- 1huaggingface模型国内网络下载_huggfaceing
- 2pyqt5 python3.7教程_Python3.7安装PyQt5的方法
- 3c语言仿ce内存搜索工 源代码_CE的AOB_scan功能源码内存搜索特征码
- 4创建一个完整的购物商城系统是一个复杂的项目,涉及到前端、后端、数据库和支付接口等多个方面。
- 5【数据结构初阶】线性表——单链表(手撕单链表)
- 6AIGC - 大模型:InternLM 模型部署_ubuntu internlm
- 7计算机毕业/课程设计系列基于SpringBoot+Vue的高校图书管理和座位预约系统_基于springboot、vue高校图书管理系统
- 8Qt 文件操作_qt 读取单个单词
- 9【毕业设计】大数据住房数据分析可视化系统 - python_租房数据分析论文
- 10自动化使用 ChatGPT 生成 PPT 大纲 - 基于 Python 和 PyAutoGUI
linux--shell学习_gdm配置环境变量lang
赞
踩
目录
script的执行方式区别(source,sh script,./script)
变量
变量的设置规则:
echo用于显示变量,需要在变量名称前加上$,或者是以${变量}的方式显示。
1.变量与变量内容以一个等号"="来连接
- mali@mali:~$ myname=Anna
- mali@mali:~$ echo $myname
- Anna
- mali@mali:~$ echo ${myname}
- Anna
-
2. 等号两边不能直接接空格符
- mali@mali:~$ myname= Anna
- Anna: command not found
- mali@mali:~$ myname=hello kitty
- kitty: command not found
3.变量内容若有空格符可使用双引号或单引号将变量内容结合起来,
- mali@mali:~$ myname="hello kitty"
- mali@mali:~$ echo $myname
- hello kitty
- mali@mali:~$ myname='hello kitty'
- mali@mali:~$ echo $myname
- hello kitty
但是双引号内的特殊字符如$等,可以保有原本的特性:
- mali@mali:~$ var="lang is $LANG"
- mali@mali:~$ echo $var
- lang is en_US.UTF-8
单引号内的特殊字符仅为一般字符(纯文本):
- mali@mali:~$ var='lang is $LANG'
- mali@mali:~$ echo $var
- lang is $LANG
4、可使用转义字符"\"将特殊符号(如$、\、空格符、!等)变为一般字符
- mali@mali:~$ var="lang is \$LANG"
- mali@mali:~$ echo $var
- lang is $LANG
5. 在一串命令中,还需要通过其他的命令提供的信息,可以使用反单引号"`命令`"或"$(命令)"。
例如想要取得内核版本的设置:
- mali@mali:~$ version=`uname -r`
- mali@mali:~$ echo $version
- 4.10.0-28-generic
- mali@mali:~$ version=$(uname -r)
- mali@mali:~$ echo $version
- 4.10.0-28-generic
6.若该变量为了增加内容时,可用"$变量名称"或者${变量}累加内容:
- mali@mali:~$ myname=tom
- mali@mali:~$ myname="$myname":jerry
- mali@mali:~$ echo $myname
- tom:jerry
- mali@mali:~$ myname=${myname}:_kathy
- mali@mali:~$ echo $myname
- tom:jerry:_kathy
- #如果想要myname的内容多出"yes"
- mali@mali:~$ myname=$mynameyes
- mali@mali:~$ echo $myname
-
- mali@mali:~$
- #可以看到,如果没有双引号,那么myname的内容是$mynameyes这个变量,由于没有设置过这个变量,因此没有显示结果
-
7.若该变量需要在其他子进程进行,则需要以export来使变量变为环境变量:
- mali@mali:~$ name=jerry
- mali@mali:~$ echo $name
- jerry
- mali@mali:~$ bash #进入到子进程
- mali@mali:~$ echo $name #没有显示name的值
-
- mali@mali:~$ exit #离开子进程
- exit
- mali@mali:~$ export name
- mali@mali:~$ bash
- mali@mali:~$ echo $name
- jerry
- mali@mali:~$ exit
- exit
- mali@mali:~$
Q:“什么是子进程?”
