- 1RK3568/RK3588 + YT 9215交换机芯片,MAC TO MAC 调试记录_yt9215
- 2MHA、MQA、GQA区别和联系_mqa和gqa
- 3接口入参形式_接口测试,接口协议以及常用接口测试工具详解
- 4【产业互联网周报】微软、OpenAI阻止俄罗斯、朝鲜黑客使用AI大模型;OpenAI发布首个视频生成模型Sora;...
- 5测试用例篇
- 6【Flask】在Flask中配置ssl证书,将http升级为https,并且使用Blueprint添加子域名_flask ssl
- 7github访问不了?详细解决方法_github打不开
- 8yolov5-v6.0详细解读_yolov5各版本性能
- 9Android性能优化系列:内存优化_android 内存优化
- 10探索量子计算:打开未来技术的大门
Spring框架学习
赞
踩
Spring框架
1、Spring框架介绍及搭建
Spring简介(官网:Spring | Home)
Spring框架是一个开放源代码的J2EE应用程序框架,由Rod Johnson发起,是针对bean的生命周期进行管理的轻量级容器(lightweight container)。 Spring解决了开发者在J2EE开发中遇到的许多常见的问题,提供了功能强大IOC、AOP及Web MVC等功能。Spring可以单独应用于构筑应用程序,也可以和Struts、Webwork、Tapestry等众多Web框架组合使用,并且可以与 Swing等桌面应用程序AP组合。因此, Spring不仅仅能应用于J2EE应用程序之中,也可以应用于桌面应用程序以及小应用程序之中。Spring框架主要由七部分组成,分别是 Spring Core、 Spring AOP、 Spring ORM、 Spring DAO、Spring Context、 Spring Web和 Spring Web MVC。
简略核心解释
spring是一个轻量级的开源框架。
spring为了解决企业级应用开发的业务逻辑层和其他各层的耦合问题。
spring是一个IOC和AOP的容器框架。
Spring框架特征
-
轻量(Lightweight)
-
控制反转(IOC [Inverse of Control] )
-
面向切面(AOP [Aspect Oriented Programming])
-
容器(Container)
-
框架(Framework)
-
MVC
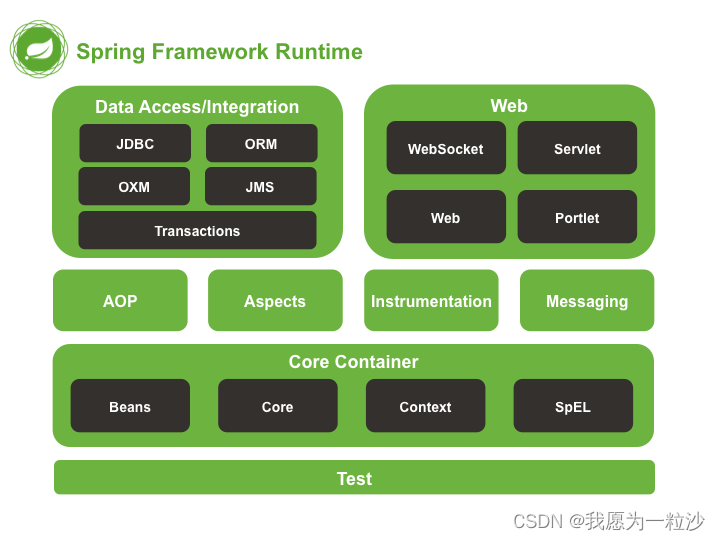
Spring 主要模块
-
Spring Core: Spring 其他所有的功能都需要依赖于该类库,主要提供 IoC 依赖注入功能。
-
Spring Aspects : 该模块为与 AspectJ 的集成提供支持。
-
Spring AOP :提供了面向切面的编程实现。
-
Spring JDBC : Java 数据库连接。
-
Spring JMS :Java 消息服务。
-
Spring ORM : 用于支持 Hibernate 等 ORM 工具。
-
Spring Web : 为创建 Web 应用程序提供支持。
-
Spring Test : 提供了对 JUnit 和 TestNG 测试的支持。
Spring框架搭建
-
创建java项目,导入jar包,配制xml文件
-
创建maven项目,注解+xml
-
创建springboot项目,编写javaconfig
2、Spring IOC的xml配置使用
- public class SqlServiceImpl implements SqlService {
- private MysqlDao mysqlDao;
- public SqlServiceImpl(){
- // mysqlDao=new MysqlDaoImpl();
- mysqlDao=new OracleDaoImpl();
- }
- public void show() {
- mysqlDao.show();
- }
- }
为啥使用IOC?
