- 1JAVA微信公众号完整版教程扫一扫登录/自动回复/客服消息_wx-java-mp实现微信扫码登录
- 2数值分析复习:Newton插值
- 3html2canvas.min.js(生成图片插件)
- 4crossover软件干嘛的 手把手教你怎么激活crossover_crossover软件是干嘛的
- 5使用YOLOv5实现人脸口罩佩戴检测(详细)_基于yolov5的人脸口罩检测
- 6android适配鸿蒙系统开发_androidstudio可以迁移harmonyos吗
- 7Android Studio 3.5安装教程_android studio3.5下载安装教程
- 8php清除页面别人挂的马_hjb564.top
- 9小型IT咨询公司发展迅猛_it咨询公司创建
- 10Pycharm服务器配置与内网穿透工具结合实现远程开发的解决方法_pycorrector 内网接口使用
windows insightface库 人脸识别入门教程_insightface教程
赞
踩
初学insightface,在网上找了几天的博客,但是大多都是在Linux上运行的教程。而且我下的源代码跟他们的结构完全不一样,一度怀疑自己下错了。后来发现是因为作者一直在迭代更新,到现在跟之前已经有很大不同了。为了便于自己入门,所以我去github上下载了作者19年的版本。
环境配置
环境配置按照https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33750684所说就行,cuda10.1也可以运行。
源码下载
https://github.com/deepinsight/insightface#test-on-megaface
可以找19年的版本,能看懂也可以直接用新的。
库目录
我下载下来的库文件如图,版本不同会有小差别,大致差不多就行。
之后的操作都是再deploy目录中进行的。
模型下载
在网盘中下载好模型
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1jKahEXw
下载好后放在models文件夹中
之后就可以在deploy目录下的test.py中进行人脸识别了。
路径配置
里面会有一些红线是不用管的。
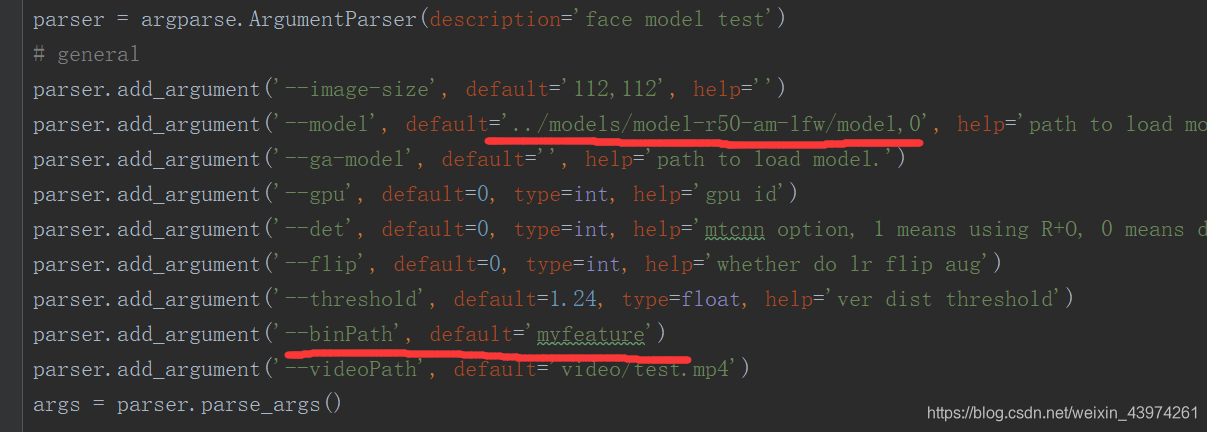
之后是路径的配置,将你模型的路径填进去,还有存放人脸特征的路径,由于我做的视频的人脸识别,所以最后是视频的路径。

之后可以通过这些方式进行调用。
人脸识别
人脸识别的工作原理是用检测到的人脸输入进模型,得到特征值后,与特征库中的人脸数据进行对比,计算它与特征库中每个数据的距离。之后取距离最短的一个数据的标签作为该人脸的识别结果。所以需要先进行人脸特征的持久化,之后进行人脸识别操作。
人脸特征持久化
import face_model import argparse import cv2 import sys import numpy as np import os parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='face model test') # general parser.add_argument('--image-size', default='112,112', help='') parser.add_argument('--model', default='../models/model-r50-am-lfw/model,0', help='path to load model.') parser.add_argument('--ga-model', default='', help='path to load model.') parser.add_argument('--gpu', default=0, type=int, help='gpu id') parser.add_argument('--det', default=0, type=int, help='mtcnn option, 1 means using R+O, 0 means detect from begining') parser.add_argument('--flip', default=0, type=int, help='whether do lr flip aug') parser.add_argument('--threshold', default=1.24, type=float, help='ver dist threshold') parser.add_argument('--binPath', default='myfeature') parser.add_argument('--videoPath', default='video/test.mp4') args = parser.parse_args() videoPath = args.videoPath binPath = args.binPath threshold = float(args.threshold) feature = [] label = [] # model = face_model_v2.FaceModel(args) #查看是否存在路径,没有则创建 if not os.path.exists(binPath): os.makedirs(binPath) #调用模型 model = face_model.FaceModel(args) #遍历路径中的图片,将他们的名字保存到label for s in os.listdir('imgs'): img = cv2.imread('imgs/'+s) img = model.get_input(img) f1 = model.get_feature(img) f1.tofile('myfeature/%s.bin'%s.split('.')[0])
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
运行后可以得到bin文件
图片人脸识别
计算两个人脸的距离代码:
# 查找当前特征最接近的特征 def findNear(feature, f, threshold, label): dist_list = [] # 遍历特征库 for feature_unit in feature: # 距离的定义是(特征1-特征2)开根号并求和 dist = np.sum(np.square(feature_unit - f)) # dist_list作用是将所有距离都保存下来,以便获得最小距离 dist_list.append(dist) # 寻找到最小距离 minDist = np.min(dist_list) print(minDist) # 如果最小距离小于等于阈值 if minDist <= threshold: # 求出最小距离对应的索引 minIdx = np.argmin(dist_list) # 找到姓名 print(label[minIdx]) #返回姓名和概率 return label[minIdx],(threshold-minDist)/threshold else: # 如果没有满足条件的,就返回'none' return 'none',0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
在进行识别之前修改一下face_model.py中的部分代码,因为源代码每次只能检测一张人脸,在建立人脸特征库时够用,但进行人脸检测时照片里不止一个人,因此需要做一些修改。
复制粘贴face_model.py,将名字改为Face_model_v2.py.
之后修改其中的get_input的方法。
# 主要修改get_input方法 def get_input(self, face_img): # print('into face_model_v2') ret = self.detector.detect_face(face_img, det_type=self.args.det) if ret is None: return None bbox, points = ret # 存放所有检测的人脸图像 aligned_list = [] # 存放所有人脸坐标 bbox_list = [] if bbox.shape[0] == 0: return None for i in range(bbox.shape[0]): # 获取每一个坐标 bbox_ = bbox[i, 0:4] # 存放坐标 bbox_list.append(bbox_) # 获取每一个特征点 points_ = points[i, :].reshape((2, 5)).T nimg = face_preprocess.preprocess(face_img, bbox_, points_, image_size='112,112') nimg = cv2.cvtColor(nimg, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) aligned = np.transpose(nimg, (2, 0, 1)) # 存放坐标 aligned_list.append(aligned) return aligned_list, bbox_list
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
修改完后记得将之前持久化导入的模型改为
model = face_model_v2.FaceModel(args)
- 1
照片人脸识别代码:
# 遍历目录获得目录中文件名字作为label,文件内容加入feature for bin_ in os.listdir(binPath): # 注意要指定dtype feature.append(np.fromfile(binPath + '/' + bin_, dtype=np.float32)) label.append(bin_.split('.')[0]) img=cv2.imread('hezhao.jpg') # img=cv2.resize(img,(500,500)) imgs, bbox = model.get_input(img) for img_unit, bbox_unit in zip(imgs, bbox): if img_unit.shape: # 获得特征 f = model.get_feature(img_unit) # 找到匹配信息 res,dist = findNear(feature, f, threshold, label) # 如果匹配到了姓名 if res != 'none': # 用方框标注,bbox_unit中的值为(左,上,右,下) # 按照cv2.rectangle的参数写入 cv2.rectangle(img, (int(bbox_unit[0]), int(bbox_unit[1])), (int(bbox_unit[2]), int(bbox_unit[3])), (0, 0, 255)) # 标记文字到图像中,参数:图像,文字,位置,字体,大小,颜色,宽度 img = cv2.putText(img, res+"%.2f"%float(dist), (int(bbox_unit[0])-2, int(bbox_unit[1])),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 1) cv2.imshow('name',img) cv2.waitKey(0)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
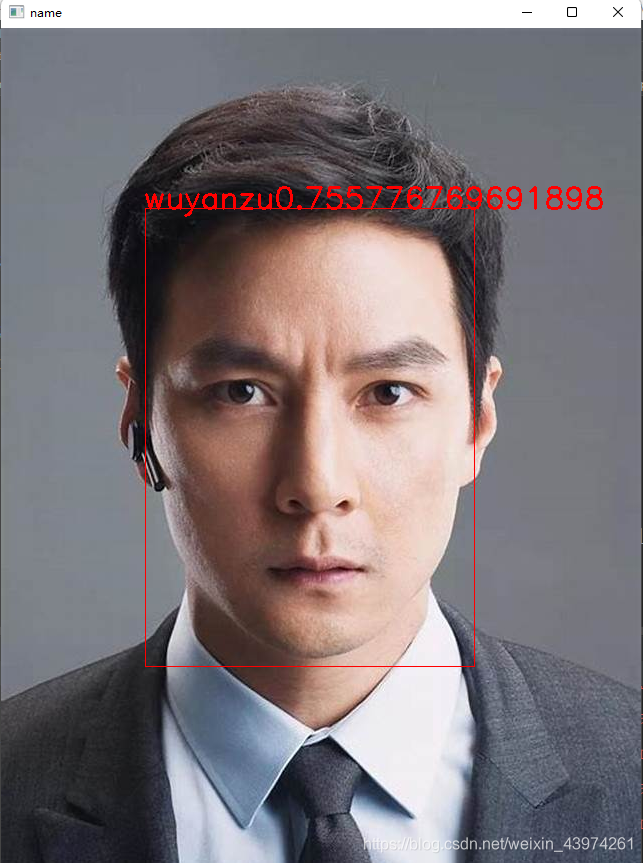
用博主的自拍测试了下

之后用合照测试:

总的代码:
import face_model_v2 import face_model import argparse import cv2 import sys import numpy as np import os parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='face model test') # general parser.add_argument('--image-size', default='112,112', help='') parser.add_argument('--model', default='../models/model-r50-am-lfw/model,0', help='path to load model.') parser.add_argument('--ga-model', default='', help='path to load model.') parser.add_argument('--gpu', default=0, type=int, help='gpu