A:在当前shell的情况下,去打开另一个新的shell,这个新的shell就是子进程。在一般的状态下,父进程的自定义变量时无法在子进程内使用的,但是通过export将变量变成环境变量后,就能够在子进程下面应用。
8.取消变量的方法为使用"unset 变量名称"
- mali@mali:~$ myname=jimmy
- mali@mali:~$ echo $myname
- jimmy
- mali@mali:~$ unset myname
- mali@mali:~$ echo $myname
-
- mali@mali:~$
环境变量的功能:
1. 用env查看环境变量:
- mali@mali:~$ env
- SHELL=/bin/bash #告知目前这个环境使用的shell是哪个程序
- VTE_VERSION=4205
- TERM=xterm-256color
- QT_LINUX_ACCESSIBILITY_ALWAYS_ON=1
- LC_NUMERIC=zh_CN.UTF-8
- WINDOWID=67108874
- GNOME_KEYRING_CONTROL=
- UPSTART_SESSION=unix:abstract=/com/ubuntu/upstart-session/1000/1537
- GTK_MODULES=gail:atk-bridge:unity-gtk-module
- name=jerry
- USER=mali #用户的名称
- SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/run/user/1000/keyring/ssh
- DEFAULTS_PATH=/usr/share/gconf/ubuntu.default.path
- XDG_CONFIG_DIRS=/etc/xdg/xdg-ubuntu:/usr/share/upstart/xdg:/etc/xdg
- PATH=/home/mali/bin:/home/mali/.local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin //执行文件查找的路径
- DESKTOP_SESSION=ubuntu
- QT_QPA_PLATFORMTHEME=appmenu-qt5
- QT_IM_MODULE=ibus
- LC_IDENTIFICATION=zh_CN.UTF-8
- JOB=gnome-session
- PWD=/home/mali #目前用户所在的工作目录
- XDG_SESSION_TYPE=x11
- XMODIFIERS=@im=ibus
- LANG=en_US.UTF-8 #语系数据
- GNOME_KEYRING_PID=
- MANDATORY_PATH=/usr/share/gconf/ubuntu.mandatory.path
- GDM_LANG=en_US
- LC_MEASUREMENT=zh_CN.UTF-8
- IM_CONFIG_PHASE=1
- COMPIZ_CONFIG_PROFILE=ubuntu
- GDMSESSION=ubuntu
- GTK2_MODULES=overlay-scrollbar
- SESSIONTYPE=gnome-session
- XDG_SEAT=seat0
- HOME=/home/mali #用户的主文件夹
- mali@mali:~$

2. $(关于本shell的PID)
“$”本身也是个变量,这个代表的是目前这个shell的线程代号,即是所谓的PID(Process ID)。
- mali@mali:~$ echo $$
- 11284
3. ?(关于上个执行命令的回传码)
当我们执行某些命令时,这些命令都会回传一个执行后的代码。一般来说,如果成功执行该命令,则会回传一个0值,如果执行过程发生错误,就会回传“错误代码”。
- mali@mali:~$ echo $SHELL
- /bin/bash
- mali@mali:~$ echo $?
- 0
- mali@mali:~$ name= jerry
- jerry: command not found
- mali@mali:~$ echo $?
