- 1测试C#图像文本识别模块Tesseract的基本用法_c# tesseract
- 2算法沉淀——动态规划之完全背包问题(leetcode真题剖析)_动态规划求完全背包
- 3VisualStudioCode上传到Gitee教程_visual studio 推送到gittee
- 4EtherCAT在PC上编译结束,通过ftp服务器直接下载到开发板上_ethercat开发板
- 5计算机mfc140.dll文件缺失的修复方法分析,一键修复mfc140.dll
- 6人工智能+的广泛应用,已渗透到生活的方方面面
- 7数据可视化的自然语言处理与AI融合
- 8Django的render()函数的三个主要参数详解,特别是第三个字典类型的参数context_django render
- 9StreamWriter和StreamReader_streamwriter 创建文件吗
- 10YOLOv5三轮车识别_三轮车 数据集
Android代码检查规则Lint的自定义与应用_android lint
赞
踩
前言:
在日常的代码开发中,此处相信每个开发人员对代码质量都是高要求,有自己的一套代码规范,但是我们不是单独作战,往往大家都是团队作战,人是最大的变量,各人各异,如何保证团队的代码质量和代码规范呢?靠开发者自觉吗?也许有的团队有严格的CR机制,在MR阶段会进行CR,CR不通过的MR是不允许合入的,但是这样会使Reviewer花费较多的时间去校验,那么这时候我们就需要在编码过程中提供一种代码检测机制。
例如:期望表现的效果就是在编码时可以展示异常检测的方法,高亮或者标红,当鼠标悬停在高亮的代码上时,会提供问题的描述和解决方法。需要这种效果,就需要自定义lint了。
什么是Lint
在Android Studio中提供的代码扫描工具Lint,可在无需实际执行该应用,也不必编写测试用例的情况下帮助开发者发现代码质量问题和提出一些改进建议。
Lint工具可检查您的 Android 项目源文件是否包含潜在错误,以及在正确性、安全性、性能、易用性、便利性和国际化方面是否需要优化改进。在使用 Android Studio 时,配置的 Lint 和 IDE 检查会在您每次构建应用时运行。不过,您可以手动运行检查或从命令行运行 Lint。
android studio内置了较多的lint规则,但内置的lint规则无法满足直观的适合我们时,就需要我们自定义lint了。
自定义Lint流程:
1. 新创建module,Module类型选择Java or Kotlin Library, 暂时命名lint_tools
2. 在build.gradle中引入lint的依赖
dependencies {
compileOnly 'com.android.tools.lint:lint-api:27.2.2'
compileOnly 'com.android.tools.lint:lint-checks:27.2.2'
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
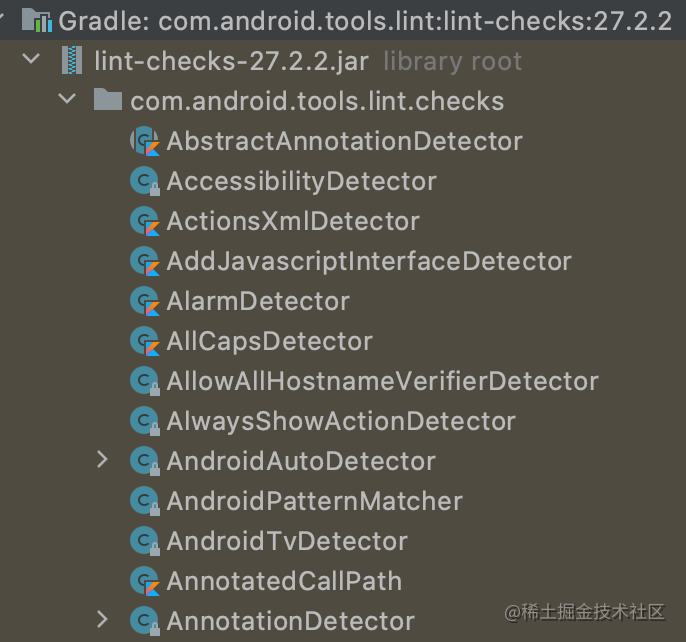
在moudle中依赖了lint-api和lint-checks,其中lint-api就是lint相关的api,lint-checks就是android studio里自定义的一些lint规则,我们自定义lint可以参考lint-checks里面的写法。
3. 本地创建个资源id命名检查规则,用来规范项目中的id统一命名
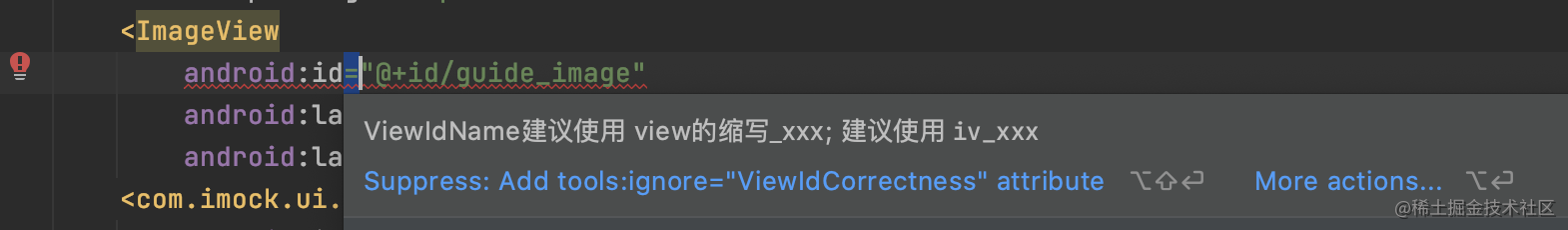
创建ViewIdDetector,直接继承LayoutDetector(也可以继承ResourceXmlDetector 或者 继承Detector实现的接口是XmlScanner,方式多样)
