热门标签
热门文章
- 1Machine Learning for Computer Systems and Networking:A Survey ---综述阅读 对于计算机系统和网络的机器学习_a survey on the use of machine learning for the in
- 2前中后序遍历(递归法和迭代法)_后序遍历递归算法0xfffffffffffffff7
- 3sed命令批量修改查找所有文件_sed 目录下所有文件
- 4逻辑回归(Logistic Regression):原理、实现与应用_1.掌握逻辑回归的数学原理及推导过程; 2.编程实现逻辑回归函数,并应用与给定手
- 5中文乱码_乱码123
- 6如何安装Anaconda(linux版)_linux安装anaconda
- 7python代码实现文本摘要的核心算法
- 8Android Studio 另一个程序正在使用此文件,进程无法访问_android studio另一个程序正在使用此文件,进程无法访问。
- 9AndroidStudio自带的模拟器如何联网_androidstudio模拟器联网
- 10HarmonyOS应用开发者基础、高级认证证书_harmonyos应用开发者高级认证属于什么证书
当前位置: article > 正文
LLM大语言模型(三):使用ChatGLM3-6B的函数调用功能前先学会Python的装饰器_chatglm3如何使用工具,调用天气函数
作者:我家自动化 | 2024-03-09 19:19:47
赞
踩
chatglm3如何使用工具,调用天气函数
目录
ChatGLM3-6B的函数调用模式示例
ChatGLM3-6B目前有三种使用模式:
- 对话模式
- 工具模式(也就是本文要介绍的函数调用)
- 代码解释器模式
函数调用模式示例:
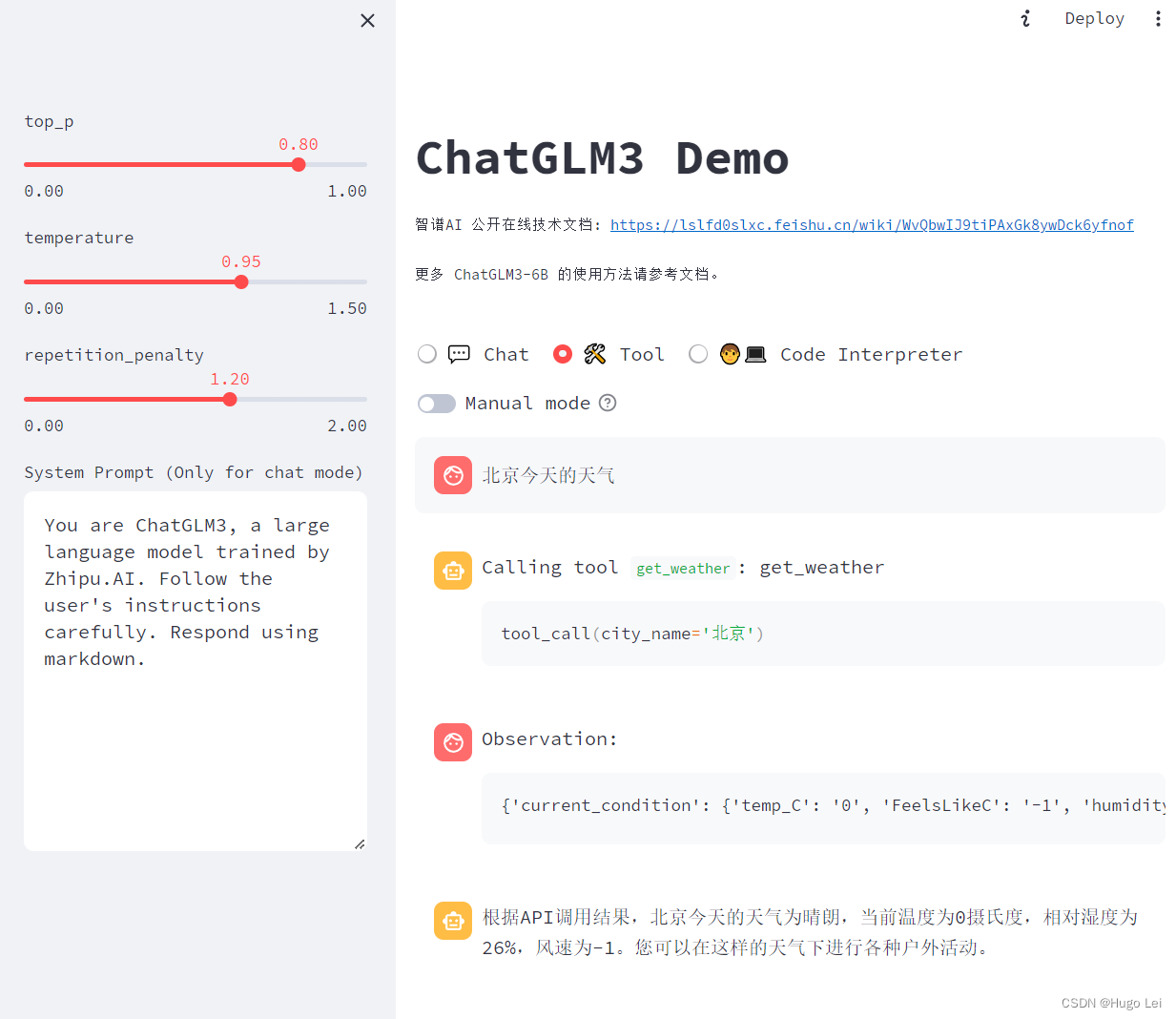
函数调用模式介绍:
- 首先进入Tool工具模式
- 询问“北京今天的天气”
- 大模型自动识别出,要调用get_weather工具(函数),且参数是“北京”
- 大模型接着调用get_weather,入参=北京,获取到函数执行的结果
- <|Observation|>展示的是函数的执行结果
- 紧接着大模型根据上述内容,继续生成回答“根据APIxxxxxxxxxxxx”
本地启动ChatGLM3-6B工具模式
进入conda对应的环境
conda activate chatglm进入composite_demo目录
cd composite_demo修改为使用本地模型,参考LLM大语言模型(一):ChatGLM3-6B本地部署-CSDN博客
- # 修改client.py
- MODEL_PATH = os.environ.get('MODEL_PATH', '====你的本地模型的绝对路径====')
启动模型
- # 在composite_demo目录下
- streamlit run main.py
然后在页面选择Tool模式即可。
如何在ChatGLM3-6B里新增一个自定义函数呢?
首先我们看下get_weather函数是如何实现的。
在composite_demo目录下有个tool_registry.py文件,里面包含两个已经定义好的函数:
-
random_number_generator
-
get_weather
其中get_weather就是上文对话中用到的函数。