IOC演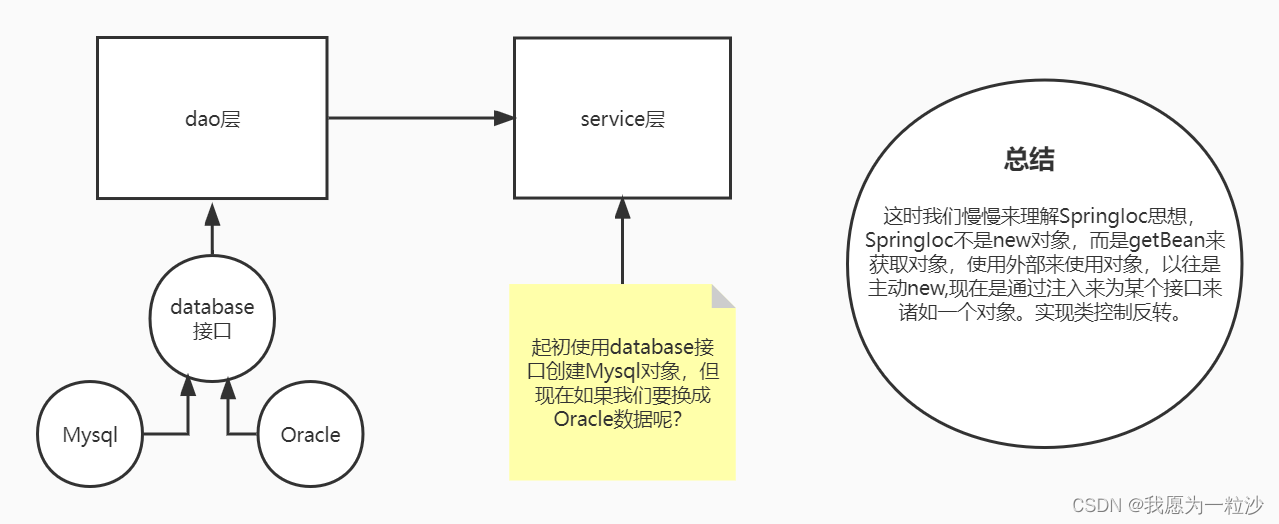 变
变
当我们面向接口编程,创建完接口和实现类后,发现实现类跟接口类之间存在耦合(牵一发而动全身),后来使用工厂模式,类的创建交给工厂类完成,这样实现类又与工厂有耦合,最后采用工厂+反射+配置文件的模式。(工厂类里面的getBean方法根据id参数返回实例对象,通过反射创建实例。)
IOC简单的来说就是:将原本在程序中手动创建实现类对象的控制权,交由spring 框架管理,即创建实现类对象控制权被反正到了spring框架。
DI(Dependecy Injection)
DI:依赖注入的概念,就是在spring创建这个对象的过程,将这个对象所依赖的属性注入进去。
IOC与DI关系
DI是实现IOC的方式,通过DI依赖注入达到IOC控制反转的效果。
IOC的Hello测试
-
导入spring相关依赖
- <!--maven会添加context所依赖的其他依赖-->
- <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
- <version>5.3.20</version>
- </dependency>
- <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/junit/junit -->
- <dependency>
- <groupId>junit</groupId>
- <artifactId>junit</artifactId>
- <version>4.13.2</version>
- <scope>test</scope>
- </dependency>
-
创建清晰的结构层次
- //第一层dao层
- //HelloDao接口
- public interface HelloDao {
- public void show();
- }
- //HelloDaoImpl
- public class HelloDaoImpl implements HelloDao {
- public void show() {
- System.out.println("Input hello!");
- }
- }
- //HelloService
- public interface HelloService {
- public void show();
- }
- //HelloServiceImpl
- public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
- private HelloDao helloDao;
- public void setHelloDao(HelloDao helloDao) {
- this.helloDao = helloDao;
- }
- public void show() {
- helloDao.show();
- }
- }
-
创建spring的xml文件
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
-
- <bean class="com.my.dao.impl.HelloDaoImpl" id="h1"></bean>
- <bean class="com.my.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl" id="hello">
- <property name="helloDao" ref="h1"></property>
- </bean>
- </beans>
-
测试代码
- public class HelloTest {
- private HelloService helloService;
- @Test
- public void test(){
- ApplicationContext context= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Hello.xml");
- helloService =(HelloServiceImpl) context.getBean("hello");
- helloService.show();
- }
- }
容器概念
//applicationContext是springIOC容器的代表,它负责实例化,配置和组装Bean
//applicationContext spring顶层核心接口
//ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 根据项目路径的xm1配置来实例化spring容器
//FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 根据磁盘路径的xml配置来实例化spring容器
//AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 根据javaconfig来配置实例化spring容器
ApplicationContext context= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Hello.xml");
//容器实例化就会加载所有bean,**bean的存在结构是map**
//加载多个xml,只需要ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Hello.xml","dao.xml");
AppicationContext是Spring loC容器实现的代表,它负责实例化,配置和组装Bean。容器通过读取配置元数据获取有关实例化、配置和组装哪些对象的说明。配置元数据可以使用XML、Java注解或Java代码来呈现。它允许你处理应用程序的对象与其他对象之间的互相依赖关系。
配置元数据
-
使用xml的配置
-
基于注解的配置
-
基于Java的配置
获取Bean
helloService =(HelloServiceImpl) context.getBean("hello");
/*
1、通过类来获取Bean getBean(User.class)
2、通过Bean的名字或者id来获取Bean getBean("user"),需要强制转化
3、通过Bean的名字加上类型 getBean("user",User.class)
*/
XML文件标签
<!-- 导入.xml文件 --> <import resource="spring.xml"></import> <!-- 设置别名 --> <alias name="user" alias="employye"></alias> <!-- description用于描述 --> <!-- name可以设置多个名字,但要用空格或者逗号及冒号 --> <bean class="com.my.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl" id="hello" name="user user1,user2:user3"> <description>你好呀</description> <property name="helloDao" ref="h1"></property> </bean>
外来知识@Before
@Before
public void before(){
......
}
//放在测试类中,会在所有测试类加载之前,就加载。
依赖注入方式
-
基于setter的依赖注入
<bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user">
<property name="id" value="1"></property>
</bean>
<!-- setter注入,property属性的name是找的setName方法名,对应如setXXX,name="XXX" -->
-
基于构造函数的方法注入
<bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user">
<constructor-arg name="id" value="1"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- constructor-arg中属性name可以省略,但要按照顺序来;也可以使用index来给设置的值找对应的下标,下标从0开始;可以使用type来指定参数类型 -->
不同数据类型值的注入
- <bean>
- <property name="list">
- <null></null>
- </property>
- <property name="list">
- <list>
- <value></value>
- <value></value>
- </list>
- </property>
- <property name="map">
- <map>
- <entry key="" value=""></entry>
- <entry value-ref="Object"></entry>
- </map>
- </property>
- <property name="Object">
- <bean>
- </bean>
- </property>
- </bean>
p命名空间简化基于setter属性注入
- xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
- <!--spring默认调用无参构造函数,所以定义了有参构造函数,最好同时定义无参构造函数-->
- <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user" p:id="1" p:name="张三" p:password="123456"></bean>
- <!--p命名空间不支持集合的,p:--》alt+enter-->
- <!--如果是集合-->
- <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user" p:id="1" p:name="张三" p:password="123456">
- <property>
- <list>
- ......