import com.android.SdkConstants import com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.* import com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Category.Companion.CORRECTNESS import com.android.tools.lint.detector.api.Scope.Companion.RESOURCE_FILE_SCOPE import org.w3c.dom.Element class ViewIdDetector : LayoutDetector() { override fun getApplicableElements(): Collection<String>? { return listOf( SdkConstants.TEXT_VIEW, SdkConstants.IMAGE_VIEW, SdkConstants.BUTTON ) } override fun visitElement(context: XmlContext, element: Element) { if (!element.hasAttributeNS(SdkConstants.ANDROID_URI, SdkConstants.ATTR_ID)) { return } val attr = element.getAttributeNodeNS(SdkConstants.ANDROID_URI, SdkConstants.ATTR_ID) val value = attr.value if (value.startsWith(SdkConstants.NEW_ID_PREFIX)) { val idValue = value.substring(SdkConstants.NEW_ID_PREFIX.length) var matchRule = true var expMsg = "" when (element.tagName) { SdkConstants.TEXT_VIEW -> { expMsg = "tv" matchRule = idValue.startsWith(expMsg) } SdkConstants.IMAGE_VIEW -> { expMsg = "iv" matchRule = idValue.startsWith(expMsg) } SdkConstants.BUTTON -> { expMsg = "btn" matchRule = idValue.startsWith(expMsg) } } if (!matchRule) { context.report( ISSUE, attr, context.getLocation(attr), "ViewIdName建议使用view的缩写_xxx; ${element.tagName} 建议使用 `${expMsg}_xxx`" ) } } } companion object { val ISSUE: Issue = Issue.create( "ViewIdCheck", "ViewId命名不规范", "ViewIdName建议使用 view的缩写加上_xxx,例如tv_xxx, iv_xxx", CORRECTNESS, 5, Severity.ERROR, Implementation( ViewIdDetector::class.java, RESOURCE_FILE_SCOPE ) ) } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
