热门标签
热门文章
- 1html添加B站视频,iframe嵌入BiliBili视频方法B站视频外链
- 2Python 入门实践_l = [m+n for m in ‘abc’ for n in ‘123’]
- 3【HaaS Python硬件积木】土壤湿度传感器_lm393土壤湿度传感器电路
- 4java计算机毕业设计基于springboot+vue+elementUI的结婚婚庆婚纱拍摄管理系统(前后端分离)_sprnigboot vue婚纱影楼管理系统 github
- 5有关安卓的Activity前后台切换_android 前后台切换
- 6java 微信支付成功后重复执行回调函数_java 微信支付回调函数一直被调用好几次
- 7Docker管理工具Portainer忘记admin登录密码怎么办?_portainer忘记用户名密码
- 8 用ES6封装AJAX函数,支持GET/POST
- 9tcp port numbers reused出现原因_从TCP协议的原理来谈谈rst复位攻击
- 10入门系列-在AspNet Core MVC Web Application中使用ABP_app.initializeapplication
当前位置: article > 正文
Android 3D效果的实现_android 3d图像和文字
作者:小丑西瓜9 | 2024-03-03 23:17:05
赞
踩
android 3d图像和文字
系列文章目录
Android 3D效果的实现
前言
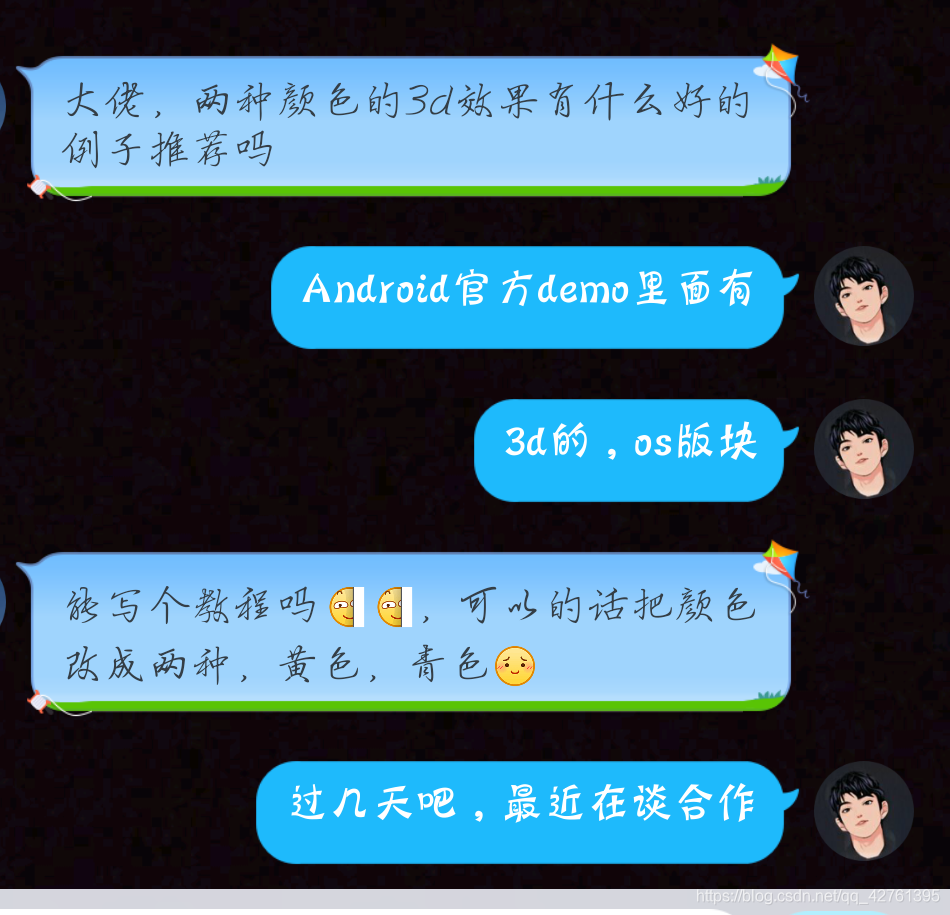
前几天有粉丝要求计蒙写一个3d效果的简单教程,其实这个在Android官方demo中是有的,可能对于新手而言看不太明白,于是根据本人自己的理解来写一个教程,并改成粉丝要求的样子。
文章最后将会贴出源码(照顾新手附加注释),欢迎留言。
一、先看看聊天(需求)
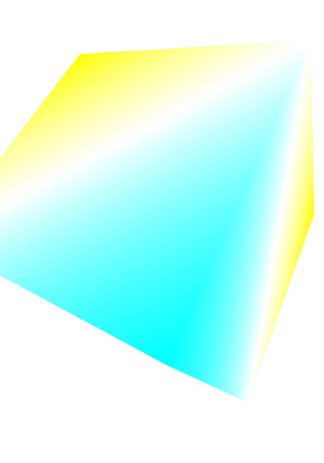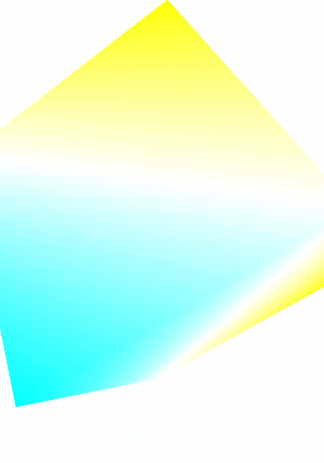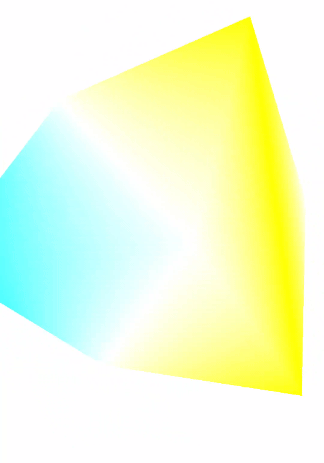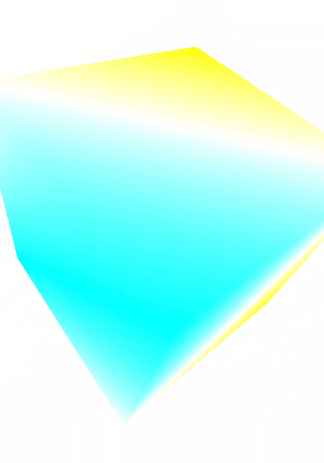
二、实现效果
三.实现
前五步传感器内容。
1.通过getSystemService获得SensorManager实例对象
mSensorManager = (SensorManager)context.getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE);
- 1
2.通过SensorManager实例对象获得想要的传感器对象:参数决定获取哪个传感器
mRotationVectorSensor = mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(
Sensor.TYPE_ROTATION_VECTOR);
- 1
- 2
3.在获得焦点时注册传感器并让本类实现SensorEventListener接口
mSensorManager.registerListener(this, mRotationVectorSensor, 10000);
- 1
- 第一个参数:SensorEventListener接口的实例对象
- 第二个参数:需要注册的传感器实例
- 第三个参数:传感器获取传感器事件event值频率:
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_FASTEST = 0:对应0微秒的更新间隔,最快,1微秒 = 1 % 1000000秒
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_GAME = 1:对应20000微秒的更新间隔,游戏中常用
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI = 2:对应60000微秒的更新间隔
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL = 3:对应200000微秒的更新间隔
键入自定义的int值x时:对应x微秒的更新间隔
4.必须重写的两个方法:onAccuracyChanged,onSensorChanged
- onSensorChanged: 传感器事件值改变时的回调接口:执行此方法的频率与注册传感器时的频率有关.
