热门标签
热门文章
- 1政企云平台“一云多芯”路线全景图_飞天企业版 阿里云 一云多芯
- 2git学习笔记(1)
- 3Nacos对spring-cloud服务注册的实现_de-registering
- 4巴比特 | 元宇宙每日必读:地方大模型竞赛开启?成都发布促进人工智能发展征求意见稿,提出多条资金补贴和奖励措施,最高奖1000万...
- 5推荐开源项目:AiAPI - 利用Claude的强大功能,无缝对接OpenAI API
- 6Failed to connect to github.com port 443 after 75015 ms: Couldn‘t connect to server_github port 443 after 75005 ms: couldn't connect t
- 7【花雕学编程】Arduino BLDC 之基于深度学习的自主导航机器人控制
- 8HashTable HashMap ConcurrentHashMap 的介绍以及区别_hashtable,hashmap,concurrent
- 9深度测评:ONLYOFFICE 8.1 的安装与使用——功能全面的 PDF 编辑器、幻灯片版式、优化电子表格的协作_onlyoffice pdf
- 10法考备考攻略(内附分享链接)_法考笔记 百度网盘
当前位置: article > 正文
【Diffusion实战】训练一个diffusion模型生成S曲线(Pytorch代码详解)_diffusion model pytorch示例
作者:喵喵爱编程 | 2024-08-02 11:17:56
赞
踩
diffusion model pytorch示例
看了不少资料,终于大概理解diffusion每一步的流程与推导了,搞一个案例实践一下,把代码跟公式对一对加深理解。
0、前向与逆向过程
原论文:Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models

1、数据集准备
选一个数据集,本例采用sklearn自带数据集:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_s_curve
import torch
s_curve, _ = make_s_curve(10**4, noise=0.1)
s_curve = s_curve[:,[0,2]]/10.0 # 每个点取第0维和第2维, 再除以10
print("shape of s:", np.shape(s_curve))
data = s_curve.T
fig,ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(*data,color='orange',edgecolor='white');
ax.axis('off')
dataset = torch.Tensor(s_curve).float() # 将S曲线构建成一个张量
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
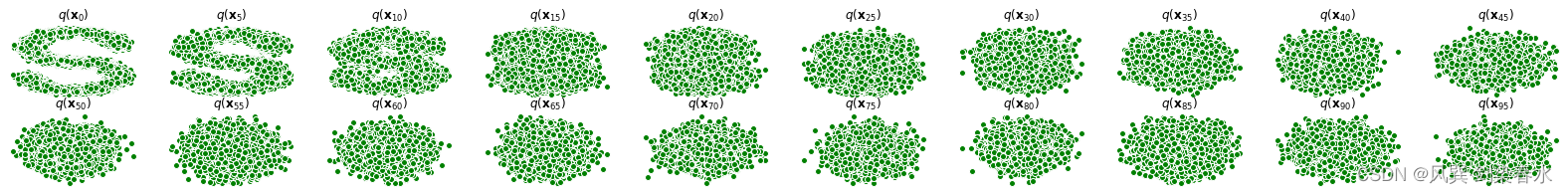
S曲线显示:

2、参数计算
计算前向过程中需要的常数:
# 准备好alpha(αt), beta(βt), αt^, 根号下αt^, 根号下(1-αt^)等值
num_steps = 100 # 设置步长
# 制定每一步的beta
betas = torch.linspace(-6, 6, num_steps) # 逐渐递增
betas = torch.sigmoid(betas)*(0.5e-2 - 1e-5)+1e-5 # β0,β1,...,βt
# 计算alpha、alpha_prod、alpha_prod_previous、alpha_bar_sqrt等变量的值
alphas = 1 - betas # αt = 1 - βt
alphas_prod = torch.cumprod(alphas,0) # αt^ = αt的累乘
# αt^往右平移一位, 原第t步的值维第t-1步的值, 第0步补1
alphas_prod_p = torch.cat([torch.tensor([1]).float(), alphas_prod[:-1]], 0) # αt-1 ^
alphas_bar_sqrt = torch.sqrt(alphas_prod) # αt^ 开根号
one_minus_alphas_bar_log = torch.log(1 - alphas_prod) # log(1-αt^)
one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt = torch.sqrt(1 - alphas_prod) # 根号下(1-αt^)
assert alphas.shape==alphas_prod.shape==alphas_prod_p.shape==alphas_bar_sqrt.shape==one_minus_alphas_bar_log.shape==one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt.shape
print("all the same shape",betas.shape)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
3、前向过程
确定扩散过程任意时刻的采样值:
# 计算任意时刻的x采样值,基于x_0和重参数化
def q_x(x_0, t):
"""
作用:前向过程, 可以基于x[0]得到任意时刻t的x[t]
输入:x_0:初始干净图像;t:采样步
输出:x_t:第t步时的x_0已成为的样子
"""
noise = torch.randn_like(x_0) # noise为从正态分布中采样的随机噪声
alphas_t = alphas_bar_sqrt[t] # 根号下αt^
alphas_1_m_t = one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt[t] # 根号下(1-αt^)
return (alphas_t * x_0 + alphas_1_m_t * noise) # 在x[0]的基础上添加噪声
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
运行
4、前向过程展示