自定义Detector可以实现一个或多个Scanner接口,选择实现哪种接口取决于你想要的扫描范围。
Lint API 中内置了很多 Scanner:
| Scanner 类型 | Desc |
|---|---|
| UastScanner | 扫描 Java、Kotlin 源文件 |
| XmlScanner | 扫描 XML 文件 |
| ResourceFolderScanner | 扫描资源文件夹 |
| ClassScanner | 扫描 Class 文件 |
| BinaryResourceScanner | 扫描二进制资源文件 |
| GradleScanner | 扫描Gradle脚本 |
4. 实现IssueRegistry并添加对应的自定义Issue:
class IMockIssueRegistry: IssueRegistry() {
override val issues: List<Issue>
get() = listOf(
ViewIdDetector.ISSUE
)
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
5. 在module(lint_tools)中对应的build.gradle中配置如下信息:
jar {
manifest {
attributes("Lint-registry-v2": "com.imock.lint.IMockIssueRegistry")
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
6. 在需要进行lint检查的module中或者app目录现的build.gradle中引用对应的lint_tools即可使用。
dependencies {
lintChecks project(path: ':lint-tools')
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
至此你可以试着自己自定义Lint了,相关语法api都可参考lint-checks中提供的Detector实现,来实现自己的Lint检查规则。
拓展一下:
1. 针对Issue.create参数了解一下:
companion object { /** * Creates a new issue. The description strings can use some simple markup; * see the [TextFormat.RAW] documentation * for details. * * @param id the fixed id of the issue * @param briefDescription short summary (typically 5-6 words or less), typically * describing the **problem** rather than the **fix** * (e.g. "Missing minSdkVersion") * @param explanation a full explanation of the issue, with suggestions for * how to fix it * @param category the associated category, if any * @param priority the priority, a number from 1 to 10 with 10 being most * important/severe * @param severity the