- 1已解决(pymysqL连接数据库报错)pymysqL.err.ProgrammingError: (1146,“Table ‘test.students‘ doesn‘t exist“)_raise errorclass(errno, errval) pymysql.err.progra
- 2vue 报错this.$Api.sendEmail is not a function 和TypeError: Cannot set property 'pageCode' of undefined_vue this.$api.不存在
- 3自用的8款AI工具!提升学习/工作/赚钱效率,轻松超过99%的人!
- 4数据结构与算法——归并排序_数据结构归并排序
- 5使用 Xcode 运行 python等脚本语言(perl, ruby)_伊织code
- 6深入理解Elasticsearch的索引映射(mapping)_elasticsearch 类型 映射
- 7三分钟掌握PHP操作数据库_php数据库
- 8远程仓库——GitHub
- 9Hadoop之HBase基本简介_hadoop hbase
- 10[深度学习]yolov8+pyqt5搭建精美界面GUI设计源码实现一_yolo pyqt界面设计代码
Linux: Netfilter 简介
赞
踩
1. 前言
2. Netfilter 简介
2.1 Netfilter 的功能
Netfilter 有如下所列 3 大功能:
1. 数据包过滤(Packet filtering)
负责根据规则对数据包进行过滤。
2. 网络地址转换(NAT,Network Address Translation)
负责转换网络数据包的 IP 地址。
NAT 是一个重要的协议,已经成为在IPv4地址耗尽的情况下保护全局地址空间的流行和必要工具。
3. 数据包篡改(Packet mangling)
负责修改数据包内容(实际上,NAT 是数据包篡改的一种,它修改源或目标 IP 地址)。
例如,可以修改 TCP SYN 数据包的最大段大小(MSS)值,以便允许在网络上传输大尺寸的数据包。- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
2.2 Netfilter 示例
本文给出一个 数据包过滤(Packet filtering)的 Netfilter 内核模块 示例,在 IPv4 协议栈的 NF_INET_LOCAL_IN hook 点,插入一个钩子函数 nf_test_in_hook(),对进入的网络包进行处理。示例 netfilter_kern_pf_test.c 代码如下:
#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/types.h> #include <linux/skbuff.h> #include <linux/ip.h> #include <linux/udp.h> #include <linux/tcp.h> #include <linux/netfilter.h> #include <linux/netfilter_ipv4.h> #define NIPQUAD(addr) \ ((unsigned char *)&addr)[0], \ ((unsigned char *)&addr)[1], \ ((unsigned char *)&addr)[2], \ ((unsigned char *)&addr)[3] #define NIPQUAD_FMT "%u.%u.%u.%u" static unsigned int nf_pf_test_in_hook(unsigned int hook, struct sk_buff *skb, const struct net_device *in, const struct net_device *out, int (*okfn)(struct sk_buff*)) { struct ethhdr *eth_header; struct iphdr *ip_header; eth_header = (struct ethhdr *)(skb_mac_header(skb)); ip_header = (struct iphdr *)(skb_network_header(skb)); pr_info("dest MAC: %pM, source MAC: %pM, protocol: %x\n", eth_header->h_dest, eth_header->h_source, eth_header->h_proto); pr_info("src IP:'"NIPQUAD_FMT"', dst IP:'"NIPQUAD_FMT"' \n", NIPQUAD(ip_header->saddr), NIPQUAD(ip_header->daddr)); return NF_ACCEPT; } static struct nf_hook_ops nf_pf_test_ops[] __read_mostly = { { .hook = (void *)nf_pf_test_in_hook, .pf = NFPROTO_IPV4, .hooknum = NF_INET_LOCAL_IN, .priority = NF_IP_PRI_FIRST, }, }; static int __init netfilter_pf_test_init(void) { int ret; ret = nf_register_net_hooks(&init_net, nf_pf_test_ops, ARRAY_SIZE(nf_pf_test_ops)); if (ret < 0) { pr_err("register nf packet-filter hook fail\n"); return ret; } pr_info("register packet-filter test hook\n"); return 0; } static void __exit netfilter_pf_test_exit(void) { pr_info("unregister nf packet-filter test hook\n"); nf_unregister_net_hooks(&init_net, nf_pf_test_ops, ARRAY_SIZE(nf_pf_test_ops)); } module_init(netfilter_pf_test_init); module_exit(netfilter_pf_test_exit); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); MODULE_DESCRIPTION("Netfliter packet-filter test");