- onAccuracyChanged:传感器精度发生改变的回调接口
5.在失去焦点时注销传感器(为Activity提供调用)
public void stop() {
mSensorManager.unregisterListener(this);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
6.draw方法中的方发详解,本案例(opengl坐标系中采用的是3维坐标)
- glEnable:启用服务器端GL功能。
- glFrontFace:定义多边形的正面和背面。多边形正面的方向。GL_CW和GL_CCW被允许,初始值为GL_CCW。
- glShadeModel:选择恒定或光滑着色模式。GL图元可以采用恒定或者光滑着色模式,默认值为光滑着色模式。当图元进行光栅化的时候,将引起插入顶点颜色计算,不同颜色将被均匀分布到各个像素片段。允许的值有GL_FLAT 和GL_SMOOTH,初始值为GL_SMOOTH。
- glVertexPointer:定义一个顶点坐标矩阵。(后续源码中会贴上各个参数以及需要注意的地方)。
- glColorPointer:定义一个颜色矩阵。size指明每个颜色的元素数量,必须为4。type指明每个颜色元素的数据类型,stride指明从一个颜色到下一个允许的顶点的字节增幅,并且属性值被挤入简单矩阵或存储在单独的矩阵中(简单矩阵存储可能在一些版本中更有效率)。
- glDrawElements:由矩阵数据渲染图元
更多建议参考Android官方文档。
四.需求中的青黄色参数
final float colors[] = {
0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1,
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
五.源码
TdRenderer.java
public class TdRenderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer, SensorEventListener { //传感器 private SensorManager mSensorManager; private Sensor mRotationVectorSensor; private Cube mCube; private final float[] mRotationMatrix = new float[16]; public TdRenderer(Context context) { //第一步:通过getSystemService获得SensorManager实例对象 mSensorManager = (SensorManager)context.getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE); //第二步:通过SensorManager实例对象获得想要的传感器对象:参数决定获取哪个传感器 mRotationVectorSensor = mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor( Sensor.TYPE_ROTATION_VECTOR); mCube = new Cube(); mRotationMatrix[ 0] = 1; mRotationMatrix[ 4] = 1; mRotationMatrix[ 8] = 1; mRotationMatrix[12] = 1; } // 第三步:在获得焦点时注册传感器并让本类实现SensorEventListener接口 public void start() { /* *第一个参数:SensorEventListener接口的实例对象 *第二个参数:需要注册的传感器实例 *第三个参数:传感器获取传感器事件event值频率: * SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_FASTEST = 0:对应0微秒的更新间隔,最快,1微秒 = 1 % 1000000秒 * SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_GAME = 1:对应20000微秒的更新间隔,游戏中常用 * SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI = 2:对应60000微秒的更新间隔 * SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL = 3:对应200000微秒的更新间隔 * 键入自定义的int值x时:对应x微秒的更新间隔 * */ mSensorManager.registerListener(this, mRotationVectorSensor, 10000); } //第四步:必须重写的两个方法:onAccuracyChanged,onSensorChanged //第五步:在失去焦点时注销传感器(为Activity提供调用) public void stop() { mSensorManager.unregisterListener(this); } //传感器事件值改变时的回调接口:执行此方法的频率与注册传感器时的频率有关 public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) { // 大部分传感器会返回三个轴方向x,y,x的event值 //float x = event.values[0]; //float y = event.values[1]; //float z = event.values[2]; if (event.sensor.getType() == Sensor.TYPE_ROTATION_VECTOR) { SensorManager.getRotationMatrixFromVector( mRotationMatrix , event.values); } } public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) { gl.glClear(GL10.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); gl.glMatrixMode(GL10.GL_MODELVIEW); gl.glLoadIdentity(); gl.glTranslatef(0, 0, -3.0f); gl.glMultMatrixf(mRotationMatrix, 0); gl.glEnableClientState(GL10.GL_VERTEX_ARRAY); gl.glEnableClientState(GL10.GL_COLOR_ARRAY); mCube.draw(gl); } public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl, int width, int height) { gl.glViewport(0, 0, width, height); float ratio = (float) width / height; gl.glMatrixMode(GL10.GL_PROJECTION); gl.glLoadIdentity(); gl.glFrustumf(-ratio, ratio, -1, 