- 1完全免费,文字转语音、AI语音合成,视频配音就用这两款软件!_字转语音软件 vpot
- 2写python爬虫的第一天,拿百度练手遇到 “ 被反爬遇到<title>百度安全验证</title> ” 的解决方案_
百度安全验证 - 3前端常用插件、工具类汇总分享
- 4Kali Linux入门教程(超详细)_kali linux 新手教程
- 5在ubuntu 22.04 上通过 Docker部署OpenGrok_grok部署
- 6Transformer中的Q/K/V理解_transformer q k v
- 7基于SSM框架的甜品店系统设计与实现_甜品店管理系统的需求分析
- 8鸿蒙HarmonyOS项目实战开发:分布式购物车_harmonyos简单的购物应用示例
- 9iOS 客户端 IM 以及列表 UI 框架_im客户端架构
- 10HarmonyOS鸿蒙开发指南:基于ArkTS开发 电话服务_鸿蒙开发 电话监控
【Sql Server】通过Sql语句批量处理数据,使用变量且遍历数据进行逻辑处理_sql 遍历
赞
踩
欢迎来到《小5讲堂》,大家好,我是全栈小5。
这是《Sql Server》系列文章,每篇文章将以博主理解的角度展开讲解,
特别是针对知识点的概念进行叙说,大部分文章将会对这些概念进行实际例子验证,以此达到加深对知识点的理解和掌握。
温馨提示:博主能力有限,理解水平有限,若有不对之处望指正!

前言
最近在进行历史数据处理,刚开始是想着通过在后端写个逻辑处理,也非常简单。
对于数据库而言,通过sql语句处理就是最好的,方便下次再处理时有个sql语句参考,
或者也方便运维人员直接使用,后端代码逻辑处理运维人员并不一定都懂。
因此,本篇文章将模拟批量数据进行sql语句遍历处理。
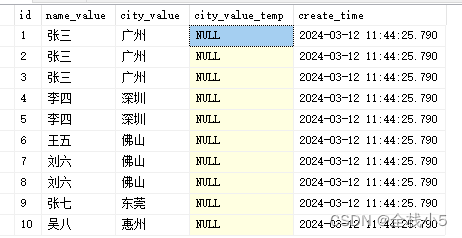
创建表
创建一张学生城市表,主要字段如下
-- 创建学生城市表
create table student_table
(
id int identity(1,1),
name_value nvarchar(50),
city_value nvarchar(50),
city_value_temp nvarchar(50),
create_time datetime default getdate()
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
模拟数据
模拟添加10条记录数据,且设置几条重复记录
-- 模拟10条记录
insert into student_table(name_value,city_value) values
('张三','广州'),
('张三','广州'),
('张三','广州'),
('李四','深圳'),
('李四','深圳'),
('王五','佛山'),
('刘六','佛山'),
('刘六','佛山'),
('张七','东莞'),
('吴八','惠州')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
分组查询
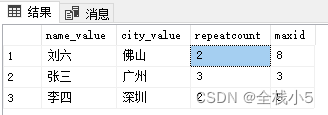
按学生和城市分组查询,且having筛选有重复记录的数据
-- 学生和城市分组查询 - 有重复记录的数据
select name_value,city_value,count(1) repeatcount,max(id) maxid
from student_table
group by name_value,city_value having count(1)>1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
while实现
进行两次while遍历,然后将学生重复的城市值,除了编号最大那条记录外,其他重复记录则加序号值并赋值到city_value_temp字段里
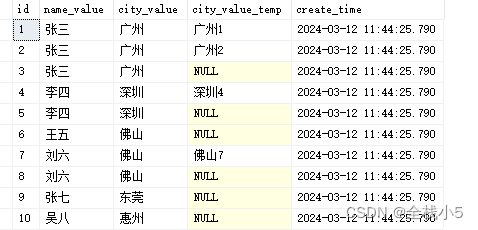
1)定义变量表 - 保存重复的学生记录
2)定量变量
3)将源表中的数据插入到表变量中
4)第一层遍历
5)第一层,每次都获取第一条记录
6)定义变量表 - 保存当前学生重复记录
7)第二层遍历
8)第二层,每次都获取第一条记录
9)将当前第二层遍历记录移除
10)更新表字段
11)将当前第一层遍历记录移除
-- =====遍历处理重复数据 - 编写处理逻辑===== -- 定义变量表 - 保存重复的学生记录 declare @temp_one_table table ( name_value nvarchar(50), city_value nvarchar(50), repeatcount int, maxid int ) -- 定量变量 declare @maxid int declare @name_value varchar(50) declare @city_value varchar(50) -- 将源表中的数据插入到表变量中 insert into @temp_one_table(name_value,city_value,repeatcount,maxid) select