- 1Pytorch项目实战聊天机器人(02.项目的准备阶段)_北京大学深度学习pytorch开发搭建nlp聊天机器人资料
- 2【Datawhale竞赛:《AI夏令营 - 机器学习实践赛事》】_datawhale ai夏令营
- 3第四题乙醇偶合制备 C4 烯烃_数学建模乙烯偶合制备c4烯烃
- 4bert模型源码详细解读_bert_config.json
- 5她不讲"武德",北航博士竟然把60年来的文本分类综述都整理了!!!
- 6HarmonyOS入门--ArkTS--基本语法
- 7防止 SQLite 数据库被下载的方法
- 8大创项目推荐 深度学习 python opencv 动物识别与检测
- 9pytorch(一):实现mnist手写数字识别_mnist数据集手写识别
- 10spyder安装+使用中的问题_runtimeerror: method 'detach' already has a docstr
【记录版】SpringBoot框架中Request请求获取方式及源码解读_请求获取request
赞
踩
SpringBoot + HttpServletRequest
背景: 我们现在有很多WEB项目基于SpringBoot开发,其中接口管理是必不可少的,接口中Request对象是核心内容,我们对参数、属性、header等等元数据的获取和配置都离不开它,常用的Filter、拦截器等操作类也都有它的身影。本篇在此基础上,从源码角度讨论获取Request的三种方式:
方式一、接口方法或全局异常处理方法参数注入
通常在开发简单POST接口时,请求参数或Header等信息都可以用*@RequestBody、@RequestParam、@PathVariable或@RequestHeader*注解直接取值,部分场景下当接口方法参数名和请求体参数名值和类型一致时,也可以赋值,如下所示:
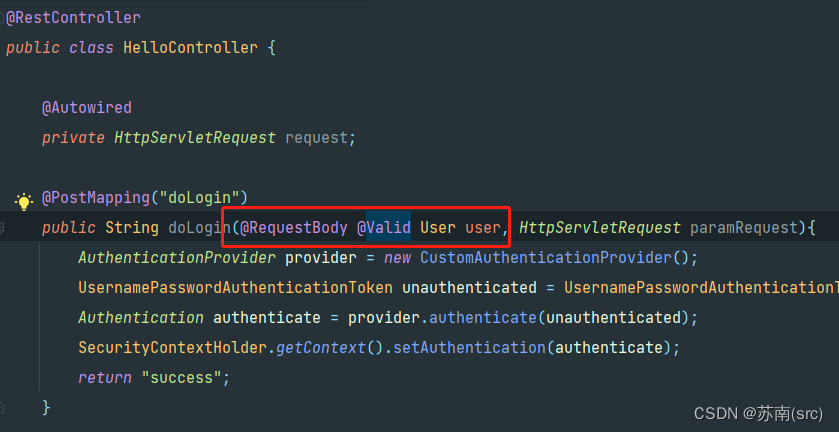
当然最原始的也可用Request实例对象,即在此接口上配置HttpServletRequest参数获取,这是最简单也是最直接的方式。(PS: 接口方法也可设置HttpSession参数控制session逻辑)
源码一、方法参数解析入口类
package org.springframework.web.method.support;
public class InvocableHandlerMethod extends HandlerMethod {
@Nullable
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
// 解析方法所有参数,并将其传给最终的反射方法对象执行invoke操作
Object[] args = this.getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
return this.doInvoke(args);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
源码二、方法参数解析类(选一:RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor)
// 方法参数解析接口
public interface HandlerMethodArgumentResolver {
boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter);
@Nullable
Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation; public class RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor extends AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor { ......省略...... public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest, @Nullable WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception { parameter = parameter.nestedIfOptional(); // 通过转换器将Request中请求流数据转换为对应的实体 Object arg = this.readWithMessageConverters(webRequest, parameter, parameter.getNestedGenericParameterType()); String name = Conventions.getVariableNameForParameter(parameter); if (binderFactory != null) { WebDataBinder binder = binderFactory.createBinder(webRequest, arg, name); if (arg != null) { // 参数校验 this.validateIfApplicable(binder, parameter); if (binder.getBindingResult().hasErrors() && this.isBindExceptionRequired(binder, parameter)) { throw new MethodArgumentNotValidException(parameter, binder.getBindingResult()); } } if (mavContainer != null) { mavContainer.addAttribute(BindingResult.MODEL_KEY_PREFIX + name, binder.getBindingResult()); } } return this.adaptArgumentIfNecessary(arg, parameter); } // 参数校验 protected void validateIfApplicable(WebDataBinder binder, MethodParameter parameter) { // 获取参数所有注解,下面将判断是否包含校验类注解 Annotation[] annotations = parameter.getParameterAnnotations(); Annotation[] var4 = annotations; int var5 = annotations.length; for(int var6 = 0; var6 < var5; ++var6) { Annotation ann = var4[var6]; // 此处获取@Valid等校验注解,如果有,binder执行校验并获取校验结果 Object[] validationHints = ValidationAnnotationUtils.determineValidationHints(ann); if (validationHints != null) { binder.validate(validationHints); break; } } } ......省略...... }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver默认有31种,覆盖绝大部分类型参数的解析,使我们从Request的API的操作中解放出来,从而关注业务逻辑的开发和管理,以下仅列出核心解析器:
1、RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor // 支持@RequestBody注解参数解析
2、ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver //支持ServletRequest、MultipartRequest及HttpSession等参数解析
3、RequestHeaderMethodArgumentResolver // 支持Header参数解析
方法二:方法体内通过RequestContextHolder全局持久化类获取
HttpServletRequest holderRequest = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
- 1
在SpringBoot项目中,有两处地方进行了上下文保存动作:
1、OrderedRequestContextFilter extends RequestContextFilter implements OrderedFilter 设置
public class RequestContextFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter { // 是否线程间传递,适用于后端存在异步线程池场景,需手工开启 private boolean threadContextInheritable = false; public void setThreadContextInheritable(boolean threadContextInheritable) { this.threadContextInheritable = threadContextInheritable; } protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException { // 请求与响应封装体 ServletRequestAttributes attributes = new ServletRequestAttributes(request, response); // 内存保存 this.initContextHolders(request, attributes); try { filterChain.doFilter(request, response); } finally { // 清除 LocaleContextHolder.resetLocaleContext(); RequestContextHolder.resetRequestAttributes(); attributes.requestCompleted(); } } // 请求&响应上下文具体保存逻辑-核心为ThreadLocal private void initContextHolders(HttpServletRequest request, ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes) { LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(request.getLocale(), this.threadContextInheritable); RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes, this.threadContextInheritable); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
OrderedRequestContextFilter是通过SpringBoot自动配置,只要是Web项目都不用手工设置,自动配置源码:
@AutoConfiguration( after = {DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class} ) @ConditionalOnWebApplication( type = Type.SERVLET ) @ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class}) @ConditionalOnMissingBean({WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class}) @AutoConfigureOrder(-2147483638) public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration { @Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false ) @Import({EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class}) @EnableConfigurationProperties({WebMvcProperties.class, WebProperties.class}) @Order(0) public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer, ServletContextAware { @Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean({RequestContextListener.class, RequestContextFilter.class}) @ConditionalOnMissingFilterBean({RequestContextFilter.class}) public static RequestContextFilter requestContextFilter() { return new OrderedRequestContextFilter(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
二、DispatcherServlet执行时设置
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
private void initContextHolders(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable LocaleContext localeContext, @Nullable RequestAttributes requestAttributes) {
if (localeContext != null) {
LocaleContextHolder.setLocaleContext(localeContext, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
if (requestAttributes != null) {
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
三、定义HttpServletRequest类实例变量,通过Spring容器注入,如@Autowired注解修饰
这种方式比较少见,但既然能够使用,说明此时我们看到的request对象,不再是前面方法里获取的Request对象,而是披了一层羊皮的代理对象,这样每个接口获取时才能找到自己的上下文,那它是怎么实现的呢?
