- 1中国人情世故的63个定律 。_达人归纳的63则中国人情世故的定律
- 2python 连接clickhouse数据库及简单操作
- 3安装visio2019Pro提示报错“0xC004F017“具体解决办法
- 4KubeEdge安装加入边缘节点报错: error unmarshaling JSON: while decoding JSON: json: cannot unmarshal number into_error decoding json: json: cannot unmarshal number
- 5深度解析Kafka中的消息奥秘
- 6HarmonyOS RUST 应用开发指导_deveco reload rust project
- 7Flask表单详解
- 8自学Python做兼职月入过万,用Python做项目有多赚钱?_python副业可以赚多少钱
- 9Nacos下载配置启动
- 10单片机:STC89C52的最小单元_单片机52最小系统显示屏元器件名称
编译原理构造LR(0)文法的Aciton表和GOTO表思路和C++实现_编译原理 action表生成
赞
踩
设计思路
设计思路简单概括:
例题已知文法G[E]:如下:
(1) E->aA
(2) E->bB
(3) A->cA
(4) A->d
(5) B->cB
(6) B->d
大致思路如下:
- 构造文法G[S]的增广文法G’[S]
- 构造G’[S]的初态
- 求出状态转移函数
- 求出完整的有限自动机
- 构造ACTION表和GOTO表
设计思路逐步分析
- 构造文法G[E]的增广文法G’[S]
这一步实际上是较为简单的,只需要增加一句S’->E即可
(0) S’->E
(1) E->aA
(2) E->bB
(3) A->cA
(4) A->d
(5) B->cB
(6) B->d - 构造G’[S]的初态
构造初态其实就是为了在->和第一个字母中间增加一个小圆点 ‘.’ 即可.
在上述例题中应该构造如下:
(0) S’->.E
(1) E->.aA
(2) E->.bB
(3) A->.cA
(4) A->.d
(5) B->.cB
(6) B->.d
但是选择合适的数据结构却比较困难.如果将小圆点直接添加到字符串中则会导致后面的小圆点位移操作十分繁琐.所以为了表达方便,另外使用一个int变量index表示小圆点的位置,如string 类型的’E->.aA’表示为string ’E->aA’ 和int index=0,index的范围为0~字符串aA的长度,即0<=index<=2,当index=2时代表可归约的终态.
另外这里用面向对象的思路,将上述数据结构封装在一个对象类production中,代码如下:
class production { private: const string symbol="."; const string fromToNext = "->"; string left; int index; string right; public: production(string str); string const toString();//返回带小圆点的字符串 string const toPrimaryString();//返回不带小圆点的字符串 bool operator==(production& right);//判断是否相同 void toAugmentedGrammar();//将一个句型设置为增广文法的句型 string getLeft(); string getRight(); int getIndex(); void indexIncrease();//小圆点右移一位 string getSymbolNext();//或许小圆点后面的字符 };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 求出状态转移函数

相当于 “E->.aA” --a–> “E->a.A”,在类production中只需要比较文法符号X和production.right[production.index+1]对应的字符与X是否相同即可,若相同则index+1,否则不变
构建GO类即图的边,为了简化表达方法用于表示I[from]—X—> I[next],该类内部只设置三个变量,具体如下:
class GO
{
public:
int from;
string X;
int next;
GO(int _from, string _X, int _next);
void show();//展示
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 求出完整的有限自动机