- </list>
- </property>
- </bean>
c命名空间简化基于构造函数属性注入
- xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
- <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user" c:id="4" c:name="张三">
- </bean>
Spring基于XML高级使用
depends-on:改变加载顺序
- <!--depends-on:会提前加载-->
- <bean class="com.my.pojo.Bos" id="bos" depends-on="user">
- <property name="name" value="你好"></property>
- <property name="age" value="22"></property>
- <property name="user" ref="user"></property>
- </bean>
- <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user">
- <property name="id" value="1"></property>
- <property name="name" value="张三"></property>
- <property name="password" value="123456"></property>
- </bean>
lazy-init:懒加载
- <!--lazy-init:true 在使用的时候才加载,为不是随着spring容器一起-->
- <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user" lazy-init="true"></bean>
Bean的作用域
-
默认单例(Singleton)作用域
<!--同一个id只会创建一个对象,scope="singleton"如果没有写,是默认的单例模式--> <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user" scope="singleton"></bean> <!--单例存在一个线程安全问题,如果多线程读写,很容易出错-->
-
原型(Propertype)
<!--多例--> <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user" c:id="4" scope="prototype"></bean>
-
其他作用域(request、session、application、websocket):需要集成web
Bean的实例化
-
默认调用无参构造函数 无法干预
-
静态工厂方法实例化Bean
<bean class="com.my.pojo.People" id="people" factory-method="createFactory"></bean> <!--通过加载com.my.pojo.People,然后调用createFactory方法来实例化对象,以此达到效果-->
-
抽象工厂方法实例化Bean
<bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user" factory-method="createFactory" factory-bean="PeopleFactory"></bean> <!--使用了抽象工厂方法-->
自动注入
一个类使用另一个类时,另一个类就是可以实现自动注入
<!--autowire:自动注入, byType:根据类型 byName:根据set方法的名字 constructor:根据构造函数的参数名匹配,再根据类型匹配--> <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user" autowire="byType"></bean>
-
优先注入
<!--primary优先:如果使用自动注入时,没有通过名字找到,但通过类型找到多个就可以使用primary来设置优先级--> <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user" primary='true'></bean> <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user2"></bean> <!--autowire-candidate="false"就是不参入注入--> <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user" autowire-candidate="false"></bean>
Bean生命周期回调实现
-
实现接口(InitializingBean, DisposableBean)
- public class Employye implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
- private int id;
- //初始化
- public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
- System.out.println("实例化Bean");
- }
- //注销
- public void destroy() throws Exception {
- System.out.println("注销Bean");
- }
- }
- @Test
- public void test3(){
- ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("user.xml");
- Employye employye=context.getBean("employye",Employye.class);
- //ApplicationContext没有close()方法,但是它的子类有
- ((ConfigurableApplicationContext)context).close();
- }
ApplicationContext没有close()方法,但是它的子类有,解决办法:Spring applicationContext爆出警告“Resource leak: 'applicationContext' is never closed” - 勤俭的搬运工 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com).close ()%3B)
-
基于配置(init-method,destroy-method)
<!--基于配置--> <bean class="com.my.pojo.Employye" id="employye" init-method="afterPropertiesSet" destroy-method="destroy"></bean>
-
基于注解(暂不学)
Spring创建第三方Bean对象
在Spring中,很多对象都是单实例的,在日常的开发中,我们经常需要使用某些外部的单实例对象,例如数据库连接池,下面我们来讲解下如何在spring中创建第三方bean实例。
<!--数据库连接配置-->
<bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="name" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC"></property>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property>
</bean>
属性文件(db.properties)的引入
注意:${}
- <bean class="com.my.pojo.User" id="user">
- <property name="id" value="${value}"></property>
- </bean>
- <!--第一种方式-->
- <context:property-placeholder location="db.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
- https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
- <!--第二种方式-->
- <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
- <property name="locations" value="db.properties"></property>
- </bean>
Spring表达式语言SpEL(Spring Expression Language)
-
#{1+2}:运算表达式 || #{其他bean.name} || #{其他bean} || #{T(方法的路径)}(这里的T表示静态方法)
3、Spring IOC的注解使用
-
@Repository 标记数据访问层
-
@Service 标记业务逻辑层
-
Controller 标记控制层
-
@Component 标记非三层以外的普通类
IOC不支持接口,所以注意不要标记在接口上。上面的注解就是将该类注入到spring容器中。
- @Controller
- public class UserController {
-
- }
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
- https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
-
- <!-- 扫描包-->
- <context:component-scan base-package="com.my"></context:component-scan>
- </beans>
- public class MyTest {
- @Test
- public void test1(){
- ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("springIoc.xml");
- UserController userController=context.getBean("userController",UserController.class);
- //spring容器会自动将类名第一字母小写,所以可以根据类名首字母小写来获取。
- //UserController userController=context.getBean(UserController.class);
- System.out.println(userController);
- }
- }
配置扫描包过滤
-
include-filter
-
exclude-filter
- <!--type:
- annotation(注解)
- assignable(类的完整限定命名)
- aspectj org.example.. *Service+根据切面表达式设置排除\包括,一般不会使用
- regex oxgl. example\. Default,*要由目标组件类名匹配的正则表达式。
- custom org.example. MyTypeFilter org. springframework.core.type . TypeFilter接口的自定义实现。
- -->
- <!--下面就是说按照注解,排除Repository-->
- <!--use-default-filters默认为true,扫描该包下所有的注解-->
- <context:component-scan base-package="com.my" use-default-filters="false">
- <context:include-filter type="assignable" expression="com.my.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
- <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/>
- </context:component-scan>
@Value设置依赖注入的属性的值
- @Component
- public class User {
- //@Value 除了写硬编码值,还可以写${} && #{}
- //@Value就可以使用properties文件中键值对
- //可以使用#{}来获取其他的Bean的属性值
- @Value("hello")
- private String name;
-
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- }
类的自动注入
- @Controller
- public class UserController {
- //@Autowired自动注入,如果没有@Autowired,就会报空指针异常
- /*
- bytype byname
- @Autowired默认优先根据类型匹配注入,没找到会根据名字找,名字没找到,就是报错
- 改变:1、重新设置名字
- 2、在注入的注解上设置value属性(@Service(value="userService"))
- 3、@Qualifier("userServiceImpl")
- 4、@primary设置自动注入的最要Bean
- 5、使用泛型T来实现自动注入限定
- */
- @Autowired
- @Qualifier("userServiceImpl")
- private UserService userService;
- public void test(){
- userService.test();
- }
- }
- //使用T泛型
- public interface PublicTestService<T> {
- T getTest();
- }
- @Service
- public class Test1Service implements PublicTestService<User> {
- public User getTest() {
- return new User();
- }
- }
- @Service
- public class Test2Service implements PublicTestService<Bos> {
-
- public Bos getTest() {
- return new Bos();
- }
- }
- @Controller
- public class UserController {
-
- // @Autowired
- // @Qualifier("userServiceImpl")
- @Autowired
- private PublicTestService<User> userService;
- public void test(){
- User user=userService.getTest();
- System.out.println(user);
- }
- }
- @Test
- public void test1(){
- UserController userController=context.getBean("userController",UserController.class);
- // UserController userController=context.getBean(UserController.class);
- userController.test();
- }
@Autowired
//Target 该方法可以标记在CONSTRUCTOR、METHOD、PARAMETER、FIELD、ANNOTATION_TYPE @Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Autowired { boolean required() default true; }
@Resource
import javax.annotation.Resource; @Controller public class UserController { @Resource //跟@Autowired作用一样,但是jdk的不是spring框架的。@Resource优先根据名字匹配 private PublicTestService<User> userService; public void test(){ User user=userService.getTest(); System.out.println(user); } }
@DependsOn("xxx")依赖某个类,由xml文件depends-on属性的作用
@Lazy懒加载,由xml文件lazy-init,要使用的时候才加载。
@Scope("singleton")默认单例模式,由xml文件scope
Bean生命周期使用注解监听
- @PostConstruct //初始化
- public void init(){
- System.out.println("初始化");
- }
-
- @PreDestroy //注销
- public void destory(){
- System.out.println("注销");
- }
问题:
-
怎样开启注解装配?