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
编译 Makefile 如下:
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),) obj-m := netfilter_kern_pf_test.o else KERNELDIR ?= /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build PWD := $(shell pwd) modules: $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules endif clean: rm -rf *.o *~ core .depend .*.cmd *.ko *.mod.c .tmp_versions .cache.mk modules.order Module.symvers
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
在 Ubuntu 16.04 系统下编译、安装、运行:
$ make
$ sudo insmod netfilter_kern_pf_test.ko
$ dmesg- 1
- 2
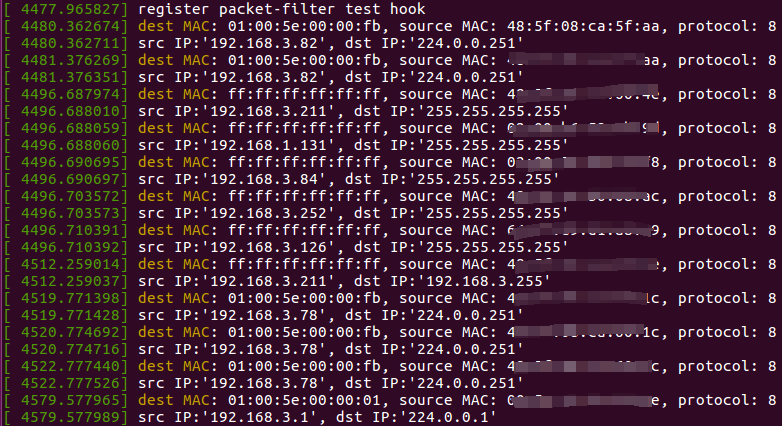
$ sudo rmmod netfilter_kern_pf_test
[ 4606.344200] unregister nf packet-filter test hook- 1
2.3 Netfilter 实现概览
Netfilter 功能,首先内核要开启 CONFIG_NETFILTER 配置。在内核代码 NF_HOOK 关键字进行搜索,就可以找到所有相关的 hook 点。本文只以 IPv4 数据收、发流程中的 5 个 Netfilter hook 点做简单分析。
2.3.1 Netfilter hook 的 注册 和 注销
内核系统如下接口来 注册 和 注销 Netfilter hook 接口:
/* include/linux/netfilter.h */
/* Function to register/unregister hook points. */
int nf_register_net_hook(struct net *net, const struct nf_hook_ops *ops);
void nf_unregister_net_hook(struct net *net, const struct nf_hook_ops *ops);
int nf_register_net_hooks(struct net *net, const struct nf_hook_ops *reg,
unsigned int n);
void nf_unregister_net_hooks(struct net *net, const struct nf_hook_ops *reg,
unsigned int n);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
static struct nf_hook_entries __rcu **nf_hook_entry_head(struct net *net, const struct nf_hook_ops *reg) { if (reg->pf != NFPROTO_NETDEV) return net->nf.hooks[reg->pf]+reg->hooknum; ... } static struct nf_hook_entries * nf_hook_entries_grow(const struct nf_hook_entries *old, const struct nf_hook_ops *reg) { ... new = allocate_hook_entries_size(alloc_entries); ... if (!inserted) { new_ops[nhooks] = (void *)reg; new->hooks[nhooks].hook = reg->hook; // Netlink hook 回调 new->hooks[nhooks].priv = reg->priv; } return new; } /* 注册 netfilter hook @reg 到 网络命名空间 @net */ int nf_register_net_hook(struct net *net, const struct nf_hook_ops *reg) { struct nf_hook_entries *p, *new_hooks; struct nf_hook_entries __rcu **pp; ... /* * 定位到 网络命名空间 @net 中 协议 / hook 类型 * (@reg->pf, @reg->hook) 对应的 Netfilter hook slot */ pp = nf_hook_entry_head(net, reg); if (!pp) return -EINVAL; mutex_lock(&nf_hook_mutex); p = nf_entry_dereference(*pp); new_hooks = nf_hook_entries_grow(p, reg); /* 新建一个 Netfilter hook 对象 */ /* * 将新建的 Netfilter hook 对象放置到 * 网络命名空间 @net 对应的 Netfilter hook slot */ if (!IS_ERR(new_hooks)) rcu_assign_pointer(*pp, new_hooks); mutex_unlock(&nf_hook_mutex); ... synchronize_net(); BUG_ON(p == new_hooks); kvfree(p); return 0; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
2.3.2 Netfilter hook 的触发
先看一张图:
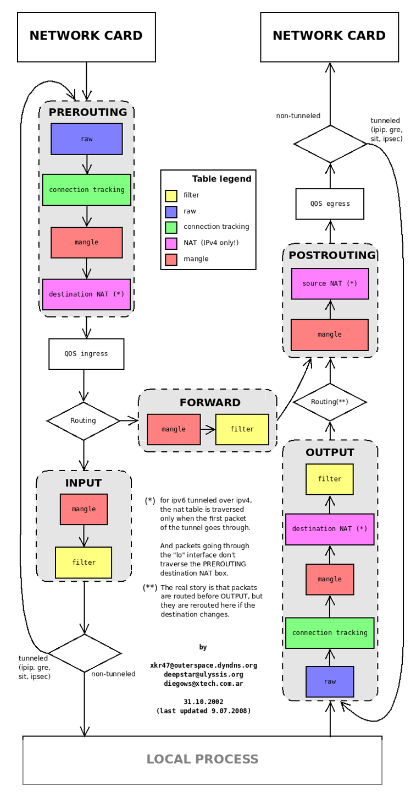