name_value,city_value,count(1) repeatcount,max(id) maxid from student_table group by name_value,city_value having count(1)>1 -- 第一层遍历 while exists(select city_value from @temp_one_table) begin -- 每次都获取第一条记录 select top 1 @maxid=maxid,@name_value=name_value,@city_value=city_value from @temp_one_table --print(@name_value) -- 定义变量表 - 保存当前学生重复记录 declare @temp_two_table table ( id int, name_value nvarchar(50), city_value nvarchar(50), create_time datetime ) insert into @temp_two_table(id,name_value,city_value,create_time) select id,name_value,city_value,create_time from student_table where name_value=@name_value and city_value=@city_value -- 第二层遍历 declare @id int while exists(select id from @temp_two_table) begin -- 第二层,每次都获取第一条记录 select top 1 @id=id from @temp_two_table print(@name_value+convert(varchar,@id)) -- 将当前第二层遍历记录移除 delete from @temp_two_table where id=@id -- 更新表字段 if @id!=@maxid begin update student_table set city_value_temp=(@city_value+convert(varchar,@id)) where id=@id end end -- 将当前第一层遍历记录移除 delete from @temp_one_table where name_value=@name_value and city_value=@city_value end select * from student_table -- =====/遍历处理重复数据 - 编写处理逻辑=====
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
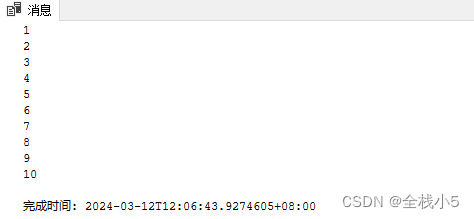
游标实现
输出编号
下面举例通过游标遍历,逐行输出编号值
-- 定义变量 declare @id int -- 定义游标并赋值 declare cursor_name cursor for select id from student_table -- 打开游标 open cursor_name -- 逐行获取数据 fetch next from cursor_name into @id while @@fetch_status=0 begin print(@id) -- 下一条记录 fetch next from cursor_name into @id end
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
结合临时表
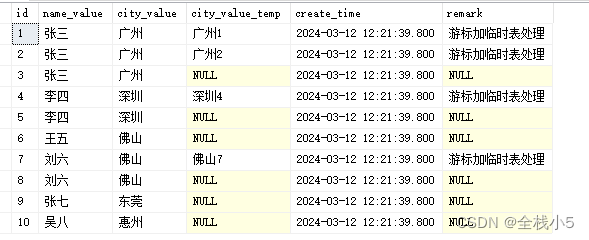
1)定义变量
2)定义游标并赋值
3)打开游标
4)逐行获取数据
5)创建局部临时表
6)第二层遍历
7)将当前第二层遍历记录移除
8)更新表字段
9)下一条记录
10)关闭游标
11)释放游标
-- 定义变量 declare @name_value nvarchar(50) declare @city_value nvarchar(50) declare @repeatcount int declare @maxid int -- 定义游标并赋值 declare cursor_name cursor for select name_value,city_value,count(1) repeatcount,max(id) maxid from student_table group by name_value,city_value having count(1)>1 -- 打开游标 open cursor_name -- 逐行获取数据 fetch next from cursor_name into @name_value,@city_value,@repeatcount,@maxid while @@fetch_status=0 begin --print(@name_value) -- 创建局部临时表并赋值 drop table #temp_table create table #temp_table ( id int, name_value