id') parser.add_argument('--det', default=0, type=int, help='mtcnn option, 1 means using R+O, 0 means detect from begining') parser.add_argument('--flip', default=0, type=int, help='whether do lr flip aug') parser.add_argument('--threshold', default=1.24, type=float, help='ver dist threshold') parser.add_argument('--binPath', default='myfeature') parser.add_argument('--videoPath', default='video/test.mp4') args = parser.parse_args() videoPath = args.videoPath binPath = args.binPath threshold = float(args.threshold) feature = [] label = [] model = face_model_v2.FaceModel(args) #查看是否存在路径,没有则创建 # if not os.path.exists(binPath): # os.makedirs(binPath) #调用模型 # model = face_model.FaceModel(args) # 遍历路径中的图片,将他们的名字保存到label # for s in os.listdir('imgs'): # img = cv2.imread('imgs/'+s) # img,_ = model.get_input(img) # f1 = model.get_feature(img) # f1.tofile('myfeature/%s.bin'%s.split('.')[0]) # 查找当前特征最接近的特征 def findNear(feature, f, threshold, label): dist_list = [] # 遍历特征库 for feature_unit in feature: # 距离的定义是(特征1-特征2)开根号并求和 dist = np.sum(np.square(feature_unit - f)) # dist_list作用是将所有距离都保存下来,以便获得最小距离 dist_list.append(dist) # 寻找到最小距离 minDist = np.min(dist_list) # 如果最小距离小于等于阈值 if minDist <= threshold: # 求出最小距离对应的索引 minIdx = np.argmin(dist_list) # 找到姓名 return label[minIdx] else: # 如果没有满足条件的,就返回'none' return 'none' # 遍历目录获得目录中文件名字作为label,文件内容加入feature for bin_ in os.listdir(binPath): # 注意要指定dtype feature.append(np.fromfile(binPath + '/' + bin_, dtype=np.float32)) label.append(bin_.split('.')[0]) # 查找当前特征最接近的特征 def findNear(feature, f, threshold, label): dist_list = [] # 遍历特征库 for feature_unit in feature: # 距离的定义是(特征1-特征2)开根号并求和 dist = np.sum(np.square(feature_unit - f)) # dist_list作用是将所有距离都保存下来,以便获得最小距离 dist_list.append(dist) # 寻找到最小距离 minDist = np.min(dist_list) print(minDist) # 如果最小距离小于等于阈值 if minDist <= threshold: # 求出最小距离对应的索引 minIdx = np.argmin(dist_list) # 找到姓名 print(label[minIdx]) return label[minIdx],(threshold-minDist)/threshold else: # 如果没有满足条件的,就返回'none' return 'none',0 img=cv2.imread('hezhao.jpg') # img=cv2.resize(img,(500,500)) imgs, bbox = model.get_input(img) for img_unit, bbox_unit in zip(imgs, bbox): if img_unit.shape: # 获得特征 f = model.get_feature(img_unit) # 找到匹配信息 res,dist = findNear(feature, f, threshold, label) # 如果匹配到了姓名 if res != 'none': # 用方框标注,bbox_unit中的值为(左,上,右,下) # 按照cv2.rectangle的参数写入 cv2.rectangle(img, (int(bbox_unit[0]), int(bbox_unit[1])), (int(bbox_unit[2]), int(bbox_unit[3])), (0, 0, 255)) # 标记文字到图像中,参数:图像,文字,位置,字体,大小,颜色,宽度 img = cv2.putText(img, res+"%.2f"%float(dist), (int(bbox_unit[0])-2, int(bbox_unit[1])),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 255), 1) cv2.imshow('name',img) cv2.waitKey(0)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
视频人脸识别
关于视频的人脸识别可以看参考文章中的博客,里面已经很详细了。
参考文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/xiaotuzigaga/article/details/89224594