-
@Component,@Controller,@Repository,@Service有何区别?
-
当使用@Autowired匹配到多个类型怎么解决?
4、Spring IOC的javaconfig使用
-
外来知识:xxx instanceof xxx,后面的类是前面的类的类,子类,接口实现类
配制自己的Bean
- @Configuration //相当于xml文件,标记spring的配置类
- @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.my") //自动扫描包,相当于<context:component-scan>
- public class IoCJavaConfig {
-
- }
- @Controller
- public class HelloController {
- public void show(){
- System.out.println("hello");
- }
- }
- public class MyTest {
- @Test
- public void test1(){
- //加载spring上下文
- ApplicationContext context=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IoCJavaConfig.class);
-
- HelloController helloController=context.getBean("helloController",HelloController.class);
- helloController.show();
- }
- }
配制第三方的Bean
- @Configuration //相当于xml文件,标记spring的配置类
- @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.my") //自动扫描包,相当于<context:component-scan>
- public class IoCJavaConfig {
-
- /*
- <bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" id="dataSource">
- <property name="name" value="root"></property>
- <property name="password" value="123456"></property>
- <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC"></property>
- <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property>
- </bean>
- */
-
- @Bean //标记方法,由于在xml文件中添加一个bean
- public DruidDataSource dataSource(){
- DruidDataSource dataSource=new DruidDataSource();
- dataSource.setPassword("1234556");
- dataSource.setUsername("root");
- dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC");
- dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
- System.out.println("druid数据源");
- return dataSource;
- }
-
- }
- @Test
- public void test2(){
- ApplicationContext context=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IoCJavaConfig.class);
- DataSource dataSource=context.getBean("dataSource",DruidDataSource.class);
- System.out.println(dataSource);
- }
基于javaconfig实现的类,可以在@Bean(init-method="")像这样注入属性。
引入properties文件
- @Component
- public class User {
- @Value("${name}") //使用properties中的key为name
- private String name;
-
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
-
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- }
//在javaconfig类上加这个注解
@PropertySource("db.properties") || @PropertySource("classpath:db.properties")
- @Test
- public void test3() {
- User user = context.getBean(User.class);
- System.out.println(user.getName());
- }
一个javaconfig类引入一个javaconfig类
@Import(IoCJavaConfig_01.class) //import除了引入,也可以注入
在javaconfig中使用依赖外部Bean,就是从传递的参数考虑。使用内部Bean直接调用方法即可
通过实现ImportSelector接口来多个引入
- @Component
- public class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
- //实现ImportSelector,给Import({""})多个引入一样
- public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
- //可以以字符串的形式返回多个Bean
- return new String[]{"com.my.pojo.User"}; //这里是类的完整限定名,因此获取必须是类名获取
- }
- }
@Import(MyImportSelector.class) //在javaconfig类上添加
通过实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口来引入
- @Component
- public class MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
- public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata
- , BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
- GenericBeanDefinition genericBeanDefinition=new GenericBeanDefinition();
- genericBeanDefinition.setBeanClass(User.class);
- registry.registerBeanDefinition("user",genericBeanDefinition);
- }
- }
@Import(MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class) //在javaconfig类上添加
-
外来知识

最后SpringIoC核心Bean注入,自动装配。
5、SpringAOP介绍与原理
AOP: Aspect Oriented Programming面向切面编程
OOP:Object Oriented Programming面向对象编程
面向切面编程:基于OOP基础之上新的编程思想,OOP面向的主要对象是类,而AOP面向的主要对象是切面,在处理日志、安全管理、事务管理等方面有非常重要的作用。AOP是Spring中重要的核心点,虽然SOC容器没有依赖AOP,但是AOP提供了非常强大的功能,用来对IOC做补充。通俗点说的话就是在程序运行期间。
在不修改原有代码的情况下增强到之前写好的方法中的指定位置这种编程的方式叫AOP,AOP是一个思想。
AOP的底层用的代理模式,代理是一种设计模式。
代理模式
-
静态代理 缺点:需要为每一个被代理的类创建一个代理类
-
动态代理(AOP的底层是用的动态)。
-
jdk动态代理(必须实现接口)
-
cglib动态代理(不需要实现接口)
-
- //静态代理
- public interface Meituan {
- public void takeOutFood();
- }
-
-
- public class MeituanWorker implements Meituan{
- private Customer customer;
- public MeituanWorker(Customer customer){
- this.customer=customer;
- }
- public void takeOutFood() {
- customer.takeOutFood();
- System.out.println("外卖工作者来了!");
- }
- }
-
-
- public class Customer implements Meituan{
- public void takeOutFood() {
- System.out.println("请求外卖小哥!");
- }
- }
-
-
- public class MyTest {
- private MeituanWorker meituanWorker=new MeituanWorker(new Customer());
- @Test
- public void test(){
- meituanWorker.takeOutFood();
- }