nvarchar(50), city_value nvarchar(50), create_time datetime ) insert into #temp_table(id,name_value,city_value,create_time) select id,name_value,city_value,create_time from student_table where name_value=@name_value and city_value=@city_value -- 第二层遍历 declare @id int while exists(select id from #temp_table) begin select top 1 @id=id from #temp_table print(@name_value+convert(varchar,@id)) -- 将当前第二层遍历记录移除 delete from #temp_table where id=@id -- 更新表字段 if @id!=@maxid begin update student_table set city_value_temp=(@city_value+convert(varchar,@id)),remark='游标加临时表处理' where id=@id end end -- 下一条记录 fetch next from cursor_name into @name_value,@city_value,@repeatcount,@maxid end -- 关闭游标 close cursor_name -- 释放游标 deallocate cursor_name select * from student_table
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
知识点
在 SQL Server 中,游标和临时表都是用于处理数据的工具,但它们的使用方式和目的略有不同。
游标(Cursor):
游标是一种用于逐行处理数据的数据库对象。通常在需要逐行访问数据并执行复杂操作时使用。游标可以使用以下步骤创建和操作:
- 声明游标:定义一个游标并指定查询的结果集。
- 打开游标:执行查询并将结果集放入游标中。
- 逐行获取数据:使用 FETCH 语句一次从游标中获取一行数据。
- 处理数据:对获取的数据进行操作。
- 关闭游标:处理完数据后关闭游标,释放资源。
示例:
DECLARE @id INT
DECLARE cursor_name CURSOR FOR
SELECT id FROM table_name
OPEN cursor_name
FETCH NEXT FROM cursor_name INTO @id
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
-- Process data
FETCH NEXT FROM cursor_name INTO @id
END
CLOSE cursor_name
DEALLOCATE cursor_name
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
临时表(Temporary Table):
临时表是一种临时存储数据的表,它们一般用于在当前会话中临时存储和处理数据。SQL Server 提供了两种类型的临时表:全局临时表和局部临时表。
- 局部临时表:以 # 开头,在当前会话中可见,在会话结束时自动删除。
- 全局临时表:以 ## 开头,对所有会话可见,当创建它的会话结束时自动删除。
示例:
-- 创建局部临时表 CREATE TABLE #temp_table ( id INT, name VARCHAR(50) ) -- 插入数据 INSERT INTO #temp_table VALUES (1, 'Alice'), (2, 'Bob') -- 查询数据 SELECT * FROM #temp_table -- 删除临时表(在会话结束时会自动删除) DROP TABLE #temp_table
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
游标用于逐行处理数据,适用于复杂逐行操作;而临时表用于临时存储和处理数据,适用于需要临时保存中间结果的情况。
在实际应用中,要根据具体需求选择合适的工具来处理数据。
文章推荐
【Sql Server】通过Sql语句批量处理数据,使用变量且遍历数据进行逻辑处理
【新星计划回顾】第六篇学习计划-通过自定义函数和存储过程模拟MD5数据
【新星计划回顾】第四篇学习计划-自定义函数、存储过程、随机值知识点
【Sql Server】Update中的From语句,以及常见更新操作方式
【Sql server】假设有三个字段a,b,c 以a和b分组,如何查询a和b唯一,但是c不同的记录
【Sql Server】新手一分钟看懂在已有表基础上修改字段默认值和数据类型
总结:温故而知新,不同阶段重温知识点,会有不一样的认识和理解,博主将巩固一遍知识点,并以实践方式和大家分享,若能有所帮助和收获,这将是博主最大的创作动力和荣幸。也期待认识更多优秀新老博主。