演示原始数据分布加噪100步后的结果,可观察到从S曲线在100步中逐渐变为高斯分布的过程:
num_shows = 20
fig,axs = plt.subplots(2, 10, figsize=(28,3))
plt.rc('text',color='black')
#共有10000个点,每个点包含两个坐标
#生成100步以内每隔5步加噪声后的图像
for i in range(num_shows):
j = i//10
k = i%10
q_i = q_x(dataset, torch.tensor([i*num_steps//num_shows])) # 生成t时刻的采样数据
axs[j,k].scatter(q_i[:,0], q_i[:,1], color='green', edgecolor='white')
axs[j,k].set_axis_off()
axs[j,k].set_title('$q(\mathbf{x}_{'+str(i*num_steps//num_shows)+'})$')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
5、模型搭建
编写拟合逆扩散过程高斯分布的模型,写一个简单的网路,用于预测噪声:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class MLPDiffusion(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_steps, num_units=128):
super(MLPDiffusion,self).__init__()
self.linears = nn.ModuleList(
[
nn.Linear(2, num_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(num_units,num_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(num_units,num_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(num_units,2),
]
)
self.step_embeddings = nn.ModuleList(
[
nn.Embedding(n_steps,num_units), # [100,128]
nn.Embedding(n_steps,num_units),
nn.Embedding(n_steps,num_units),
]
)
def forward(self, x, t):
for idx, embedding_layer in enumerate(self.step_embeddings):
t_embedding = embedding_layer(t) # 选第t步的Embedding
x = self.linears[2*idx](x) # 先送入Linear层
x += t_embedding # 加上Embedding
x = self.linears[2*idx+1](x) # 再送入ReLU层
x = self.linears[-1](x) # 最后一个Linear层, 输出为[10000, 2]
return x
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
6、损失函数
编写训练的误差函数,计算网络预测噪声与真实添加噪声的误差:
def diffusion_loss_fn(model, x_0, alphas_bar_sqrt, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt, n_steps):
"""
作用:对任意时刻t进行采样计算loss
参数:
model: 模型
x_0: 干净的图
alphas_bar_sqrt: 根号下αt^
one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt: 根号下(1-αt^)
n_steps: 采样步
"""
batch_size = x_0.shape[0]
# 对一个batchsize样本生成随机的时刻t, 覆盖到更多不同的t
t = torch.randint(0, n_steps, size=(batch_size//2,)) # 在0~99内生成整数采样步
t = torch.cat([t, n_steps-1-t], dim=0) # 一个batch的采样步, 尽量让生成的t不重复
t = t.unsqueeze(-1) # 增加一个维度(8,1)
# x0的系数
a = alphas_bar_sqrt[t] # 根号下αt^
# eps的系数
aml = one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt[t] # 根号下(1-αt^)
# 生成随机噪音eps
e = torch.randn_like(x_0)
# 构造模型的输入
x = x_0*a+e*aml # 前向过程:根号下αt^ * x0 + 根号下(1-αt^) * eps
# 送入模型,得到t时刻的随机噪声预测值
output = model(x, t.squeeze(-1)) # 模型预测的是噪声, 噪声维度与x0一样大, [10000,2]
# 与真实噪声一起计算误差,求平均值
return (e - output).square().mean()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
运行
7、逆向过程
编写逆扩散采样函数,从随机噪声生成样本:
def p_sample_loop(model, shape, n_steps, betas, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt):
"""
作用:从x[T]恢复x[T-1]、x[T-2]、...x[0]
输入:
model:模型
shape:数据大小,用于生成随机噪声
n_steps:逆扩散总步长
betas: βt
one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt: 根号下(1-αt^)
输出:
x_seq:一个序列的x, 即 x[T]、x[T-1]、x[T-2]、...x[0]
"""
cur_x = torch.randn(shape) # 随机噪声, 对应xt
