> range = zsetOps.range(0, 1); System.out.println("range = " + range); Set<String> strings = zsetOps.rangeByScore(0.2, 0.4); System.out.println("strings = " + strings); // 定义值的范围 RedisZSetCommands.Range zsetRange = new RedisZSetCommands.Range(); zsetRange.gte("value3"); zsetRange.lt("value8"); Set<String> strings1 = zsetOps.rangeByLex(zsetRange); System.out.println("strings1 = " + strings1); // 删除元素 Long value8 = zsetOps.remove("value8"); System.out.println("value8 = " + value8); Double sb = zsetOps.score("sb"); System.out.println("sb = " + sb); // 在下标区间内,,按分数排序,,返回value和score 。。。传入的是下标区间 Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> typedTuples = zsetOps.rangeWithScores(0, 3); System.out.println("typedTuples = " + typedTuples); // 在分数区间下,,按分数排序,, 传入的是分数区间 Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> typedTuples1 = zsetOps.rangeByScoreWithScores(0, 3); System.out.println("typedTuples1 = " + typedTuples1); Set<String> strings2 = zsetOps.reverseRange(2, 8); System.out.println("strings2 = " + strings2);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
spring提供了 TypedTuple接口,
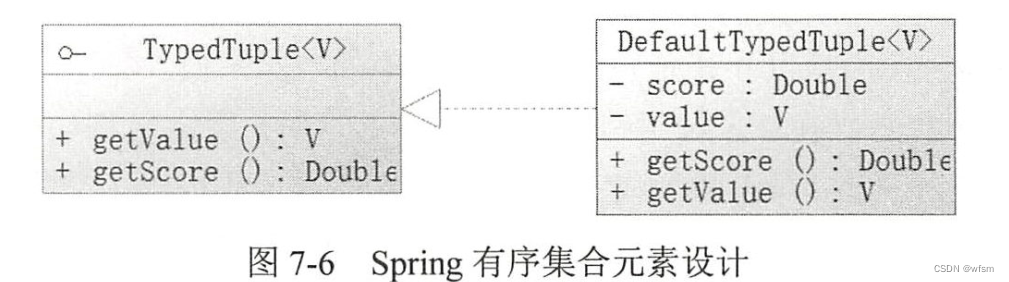
DefaultTypedTuple
spring为我们创建了Range类,可以定义值的范围,,大于,等于,大于等于,小于等于
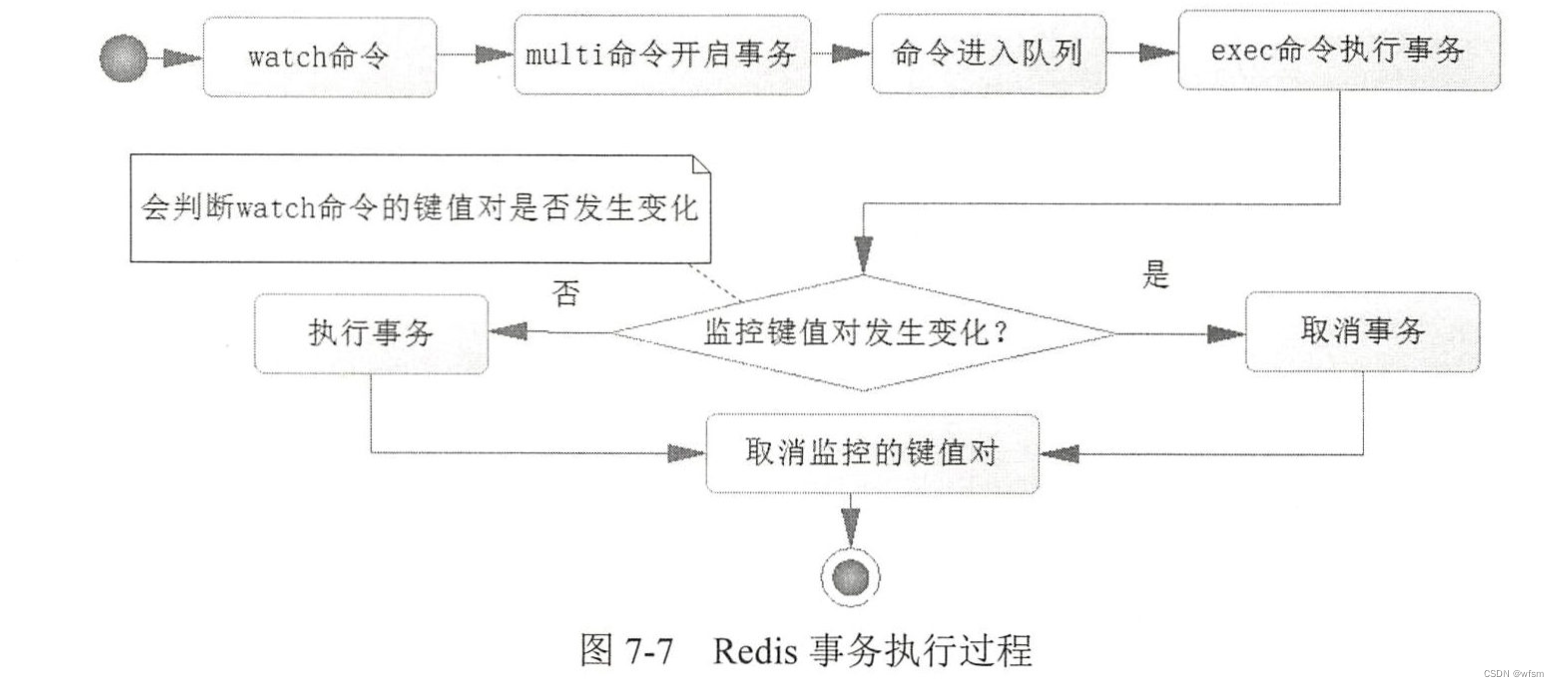
redis事务
在一个连接中执行多个命令,,使用SessionCallback
事务的命令:
- multi 开始事务
- watch : 监听一个值,是否发生过变化,,决定是否执行事务
- exec : 执行事务
List list = (List) stringRedisTemplate.execute(new SessionCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object execute(RedisOperations operations) throws DataAccessException {
operations.opsForValue().set("k1", "v1");
// 先监听一个key
operations.watch("k1");
// 开启事务
operations.multi();
operations.opsForHash().put("hash", "field1", "value1");
// 返回执行结果
return operations.exec();
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
redis事务,是先让命令进入队列,,所以一开始并没有检测这个命令是否执行成功,,只有在exec执行的时候,才能发现错误,,对于出错的命令,redis只是报错,而错误后面的命令依旧被执行
为了克服这个问题,,我们在执行事务前,,严格的检查数据,以避免这样情况发生
redis流水线
默认情况下,redis是一条条命令发送给服务器的,这样效率不高,,在关系数据库中我们可以使用批量,,也就是只有需要执行sql的时候,才一次性的发送所有的sql去执行
很多情况下不是redis性能不佳,而是网络传输的速度造成瓶颈
long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); List list = (List) stringRedisTemplate.executePipelined(new SessionCallback<Object>() { @Override public Object execute(RedisOperations operations) throws DataAccessException { for (int i = 0; i <= 100000; i++) { operations.opsForValue().set("pipeline_" + i, "value_" + i); String value = (String) operations.opsForValue().get("pipeline_" + i); if (i == 100000) { System.out.println("命令只是进入队列,值为空" + value); } } return null; } }); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("耗时:"+(end-start)); System.out.println("list = " + list);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
