- 1数据结构:二叉树的操作
- 2解析 JavaScript 代码的加密与解密过程
- 3vnc连接linux使用教程_用vnc实现windows远程连接linux桌面 vnc安装与配置教程
- 4Linux(ubuntu) 安装kotlin
- 5按键精灵调用python文件_Python&按键精灵自动化
- 6文本分类 -- 追根究底_文本互信息计算
- 7Eclipse中使用Git——快速入门教程_eclipse git
- 8Android Studio使用的那些事(三)AS不同版本安装注意点(最新版AS 3.2.1)_as各个版本
- 9Capture One 21 Pro v14.3.0.185 飞思顶级图像后期处理编辑软件_飞思吃显卡
- 10淘宝扭蛋机小程序:探索未知的惊喜之旅
[CV学习笔记]tensorrt加速篇之yolov5seg 实例分割_yolov5-seg
赞
踩
1. 前言
yolov5-7.0版本继续更新了实例分割的代码,其分割的精度与速度令人惊讶,本文将yolov5-seg进行tensorrt加速,并利用矩阵的方法对进行部分后处理.

实例分割原理:yolact
yolov5seg-cpp实现代码:Yolov5-instance-seg-tensorrt
cpp矩阵实现:algorithm-cpp
本文测试代码:https://github.com/Rex-LK/tensorrt_learning/tree/main/trt_cpp/src/trt/demo-infer/yolov5seg
欢迎正在学习或者想学的CV的同学进群一起讨论与学习,v:Rex1586662742,q群:468713665
2. 实例分割结果
yolov5-seg的结果分为两部分,一个是检测的结果,维度为25200*177,前85列为每个检测框结果,后32列为每个检测框的mask系数,另外一个是分割结果:原型mask,维度为32 * 160 * 160,实例分割的后处理就是将目标框里面的mask系数与原型mask进行加权求和,从而获得实例分割的效果。
2.1 检测结果后处理
通过置信度以及NMS可以挑选出最终的目标框,这个过程就不在过多的赘述了。
2.2 实例分割分割结果后处理
实例分割的后处理过程其实是一个矩阵相乘的过程,因此基于。。。实现cpp矩阵,在这里实现了后处理,原作者的代码是用过利用opencv里面的Mat来表示一个矩阵,然后进行一些矩阵的操作,而本文实现在在自定义Matrix上进行矩阵操作。
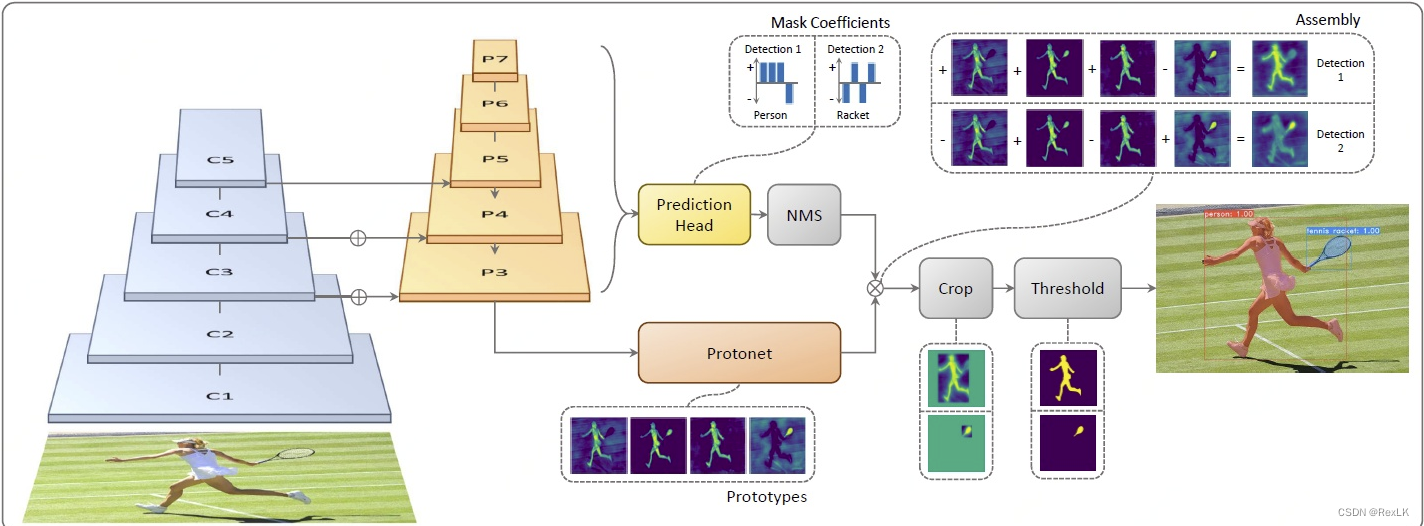
// 原型mask 32 * 160 * 160
float *seg_det = seg_out->cpu<float>();
vector<float> mask(seg_det, seg_det + segChannels * segWidth * segHeight);
// 矩阵表示
Matrix seg_proto(segChannels, segWidth * segHeight, mask);
for (int i = 0; i < box_result.size(); ++i) {
// 可以将所有的mask系数放在一起,然后利用cuda进行加速计算
// 每个目标框的mask系数 乘以原型mask 并取sigmod
Matrix resSeg = (mygemm(box_result[i].mask_cofs,seg_proto).exp(-1) + 1.0).power(-1);
Mat resMat(resSeg.data_);
resMat = resMat.reshape(0,{segHeight,segWidth});
// 如果图片预处理为直接resize,那么计算出来的resMat可以直接缩放回原图,
