热门标签
热门文章
- 1超美响应式自适应引导页带音乐播放器源码_自适应播放器html源码
- 2初中生成绩差可以学计算机吗,成绩差的初中生可以上什么学校
- 3深度学习----NLP-TextRank算法详解_pagerank算法在nlp
- 4IntelliJ IDEA插件之GsonFormat_插件错误: 插件 'gsonformat'(版本 1.5.0)被明确标记为与当前版本的 ide 不兼
- 5Java中判断数组是否为空_java判断字节数组是否全为零
- 6Java SE 小白学习笔记配套练习题_jcheng吧
- 7基于空间注意力机制的卷积神经网络结合双向长短记忆神经网络CNN-BiLSTM-SAM-attention实现数据分类附matlab实现_bilstm+cnn结合注意力机制
- 8二叉树的构建_构建二叉树
- 9c++算法学习笔记 (7) BFS
- 10网络基础④-DNS与ARP协议_apr和dns
当前位置: article > 正文
yolov5使用Grad-Cam进行热力图可视化_yolov5+grad cam
作者:小蓝xlanll | 2024-03-22 07:13:46
赞
踩
yolov5+grad cam
yolov5使用Grad-Cam进行热力图可视化
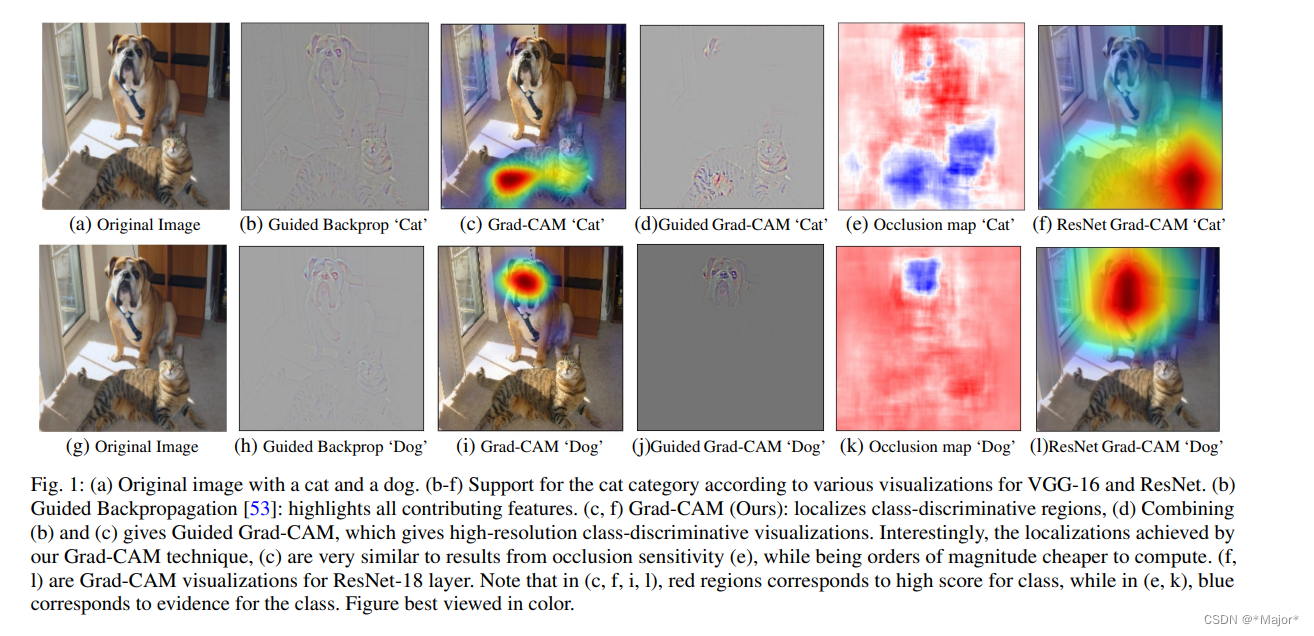
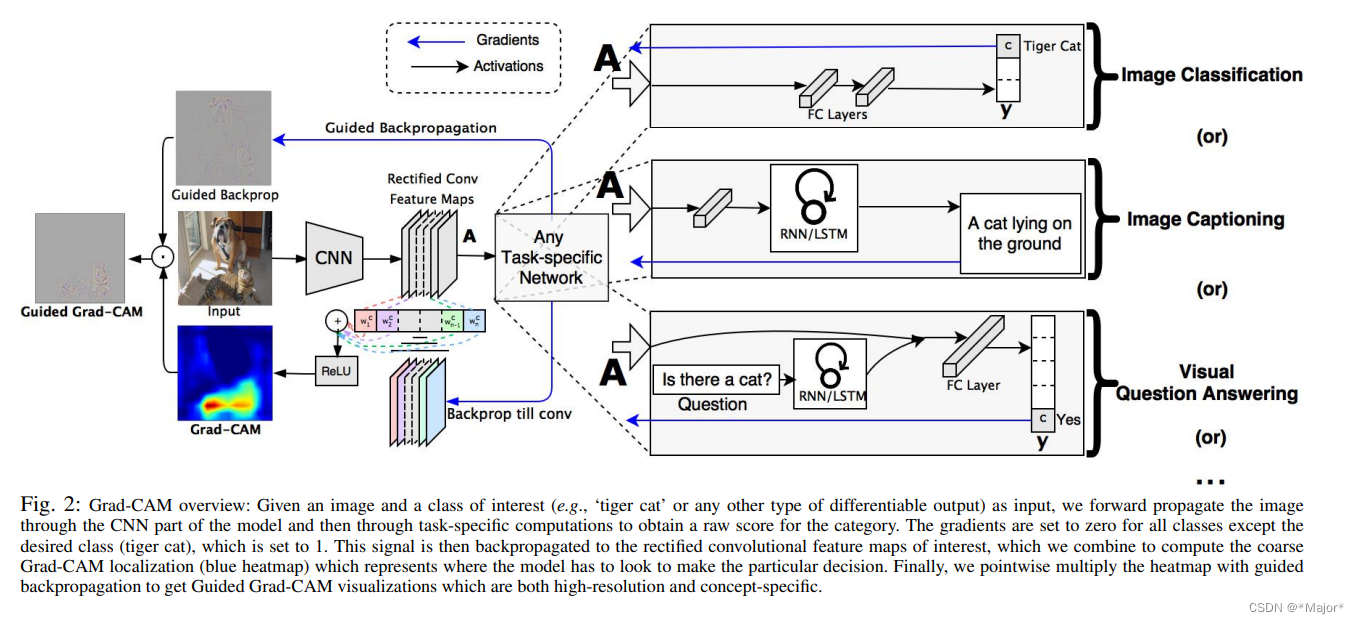
Grad-CAM(Class Activation Mapping-类别激活映射图)是非常常见的神经网络可视化的工具,用于探索模型的可解释性
grad-cam的计算,其实就是只需要两个值,一个是输出特征层,另一个是模型最后的某个类别对该特征层的梯度
类别激活映射图是一张图像,表示对预测输出的贡献分布,分数越高的地方表示原始图片对应区域对网络的响应越高、影响越大
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.02391
Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-based
Localization
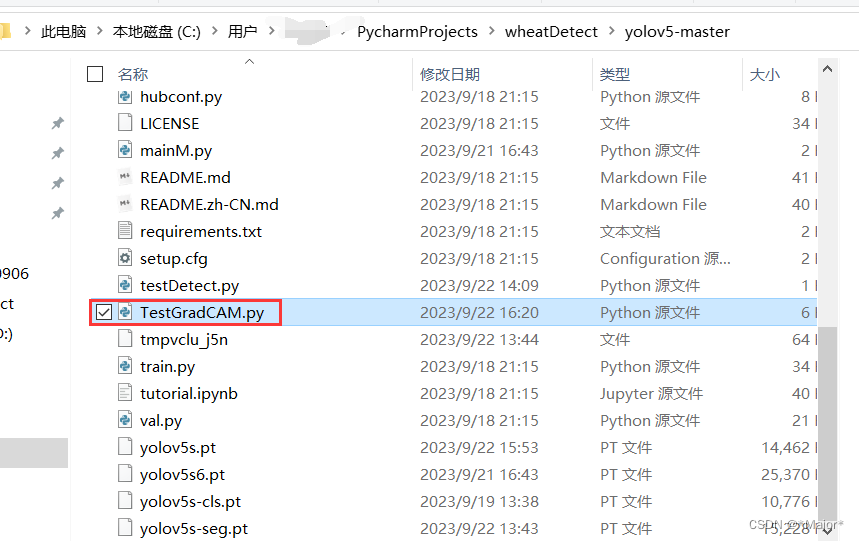
pip install grad-cam -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
- 1
pip install --upgrade numpy==1.23.5 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
- 1
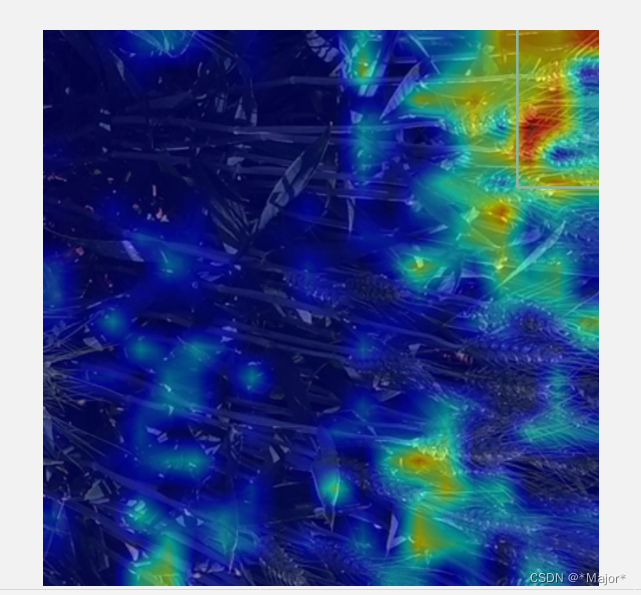
# pip install grad-cam -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') warnings.simplefilter('ignore') import torch, yaml, cv2, os, shutil import numpy as np np.random.seed(0) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from tqdm import trange from PIL import Image from models.yolo import Model from utils.general import intersect_dicts from utils.augmentations import letterbox from utils.general import xywh2xyxy from pytorch_grad_cam import GradCAMPlusPlus, GradCAM, XGradCAM from pytorch_grad_cam.utils.image import show_cam_on_image from pytorch_grad_cam.activations_and_gradients import ActivationsAndGradients class yolov5_heatmap: def __init__(self, weight, cfg, device, method, layer, backward_type, conf_threshold, genCAMNum): device = torch.device(device) ckpt = torch.load(weight) model_names = ckpt['model'].names csd = ckpt['model'].float().state_dict() # checkpoint state_dict as FP32 model = Model(cfg, ch=3, nc=len(model_names)).to(device) csd = intersect_dicts(csd, model.state_dict(), exclude=['anchor']) # intersect model.load_state_dict(csd, strict=False) # load model.eval() print(f'Transferred {len(csd)}/{len(model.state_dict())} items') target_layers = [eval(layer)] method = eval(method) colors = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(model_names), 3)).astype(np.int) self.__dict__.update(locals()) def post_process(self, result): logits_ = result[..., 4:] boxes_ = result[..., :4] # 对socre进行排序,获取排序后索引列表 sorted, indices = torch.sort(logits_[..., 0], descending=True) return logits_[0][indices[0]], xywh2xyxy(boxes_[0][indices[0]]).cpu().detach().numpy() def draw_detections(self, box, color, name, img): xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = list(map(int, list(box))) cv2.rectangle(img, (xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax), tuple(int(x) for x in color), 2) cv2.putText(img, str(name), (xmin, ymin - 5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.8, tuple(int(x) for x in color), 2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA) return img def __call__(self, img_path, save_path): # remove dir if exist if os.path.exists(save_path): shutil.rmtree(save_path) # make dir if not exist os.makedirs(save_path, exist_ok=True) # img process img = cv2.imread(img_path) img = letterbox(img)[0] img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) img = np.float32(img) / 255.0 tensor = torch.from_numpy(np.transpose(img, axes=[2, 0, 1])).unsqueeze(0).to(self.device) # init ActivationsAndGradients grads = ActivationsAndGradients(self.model, self.target_layers, reshape_transform=None) # get ActivationsAndResult result = grads(tensor) activations = grads.activations[0].cpu().detach().numpy() # postprocess to yolo output