default severity of the issue * @param implementation the default implementation for this issue * @return a new [Issue] */ @JvmStatic fun create( id: String, briefDescription: String, explanation: String, category: Category, priority: Int, severity: Severity, implementation: Implementation ): Issue { val platforms = computePlatforms(null, implementation) return Issue( id, briefDescription, explanation, category, priority, severity, platforms, null, implementation ) } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 参数id 唯一的id,简要表面当前提示的问题。
- 参数briefDescription 简单描述当前问题
- 参数explanation 详细解释当前问题和修复建议
- 参数category 问题类别
- 参数priority 优先级,从1到10,10最重要
- 参数Severity 严重程度:FATAL(奔溃), ERROR(错误), WARNING(警告),INFORMATIONAL(信息性),IGNORE(可忽略)
- 参数Implementation Issue和哪个Detector绑定,以及声明检查的范围。Scope有如下选择范围:RESOURCE_FILE(资源文件),BINARY_RESOURCE_FILE(二进制资源文件),RESOURCE_FOLDER(资源文件夹),ALL_RESOURCE_FILES(所有资源文件),JAVA_FILE(Java文件), ALL_JAVA_FILES(所有Java文件),CLASS_FILE(class文件), ALL_CLASS_FILES(所有class文件),MANIFEST(配置清单文件), PROGUARD_FILE(混淆文件),JAVA_LIBRARIES(Java库), GRADLE_FILE(Gradle文件),PROPERTY_FILE(属性文件),TEST_SOURCES(测试资源),OTHER(其他);
2. Lint API 中 UastScanner 相关回调方法介绍
-
getApplicableUastTypes 与 createUastHandler
- getApplicableUastTypes 此方法返回需要检查的AST节点的类型,类型匹配的UElement将会被createUastHandler(createJavaVisitor)创建的UElementHandler(Visitor)检查。
- createUastHandler 创建一个UastHandler来检查需要检查的UElement,对应于getApplicableUastTypes
-
getApplicableMethodNames 与 visitMethod
- getApplicableMethodNames 返回你所需要检查的方法名称列表,或者返回null,相匹配的方法将通过visitMethod方法被检查
- visitMethod 检查与getApplicableMethodNames相匹配的方法
-
getApplicableConstructorTypes 与 visitConstructor