- 127
- mali@mali:~$ echo $? #?只与“上一个执行命令”有关
- 0
4. export 自定义变量转成环境变量

我们在原本的bash下执行另一个bash,结果操作的环境接口会跑到第二个bash(子进程)去,那原本的bash就会处于暂停的情况(sleep)。
若要回到原本的bash去,就只有将第二个bash结束掉(exit)才行。
子进程仅会继承父进程的环境变量,不会继承父进程的自定义变量。
- mali@mali:~$ echo $$ #当前shell的pid
- 11284
- mali@mali:~$ myname=jerry
- mali@mali:~$ echo $myname
- jerry
- mali@mali:~$ bash #执行bash,进入子进程
- mali@mali:~$ echo $$ #显示子进程pid
- 11743
- mali@mali:~$ echo $myname
-
- mali@mali:~$ exit
- exit
- mali@mali:~$ export myname
- mali@mali:~$ bash
- mali@mali:~$ echo $myname
- jerry
- mali@mali:~$ echo $$
- 11754
- mali@mali:~$ exit
- exit
- mali@mali:~$ echo $$
- 11284

通配符(wildcard)
| 符号 | 意义 |
| * | 代表0到无穷多个任意字符 |
| ? | 代表一定有一个任意字符 |
| [] | 代表一定有一个在中括号内的字符,例如[abcd]代表一定有一个字符,可能是a,b,c,d这四个中任何一个 |
| [-] | 代表在编码顺序内的所有字符,例如[0-9]代表0到9之间的所有数字 |
| [^] | 表示原向选择,例如[^abc]代表一定有一个字符,只要是非a,b,c的其他字符都接受的意思 |
- #找出/etc/下面以cron开头的文件名
- mali@mali:~$ ll -d /etc/cron*
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/cron.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/cron.daily/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/cron.hourly/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/cron.monthly/
- -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 722 4月 6 2016 /etc/crontab
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/cron.weekly/
-
- #找出/etc/下面文件名刚好是五个字母的文件名
- mali@mali:~$ ll -d /etc/?????
- drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/avahi/
- drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/dconf/
- -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4676 7月 6 2017 /etc/drirc
- drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/emacs/
- drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/fonts/
- -rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 594 7月 14 20:03 /etc/fstab
- drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/gconf/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/gnome/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/groff/
- -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 989 7月 14 20:51 /etc/group
- -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 219 7月 14 20:06 /etc/hosts
- -rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 123 7月 14 20:06 /etc/iftab
- -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 26 7月 31 2017 /etc/issue
- -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 267 10月 23 2015 /etc/legal
- -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 111 11月 20 2015 /etc/magic
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:43 /etc/pam.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/pulse/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:43 /etc/rc0.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:42 /etc/rc1.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:42 /etc/rc2.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:42 /etc/rc3.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:42 /etc/rc4.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:42 /etc/rc5.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:43 /etc/rc6.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:43 /etc/rcS.d/
- lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 23 7月 14 20:03 /etc/vtrgb -> /etc/alternatives/vtrgb
-
- #找出/etc/文件名含有数字的文件名
- mali@mali:~$ ll -d /etc/*[0-9]*
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/at-spi2/
- drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/dbus-1/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/gtk-2.0/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/gtk-3.0/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/ImageMagick-6/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/iproute2/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/libnl-3/
- -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 967 10月 30 2015 /etc/mke2fs.conf
- -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7649 8月 1 2017 /etc/pnm2ppa.conf
- drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/polkit-1/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/python2.7/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/python3/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/python3.5/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:43 /etc/rc0.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:42 /etc/rc1.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:42 /etc/rc2.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:42 /etc/rc3.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:42 /etc/rc4.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:42 /etc/rc5.d/
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 7月 14 20:43 /etc/rc6.d/
- -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 10368 10月 2 2015 /etc/sensors3.conf
- drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 4月 2 2016 /etc/udisks2/
- drwxr-xr-x 11 root root 4096 8月 1 2017 /etc/X11/
-
- #找出/etc/下面文件名开头非为小写字母的文件名
- mali@mali:~$ ll -d /etc/[^a-z]*
- ls: cannot access '/etc/[^a-z]*': No such file or directory

命令执行的判断依据:; && ||
1. cmd;cmd
不考虑命令相关性的连续命令执行
- mali@mali:~$ date;echo $HOME
- 2019年 07月 18日 星期四 00:34:16 CST
- /home/mali
2. $?(命令回传码)与&& ||
两个命令之间有相依性,而这个相依性主要判断的地方就在于前一个命令执行的结果是否正确。
| 命令执行情况 | 说明 |
| cmd1 && cmd2 | 若cmd1执行完毕且正确执行($?=0),则开始执行cmd2 若cmd1执行完毕且为错误($?!=0),则cmd2不执行 |
| cmd1 || cmd2 | 若cmd1执行完毕且正确执行($?=0),则cmd2不执行 若cmd1执行完毕且为错误($?!=0),则开始执行cmd2 |
- #使用ls查阅目录/tmp/test是否存在,若存在则用touch创建/tmp/test/file1
- mali@mali:~$ ls /tmp/test && touch /tmp/test/file1
- ls: cannot access '/tmp/test': No such file or directory
- #ls找不到该目录,没有touch的错误,说明touch并没有执行
-
- mali@mali:~$ mkdir /tmp/test
- mali@mali:~$ ls /tmp/test && touch /tmp/test/file1
- mali@mali:~$ ll /tmp/test
- total 8
- drwxrwxr-x 2 mali mali 4096 7月 18 00:44 ./
- drwxrwxrwt 16 root root 4096 7月 18 00:44 ../