post_result, post_boxes = self.post_process(result[0]) for i in trange(self.genCAMNum): # if post_result[i][0] < self.conf_threshold: # break self.model.zero_grad() if self.backward_type == 'conf': post_result[i, 0].backward(retain_graph=True) else: # get max probability for this prediction score = post_result[i, 1:].max() score.backward(retain_graph=True) # process heatmap gradients = grads.gradients[0] b, k, u, v = gradients.size() weights = self.method.get_cam_weights(self.method, None, None, None, activations, gradients.detach().numpy()) weights = weights.reshape((b, k, 1, 1)) saliency_map = np.sum(weights * activations, axis=1) saliency_map = np.squeeze(np.maximum(saliency_map, 0)) saliency_map = cv2.resize(saliency_map, (tensor.size(3), tensor.size(2))) saliency_map_min, saliency_map_max = saliency_map.min(), saliency_map.max() if (saliency_map_max - saliency_map_min) == 0: continue saliency_map = (saliency_map - saliency_map_min) / (saliency_map_max - saliency_map_min) # add heatmap and box to image cam_image = show_cam_on_image(img.copy(), saliency_map, use_rgb=True) cam_image = self.draw_detections(post_boxes[i], self.colors[int(post_result[i, 1:].argmax())], f'{self.model_names[int(post_result[i, 1:].argmax())]} {post_result[i][0]:.2f}', cam_image) cam_image = Image.fromarray(cam_image) cam_image.save(f'{save_path}/{i}.png') def get_params(): params = { 'weight': 'best.pt', # 自己训练的模型权重 'cfg': 'models/yolov5s.yaml', # 模型对应配置文件 'device': 'cuda:0', # 设备 'method': 'XGradCAM', # 生成热力图方法GradCAMPlusPlus, GradCAM, XGradCAM 'layer': 'model.model[-2]', # 对那一层进行可视化,一般倒数第二层较佳 'backward_type': 'conf', # class or conf 'conf_threshold': 0.1, # 置信度阈值,被我注释了 'genCAMNum': 10 # 生成热力图张数。(保存时,按模型输出预测得分从高到低排序保存) } return params if __name__ == '__main__': model = yolov5_heatmap(**get_params()) # 预测图像,保存文件夹路径 model(r'.\WheatDataSet\images\train\1b43ca0a6.jpg', 'result')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/小蓝xlanll/article/detail/286168
推荐阅读
相关标签