x_seq = [cur_x]
for i in reversed(range(n_steps)):
cur_x = p_sample(model, cur_x, i, betas, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt)
x_seq.append(cur_x)
return x_seq
def p_sample(model, x, t, betas, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt):
"""
作用:从x[T]采样t时刻的重构值
输入:
model:模型
x: 采样的随机噪声x[T]
t: 采样步
betas: βt
one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt: 根号下(1-αt^)
输出:
sample: 样本
"""
t = torch.tensor([t])
coeff = betas[t] / one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt[t] # 模型输出的系数:βt/根号下(1-αt^) = 1-αt/根号下(1-αt^)
eps_theta = model(x, t) # 模型的输出: εθ(xt, t)
# (1/根号下αt) * (xt - (1-αt/根号下(1-αt^))*εθ(xt, t))
mean = (1/(1-betas[t]).sqrt())*(x-(coeff*eps_theta))
z = torch.randn_like(x) # 对应公式中的 z
sigma_t = betas[t].sqrt() # 对应公式中的 σt
sample = mean + sigma_t * z
return (sample)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
运行
8、模型训练
开始训练模型,打印loss及中间重构效果:
print('Training model...')
batch_size = 128
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
num_epoch = 4000
plt.rc('text',color='blue')
model = MLPDiffusion(num_steps) # 输出维度是2,输入是x和step
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
for t in range(num_epoch):
for idx, batch_x in enumerate(dataloader):
# 损失计算
loss = diffusion_loss_fn(model, batch_x, alphas_bar_sqrt, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt, num_steps)
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # 损失回传
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(),1.) # 梯度裁剪
optimizer.step()
if(t % 100 == 0):
print(loss)
x_seq = p_sample_loop(model, dataset.shape, num_steps, betas, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 10, figsize=(28,3))
for i in range(1, 11):
cur_x = x_seq[i*10].detach()
axs[i-1].scatter(cur_x[:,0],cur_x[:,1],color='red',edgecolor='white');
axs[i-1].set_axis_off();
axs[i-1].set_title('$q(\mathbf{x}_{'+str(i*10)+'})$')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
训练过程如下,cpu训练约30min完成:

重构效果展示(分别为0、1000、2000、3000、4000epoch的结果):
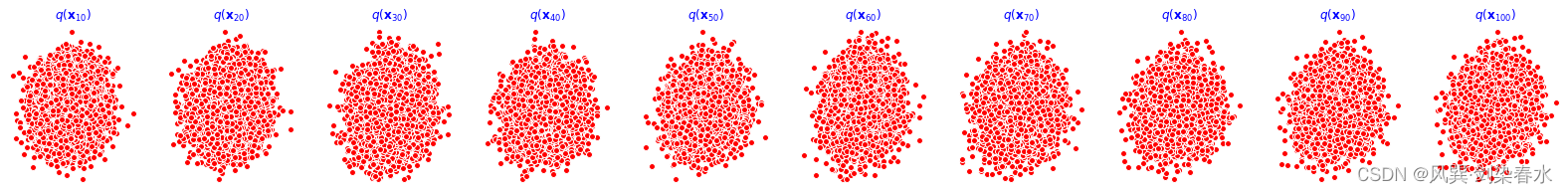

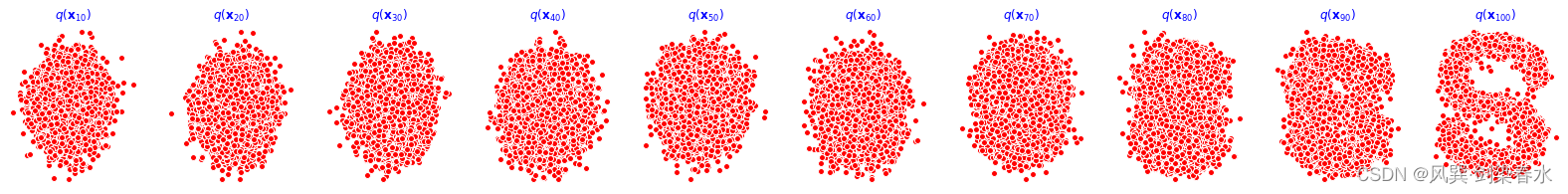
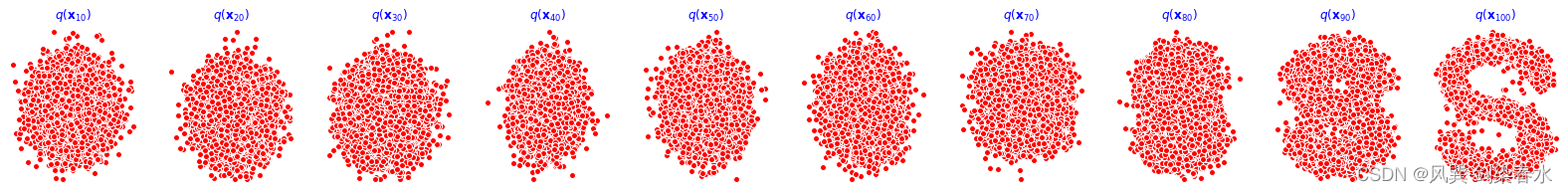
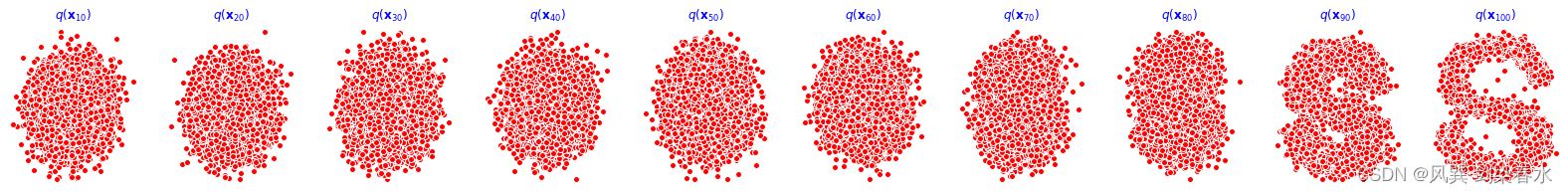
9、动态可视化:
import io
from PIL import Image
# 前向过程
imgs = []
for i in range(100):
plt.clf()
q_i = q_x(dataset,torch.tensor([i]))
plt.scatter(q_i[:,0],q_i[:,1],color='red',edgecolor='white',s=5);
plt.axis('off');
img_buf = io.BytesIO()
plt.savefig(img_buf,format='png')
img = Image.open(img_buf)
imgs.append(img)
# 逆向过程
reverse = []
for i in range(100):
plt.clf()
cur_x = x_seq[i].detach()
plt.scatter(cur_x[:,0],cur_x[:,1],color='red',edgecolor='white',s=5);
plt.axis('off')
img_buf = io.BytesIO()
plt.savefig(img_buf,format='png')
img = Image.open(img_buf)
reverse.append(img)
imgs = imgs
imgs[0].save("diffusion_qian.gif", format='GIF', append_images=imgs, save_all=True, duration=100, loop=0)