即构造完整的有限自动机I的集合,同时需要给出对应的转移表
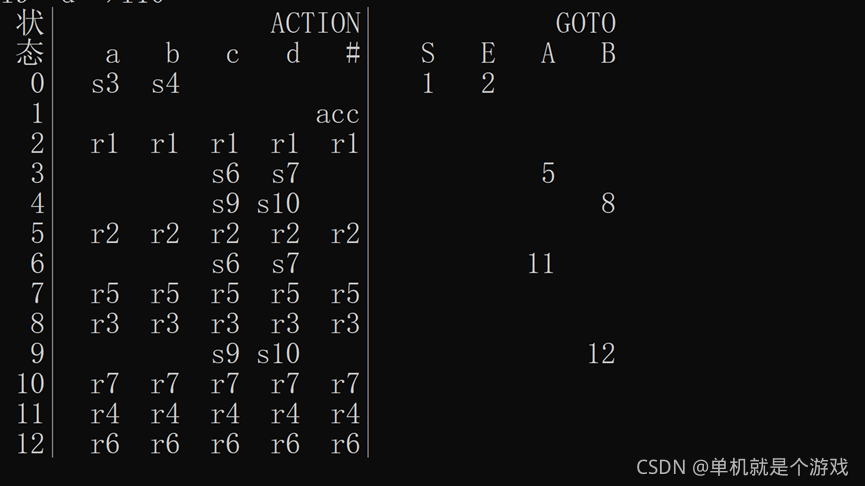
 由给出的例题求得的LR(0)FSM如下
由给出的例题求得的LR(0)FSM如下
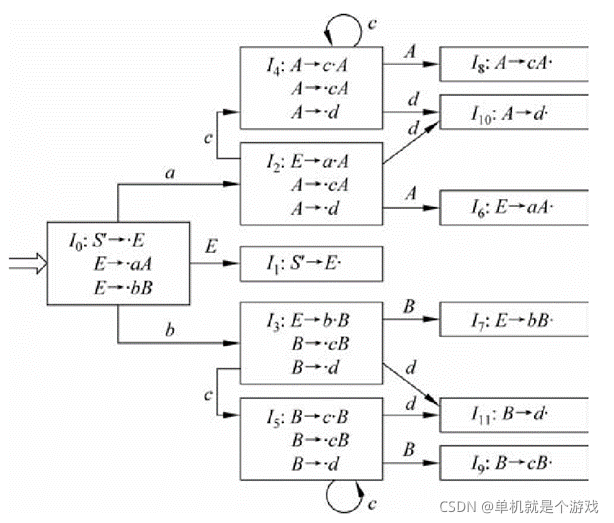
首先需要实现的数据结构如下: - List itemproduction类的集合构成Ix,如I0,I1等
class I
{
private:
vector<production> vectorProduction;
public:
I();//构建一个初始的I
void addNewProduction(production pro);//加入新句子
void show();//展示
bool operator==(I& right);//匹配I下的句子是否相同
void fill(string Terminators, vector<production> productionVector);//根据小圆点后是否为非终结符来循环填充I
vector<production> getVectorProduction();
I makeNewI(string nextStr);//根据转移字符生成下一个I
void productionIncrease();//I下的所有句子小圆点无条件右移一位,用于初始化I
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- List itemIx和转移字符构成LR(0)FSM有限状态机
class FSM { private: string nonTerminators;//非终结符集合EAB string terminators;//终结符集合abcd vector<production> productionVector;//原文法 vector<production> augmentedGrammarProduction;//增广文法 map<int, map<string, string>> mapACTION; map<int, map<string, string>> mapGOTO; vector<GO> vectorGO; vector<I> vectorI; void fill(int indexI); int findSameI(I i); public: FSM(string str[], int strLen, string nonterminator, string Terminators); void show();//展示ACTION和GOTO void outPutToFile(string path);//输出到文本 void buildFSM();//构建FSM void buildACTIONandGOTO();//构建ACTION和GOTO bool contain(production pro);//查看有无相同句子 };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
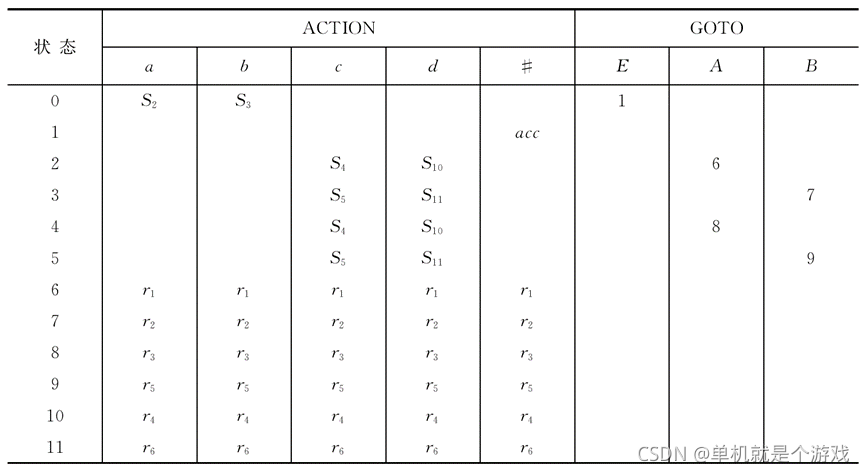
- 构造ACTION表和GOTO表
构造方法如下:

按照如上方法,例题解析如下:
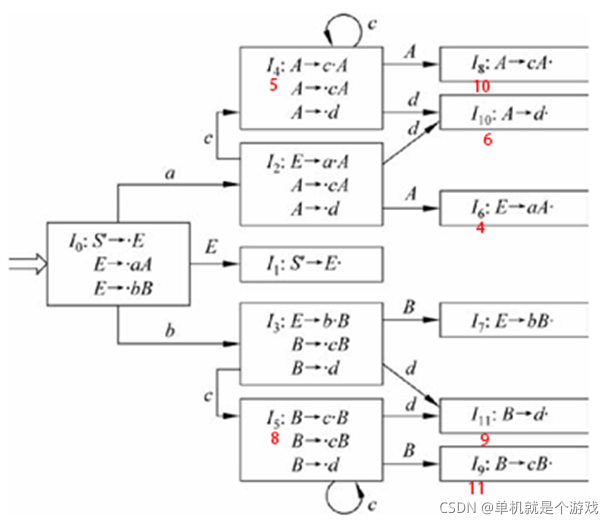
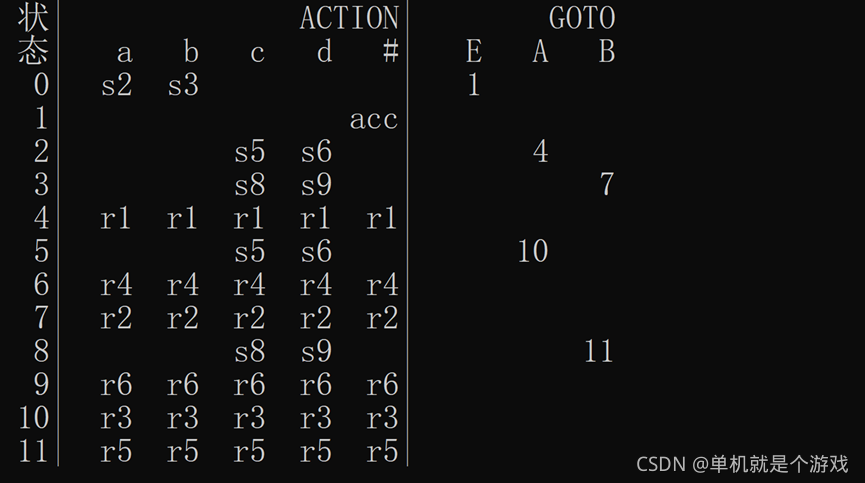
算法难点分析
1. 如何根据初态构造FSM状态图即下图
(1) 首先是完善初态I0,如一开始的S’->.E,因为 ‘.’ 后是非终结符,所以要将文法G[S]中的以E开头的句子填入I中
实现如下算法
void I::fill(string nonTerminators, vector<production> primaryGrammerProductionVector) {//根据小圆点后是否为非终结符来循环填充I for (int j = 0; j < vectorProduction.size(); j++) { //next是小圆点符号'.'后面的那个字母,为终结符或非终结符 string right = vectorProduction[j].getRight(); int index = vectorProduction[j].getIndex(); string next = right.substr(index, 1); if (nonTerminators.find(next)!