- 1sysbench压力测试工具使用_sysbench mem
- 2特征增强自蒸馏卷积神经网络
- 3搭建excel在线编辑服务器,开源免费!自动动手搭建一款更加强大的在线Excel工具...
- 4pycharm打包python文件为exe文件(图文教程)
- 5Redis持久化详解
- 6[内附完整源码和文档] 基于C#和Access的智能聊天机器人_c# 模拟人工智能对话
- 7基于Pytorch深度学习垃圾分类系统设计与实现_毕业论文基于python的垃圾检测分类系统设计
- 8C++list类_c++ list
- 9tortoise git 冲突解决_tortoisegit 冲突
- 10第4.3章:StarRocks数据导出--Spark Connector_starrocks-spark-connector
LDA模型原理+代码+实操_lda代码
赞
踩
LDA模型主要用来生成TOPIC
前言
LDA模型需要一定的数学基础去理解,但是理解成黑盒也能一样用。
一、原理
可以通过以下资料详细了解原理。
【python-sklearn】中文文本 | 主题模型分析-LDA(Latent Dirichlet Allocation)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
https://www.jianshu.com/p/5c510694c07e
主题模型:LDA原理详解与应用_爱吃腰果的李小明的博客-CSDN博客_lda模型
主题模型-潜在狄利克雷分配-Latent Dirichlet Allocation(LDA)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
隐含狄利克雷分布(Latent Dirichlet Allocation,LDA),是一种主题模型(topic model),典型的词袋模型,即它认为一篇文档是由一组词构成的一个集合,词与词之间没有顺序以及先后的关系。一篇文档可以包含多个主题,文档中每一个词都由其中的一个主题生成。它可以将文档集中每篇文档的主题按照概率分布的形式给出,对文章进行主题归纳,属于无监督学习。
需要区分的是,另外一种经典的降维方法线性判别分析(Linear Discriminant Analysis, 简称也为LDA)。此LDA在模式识别领域(比如人脸识别,舰艇识别等图形图像识别领域)中有非常广泛的应用
LDA在训练时不需要手工标注的训练集,需要的仅仅是文档集以及指定主题的数量k即可。此外LDA的另一个优点则是,对于每一个主题均可找出一些词语来描述它。选择模型中topic的数量——人为设置参数,之后输入的每篇文章都给一个topic的概率 每个topic再给其下单词概率,topic的具体实现由自己来定

具体的生成模型类比如下图所示:
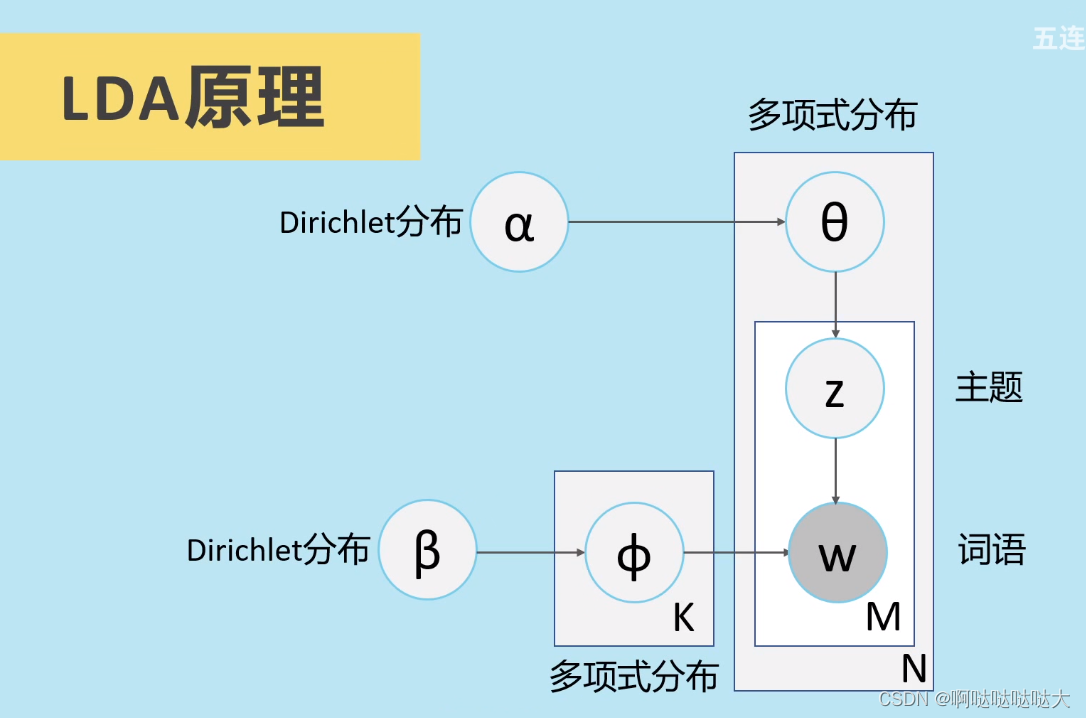
二、代码
1.引入库
- import os
- import pandas as pd
- import re
- import jieba
- import jieba.posseg as psg
2.路径读取
- output_path = '../result'
- file_path = '../data'
- os.chdir(file_path)
- data=pd.read_excel("data.xlsx")#content type
- os.chdir(output_path)
- dic_file = "../stop_dic/dict.txt"
- stop_file = "../stop_dic/stopwords.txt"
和相同目录下创建三个文件夹:result、data、stop_dic
3.分词