// 如果是填充黑边的resize,可以参考原代码将原型mask恢复到原图大小
resize(resMat, resMat, Size(INPUT_H,INPUT_W), INTER_NEAREST);
// 获取原型mask里面目标框的区域
Rect temp_rect = box_result[i].box;
// 将目标框区域 大于0.5的值变为255
cv::Mat binaryMat;
inRange(resMat(temp_rect), 0.5, 1, binaryMat);
box_result[i].boxMask = binaryMat;
// cv::imwrite(to_string(i) + "_.jpg", b);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
下面为利用cpp实现的矩阵,可以实现一些简单的矩阵运算。
class Matrix{
public:
Matrix();
Matrix(int rows, int cols, const std::initializer_list<float>& pdata={});
Matrix(int rows, int cols, const std::vector<float>&v);
const float& operator()(int irow, int icol)const {return data_[irow * cols_ + icol];}
float& operator()(int irow, int icol){return data_[irow * cols_ + icol];}
Matrix element_wise(const std::function<float(float)> &func) const;
Matrix operator*(const Matrix &value) const;
Matrix operator*(float value) const;
Matrix operator+(float value) const;
Matrix operator-(float value) const;
Matrix operator/(float value) const;
int rows() const{return rows_;}
int cols() const{return cols_;}
Matrix view(int rows, int cols) const;
Matrix power(float y) const;
float reduce_sum() const;
float* ptr() const{return (float*)data_.data();}
Matrix exp(float value);
public:
int rows_ = 0;
int cols_ = 0;
std::vector<float> data_;
};
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
3. 测试
下载本代码
修改CMakeLists.txt 里面的cuda、tensorrt、protobuf路径
修改main.cpp里面的路径,修改yolov5seg.cu里面的模型路径以及图片路径。
cd trt_cpp
mkdir build && cd biild
cmake … && make -j
./…/workspace/demo_infer
测试结果如下:
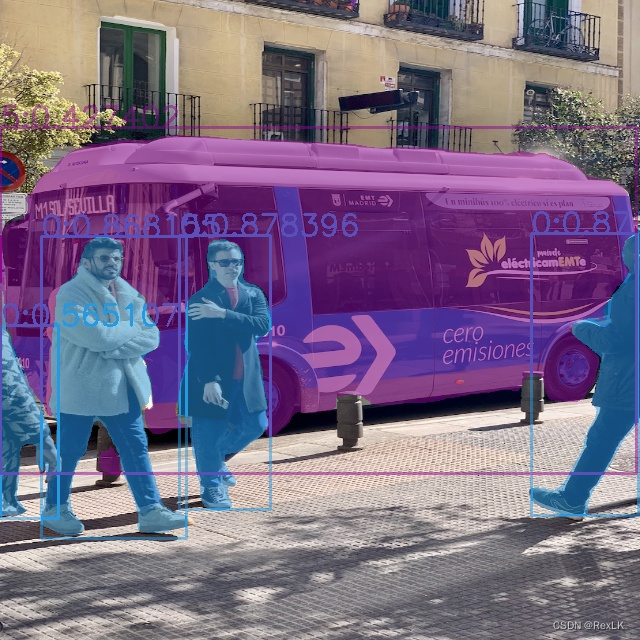

4. 总结
本次学习了yolov5实例分割的原理以及代码,通过对比原理以及代码的步骤,弄清楚了yolov5是如何实现实例的分割任务的,如果本文对各位有用,麻烦到github点个小star。