图中粗体字的 PREROUTING,INPUT,FORWARD,OUTPUT,POSTROUTING 分别对应数据收、发过程的以下 5 个 Netfilter hook 点:
/* include/uapi/linux/netfilter.h */
enum nf_inet_hooks {
NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING, // PREROUTING
NF_INET_LOCAL_IN, // INPUT
NF_INET_FORWARD, // FORWARD
NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT, // OUTPUT
NF_INET_POST_ROUTING, // POSTROUTING
NF_INET_NUMHOOKS
};- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
2.3.2.1 NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING
/* net/ipv4/ip_input.c */
/*
* Main IP Receive routine.
*/
int ip_rcv(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev, struct packet_type *pt, struct net_device *orig_dev)
{
...
return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_PRE_ROUTING,
net, NULL, skb, dev, NULL,
ip_rcv_finish);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
/* include/linux/netfilter.h */ static inline int NF_HOOK(uint8_t pf, unsigned int hook, struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *in, struct net_device *out, int (*okfn)(struct net *, struct sock *, struct sk_buff *)) { int ret = nf_hook(pf, hook, net, sk, skb, in, out, okfn); if (ret == 1) ret = okfn(net, sk, skb); return ret; } /** * nf_hook - call a netfilter hook * * Returns 1 if the hook has allowed the packet to pass. The function * okfn must be invoked by the caller in this case. Any other return * value indicates the packet has been consumed by the hook. */ static inline int nf_hook(u_int8_t pf, unsigned int hook, struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *indev, struct net_device *outdev, int (*okfn)(struct net *, struct sock *, struct sk_buff *)) { struct nf_hook_entries *hook_head; int ret = 1; ... rcu_read_lock(); hook_head = rcu_dereference(net->nf.hooks[pf][hook]); // 网络命名空间 @net 的 Netfilter hook 表 if (hook_head) { struct nf_hook_state state; nf_hook_state_init(&state, hook, pf, indev, outdev, sk, net, okfn); ret = nf_hook_slow(skb, &state, hook_head, 0); } rcu_read_unlock(); return ret; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
/* net/netfilter/core.c */ /* Returns 1 if okfn() needs to be executed by the caller, * -EPERM for NF_DROP, 0 otherwise. Caller must hold rcu_read_lock. */ int nf_hook_slow(struct sk_buff *skb, struct nf_hook_state *state, const struct nf_hook_entries *e, unsigned int s) { unsigned int verdict; int ret; for (; s < e->num_hook_entries; s++) { // 调用 nf_register_net_hooks() 系列接口注册的 hook, 如前面 // 示例代码中的 nf_pf_test_in_hook() 接口。 verdict = nf_hook_entry_hookfn(&e->hooks[s], skb, state); switch (verdict & NF_VERDICT_MASK) { case NF_ACCEPT: // 接受包 break; case NF_DROP: // 丢弃包 kfree_skb(skb); ret = NF_DROP_GETERR(verdict); if (ret == 0) ret = -EPERM; return ret; case NF_QUEUE: ret = nf_queue(skb, state, e, s, verdict); if (ret == 1) continue; return ret; default: /* Implicit handling for NF_STOLEN, as well as any other * non conventional verdicts. */ return 0; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
