- 1日常运维(1)w命令,vmstat命令,top命令,sar命令,nload命令_vmstat -w 1
- 2git pull 提示Not possible to fast-forward,无法提交也无法更新
- 3Tensorflow--MNIST分类模型_mnist模型
- 4Flink checkpoint机制_flink sql采集checkpoint
- 5大模型从入门到应用——LangChain:模型(Models)-[大型语言模型(LLMs):基础知识]_langchain model适配
- 6JDBC 设置超时时间,避免sql查询时时间过长_jdbc超时时间
- 7MySql事务_read view 匹配条件规则
- 8Oracle 数据去重_oracle去重查询
- 9深入OceanBase分布式数据库:MySQL 模式下的 SQL 基本操作_oceanbase mysql
- 10实用干货丨Eolink Apikit 配置和告警规则的各种用法
MM-LLMs :多模态大语言模型综述
赞
踩
MM-LLMs:
Recent Advances in MultiModal Large Language Models

https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.13601

In the past year, MultiModal Large Language Models (MM-LLMs) have undergone substantial advancements, augmenting off-the-shelf LLMs to support MM inputs or outputs via cost-effective training strategies. The resulting models not only preserve the inherent reasoning and decision-making capabilities of LLMs but also empower a diverse range of MM tasks. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive survey aimed at facilitating further research of MM-LLMs. Initially, we outline general design formulations for model architecture and training pipeline. Subsequently, we introduce a taxonomy encompassing 126 MM-LLMs, each characterized by its specific formulations. Furthermore, we review the performance of selected MM-LLMs on mainstream benchmarks and summarize key training recipes to enhance the potency of MM-LLMs. Finally, we explore promising directions for MM-LLMs while concurrently maintaining a real-time tracking website1 for the latest developments in the field. We hope that this survey contributes to the ongoing advancement of the MM-LLMs domain.
在过去一年中,多模态大型语言模型(MM-LLMs)取得了显著进展,通过成本效益高的训练策略,增强了现成的LLMs(大型语言模型),以支持多模态输入或输出。这些模型不仅保留了LLMs固有的推理和决策能力,还增强了多种多模态任务的处理能力。本文旨在通过全面综述,促进MM-LLMs领域的进一步研究。
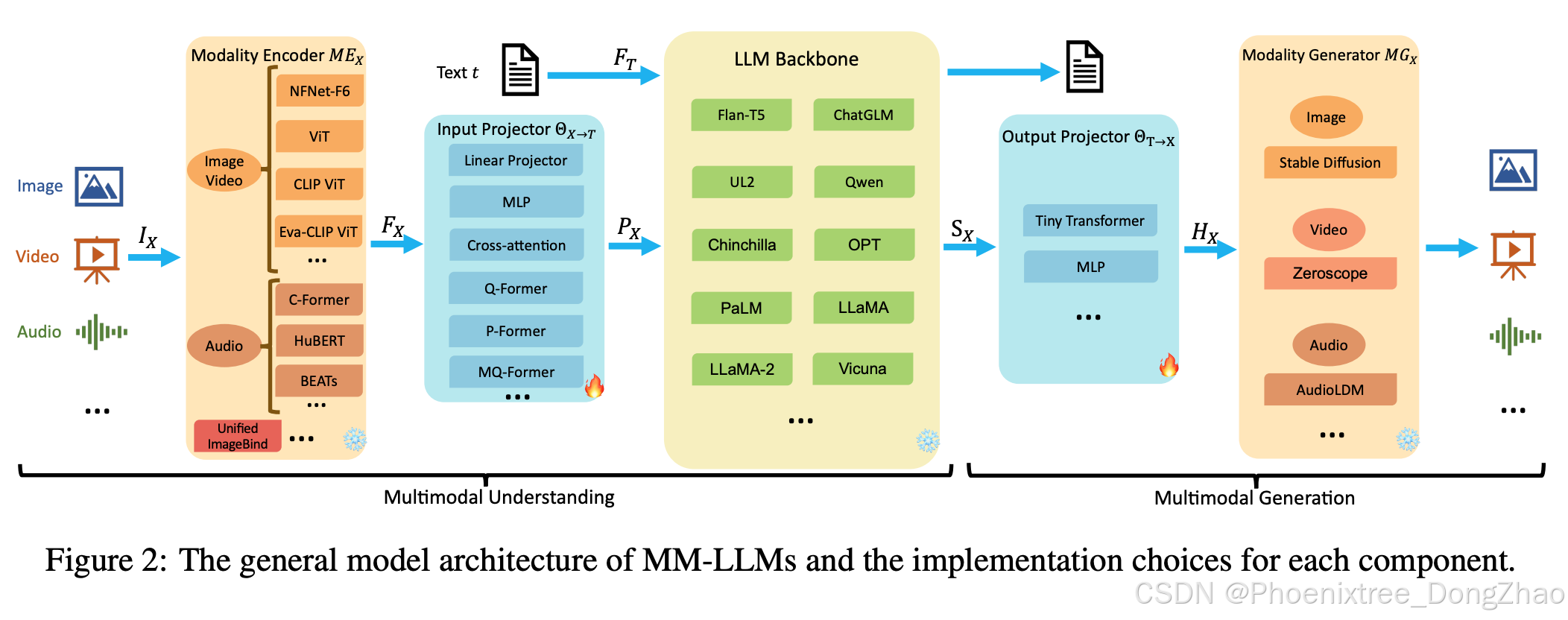
首先,本文概述了模型架构和训练流程的一般设计公式。
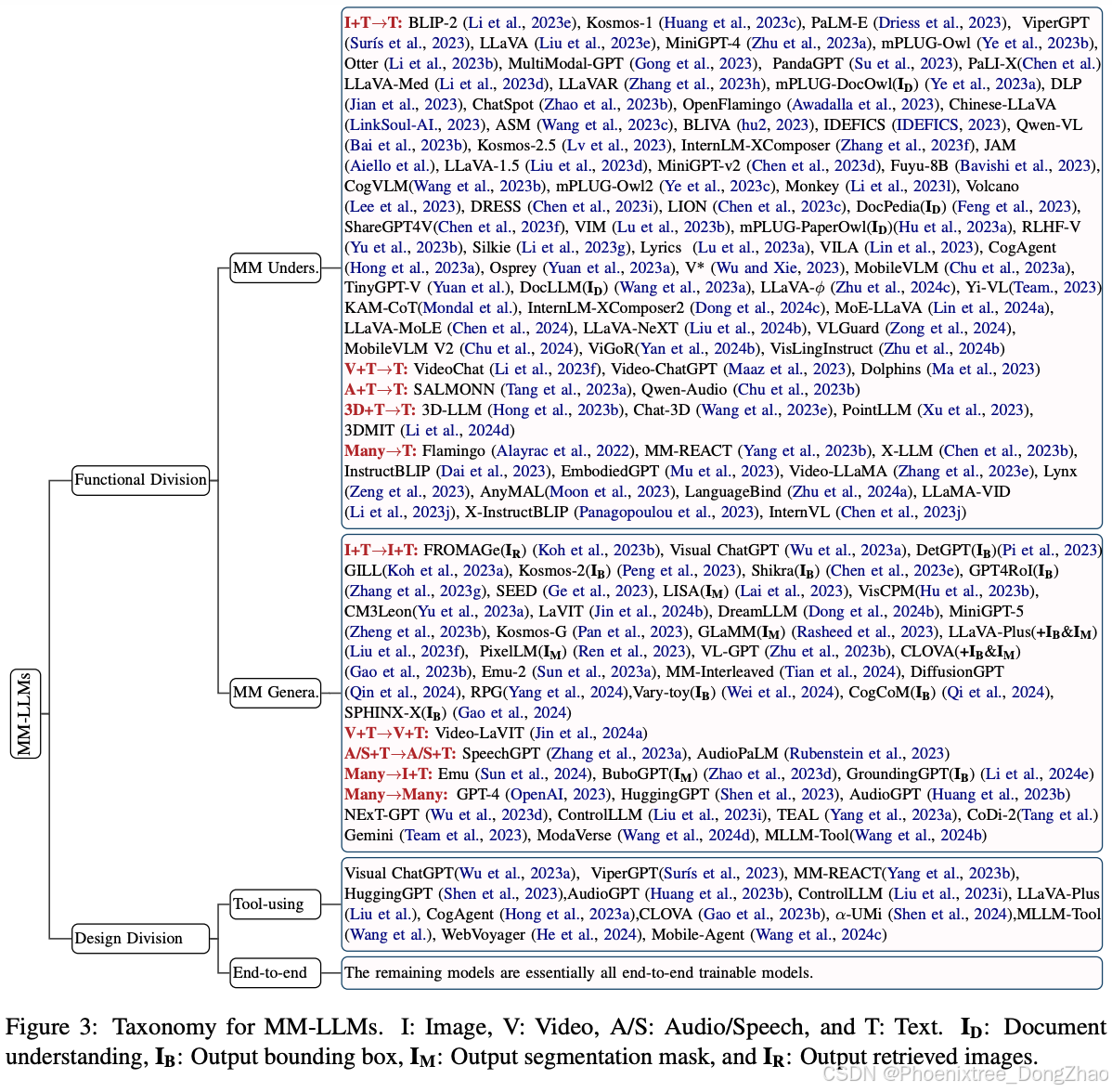
随后,本文引入了一个包含126个MM-LLMs的分类体系,每个模型都有其特定的设计公式。
此外,本文还回顾了部分MM-LLMs在主流基准测试中的表现,并总结了增强MM-LLMs效能的关键训练策略。
最后,本文在探索MM-LLMs未来发展方向的同时,还维护了一个实时跟踪网站1,以关注该领域的最新进展。我们希望本次综述能为MM-LLMs领域的持续发展做出贡献。