- getApplicableConstructorTypes 返回需要检查的构造函数类型列表,类型匹配的方法将通过visitConstructor被检查
- visitConstructor 检查与getApplicableConstructorTypes相匹配的构造方法
-
getApplicableReferenceNames 与 visitReference
- getApplicableReferenceNames 返回需要检查的引用路径名,匹配的引用将通过visitReference被检查
- visitReference 检查与getApplicableReferenceNames匹配的引用
-
appliesToResourceRefs 与 visitResourceReference
- appliesToResourceRefs 返回需要检查的资源引用,匹配的引用将通过visitResourceReference被检查
- visitResourceReference 检查与appliesToResourceRefs匹配的资源引用
-
applicableSuperClasses 与 visitClass
- applicableSuperClasses 返回需要检查的父类名列表,此处需要类的全路径名
- visitClass 检查applicableSuperClasses返回的类

文末
如果你想成为架构师,那就不要局限在编码,业务,要会选型、扩展,提升编程思维。此外,良好的职业规划也很重要,学习的习惯很重要,但是最重要的还是要能持之以恒,任何不能坚持落实的计划都是空谈。
如果你没有方向,这里给大家分享一套由阿里高级架构师编写的《Android八大模块进阶笔记》,帮大家将杂乱、零散、碎片化的知识进行体系化的整理,让大家系统而高效地掌握Android开发的各个知识点。
相对于我们平时看的碎片化内容,这份笔记的知识点更系统化,更容易理解和记忆,是严格按照知识体系编排的。
一、架构师筑基必备技能
1、深入理解Java泛型
2、注解深入浅出
3、并发编程
4、数据传输与序列化
5、Java虚拟机原理
6、高效IO
……
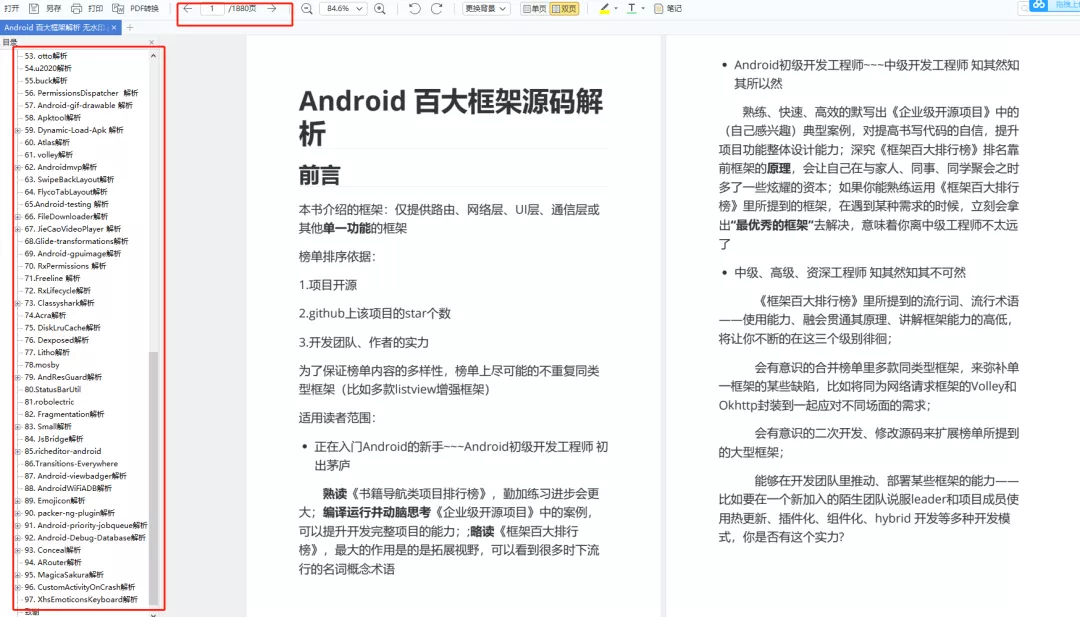
二、Android百大框架源码解析
1.Retrofit 2.0源码解析
2.Okhttp3源码解析
3.ButterKnife源码解析
4.MPAndroidChart 源码解析
5.Glide源码解析
6.Leakcanary 源码解析
7.Universal-lmage-Loader源码解析
8.EventBus 3.0源码解析
9.zxing源码分析
10.Picasso源码解析
11.LottieAndroid使用详解及源码解析
12.Fresco 源码分析——图片加载流程
三、Android性能优化实战解析
- 腾讯Bugly:对字符串匹配算法的一点理解
- 爱奇艺:安卓APP崩溃捕获方案——xCrash
- 字节跳动:深入理解Gradle框架之一:Plugin, Extension, buildSrc
- 百度APP技术:Android H5首屏优化实践
- 支付宝客户端架构解析:Android 客户端启动速度优化之「垃圾回收」
- 携程:从智行 Android 项目看组件化架构实践
- 网易新闻构建优化:如何让你的构建速度“势如闪电”?
- …
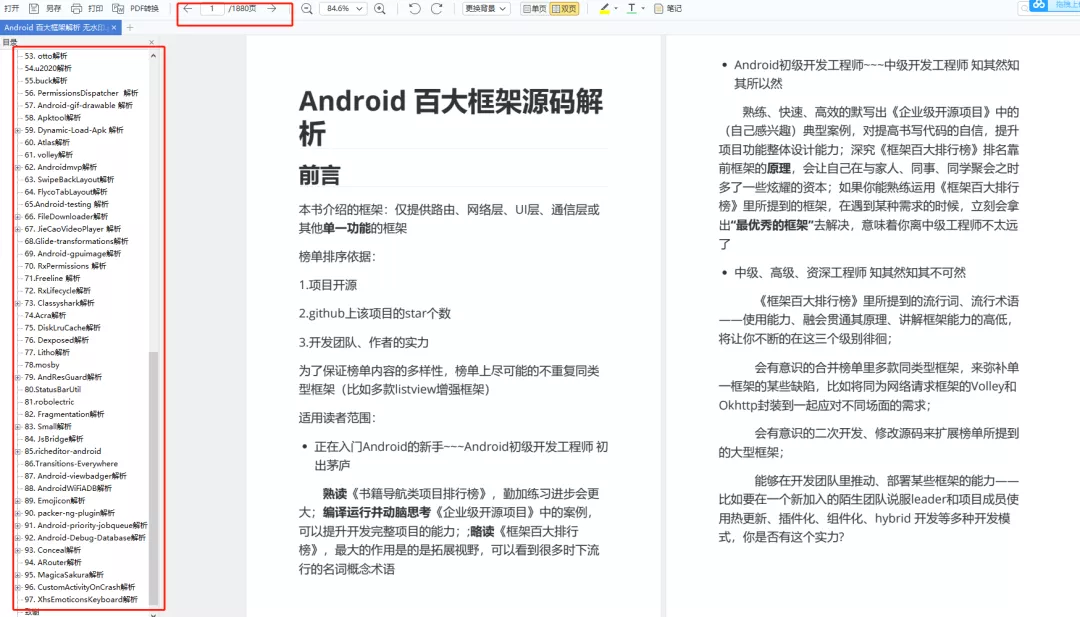
四、高级kotlin强化实战
1、Kotlin入门教程
2、Kotlin 实战避坑指南
3、项目实战《Kotlin Jetpack 实战》
-
从一个膜拜大神的 Demo 开始
-
Kotlin 写 Gradle 脚本是一种什么体验?