get_weather基于Python的装饰器实现
- @register_tool
- def get_weather(
- city_name: Annotated[str, 'The name of the city to be queried', True],
- ) -> str:
- """
- Get the current weather for `city_name`
- """
-
- if not isinstance(city_name, str):
- raise TypeError("City name must be a string")
-
- key_selection = {
- "current_condition": ["temp_C", "FeelsLikeC", "humidity", "weatherDesc", "observation_time"],
- }
- import requests
- try:
- resp = requests.get(f"https://wttr.in/{city_name}?format=j1")
- resp.raise_for_status()
- resp = resp.json()
- ret = {k: {_v: resp[k][0][_v] for _v in v} for k, v in key_selection.items()}
- except:
- import traceback
- ret = "Error encountered while fetching weather data!\n" + traceback.format_exc()
-
- return str(ret)

get_weather功能很简洁,最终是从
https://wttr.in/{city_name}?format=j1获取天气信息(https://wttr.in/%E5%8C%97%E4%BA%AC?format=j1)
函数注解@register_tool
register_tool的功能是将自定义的函数,转化为大模型需要的格式。
- def register_tool(func: callable):
- tool_name = func.__name__
- tool_description = inspect.getdoc(func).strip()
- python_params = inspect.signature(func).parameters
- tool_params = []
-
- # 解析param的Annotation
-
- for name, param in python_params.items():
- annotation = param.annotation
- if annotation is inspect.Parameter.empty:
- raise TypeError(f"Parameter `{name}` missing type annotation")
- if get_origin(annotation) != Annotated:
- raise TypeError(f"Annotation type for `{name}` must be typing.Annotated")
-