- def chinese_word_cut(mytext):
- jieba.load_userdict(dic_file)
- jieba.initialize()
- try:
- stopword_list = open(stop_file,encoding ='utf-8')
- except:
- stopword_list = []
- print("error in stop_file")
- stop_list = []
- flag_list = ['n','nz','vn']
- for line in stopword_list:
- line = re.sub(u'\n|\\r', '', line)
- stop_list.append(line)
-
- word_list = []
- #jieba分词
- seg_list = psg.cut(mytext)
- for seg_word in seg_list:
- word = re.sub(u'[^\u4e00-\u9fa5]','',seg_word.word)
- find = 0
- for stop_word in stop_list:
- if stop_word == word or len(word)<2: #this word is stopword
- find = 1
- break
- if find == 0 and seg_word.flag in flag_list:
- word_list.append(word)
- return (" ").join(word_list)

data["content_cutted"] = data.content.apply(chinese_word_cut)这一步稍微需要一点时间,分词处理
4.LDA分析
- from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer, CountVectorizer
- from sklearn.decomposition import LatentDirichletAllocation
需要sklearn库
- def print_top_words(model, feature_names, n_top_words):
- tword = []
- for topic_idx, topic in enumerate(model.components_):
- print("Topic #%d:" % topic_idx)
- topic_w = " ".join([feature_names[i] for i in topic.argsort()[:-n_top_words - 1:-1]])
- tword.append(topic_w)
- print(topic_w)
- return tword
-
- n_features = 1000 #提取1000个特征词语
- tf_vectorizer = CountVectorizer(strip_accents = 'unicode',
- max_features=n_features,
- stop_words='english',
- max_df = 0.5,
- min_df = 10)
- tf = tf_vectorizer.fit_transform(data.content_cutted)
-
- n_topics = 8
- lda = LatentDirichletAllocation(n_components=n_topics, max_iter=50,
- learning_method='batch',
- learning_offset=50,
- # doc_topic_prior=0.1,