=-1) {//如果是非终结符,则执行如下算法 for (int i = 0; i < primaryGrammerProductionVector.size(); i++) {//遍历原文法 if (contain(primaryGrammerProductionVector[i])) {//如果I中的句子已经有该句子,则跳过 continue; } if (primaryGrammerProductionVector[i].getLeft() == next) {//如果句子左边是和next相同的则加入I this->vectorProduction.push_back(primaryGrammerProductionVector[i]); } } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
(2) 如何根据I0和边上的字符生成下一个I
有了上面这个算法的基础,直接匹配就可,参数nextStr为传入的字符串
I I::makeNewI(string nextStr)//根据转移字符生成下一个I
{
I result;
for (int i = 0; i < vectorProduction.size(); i++) {//遍历I下的所有句子
if (vectorProduction[i].getSymbolNext() == nextStr) {//如果该句子小圆点后面的字符与传入的字符相同
production newProduction = vectorProduction[i];//生成新句子
newProduction.indexIncrease();//句子小圆点右移
result.addNewProduction(newProduction);//则返回的新I中加入该句子
//break;
}
}
return result;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
(3) 有了上述两个算法,就可以实现FSM类的构建算法
首先初始化I0,然后for循环遍历可以插入的边,用makeNewI()生成新的I,然后用fill算法填充I,最后根据生成的I的数量来初始化ACTION表和GOTO表
void FSM::buildFSM() { I I0; I0.addNewProduction(augmentedGrammarProduction[0]); vectorI.push_back(I0);//初始化I0 fill(0); for (int i = 0; i < vectorI.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < vectorI[i].getVectorProduction().size(); j++) { //获取小圆点后的字符 string strAfterSymbpol = vectorI[i].getVectorProduction()[j].getSymbolNext(); if (strAfterSymbpol == "") {//当index值和句子右端长度相同即小圆点在最末尾时返回空串 break;//说明是规约项目,不再继续往下做 } I newI=vectorI[i].makeNewI(strAfterSymbpol);//获取通过转移符号获得的新的I //newI.productionIncrease();//新I的第一个句子小圆点右移一位 newI.fill(nonTerminators, productionVector);//若小圆点右边为终结符则将以该终结符为左端的句子加入I int to= findSameI(newI);//to为GO的to,在这里暂定为查找相同的I的下标值 if (to ==-1) {//如果这个新I是集合I里面有的,则不再加入,否则,则加入 vectorI.push_back(newI); to = vectorI.size()-1; } GO go(i, strAfterSymbpol, to); vectorGO.push_back(go); } } //初始化ACTION和GOTO表 for (int i = 0; i < vectorI.size(); i++) { map<string, string> t1; map<string, string> t2; for (int i = 0; i < terminators.size(); i++) { t1.emplace(terminators.substr(i, 1), ""); } for (int i = 0; i < nonTerminators.size(); i++) { t2.emplace(nonTerminators.substr(i, 1), ""); } mapACTION.emplace(i, t1); mapGOTO.emplace(i, t2); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