- -rw-rw-r-- 1 mali mali 0 7月 18 00:44 file1
- #测试/tmp/test是否存在,若不存在则予以创建,若存在就不做任何事情
- mali@mali:~$ rm -r /tmp/test #先删除此目录以方便测试
- mali@mali:~$ ls /tmp/test || mkdir /tmp/test
- ls: cannot access '/tmp/test': No such file or directory
- mali@mali:~$ ll -d /tmp/test
- drwxrwxr-x 2 mali mali 4096 7月 19 20:43 /tmp/test/
-
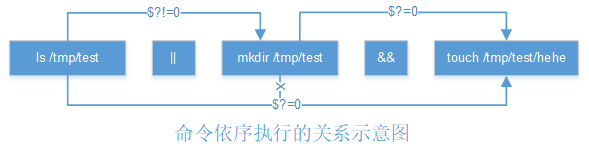
- #不清楚/tmp/test是否存在,但就是要创建/tmp/test/hehe文件
- #该指令总是会创建/tmp/test/hehe,无论/tmp/abc是否存在
- mali@mali:~$ ls /tmp/test || mkdir /tmp/test && touch /tmp/test/hehe
-
- 1./tmp/test 存在
- mali@mali:~$ ll -d /tmp/test
- drwxrwxr-x 2 mali mali 4096 7月 19 20:43 /tmp/test/
- mali@mali:~$ ls /tmp/test || mkdir /tmp/test && touch /tmp/test/hehe
- mali@mali:~$ ll /tmp/test
- total 8
- drwxrwxr-x 2 mali mali 4096 7月 19 20:50 ./
- drwxrwxrwt 18 root root 4096 7月 19 20:43 ../
- -rw-rw-r-- 1 mali mali 0 7月 19 20:50 hehe
- #可以看到,成功创建了/tmp/test/hehe
-
- #2./tmp/test不存在
- mali@mali:~$ rm -r /tmp/test
- mali@mali:~$ ls /tmp/test || mkdir /tmp/test && touch /tmp/test/hehe
- ls: cannot access '/tmp/test': No such file or directory
- mali@mali:~$ ll /tmp/test
- total 8
- drwxrwxr-x 2 mali mali 4096 7月 19 20:55 ./
- drwxrwxrwt 18 root root 4096 7月 19 20:55 ../
- -rw-rw-r-- 1 mali mali 0 7月 19 20:55 hehe
-
-

分析:
若/tmp/test存在,故回传$?=0,因为||遇到$?=0不会执行,此时$?=0继续向后传,&&遇到$?=0就开始创建/tmp/test/hehe
若/tmp/test不存在,故回传$?!=0,因为||遇到$?!=0会执行,故执行mkdir /tmp/test,由于mkdir /tmp/test会成功进行,所以回传$?=0,&&遇到$?=0就开始创建/tmp/test/hehe
管道命令(pipe)
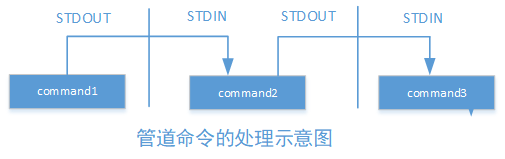
- 管道命令仅会处理standard output,对于standard error 会予以忽略
- 管道命令必须能够接收来自前一个命令的数据成为standard input继续处理才行
选取命令:cut grep
cut
可以将一段信息的某一段'切'出来,处理的信息以'行'为单位
- cut -d '分隔字符' -f fields #用于分隔字符
- cut -c 字符范围 #用于排列整齐的信息
-
- 参数:
- -d: 后面接分隔字符,与-f一起使用
- -f: 根据-d的分隔字符将一段信息切割成数段,用-f取出第几段的意思
- -c: 以字符(characters)的单位取出固定字符区间
-
- mali@mali:~$ echo $PATH
- /home/mali/bin:/home/mali/.local/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin
-
- #找出PATH的第五个路径
- mali@mali:~$ echo $PATH | cut -d ':' -f 5
- /usr/sbin
-
- #找出PATH的第三和第五个路径
- mali@mali:~$ echo $PATH | cut -d ':' -f 3,5
- /usr/local/sbin:/usr/sbin
-
- mali@mali:~$ export
- declare -x CLUTTER_IM_MODULE="xim"
- declare -x COMPIZ_CONFIG_PROFILE="ubuntu"
- declare -x DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS="unix:abstract=/tmp/dbus-xsmwfFeSMm"
- declare -x DEFAULTS_PATH="/usr/share/gconf/ubuntu.default.path"
- declare -x DESKTOP_SESSION="ubuntu"
- declare -x DISPLAY=":0"
- declare -x GDMSESSION="ubuntu"
- declare -x GDM_LANG="en_US"
- declare -x GNOME_DESKTOP_SESSION_ID="this-is-deprecated"
- declare -x GNOME_KEYRING_CONTROL=""
- declare -x GNOME_KEYRING_PID=""
- declare -x GPG_AGENT_INFO="/home/mali/.gnupg/S.gpg-agent:0:1"
- declare -x GTK2_MODULES="overlay-scrollbar"
- declare -x GTK_IM_MODULE="ibus"
- declare -x GTK_MODULES="gail:atk-bridge:unity-gtk-module"
- declare -x HOME="/home/mali"
- ......