- }
- //jdk动态代理
- public interface Subject {
- public void request();
- }
-
-
-
- public class RealSubject implements Subject{
- public void request() {
- System.out.println("RealSubject类");
- }
- }
-
-
-
- public class MyProxy implements InvocationHandler {
- private Object target;//声明被代理的对象
- public MyProxy(Object target){
- this.target=target;
- }
- public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
- System.out.println("InvocationHandler代理了!");
- Object o=method.invoke(target,args);
- return o;
- }
- }
-
-
-
- public class MyTest {
- @Test
- public void test(){
- /*
- ClassLoader loader, //类加载器,通常指被代理类的接口的类加载器
- Class<?>[] interfaces, //类型,通常指被代理类的接口类型
- InvocationHandler h //委托执行的处理类
- */
- ClassLoader loader=Subject.class.getClassLoader();
- Class<?>[] interfaces=new Class[]{Subject.class};
- InvocationHandler handler=new MyProxy(new RealSubject());
- Subject o=(Subject)Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader,interfaces,handler);
- System.out.println(o.getClass());
- o.request();//这个方法进入MyProxy类中的invoke方法
- }
- }
SpringAOP使用简单注解就解决了动态代理的复杂度。
SpringAOP切面、连接点、通知、切点
切面(Aspect) :指关注点横块化,这个关注点可能会横切多个对象,事务管理是企业级Java应用中有关横切关注点的例子,在Spring AOP中,切面可以使用遇用类基于模式的方式(schema-based approach)或者在曾通奥中以@Aspect注解(@Aspect注解方式)来实现。
连接点(join point):在程序执行过程中某个特定的点,例如展个方法调甲的时间点或者处理异常的时间点。在Spring AOP中,一个逐接点总是代表一个方法的执行。
通如(Advce):在切面的某个特定的连推点上执行的助作。通如有多种类型,包括“around", "belore’ and "afnter”等等。爆如的美型将在后围的章节进行讨论,许多AOP框菜,包括Spring在内。都是以拦截器骷遏知模型的。井榷护着一个以连接点为中心的翱截器链。
切点(Pointcut) :匹配连接点的断言。通知和切点表达式相关联,并在满足这个切点的连接点上运行(例如,当执行某个特定名称的方法时),切点表达式如何和连榱点匹配胜AOP的核心: Spring认使用Aspect切点语义。

通知类型
-
前置通知(Before adice):在连接点之帅运行但无法阻止执行流程进入连接点的通知(除非它引发异常).
-
后置返回通知(After returming advice):在连接点正常完成后执行的通知(例如,当方法没有抛出任何异常并正常返回时) .
-
后置异常通知(After throwing advice):在方法孢出异常混出时执行的通知.。
-
后置通知(总会执行)(After (finally) advice):当连接点退出的时候执行的通知(无论是正常返回还是异常退出).
-
环绕通知(Around Advice):环绕连接点的通知,例如方法调用。这是最强大的一种通知类型,环绕通知可以在方法调用前后完成自定义的行为。它可以选择是否继续执行连接点或直接返回自定义的返回值又或抛出异常将执行结束。
SpringAOP依赖
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
- <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
- <version>1.9.6</version>
- </dependency>
- <dependency>
- <groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
- <artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
- <version>5.2.12.RELEASE</version>
- </dependency>
-
@Aspect 声明切面
-
@Component 注入spring容器
-
什么是AOP?
-
Spring AoP and AspectJ AOP有什么区别?AOP有哪些实现方式?
-
JDK动态代理和CGLIB动态代理的区别
-
如何理解Spring 中的代理?
-
解释一下Spring AOP里面的几个名词
-
搭建springAOP
6、SpringAOP使用详解
AOP切入点表达式
-
Spring AOP支持使用以下AspectJ切点标识符(PCD).用于切点表达式:
-
execution:用于匹配方法执行连接点。这是使用Spring AOP时使用的主要切点标识符。
-
within:限制匹配特定类型中的连接点(在使用Spring AOP时,只需执行在匹配类型中声明的方法)。
-
this:匹配实现了某个接口
-
target:限制匹配到连接点(使用Spring AOP时方法的执行),其中目标对象(正在代理的应用程序对象)是给定类型的实例。
-
args:限制与连接点的匹配(使用Spring AOP时方法的执行),其中变量是给定类型的实例。AOP) where the arguments are instances of the given types.
-
@target:限制与连接点的匹配(使用Spring AOP时方法的执行),其中执行对象的类具有给定类型的注解。
-
@args:;限制匹配连接点(使用Spring AOP时方法的执行),其中传递的实际参数的运行时类型具有给定类型的注解。
-
@within:限制与具有给定注解的类型中的连接点匹配(使用Spring AOP时在具有给定注解的类型中声明的方法的执行)。
-
@annotation:限制匹配连接点(在Spring AOP中执行的方法具有给定的注解)
execution语法:细粒度

其中:基本上类型都是完整限定名
within语法:粗粒度
只能指定到类,无法具体到某个方法。但可以将该类下的所有方法都匹配到。
within("com.my.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.*")
//因为指定到类,所以返回值类型可以不用写,默认多个*,方法也不用写,参数不用
@Annotation:可以根据注解的完整限定名来实现
@Annotation("java.lang.Override")
// @Override
//这里使用使用java.lang.Override不会起作用,可以换成@Longer注解的类,这里只是说明而已
外来小知识@Retention(RetentionPolicy.Source),如果编译为.class文件下不会有该接口或类
合并切点表达式 && ||
within("com.my.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.*")&&@Annotation("java.lang.Override")
//&& 和
通知顺序
try{
前置通知
后置通知
}catch{
后置异常通知
}finally{
后置返回通知
}
//正常顺序:前置通知、后置通知、 后置返回通知(这个可以按照)
//异常顺序:前置通知、后置通知、 后置异常通知(不能按照上面理解)
环绕通知
- //环绕通知
- @Around(value = "pointCut()")
- public Object arround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
- String methodName=joinPoint.getSignature().getName();//方法名
- Object[] args=joinPoint.getArgs();//参数
- Object proceed=null;
- try {
- System.out.println("环绕的前置通知"+methodName+"方法开始,参数是"+Arrays.asList(args));
- proceed=joinPoint.proceed(args);
- System.out.println("环绕的返回通知"+methodName+"方法开始,返回值时"+proceed);
- } catch (Throwable throwable) {
- System.out.println("环绕的异常通知"+methodName+"方法异常,异常信息是"+throwable);
- }finally {
- System.out.println("环绕的后置通知"+methodName+"方法结束!");
- }
- return proceed;
- }
基于注解实现AOP
- @Configuration //为实现xml方式,注销该注解
- @Aspect
- public class LogAspect {
-
-
- @Pointcut("execution(* com.my.service.impl.*.*(..))")