imgs = reverse
imgs[0].save("diffusion_ni.gif", format='GIF', append_images=imgs, save_all=True, duration=100, loop=0)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
前向过程:

逆向过程:

10、代码汇总:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import make_s_curve
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import io
from PIL import Image
### 1、选择一个数据集-----------------------------------------------------------
s_curve, _ = make_s_curve(10**4, noise=0.1)
s_curve = s_curve[:,[0,2]]/10.0 # 每个点取第0维和第2维, 再除以10
print("shape of s:", np.shape(s_curve))
data = s_curve.T
fig,ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(*data,color='orange',edgecolor='white');
ax.axis('off')
dataset = torch.Tensor(s_curve).float() # 将S曲线构建成一个张量
### -------------------------------------------------------------------------
### 2、确定超参数的值-----------------------------------------------------------
# 准备好alpha(α), beta(β)等值
num_steps = 100 # 设置步长
# 制定每一步的beta
betas = torch.linspace(-6, 6, num_steps) # 逐渐递增
betas = torch.sigmoid(betas)*(0.5e-2 - 1e-5)+1e-5 # β0,β1,...,βt
# 计算alpha、alpha_prod、alpha_prod_previous、alpha_bar_sqrt等变量的值
alphas = 1 - betas # αt = 1 - βt
alphas_prod = torch.cumprod(alphas,0) # αt^ = αt的累乘
# αt^往右平移一位, 原第t步的值维第t-1步的值, 第0步补1
alphas_prod_p = torch.cat([torch.tensor([1]).float(), alphas_prod[:-1]], 0) # αt-1^
alphas_bar_sqrt = torch.sqrt(alphas_prod) # αt^ 开根号
one_minus_alphas_bar_log = torch.log(1 - alphas_prod) # log(1-αt^)
one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt = torch.sqrt(1 - alphas_prod) # 根号下(1-αt^)
assert alphas.shape==alphas_prod.shape==alphas_prod_p.shape==\
alphas_bar_sqrt.shape==one_minus_alphas_bar_log.shape\
==one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt.shape
print("all the same shape",betas.shape)
### ------------------------------------------------------------------------
### 3、确定扩散过程任意时刻的采样值----------------------------------------------
# 计算任意时刻的x采样值,基于x_0和重参数化
def q_x(x_0, t):
"""
作用:可以基于x[0]得到任意时刻t的x[t]
输入:x_0:初始干净图像;t:采样步
输出:x_t:第t步时的x_0的样子
"""
noise = torch.randn_like(x_0) # noise为从正态分布中采样的随机噪声
alphas_t = alphas_bar_sqrt[t]
alphas_1_m_t = one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt[t]
return (alphas_t * x_0 + alphas_1_m_t * noise) # 在x[0]的基础上添加噪声
### ------------------------------------------------------------------------
### 4、演示原始数据分布加噪100步后的结果-----------------------------------------
num_shows = 20
fig,axs = plt.subplots(2, 10, figsize=(28,3))
plt.rc('text',color='black')
#共有10000个点,每个点包含两个坐标
#生成100步以内每隔5步加噪声后的图像
for i in range(num_shows):
j = i//10
k = i%10
q_i = q_x(dataset, torch.tensor([i*num_steps//num_shows])) # 生成t时刻的采样数据
axs[j,k].scatter(q_i[:,0], q_i[:,1], color='green', edgecolor='white')
axs[j,k].set_axis_off()
axs[j,k].set_title('$q(\mathbf{x}_{'+str(i*num_steps//num_shows)+'})$')