-
Kotlin 编程的三重境界
-
Kotlin 高阶函数
-
Kotlin 泛型
-
Kotlin 扩展
-
Kotlin 委托
-
协程“不为人知”的调试技巧
-
图解协程:suspend
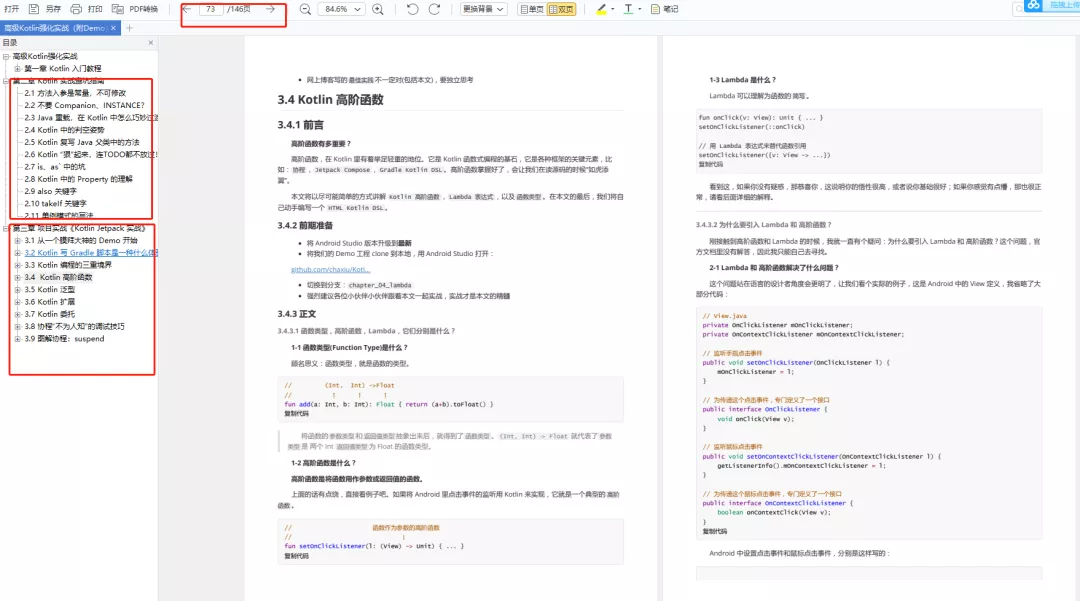
五、Android高级UI开源框架进阶解密
1.SmartRefreshLayout的使用
2.Android之PullToRefresh控件源码解析
3.Android-PullToRefresh下拉刷新库基本用法
4.LoadSir-高效易用的加载反馈页管理框架
5.Android通用LoadingView加载框架详解
6.MPAndroidChart实现LineChart(折线图)
7.hellocharts-android使用指南
8.SmartTable使用指南
9.开源项目android-uitableview介绍
10.ExcelPanel 使用指南
11.Android开源项目SlidingMenu深切解析
12.MaterialDrawer使用指南
六、NDK模块开发
1、NDK 模块开发
2、JNI 模块
3、Native 开发工具
4、Linux 编程
5、底层图片处理
6、音视频开发
7、机器学习
七、Flutter技术进阶
1、Flutter跨平台开发概述
2、Windows中Flutter开发环境搭建
3、编写你的第一个Flutter APP
4、Flutter开发环境搭建和调试
5、Dart语法篇之基础语法(一)
6、Dart语法篇之集合的使用与源码解析(二)
7、Dart语法篇之集合操作符函数与源码分析(三)
…
八、微信小程序开发
1、小程序概述及入门
2、小程序UI开发
3、API操作
4、购物商场项目实战……
全套视频资料:
一、面试合集
二、源码解析合集
三、开源框架合集

欢迎大家一键三连支持,若需要文中资料,直接点击文末CSDN官方认证微信卡片免费领取【保证100%免费】↓↓↓