- public void pointCut(){
- //提取公共部分
- }
- /*
- 前置通知
- 后置通知
- 环绕通知
- 后置异常通知
- 后置返回通知
- */
-
- @Before("pointCut() && @annotation(logger)")
- public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint, Logger logger){
- //JoinPoint连接点
- System.out.println(logger.name());//这样可以用于用户查询上,可以标注执行的方法,这里只是那@Logger这个注解做例子
-
- //获取方法名
- System.out.println("joinPoint.getSignature().getName() = " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
- //获取所有的参数
- Object[] args=joinPoint.getArgs();
- // for (Object arg : args) {
- // System.out.println(arg);
- // }
- //Arrays.asList(args)
- System.out.println("当前"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()+"运行了!");
- System.out.println("参数为"+ Arrays.asList(args));
- }
-
- @After("execution(* com.my.service.impl.*.*(..))")
- public void after(){
- System.out.println("后置通知after!");
- }
-
- @AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.my.service.impl.*.*(..))",throwing = "ex")
- public void afterThrowing(Exception ex){
- // System.out.println("后置异常通知afterThrowing!");
- // System.out.println("报错异常为"+ex);
-
-
- //java 记录异常栈
- StringWriter sw=new StringWriter();
- ex.printStackTrace(new PrintWriter(sw,true));
- System.out.println("后置异常通知"+sw.getBuffer().toString());
- }
-
- @AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.my.service.impl.*.*(..))",returning = "obj")
- public void afterReturning(Object obj){
- System.out.println("后置返回通知afterReturning!");
- System.out.println("返回值:"+obj);
- }
-
- //环绕通知
- @Around(value = "pointCut()")
- public Object arround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
- String methodName=joinPoint.getSignature().getName();//方法名
- Object[] args=joinPoint.getArgs();//参数
- Object proceed=null;
- try {
- System.out.println("环绕的前置通知"+methodName+"方法开始,参数是"+Arrays.asList(args));
- proceed=joinPoint.proceed(args);
- System.out.println("环绕的返回通知"+methodName+"方法开始,返回值时"+proceed);
- } catch (Throwable throwable) {
- System.out.println("环绕的异常通知"+methodName+"方法异常,异常信息是"+throwable);
- }finally {
- System.out.println("环绕的后置通知"+methodName+"方法结束!");
- }
- return proceed;
- }
-
- }
- public class MyTest {
-
- @Autowired
- private UserController userController;
-
- @Test
- public void test(){
- ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/springAop.xml");
- userController=context.getBean(UserController.class);
- System.out.println(userController.getClass());
- /*
- 没有被代理返回class com.my.controller.UserController
- */
- userController.test();
- }
-
- @Test
- public void test1(){
- ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/springAop.xml");
- UserService userService=context.getBean(UserService.class);
- System.out.println(userService.getClass());
- /*
- userService.getClass()被AOP代理返回class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy22 这是一个动态代理类
- 这里也就解释了为什么我们要使用接口来接收返回值,而不能使用具体类,因为接口下可有多个实现类,具体类就不一样了.
- springAOP会使用jdk,cglib代理,关键看代理的类是否实现接口.
- 这里为什么是接口.class UserService.class
- 因为ioc在注入时,被aop截取,从而被代理,然后返回代理类存入spring容器com.sun.proxy.$Proxy22,
- 因此我们通过具体实现类会报找不到bean出错,而接口就不一样了,代理类也会实现原始接口,所有接口.class就能获取到
- 想要的Bean,但可以根据名字获取.
- */
- User user=new User(1,"ni","122");
- userService.add(user);
- }
- }
基于xml的方式实现AOP(也可叫基于Schema的方式)
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
- xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
- https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
- https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
-
- <context:component-scan base-package="com.my"></context:component-scan>
-
- <bean class="com.my.config.LogAspectTwo" id="logAspectTwo"></bean>
- <!-- AOP实现-->
- <aop:config>
- <aop:aspect ref="logAspectTwo">
- <aop:pointcut id="cutAllService" expression="execution(* com.my.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
- <aop:before method="before"
- pointcut="execution(* com.my.service.impl.*.*(..)) && @annotation(logger)"></aop:before>
- <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="cutAllService"></aop:after>
- <aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="cutAllService" throwing="ex"></aop:after-throwing>
- <aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" returning="obj" pointcut-ref="cutAllService"></aop:after-returning>
-
- <aop:around method="arround" pointcut-ref="cutAllService"></aop:around>
- </aop:aspect>
- </aop:config>
- </beans>
-
Spring通知有哪些类型?