- #将export输出的信息取得第12字符以后的所有字符串
- mali@mali:~$ export | cut -c 12-
- CLUTTER_IM_MODULE="xim"
- COMPIZ_CONFIG_PROFILE="ubuntu"
- DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS="unix:abstract=/tmp/dbus-xsmwfFeSMm"
- DEFAULTS_PATH="/usr/share/gconf/ubuntu.default.path"
- DESKTOP_SESSION="ubuntu"
- DISPLAY=":0"
- GDMSESSION="ubuntu"
- GDM_LANG="en_US"
- GNOME_DESKTOP_SESSION_ID="this-is-deprecated"
- GNOME_KEYRING_CONTROL=""
- GNOME_KEYRING_PID=""
- GPG_AGENT_INFO="/home/mali/.gnupg/S.gpg-agent:0:1"
- GTK2_MODULES="overlay-scrollbar"
- GTK_IM_MODULE="ibus"
- GTK_MODULES="gail:atk-bridge:unity-gtk-module"
- HOME="/home/mali"

grep
分析一行信息,若当中有我们所需要的信息,就将该行拿出来
- grep [-acinv] [--color=auto] '查找字符串' filename
-
- 参数:
- -a: 将binary文件以text文件的方式查找数据
- -c: 计算找到'查找字符串'的次数
- -i: 忽略大小写的不同
- -n: 输出行号
- -v: 反向选择,即显示出没有'查找字符串'内容的那一行
- --color=auto: 可以将找到的关键字部分加上颜色显示
-
- mali@mali:~$ last
- mali tty7 :0 Mon Jul 29 06:47 gone - no logout
- reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Mon Jul 29 06:46 still running
- mali tty7 :0 Thu Jul 25 22:24 - crash (3+08:21)
- reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Thu Jul 25 22:22 still running
- mali tty7 :0 Wed Jul 24 23:00 - crash (23:22)
- reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Wed Jul 24 22:58 still running
- guest-cb tty8 :1 Sun Jul 21 23:39 - crash (2+23:18)
- mali tty7 :0 Mon Jul 15 19:04 - crash (9+03:54)
- reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Mon Jul 15 19:03 still running
- mali tty7 :0 Sun Jul 14 20:53 - crash (22:09)
- reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Sun Jul 14 20:52 still running
- mali tty7 :0 Sun Jul 14 20:47 - crash (00:05)
- reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Sun Jul 14 20:47 still running
-
- wtmp begins Sun Jul 14 20:47:10 2019
-
- 示例1:将last当中有出现mali的那一行选取出来
- mali@mali:~$ last | grep -n 'mali'
- 1:mali tty7 :0 Mon Jul 29 06:47 gone - no logout
- 3:mali tty7 :0 Thu Jul 25 22:24 - crash (3+08:21)
- 5:mali tty7 :0 Wed Jul 24 23:00 - crash (23:22)
- 8:mali tty7 :0 Mon Jul 15 19:04 - crash (9+03:54)
- 10:mali tty7 :0 Sun Jul 14 20:53 - crash (22:09)
- 12:mali tty7 :0 Sun Jul 14 20:47 - crash (00:05)
-
-
- 示例2:输出没有出现mali的行
- mali@mali:~$ last | grep -vn 'mali'
- 2:reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Mon Jul 29 06:46 still running
- 4:reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Thu Jul 25 22:22 still running
- 6:reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Wed Jul 24 22:58 still running
- 7:guest-cb tty8 :1 Sun Jul 21 23:39 - crash (2+23:18)
- 9:reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Mon Jul 15 19:03 still running
- 11:reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Sun Jul 14 20:52 still running
- 13:reboot system boot 4.10.0-28-generi Sun Jul 14 20:47 still running
- 14:
- 15:wtmp begins Sun Jul 14 20:47:10 2019

正则表达式
通配符代表的是bash的一个功能,而正则表达式则是一种字符串处理的表示方式。
基础正则表达式字符
| RE字符 | 意义与范例 |
| ^word | 待查找的字符串(word)在行首 范例:查找行首为#的那一行,并列出行号 grep -n '^#' regular_express.txt |
| word$ | 待查找的字符串(word)在行尾 范例:查找行尾为!的那一行,并列出行号 grep -n '!$' regular_express.txt |
