热门标签
热门文章
- 1FlowUs科研工作者的第二大脑|论文整理与知识库构建的终极解决方案|FlowUs不愧是论文神器PDF智能分析高效科研必备|学术写作团队协作学术资源整合科研效率提升选FlowUs
- 2ACC-UNet——基于Transformers与UNet的语义分割模型_unet transformer
- 32023年银行校招上岸全攻略分享(附历年商业银行笔试真题和备_银行校招笔试真题
- 4各大人工智能顶会近三年的paper网址_aaai digital library
- 5爬虫实战5:爬取百度图片_爬虫实现可视化爬取百度图片案例
- 6最近面了12个人,发现这个测试基础题都答不上来..._请用 python 打印出 10000 以内的对称数(对称数特点:数字左右对称,如:1,2,11,
- 7互联网行业采购堡垒机的四个必要性看这里!
- 8爬取百度图片_百度图片爬取
- 9spring boot druid spring监控_spring-boot-maven-plugin not found
- 10python3.5+selenium3.4自动化测试6_selenium的Webdriver-API整理(上)_from seleniumn import webdriver 3.4版本
当前位置: article > 正文
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
作者:寸_铁 | 2024-07-10 12:32:49
赞
踩
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
文章内容是自己刷leetcode题目的一些总结。
文章内容参考公众号: 代码随想录。
喜欢的话,希望大家可以点点赞 ^ - ^
一.题目描述
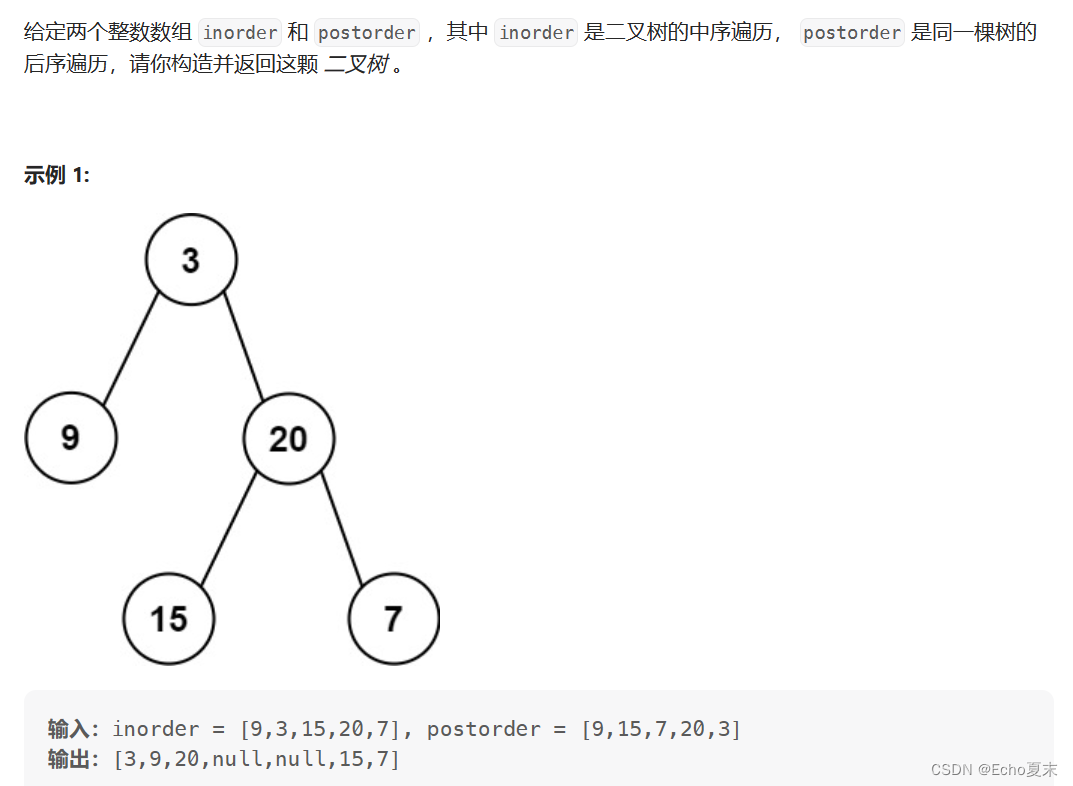
二.题目分析
我们知道中序遍历是左中右,后序遍历是左右中,那么我们可以根据中间节点在中序与后序遍历中的的位置来构造二叉树。
我们采用递归的方式来处理这道问题。
终止条件是遇到空节点终止。
在每次递归中,我们先取出根节点,也就是后序遍历的最后一个元素,那么用它构造树的根节点。
然后在中序遍历中寻找根节点的位置作为切割点,将中序遍历分为左右子树,根据中序遍历左右子树的大小来分割后序遍历,也将其分为左右区间。分割中序遍历与后序遍历为两个左右区间,他们代表的就是根节点的左右子树。
最后根据分割后的左右子树进行递归。
三.递归代码
class Solution { public: TreeNode* traversalTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) { //空数组直接终止 if(postorder.size() == 0) { return nullptr; } //后序遍历最后一个元素为根节点 int rootValue = postorder[postorder.size() - 1]; TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(rootValue); //根据根节点在中序遍历划分左右区间 //找切割点 int idx; for(idx = 0; idx < inorder.size(); idx ++) { if(inorder[idx] == rootValue) break; } vector<int> inleft(inorder.begin(), inorder.begin() + idx); //左闭右开 vector<int> inright(inorder.begin() + idx + 1, inorder.end()); //切割后序遍历数组(利用中序遍历和后序遍历个数相同) postorder.resize(postorder.size() - 1); //根节点已经用过了 vector<int> postleft(postorder.begin(), postorder.begin() + inleft.size()); vector<int> postright(postorder.begin() + inleft.size(), postorder.end()); //递归 root->left = traversalTree(inleft, postleft); root->right = traversalTree(inright, postright); return root; } TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) { if(inorder.size() == 0) { return nullptr; } return traversalTree(inorder, postorder); } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
三.总结
通过此题我们可以知道根据一棵二叉树的中序遍历与后序遍历可以还原出这棵二叉树。
那么同样的,给出一颗二叉树的前序遍历与中序遍历也可以还原出二叉树。
但是只给出前序遍历和后序遍历无法构造出唯一的一棵二叉树。
前序和后序在本质上都是将父节点与子结点进行分离,但并没有指明左子树和右子树的能力,因此得到这两个序列只能明确父子关系,而不能确定一个二叉树。而中序遍历在知道根节点后可以指明左右子树的关系。
所以只能根据前序或者后序遍历先确定根节点,然后再利用中序遍历划分左右子树。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/寸_铁/article/detail/806285
推荐阅读
相关标签