2. 如何根据FSM状态图构造ACTION表和GOTO表
分两部分
(1) 首先遍历每条边,每次遍历边左边的I下的所有句子,匹配边上的字符和对应的句子,找到对应的句子后,:
a) 若小圆点为倒数第二个,则表示的对应下一个I的句子为归约或接受项目,若为终结符则置Sx,为非终结符则GOTO
b) 小圆点在末尾,跳过
c) 小圆点不在倒数第二个和末尾,置Sx
(2) 接着遍历每个I,找到归约项目,置rx即可
void FSM::buildACTIONandGOTO() { int from; int next; string X; for (int i = 0; i < vectorGO.size(); i++) {//遍历每个GO from = vectorGO[i].from; next = vectorGO[i].next; X = vectorGO[i].X; I Inext = vectorI[next]; I Ifrom = vectorI[from]; for (int j = 0; j < Ifrom.getVectorProduction().size(); j++) { //遍历每个Ifrom下的句子,查询对应的句子,如A->.aE,而GO为0--a-->1 //则表示对应,即小圆点后的字符相同 production productionFrom = Ifrom.getVectorProduction()[j]; if (productionFrom.getSymbolNext() != X) { continue; } if (productionFrom.getIndex() == productionFrom.getRight().size() - 1) { //若小圆点为倒数第二个,则表示的对应下一个I的句子为归约或接受项目 if (productionFrom.getLeft().back() == '\'') { //左端为S',即增广文法新添的,则为接受项目 mapACTION[next]["#"] = "acc"; } //左端不为S',则为归约项目或移进项目 if (terminators.find(X) != -1) {//为终结符的一种,置Sx mapACTION[from][X] = "s" + to_string(next); } else if (nonTerminators.find(X) != -1) {//为非终结符的一种,置GOTO mapGOTO[from][X] = to_string(next); } } else if (productionFrom.getIndex() == productionFrom.getRight().size()) { //小圆点在末尾,跳过 continue; } else { //小圆点不在倒数第二个和末尾 if (terminators.find(X) != -1) {//为终结符的一种,置Sx mapACTION[from][X] = "s" + to_string(next); } } } } for (int i = 0; i < vectorI.size(); i++) { if (vectorI[i].getVectorProduction().size() != 1) { continue; } production prod = vectorI[i].getVectorProduction()[0]; if (prod.getLeft().back() != '\'' && prod.getIndex() != prod.getRight().size()) { continue; } //设置rx的值 for (int g = 0; g < productionVector.size(); g++) { if (prod.toPrimaryString() == productionVector[g].toPrimaryString()) { for (int gg = 0; gg < terminators.size(); gg++) { //循环设置r的值 mapACTION[i][terminators.substr(gg, 1)] = "r" + to_string(g+1); } break; } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
当输入的文法为

其输出为