### ------------------------------------------------------------------------
### 5、编写拟合逆扩散过程高斯分布的模型-----------------------------------------
class MLPDiffusion(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_steps, num_units=128):
super(MLPDiffusion,self).__init__()
self.linears = nn.ModuleList(
[
nn.Linear(2, num_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(num_units,num_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(num_units,num_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(num_units,2),
]
)
self.step_embeddings = nn.ModuleList(
[
nn.Embedding(n_steps,num_units), # [100,128]
nn.Embedding(n_steps,num_units),
nn.Embedding(n_steps,num_units),
]
)
def forward(self, x, t):
for idx, embedding_layer in enumerate(self.step_embeddings):
t_embedding = embedding_layer(t) # 选第t步的Embedding
x = self.linears[2*idx](x) # 先送入Linear层
x += t_embedding # 加上Embedding
x = self.linears[2*idx+1](x) # 再送入ReLU层
x = self.linears[-1](x) # 最后一个Linear层, 输出为[10000, 2]
return x
### ------------------------------------------------------------------------
### 6、编写训练的误差函数------------------------------------------------------
def diffusion_loss_fn(model, x_0, alphas_bar_sqrt, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt, n_steps):
"""
作用:对任意时刻t进行采样计算loss
参数:
model: 模型
x_0: 干净的图
alphas_bar_sqrt: αt^开根号
one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt: 根号下(1-αt^)
n_steps: 采样步
"""
batch_size = x_0.shape[0]
# 对一个batchsize样本生成随机的时刻t, 覆盖到更多不同的t
t = torch.randint(0, n_steps, size=(batch_size//2,)) # 在0~99内生成整数采样步
t = torch.cat([t, n_steps-1-t], dim=0) # 一个batch的采样步, 尽量让生成的t不重复
t = t.unsqueeze(-1) # 增加一个维度(8,1)
# x0的系数
a = alphas_bar_sqrt[t] # 根号下αt^
# eps的系数
aml = one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt[t] # 根号下(1-αt^)
# 生成随机噪音eps
e = torch.randn_like(x_0)
# 构造模型的输入
x = x_0*a+e*aml # 前向过程:根号下αt^ * x0 + 根号下(1-αt^) * eps
# 送入模型,得到t时刻的随机噪声预测值
output = model(x, t.squeeze(-1)) # 模型预测的是噪声, 噪声维度与x0一样大, [10000,2]
# 与真实噪声一起计算误差,求平均值
return (e - output).square().mean()
### ------------------------------------------------------------------------
### 7、编写逆扩散采样函数(inference)------------------------------------------
def p_sample_loop(model, shape, n_steps, betas, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt):
"""
作用:从x[T]恢复x[T-1]、x[T-2]、...x[0]
输入:
model:模型
shape:数据大小,用于生成随机噪声
n_steps:逆扩散总步长
betas: βt
one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt: 根号下(1-αt^)
输出:
x_seq:一个序列的x, 即 x[T]、x[T-1]、x[T-2]、...x[0]
"""
cur_x = torch.randn(shape) # 随机噪声, 对应xt
x_seq = [cur_x]
for i in reversed(range(n_steps)):
cur_x = p_sample(model, cur_x, i, betas, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt)
x_seq.append(cur_x)
return x_seq
def p_sample(model, x, t, betas, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt):
"""
作用:从x[T]采样t时刻的重构值
输入:
model:模型
x: 采样的随机噪声x[T]
t: 采样步
betas: βt