| . | 代表一定有一个任意字符的字符 范例:查找的字符串可以是(eve)(eae)(eee)(e e),但不能为(ee) 即e与e中间一定且仅有一个字符 grep -n 'e.e' regular_express.txt |
| \ | 转义字符,将特殊符号的特殊意义去除 范例: 查找含有单引号的那一行 grep -n \' regular_express.txt |
| * | 重复零个到无穷多个的前一个字符 范例:找出含有(es)(ess)(esss)等的字符串,注意,因为*可以是0个,所以es也是符号待查找字符串 grep -n ‘ess*’ regular_express.txt |
| [list] | 从字符集合的RE字符里面找出想要选取的字符 范例:查找含有(gl)或(gd)的那一行 grep -n ‘g[ld]' regular_express.txt |
| [n1-n2] | 从字符集合的RE字符里面找出想要选取的字符范围 范例:查找含有任意数字的那一行 grep -n '[0-9]' regular_express.txt |
| [^list] | 从字符集合的RE字符里面找出不要的字符串或范围 范例:查找的字符串可以是(oog)(ood)但不能是(oot) grep -n 'oo[^t]' regular_express.txt |
| \{n,m\} | 连续n到m个的前一个RE字符,若为\{n\}则是连续n个的前一个RE字符,若为\{n,\}则是连续n个以上的前一个RE字符 范例:在g与g之间有2个到3个的o存在的字符串 grep -n 'go\{2,3\}' regular_express.txt |
- #以ls -l配合grep 找出/etc/下面文件类型为连接文件属性的文件名
- mali@mali:~$ ls -l /etc | grep '^l'
- lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 33 7月 21 13:46 localtime -> /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai
- lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 19 7月 14 20:41 mtab -> ../proc/self/mounts
- lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 21 7月 14 20:03 os-release -> ../usr/lib/os-release
- lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 22 7月 21 13:45 printcap -> /var/run/cups/printcap
- lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 29 7月 14 20:06 resolv.conf -> ../run/resolvconf/resolv.conf
- lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 23 7月 14 20:03 vtrgb -> /etc/alternatives/vtrgb
script的执行方式区别(source,sh script,./script)
1.直接命令执行:shell.sh文件必须要具备可读与可执行(rx)的权限
- 绝对路径:使用/home/mali/shell.sh来执行命令;
- 相对路径:假设工作目录在/home/mali/,则使./shell.sh来执行
- 变量PATH功能: 将shell.sh放在PATH指定的目录内,例如:~/bin/.(shell.sh在~/bin内且具有rx的权限,直接输入shell.sh即可执行该脚本程序)
2.以bash进程来执行:通过bash shell.sh或sh shell.sh来执行
/bin/sh 其实就是/bin/bash,使用sh shell.sh即告诉系统,我想要直接以bash的功能来执行shell.sh这个文件内的相关命令的意思,所以此时你的shell.sh只要有r的权限即可被执行
这两种方式都会使用一个新的bash环境来执行脚本内的命令。也就是说,使用这种执行方式时,其实script是在子进程的bash内执行的
当子进程完成后,子进程内的各项变量或操作将会结束而不会传回父进程中
3.利用source来执行脚本:在父进程中执行
编写script,可以让用户输入firstname和lastname,最后在屏幕输出
- mali@mali:~$ vim shell.sh
- mali@mali:~$ cat shell.sh
- #!/bin/bash
-
- read -p "please input your first name: " firstname
- read -p "please input your last name: " lastname
- echo -e "\n Your full name is: $firstname $lastname"
- #使用sh shell.sh执行
- mali@mali:~$ sh shell.sh
- please input your first name: Li
- please input your last name: Ma
-
- Your full name is: Li Ma
- mali@mali:~$ echo $firstname $lastname
-
- #使用source shell.sh执行
- mali@mali:~$ source shell.sh
- please input your first name: Li
- please input your last name: Ma
-
- Your full name is: Li Ma
- mali@mali:~$ echo $firstname $lastname
- Li Ma
- #使用相对路径执行
- mali@mali:~$ ./shell.sh
- bash: ./shell.sh: Permission denied
- mali@mali:~$ ls -al shell.sh
- -rw-rw-r-- 1 mali mali 166 7月 29 08:00 shell.sh
- mali@mali:~$ chmod +x shell.sh
- mali@mali:~$ ls -al shell.sh
- -rwxrwxr-x 1 mali mali 166 7月 29 08:00 shell.sh
- mali@mali:~$ ./shell.sh
- please input your first name: Li
- please input your last name: Ma
-
- Your full name is: Li Ma