- typ, (description, required) = annotation.__origin__, annotation.__metadata__
- typ: str = str(typ) if isinstance(typ, GenericAlias) else typ.__name__
- if not isinstance(description, str):
- raise TypeError(f"Description for `{name}` must be a string")
- if not isinstance(required, bool):
- raise TypeError(f"Required for `{name}` must be a bool")
-
- tool_params.append({
- "name": name,
- "description": description,
- "type": typ,
- "required": required
- })
- tool_def = {
- "name": tool_name,
- "description": tool_description,
- "params": tool_params
- }
-
- print("[registered tool] " + pformat(tool_def))
- _TOOL_HOOKS[tool_name] = func
- _TOOL_DESCRIPTIONS[tool_name] = tool_def
-
- return func

register_tool函数实现了装饰器,它将自定义的函数转换为tool_def dict,其中自动生成了name,description,params等信息
- {
- 'name': 'get_weather',
- 'description': 'Get the current weather for `city_name`',
- 'params': [
- {
- 'name': 'city_name',
- 'description': 'The name of the city to be queried',
- 'type': 'str',
- 'required': True
- }
- ]
- }
最终通过get_tools()将自定义的函数都暴露出去。
在上述demo中,其实是demo_tool.py里调用了get_tools()获取到所有的自定义函数。
-
- def get_tools() -> dict:
- return copy.deepcopy(_TOOL_DESCRIPTIONS)
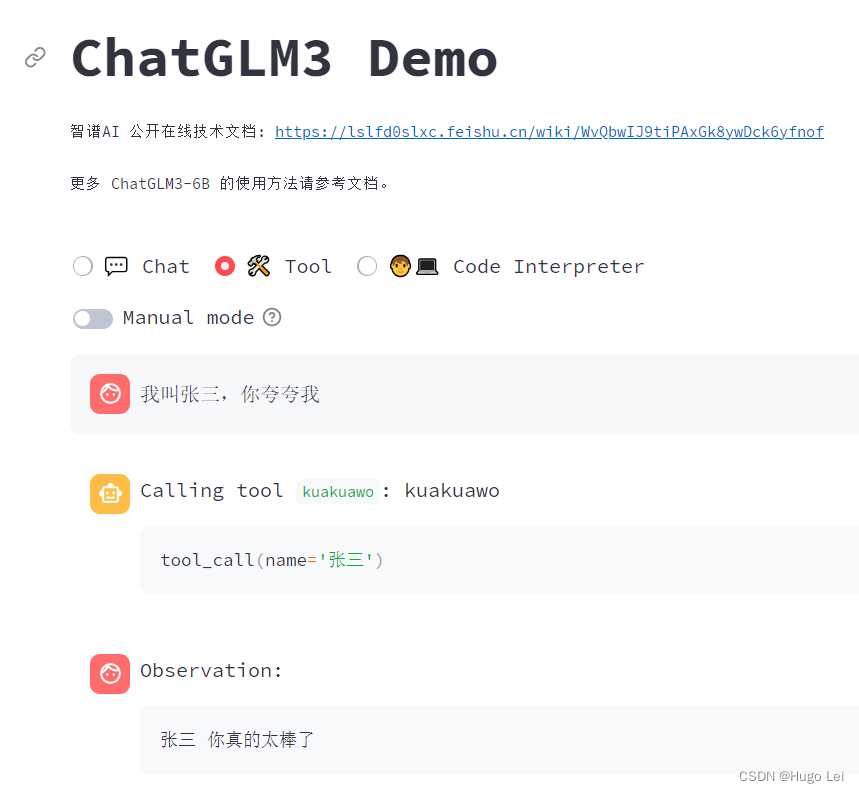
现在我们来自定义一个kuakuawo()函数
-
- @register_tool
- def kuakuawo(
- name: Annotated[str, 'The name of the user', True],
- ) -> str:
- """
- Generates a awesome praise for user
- """
-
- return f"{name} 你真的太棒了"
看看效果
参考:
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/我家自动化/article/detail/216285
推荐阅读
相关标签