注意的问题:
- 内存消耗: 如果过多的命令执行,返回的List很大,在高并发网站中就很容易JVM内存溢出,,考虑迭代执行redis命令
- 与事务一样,使用流水线
pipeline,,所有的命令也只是进入队列而没有执行,,返回的值为空
redis发布订阅
- 定义一个 MessageListener 消息监听器: 收到这个消息要干什么
- 定义一个 RedisMessageListenerContainer 容器,,将 MessageListener 和 topic 绑定在一起,,监听消息
publish topic message或者redisTemplate.convertAndSend()
@Configuration public class RedisConfig { @Autowired RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Autowired RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory; @Autowired RedisMessageListener redisMessageListener; @Bean public ThreadPoolTaskScheduler initTaskScheduler(){ ThreadPoolTaskScheduler taskScheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler(); taskScheduler.setPoolSize(20); return taskScheduler; } /** * 定义 redis 监听容器 * @return */ @Bean public RedisMessageListenerContainer initRedisContainer(){ RedisMessageListenerContainer container = new RedisMessageListenerContainer(); // 设置连接工厂 container.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); // 设置运行任务池 container.setTaskExecutor(initTaskScheduler()); // 定义监听渠道 ChannelTopic topic = new ChannelTopic("topic1"); // 使用 监听器 监听 redis这个主题 container.addMessageListener(redisMessageListener,topic); return container; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
stringRedisTemplate.convertAndSend("topic1","hehe");
- 1
lua脚本
redis两种运行lua方法:
- 直接发送lua到redis服务器
- 先把lua发送给redis,,redis会对lua进行缓存,返回一个SHA1的32位编码: 如果lua脚本很长,网络传输就会称为redis执行的瓶颈,,如果只是传递32位编码和参数,极大地减少网络传输内容
spring提供了 RedisScript…DefaultRedisScript

DefaultRedisScript<String> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
redisScript.setScriptText("return 'hello world'");
redisScript.setResultType(String.class);
RedisSerializer stringSerializer = redisTemplate.getStringSerializer();
String s = (String) redisTemplate.execute(redisScript, stringSerializer, stringSerializer, null);
System.out.println("s = " + s);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
redis.call("set",KEYS[1],ARGV[1])
redis.call("set",KEYS[2],ARGV[2])
local str1 = redis.call("get",KEYS[1])
local str2 = redis.call("get",KEYS[2])
if str2==str1 then
return 1
end
return 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
DefaultRedisScript<Long> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
// redisScript.setScriptText("return 'hello world'");
redisScript.setLocation(new ClassPathResource("1.lua"));