-
解释基于XML Schema方式的切面
-
实现解释基于注解的切面实现
7、Spring声明式事务(外加jdbc操作)
事务:把一组业务当成一个业务来做;要么都成功,要么都失败,保证业务操作完整性的一种数据库机
实例:转账业务,一个人转账,一个人收账,要保证业务完整性。
SpringJdbcTemplate 操作jdbc的模板方法
jdbc.username=root password=123456 url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=utf-8 driverName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
- <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
- https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
-
- <context:component-scan base-package="com.my"></context:component-scan>
-
- <context:property-placeholder location="db.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
-
- <bean class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" id="dataSource">
- <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
- <property name="password" value="${password}"></property>
- <property name="url" value="${url}"></property>
- <property name="driverClassName" value="${driverName}"></property>
- </bean>
-
- <!-- 两个template-->
- <bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" id="jdbcTemplate">
- <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
- </bean>
-
- <bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate" id="jdbcTemplate2">
- <constructor-arg type="javax.sql.DataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
- </bean>
- </beans>
- public class MyTest {
-
- ApplicationContext context;
-
- @Before
- public void before(){
- context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/springaop.xml");
- }
-
- @Test
- public void test(){
- DruidDataSource dataSource=context.getBean(DruidDataSource.class);
- System.out.println(dataSource);
- }
-
- @Test
- public void test1(){
- JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate=context.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
- Long aLong = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(1) from user", Long.class);
- System.out.println(aLong);
- }
-
- @Test
- public void test2(){
- JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate=context.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
- //数据库字段名与属性名一样
- // User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from user where id=2"
- // ,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<User>(User.class));
-
- //官方的
- User user=jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from user where id=2"
- ,(resultSet,i)->{
- User o=new User();
- o.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
- o.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
- o.setSex(resultSet.getString("sex"));
- return o;
- });
- System.out.println(user.toString());
- }
-
- @Test
- public void test3(){
- JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate=context.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
- List<User> users=jdbcTemplate.query("select * from user"
- ,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<User>(User.class));
- System.out.println(users);
- }
-
- @Test
- public void test4(){
- JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate=context.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
- //曾加、删除、修改都是update方法
- int i=jdbcTemplate.update("insert into user value(?,?,?)",1,"三三","男");
- System.out.println(i);
- }
-
- @Test
- public void test5(){
- // NamedParameterJdbcTemplate 具名参数
- NamedParameterJdbcTemplate template = context.getBean(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate.class);
- Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
- map.put("id",1);
- User user=template.queryForObject("select * from user where id=:id"
- ,map,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<User>(User.class));
- System.out.println(user);
- }
- }
官方推荐一个dao使用一个JDBCTemplate,所以不需要使用@Autowired。
//官方推荐
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
public void setDataSource(DruidDataSource dataSource){
this.jdbcTemplate=new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
//自己写的
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
事务的四大特性ACID
-
A原子性:原子性指的是在一组业务操作下要么都成功要么都失败原子性指的是在一组业务操作下要么都成功要么都失败
-
C一致性:事务前后的数据要保证数据的一致性
-
I隔离性:在并发情况下事物之间要相互隔离。
-
D持久性:数据一旦保存就是持久性的。
总结:在事务控制方面,主要有两个分类: 编程式事务∶在代码中直接加入处理事务的逻辑,可能需要仕代码中显示调用beginTransaction()、commit()、rollback()等事务管理相关的方法
声明式事务∶在方法的外部添加注解或者直接在配置文件中正,通过AOP方法模块化,进而实现事务管理。spring的AOP恰好可以完成此功能:事务管理代码的固定模式作为一种横切关注点,通过AOP方法模块化,进而实现 声明式事务。
声明事物就是利用了AOP思想,对某个面进行监控管理,spring提供了@Transacation(标记在方法和类),事务的本质是根据connection来管理的,不同的数据源(jdbc、mybatis等等)的事务管理器不同
@Transacation写在方法上面,控制粒度更细,建议@Transactional写在业务逻辑层上,因为只有业务逻辑层才会有嵌套调用的情况。
- <!--事物管理配置-->
- <bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="transactionManager">
- <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
- </bean>
-
- <!--基于注解的方式的事务,开启事务的注解驱动-->
- <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
事务属性
-
isolation:设置事务的隔离级别
-
propagation:事务的传播行为
-
noRollbackFor:那些异常事务可以不回滚
-
noRollbackForClassName:填写的参数是全类名
-
rollbackFor:哪些异常事务需要回滚
-
rollbackForClassName:填写的参数是全类名
-
readOnly:设置事务是否为只读事务
-
timeout:事务超出指定执行时长后自动终止并回滚,单位是秒
事务隔离级别
用来解决并发事务所产生一些问题: 并发:同一个时间,多个线程同时进行请求。 什么时候会生成并发问题:在并发情况下,对同一个数据(变量、对象)进行读写操作才会产生并发问题并发会产生什么问题?
-
脏读(解决:@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)),脏读就是例如两个人同时访问一个东西,一个人改变这个东西(但没有提交),另一个人的数据会变。这就导致另一个人数据不一致,所以使用READ_COMMITTED,但一个人提交后,数据才变。这个问题数据库已经默认实现了。
-
不可重复读(解决:@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.REPEATABLE_READ),简称行锁),不可重复读就是在脏读中事务已提交,但那个人再次查询时,发现数据不一致,这导致一次访问前后数据改变,因此这就使用到了行锁,表示有人操作时,给数据上了一把锁(使其另一个线程静止增删查改等操作)。
-
幻影读(解决:@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.SERIALIZABLE)),幻影读其实跟不可重复读一样,只是不可重复读针对行,解决方式行锁,幻影读针对的是表,解决方式就是表锁。表锁运行效率低。
隔离级别阻止并发问题
| 脏读 | 幻读 | 不可重复读 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Read uncommitted | √ | √ | √ |
| Read committed | × | √ | √ |
| Repeatable read | × | √ | × |
| Serializable | × | × | × |
-
并发安全:SERIALIZABLE>REPEATABLE_READ>READ_COMNMITTED
-
运行效率:READ_COMITTED>REPEATABLE_READ>SERIALIZABLE
外来小知识数据库的默认事物隔离级别:通过select @@tx_isolation; #MYSQL: REPEATABLE-READ #ORACLE: READ_COMMITTED
mysql默认级别 REPEATABLE-READ
事务传播性
事务的传播特性指的是当一个事务方法(@Transactional这个注解诸如的方法)被另一个事务方法调用时,这个事务方法应该如何进行?