/* include/linux/netfilter.h */
static inline int
nf_hook_entry_hookfn(const struct nf_hook_entry *entry, struct sk_buff *skb,
struct nf_hook_state *state)
{
return entry->hook(entry->priv, skb, state);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2.3.2.2 NF_INET_LOCAL_IN
/* net/ipv4/ip_input.c */ /* * Deliver IP Packets to the higher protocol layers. */ int ip_local_deliver(struct sk_buff *skb) { /* * Reassemble IP fragments. */ struct net *net = dev_net(skb->dev); ... return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_LOCAL_IN, net, NULL, skb, skb->dev, NULL, ip_local_deliver_finish); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
NF_HOOK() 在 2.3.1 已经分析过,在此不再赘述。
2.3.2.3 NF_INET_FORWARD
/* net/ipv4/ip_forward.c */
int ip_forward(struct sk_buff *skb)
{
...
return NF_HOOK(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_FORWARD,
net, NULL, skb, skb->dev, rt->dst.dev,
ip_forward_finish);
...
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
NF_HOOK() 在 2.3.1 已经分析过,在此不再赘述。
2.3.2.4 NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT
/* net/ipv4/ip_output.c */
int __ip_local_out(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb)
{
...
return nf_hook(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_LOCAL_OUT,
net, sk, skb, NULL, skb_dst(skb)->dev,
dst_output);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
NF_HOOK() 在 2.3.1 已经分析过,在此不再赘述。
2.3.2.5 NF_INET_POST_ROUTING
/* net/ipv4/ip_output.c */ int ip_mc_output(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) { ... return NF_HOOK_COND(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_POST_ROUTING, net, sk, skb, NULL, skb->dev, ip_finish_output, !(IPCB(skb)->flags & IPSKB_REROUTED)); } int ip_output(struct net *net, struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb) { ... return NF_HOOK_COND(NFPROTO_IPV4, NF_INET_POST_ROUTING, net, sk, skb, NULL, dev, ip_finish_output, !(IPCB(skb)->flags & IPSKB_REROUTED)); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
3. Netfilter 的经典应用
Netfilter 的经典应用示范是 iptables,IPv4协议下,iptables 通过 setsockopt() 接口和内核模块 net/ipv4/netfilter/ip_tables.c 进行交互,感兴趣的读者可自行阅读相关源码。
看两个简单的 iptables 操作的示例:
# Drop all incoming packets from address 192.168.12.8
iptables -I INPUT -s 192.168.12.8 -j DROP
# 拒绝 ping 任何主机:将所有外发的 ICMP 包丢弃
iptables -A OUTPUT -p icmp -j DROP- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
4. 参考资料
[1] Netfilter’s flowtable infrastructure
[2] Nftables - Packet flow and Netfilter hooks in detail
[3] A Deep Dive into Iptables and Netfilter Architecture
[4] [译] 深入理解 iptables 和 netfilter 架构
[5] 一图带你看懂 Iptables 底层架构 Netfilter
[6] 理解 Linux 下的 Netfilter/iptables
[7] 走进Linux内核之Netfilter框架
[8] 从零开始基于Netfilter编写一个Linux防火墙