- # topic_word_prior=0.01,
- random_state=0)
- lda.fit(tf)

5.输出每个主题对应词语
- n_top_words = 25
- tf_feature_names = tf_vectorizer.get_feature_names()
- topic_word = print_top_words(lda, tf_feature_names, n_top_words)
6.输出每篇文章对应主题
- import numpy as np
- topics=lda.transform(tf)
- topic = []
- for t in topics:
- topic.append(list(t).index(np.max(t)))
- data['topic']=topic
- data.to_excel("data_topic.xlsx",index=False)
- topics[0]#0 1 2
7.可视化
- import pyLDAvis
- import pyLDAvis.sklearn
- pyLDAvis.enable_notebook()
- pic = pyLDAvis.sklearn.prepare(lda, tf, tf_vectorizer)
- pyLDAvis.save_html(pic, 'lda_pass'+str(n_topics)+'.html')
- pyLDAvis.show(pic)
8.困惑度
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- plexs = []
- scores = []
- n_max_topics = 16
- for i in range(1,n_max_topics):
- print(i)
- lda = LatentDirichletAllocation(n_components=i, max_iter=50,
- learning_method='batch',
- learning_offset=50,random_state=0)
- lda.fit(tf)
- plexs.append(lda.perplexity(tf))
- scores.append(lda.score(tf))
-
- n_t=15#区间最右侧的值。注意:不能大于n_max_topics
- x=list(range(1,n_t))
- plt.plot(x,plexs[1:n_t])
- plt.xlabel("number of topics")
- plt.ylabel("perplexity")
- plt.show()

- n_t=15#区间最右侧的值。注意:不能大于n_max_topics
- x=list(range(1,n_t))
- plt.plot(x,scores[1:n_t])
- plt.xlabel("number of topics")
- plt.ylabel("score")
- plt.show()
三、实操
运行起来遇到了一些问题,经过查阅搜索都是环境和版本的问题,通过调整版本解决了;建议大家在conda=4.12.0,pandas=1.3.0,pyLDAvis=2.1.2的版本下进行运行,基本不会出现什么问题。
最后的结果如下: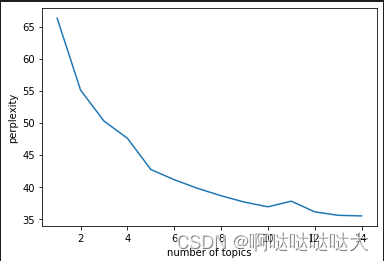
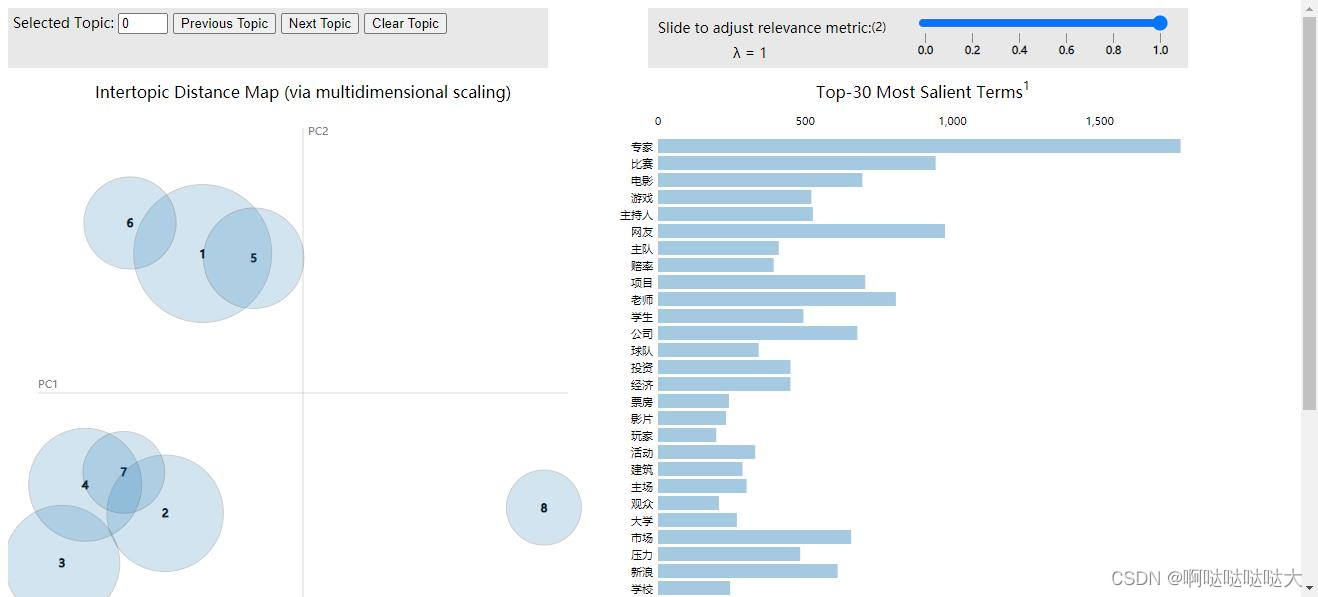
总结
关于LDA模型理解的还不是很透彻,代码的运行中目前用csv文件的话只要改read_csv()就可以,还出了一些编码解码的问题,大家可以尝试换gbk什么的,菜鸡一枚,希望有大佬可以指教。