redisScript.setResultType(Long.class);
RedisSerializer stringSerializer = redisTemplate.getStringSerializer();
Long result = (Long) redisTemplate.execute(redisScript, stringSerializer, stringSerializer, Arrays.asList("k1","k2"),"hehe1","hehe");
System.out.println("s = " + result);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
java会把整数当作长整型 Long,,所以返回值设置为Long
springboot缓存
spring支持多种缓存,,存在多种缓存处理器,提供了缓存处理器接口CacheManager和与之相关的类
RedisCacheManager

启用缓存@EnableCaching
spring.cache.type=redis
spring.cache.cache-name=redisCache
- 1
- 2
@Cacheable() : 先从缓存里面找,,找到返回,找不到执行
@CachePut() : 将返回结果放在缓存中
@CacheEvict() : 移除缓存,,
condition:设置条件
beforeInvocation配置在方法执行之前 移除 还是之后
#result
#a[1]
@Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { @Autowired UserMapper userMapper; @Override // @Transactional // 使用缓存,,,如果没有,,存入 @Cacheable(value = "redisCache",key = "'redis_key_'+#id") public User getUserById(Long id) { return userMapper.getUserById(id); } @Override // 将返回的结果,,放入缓存中 @CachePut(value = "redisCache",key = "'redis_key_'+#result.id") public User insertUser(User user) { // 返回row ,,,但是会将自增id填进去 userMapper.insertUser(user); return user; } @Override @CachePut(value = "redisCache",condition = "#result !=null",key = "'redis_key_'+#id") public User updateUserName(Long id, String userName) { // 这里的缓存@Cacheable失效,,会执行sql,, User user = this.getUserById(id); if (user == null){ return null; } user.setUsername(userName); userMapper.updateUser(user); return user; } // 命中率低,,不采用缓存 @Override public List<User> findUsers(String userName, String address) { return userMapper.findUsers(userName,address); } @Override // beforeInvocation : 执行之前 @CacheEvict(value = "redisCache",key = "'redis_key_'+#id",beforeInvocation = false) public int deleteUser(Long id) { return userMapper.deleteUser(id); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
自定义缓存器RedisCacheManager
@Bean(name = "redisCacheManager") public RedisCacheManager initRedisCacheManager(){ // redis 加锁的写入器 RedisCacheWriter writer = RedisCacheWriter.lockingRedisCacheWriter(redisConnectionFactory); // redis缓存的默认配置 RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig(); // 设置jdk序列化器 config = config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer())); // 禁用前缀 config = config.disableKeyPrefix(); // 设置10min 超时 config = config.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(10)); RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(writer, config); return redisCacheManager; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21