one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt: 根号下(1-αt^)
输出:
sample: 样本
"""
t = torch.tensor([t])
coeff = betas[t] / one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt[t] # 模型输出的系数:βt/根号下(1-αt^) = 1-αt/根号下(1-αt^)
eps_theta = model(x, t) # 模型的输出: εθ(xt, t)
# 均值: (1/根号下αt) * (xt - (1-αt/根号下(1-αt^))*εθ(xt, t))
mean = (1/(1-betas[t]).sqrt())*(x-(coeff*eps_theta))
z = torch.randn_like(x) # 对应公式中的 z
sigma_t = betas[t].sqrt() # 对应公式中的 σt
sample = mean + sigma_t * z
return (sample)
### ------------------------------------------------------------------------
### 8、开始训练模型,打印loss及中间重构效果---------------------------------------
print('Training model...')
batch_size = 128
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
num_epoch = 4000
plt.rc('text',color='blue')
model = MLPDiffusion(num_steps) # 输出维度是2,输入是x和step
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
for t in range(num_epoch):
for idx, batch_x in enumerate(dataloader):
# 损失计算
loss = diffusion_loss_fn(model, batch_x, alphas_bar_sqrt, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt, num_steps)
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # 损失回传
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(),1.) # 梯度裁剪
optimizer.step()
if(t % 100 == 0):
print(loss)
x_seq = p_sample_loop(model, dataset.shape, num_steps, betas, one_minus_alphas_bar_sqrt)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 10, figsize=(28,3))
for i in range(1, 11):
cur_x = x_seq[i*10].detach()
axs[i-1].scatter(cur_x[:,0],cur_x[:,1],color='red',edgecolor='white');
axs[i-1].set_axis_off();
axs[i-1].set_title('$q(\mathbf{x}_{'+str(i*10)+'})$')
### ------------------------------------------------------------------------
### 9、动画演示扩散过程和逆扩散过程----------------------------------------------
# 前向过程
imgs = []
for i in range(100):
plt.clf()
q_i = q_x(dataset,torch.tensor([i]))
plt.scatter(q_i[:,0],q_i[:,1],color='red',edgecolor='white',s=5);
plt.axis('off');
img_buf = io.BytesIO()
plt.savefig(img_buf,format='png')
img = Image.open(img_buf)
imgs.append(img)
# 逆向过程
reverse = []
for i in range(100):
plt.clf()
cur_x = x_seq[i].detach()
plt.scatter(cur_x[:,0],cur_x[:,1],color='red',edgecolor='white',s=5);
plt.axis('off')
img_buf = io.BytesIO()
plt.savefig(img_buf,format='png')
img = Image.open(img_buf)
reverse.append(img)
imgs = imgs
imgs[0].save("diffusion_qian.gif", format='GIF', append_images=imgs, save_all=True, duration=100, loop=0)
imgs = reverse
imgs[0].save("diffusion_ni.gif", format='GIF', append_images=imgs, save_all=True, duration=100, loop=0)
### ------------------------------------------------------------------------
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
参考资料与扩展阅读:
1、Probabilistic Diffusion Model概率扩散模型理论与完整PyTorch代码详细解读
2、扩散模型之DDPM
把公式与代码对应起来,就会大彻大悟~
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/喵喵爱编程/article/detail/918405
推荐阅读
相关标签