希望如果外部存在事务就用外部的,外部不存在就自己开启事务
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
| 事务传播行为类型 | 外部不存在事务 | 外部存在事务 | 使用方式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| REQUIRED(默认) | 开启新的事务 | 融合到外部事务中 | @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)适用增删改查 |
| SUPPORTS | 不开启新的事务 | 融合到外部事务中 | @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS)适用查询 |
| REQUIRES NEW | 开启新的事务 | 挂起外部事务,创建新的事务 | @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)适用内部事务和外部事务不存在业务管理情况,如日志 |
| NOT_SUPPORTED | 不开启新的事务 | 挂起外部事务 | @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED)不常用 |
| NEVER | 不开启新的事务 | 抛出异常 | @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NEVER)不常用 |
| MANDATORY | 抛出异常 | 融合到外部事务中 | @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.MANDATORY)不常用 |
REQUIRES NEW使用时要多创建一个类,分为父子方法,父子方法存在不同类上。
超时属性(timeout):指定事务等待的最长时间(秒)
当前事务访问数据时,有可能访问的数据被别的数据进行加锁的处理,那么此时事务就必须等待,如果等待时间过长给用户造成的体验感差。
基于xml实现
- <!-- 声明事务切入的-->
- <aop:config>
- <aop:pointcut id="transactionPointCut" expression="execution(* com.my.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
- </aop:config>
- <!--用来明确切点匹配到的方法,哪些方法需要使用事务-->
- <tx:advice id="advice">
- <tx:attributes>
- <!-- 可以使用通配符-->
- <tx:method name="add*"/>
- <tx:method name="delete*"/>
- <tx:method name="update*"/>
- <tx:method name="get*" read-only="true" propagation="SUPPORTS"></tx:method>
- </tx:attributes>
- </tx:advice>
基于注解实现
- @Service
- public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
-
- @Autowired
- private UserDao userDao;
-
- /*
- 扣钱
- */
- @Override
- @Transactional(timeout = 3) //可以通过捕获异常设置提醒
- public void reduceAge() {
-
- try {
- Thread.sleep(4);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- System.out.println("reduce!");
- userDao.reduceAge();
- }
-
- /*
- 转账
- */
- @Override
- @Transactional(isolation = Isolation.SERIALIZABLE)
- public void trans() {
- reduceAge();//一个减
- // int i=1/0; 通过这个来看事务处理情况,前面执行了,后面没有执行,这就是没有@Transactional
- addAge();//一个加
- }
-
- /*
- 存钱
- */
- @Override
- @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
- public void addAge() {
- System.out.println("add!");
- userDao.addAge();
- }
- }
-
Spring事务的实现方式和实现原理
-
说一下Spring的事务传播行为
-
说一下spring的事务隔离?
-
Spring框架的事务管理有哪些优点?
8、Spring源码详解(未完工)
总结
什么是Spring框架,Spring框架主要包含哪些模块
Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是一个轻量级的Java开发框架。它是为了解决企业应用开发的复杂性而创建的。框架的主要优势之一就是其分层架构,分层架构允许使用者选择使用哪一个组件。同时为J2EE应用程序开发提供集成的框架。Spring使用基本的JavaBean来完成以前只可能由EJB完成的事情。然而,Spring的用途不仅限于服务器端的开发。从简单性、可测试性和松耦合的角度而言,任何Java应用都可以从Spring中受益。Spring的核心是控制反转(loC)和面向切面(AOP)。简单来说,Spring是一个分层的full-stack(一站式)轻量级开源框架。
架构发展历程
单一应用架构 当网站流量很小时,只需一个应用,将所有功能都部署在一起,以减少部署节点和成本。此时,用于简化增删改查工作量的数据访问框架(ORM)是关键。
垂直应用架构 当访问量逐渐增大,单一应用增加机器带来的加速度越来越小,提升效率的方法之一是将应用拆成互不相干的几个用,以提升效率。此时,用于加速前端页面开发的Web框架(MVC)是关键。
分布式服务架构 当垂直应用越来越多,应用之间交互不可避免,将核心业务抽取出来,作为独立的服务,逐渐形成稳定的服务中心,使前端应用能更快速的响应多变的市场需求。此时用于提高业务复用及整合的分布式服务框架(RPC)是关键。
流动计算架构 当服务越来越多,容量的评估,小服务资源的浪费等问题逐渐显现,此时需增加一个调度中心基于访问压力实时管理集群容量,提高集群利用率。此时,用于提高机器利用率的资源调度和治理中心(SOA)是关键。
什么是Spring? spring是一个轻量级的开源框架。 spring为了解决企业级应用开发的业务运辑层和其他各层的耦合问题 。 spring是一个IOC和AOP的容器框架。 lOC:控制反转 AOP:面向切面编程 容器:包含并管理应用对象的生命周期
Spring框架的优势 1、Spring通过DI、AOP和消除样板式代码来简化企业级Java开发 2、Spring框架之外还存在一个构建在核心框架之上的庞大生态圈,它将Spring扩展到不同的领域,如Web服务、REST、移动开发以及NoSQL 3、低侵入式设计,代码的污染极低 4、独立于各种应用服务器,基于Spring框架的应用,可以真正实现Write Once,RunAnywhere的承诺 5、Spring的loC容器降低了业务对象替换的复杂性,提高了组件之间的解 6、Spring的AOP允许将一些用士分刚文主、提供了更好的复用 7、Spring的ORM和DAO提供了与第三方持久层框架的的良好整合,并简化了底层的数据库访问 8、Spring的高度开放性,并不强制应用完全依赖于Spring。开发者可自由选用Spring框架的部分或全部
Ioc和D是什么? 1、控制反转是就是应用本身不负责依赖对象的创建和维护,依赖对象的创建及维护是由外部容器负责的.这样控制权就有应用转移到了外部容器.控制权的转移就是控制反转 2、依赖注入是指:在程序运行期间,由外部容器动态地将依赖对象注入到组件中如:一般,通过构造函数注入或者setter注入
描述下Spring lOc容器的初始化过程 Spring IOC容器的初始化简单的可以分为三个过程: 第一个过程是Resource资源定位。这个Resouce指的是BeanDefinition的资源定位。这个过程就是容器找数据的过程,就像水桶装水需要先找到水一样。 第二个过程是BeanDefinition的载入过程。这个载入过程是把用户定义好的Bean表示成loc容器内部的数据结构。而这个容器内部的数据结构就是BeanDefition。 第三个过程是向IOC容器注册这些BeanDefinition的过程,这个过程就是将前面的BeanDefition保存到HashMap中的过程。
看源代码总结问题
-
源代码中的包结构
-
源代码可以从切入点看
-
注释加笔记做好
-
做好代码模块化