熟悉Spring框架的话,就会知道容器在实例化外部控制器实例时,会在BeanPostProcessor等处优先处理需要注入的实例,当需要注入实例到Request变量时,BeanFactory会自动处理:
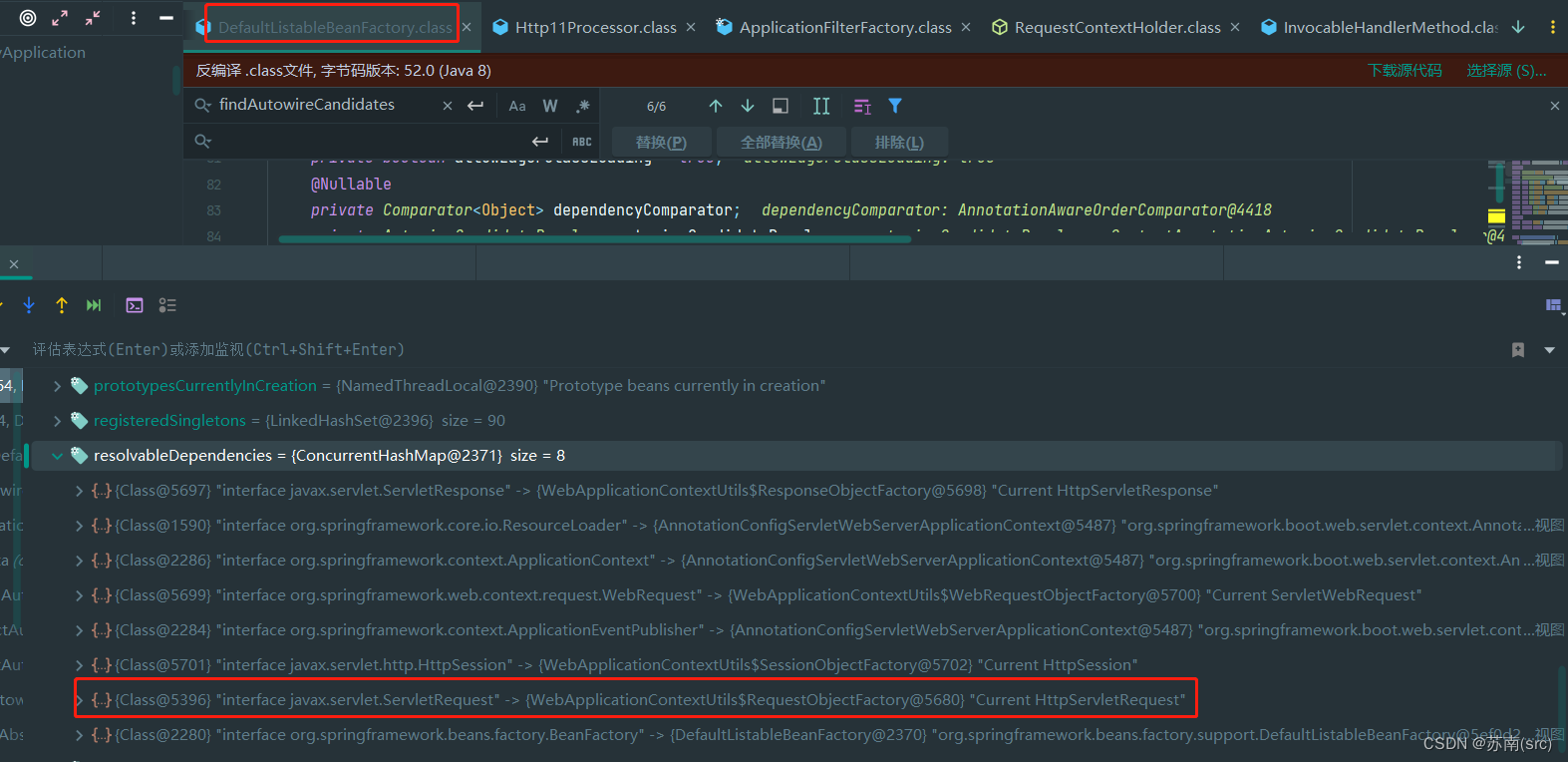
// Bean实例化时会执行 public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable { // beanName为外部类名称,requiredType为HttpServletRequest.class protected Map<String, Object> findAutowireCandidates(@Nullable String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) { String[] candidateNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this, requiredType, true, descriptor.isEager()); Map<String, Object> result = CollectionUtils.newLinkedHashMap(candidateNames.length); // BeanFactory所有缓存的resolvableDependencies,具体见如上截图中8个依赖 Iterator var6 = this.resolvableDependencies.entrySet().iterator(); while(var6.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> classObjectEntry = (Map.Entry)var6.next(); Class<?> autowiringType = (Class)classObjectEntry.getKey(); if (autowiringType.isAssignableFrom(requiredType)) { Object autowiringValue = classObjectEntry.getValue(); // 此处根据变量类型,获取对应的ObjectFactory工厂,再生成对应的Proxy autowiringValue = AutowireUtils.resolveAutowiringValue(autowiringValue, requiredType); if (requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) { result.put(ObjectUtils.identityToString(autowiringValue), autowiringValue); break; } } } .......... } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
abstract class AutowireUtils { public static Object resolveAutowiringValue(Object autowiringValue, Class<?> requiredType) { if (autowiringValue instanceof ObjectFactory && !requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) { ObjectFactory<?> factory = (ObjectFactory)autowiringValue; if (!(autowiringValue instanceof Serializable) || !requiredType.isInterface()) { return factory.getObject(); } // 此处使用JDK动态代理 autowiringValue = Proxy.newProxyInstance(requiredType.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{requiredType}, new ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(factory)); } return autowiringValue; } } // 私有静态内部类封装InvocationHandler具体的反射调用内容,配合JDK动态代理生成代理类 private static class ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private final ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory; ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) { this.objectFactory = objectFactory; } public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { switch (method.getName()) { case "equals": return proxy == args[0]; case "hashCode": return System.identityHashCode(proxy); case "toString": return this.objectFactory.toString(); default: try { return method.invoke(this.objectFactory.getObject(), args); } catch (InvocationTargetException var6) { throw var6.getTargetException(); } } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler是处理封装类,具体逻辑为ObjectFactory实现类提供
public abstract class WebApplicationContextUtils { public static void registerWebApplicationScopes(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, @Nullable ServletContext sc) { beanFactory.registerScope("request", new RequestScope()); beanFactory.registerScope("session", new SessionScope()); if (sc != null) { ServletContextScope appScope = new ServletContextScope(sc); beanFactory.registerScope("application", appScope); sc.setAttribute(ServletContextScope.class.getName(), appScope); } // 此处注册Request执行的工厂类 beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletRequest.class, new RequestObjectFactory()); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletResponse.class, new ResponseObjectFactory()); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(HttpSession.class, new SessionObjectFactory()); beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WebRequest.class, new WebRequestObjectFactory()); if (jsfPresent) { WebApplicationContextUtils.FacesDependencyRegistrar.registerFacesDependencies(beanFactory); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
Request代理类真实执行逻辑:
public abstract class WebApplicationContextUtils {
private static class RequestObjectFactory implements ObjectFactory<ServletRequest>, Serializable {
// ObjectFactory核心就是getObject方法,封装实例创建的过程
public ServletRequest getObject() {
// 实际获取的还是RequestContextHolder缓存的Request对象
return WebApplicationContextUtils.currentRequestAttributes().getRequest();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
总结:
1、一般需求场景,直接在接口方法上标注HttpServletRequest对象即可
2、如果需要在任意场景使用HttpServletRequest对象,方法二和方法三都可,方法三使用更加简洁
3、方法二和方法三底层都依赖ThreadLocal,如果后台使用异步线程池,需要手工设置inheritable属性为true
4、从方法一中,我们可以学到接口方法可以定义多个我们需要的上下文参数,如HttpSession;从方法三中我们可以学习到全局使用Request、Response、Session等8个对象。
5、方法三虽然涉及Bean生命周期、JDK动态代理等底层知识,但实际内容还是围绕RequestContextHolder做的封装,使用时更加方便,全局场景推荐使用此方式。
6、全局注入场景,ObjectProvider类也有类似的能力,具体可见这里。