1, 1, 10); } public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl, EGLConfig config) { gl.glDisable(GL10.GL_DITHER); //指定颜色缓冲区的清理值 gl.glClearColor(1,1,1,1); } public class Cube { //opengl坐标系中采用的是3维坐标: private FloatBuffer mVertexBuffer; private FloatBuffer mColorBuffer; private ByteBuffer mIndexBuffer; public Cube() { final float vertices[] = { -1, -1, -1, 1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, -1, 1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1, 1, 1, -1, 1, 1, }; final float colors[] = { 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, }; final byte indices[] = { 0, 4, 5, 0, 5, 1, 1, 5, 6, 1, 6, 2, 2, 6, 7, 2, 7, 3, 3, 7, 4, 3, 4, 0, 4, 7, 6, 4, 6, 5, 3, 0, 1, 3, 1, 2 }; ByteBuffer vbb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(vertices.length*4); vbb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); mVertexBuffer = vbb.asFloatBuffer(); mVertexBuffer.put(vertices); mVertexBuffer.position(0); ByteBuffer cbb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(colors.length*4); cbb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); mColorBuffer = cbb.asFloatBuffer(); mColorBuffer.put(colors); mColorBuffer.position(0); mIndexBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(indices.length); mIndexBuffer.put(indices); mIndexBuffer.position(0); } public void draw(GL10 gl) { //启用服务器端GL功能。 gl.glEnable(GL10.GL_CULL_FACE); //定义多边形的正面和背面。 //参数: //mode——多边形正面的方向。GL_CW和GL_CCW被允许,初始值为GL_CCW。 gl.glFrontFace(GL10.GL_CW); //选择恒定或光滑着色模式。 //GL图元可以采用恒定或者光滑着色模式,默认值为光滑着色模式。当图元进行光栅化的时候,将引起插入顶点颜色计算,不同颜色将被均匀分布到各个像素片段。 //参数: //mode——指明一个符号常量来代表要使用的着色技术。允许的值有GL_FLAT 和GL_SMOOTH,初始值为GL_SMOOTH。 gl.glShadeModel(GL10.GL_SMOOTH); //定义一个顶点坐标矩阵。 //参数: // //size——每个顶点的坐标维数,必须是2, 3或者4,初始值是4。 // //type——指明每个顶点坐标的数据类型,允许的符号常量有GL_BYTE, GL_SHORT, GL_FIXED和GL_FLOAT,初始值为GL_FLOAT。 // //stride——指明连续顶点间的位偏移,如果为0,顶点被认为是紧密压入矩阵,初始值为0。 // //pointer——指明顶点坐标的缓冲区,如果为null,则没有设置缓冲区。 gl.glVertexPointer(3, GL10.GL_FLOAT, 0, mVertexBuffer); //定义一个颜色矩阵。 //size指明每个颜色的元素数量,必须为4。type指明每个颜色元素的数据类型,stride指明从一个颜色到下一个允许的顶点的字节增幅,并且属性值被挤入简单矩阵或存储在单独的矩阵中(简单矩阵存储可能在一些版本中更有效率)。 gl.glColorPointer(4, GL10.GL_FLOAT, 0, mColorBuffer); //由矩阵数据渲染图元 //可以事先指明独立的顶点、法线、颜色和纹理坐标矩阵并且可以通过调用glDrawElements方法来使用它们创建序列图元。 gl.glDrawElements(GL10.GL_TRIANGLES, 36, GL10.GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, mIndexBuffer); } } //传感器精度发生改变的回调接口 public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor, int accuracy) { //在传感器精度发生改变时做些操作,accuracy为当前传感器精度 } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
ThreeDimensionsRotation,java(Activity记得注册)
public class ThreeDimensionsRotation extends Activity { private GLSurfaceView mGLSurfaceView; private TdRenderer tdRenderer; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); tdRenderer=new TdRenderer(this); // 创建预览视图,并将其设置为Activity的内容 mGLSurfaceView = new GLSurfaceView(this); mGLSurfaceView.setRenderer(tdRenderer); setContentView(mGLSurfaceView); } @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); tdRenderer.start(); mGLSurfaceView.onResume(); } @Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); tdRenderer.stop(); mGLSurfaceView.onPause(); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/小丑西瓜9/article/detail/185832
推荐阅读
相关标签




