- 1Tensorflow构建自己的图片数据集TFrecords_tensorflow 自己的图片 数组
- 2群晖 Docker版qbittorrent 下载显示错误 解决方法_qbittorrent下载错误
- 3IOS下的横竖屏切换研究_ios 下的横竖屏切换研究
- 4面试经典150题——矩阵置零
- 5 在 Linux 中安装 Cassandra
- 6RuntimeError: Expected all tensors to be on the same device, but found at least two devices
- 7mybatis typehandler的使用_type-handlers-package
- 8ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ‘sklearn‘_modulenotfounderror: no module named 'sklearn
- 9学习会员上线啦,快来看看会有哪些权益吧~_scdn 学员收益:
- 10【个人笔记】OpenCV4 C++ 快速入门 26课_【个人笔记 - 目录】opencv c++ 快速入门 30讲
超体素分割_vtk 超体素
赞
踩
本文体素构建及超体素生成,参考文献《基于超体素区域增长的点云分割算法研究》与《Voxel Cloud Connectivity Segmentation - Supervoxels for Point Clouds》
体素数据---------------------体素化网格
体素(Voxel)是体积元素(Volume pixel)的简称,是数据位于三维空间内规则网格上的最小单位,体素,其物理意义类似于二维图像像素在三维空间上的推广,是一组均匀分布、位于正交网格中心的立方体的集合。体素不能表示三维空间中的位置信息,即不具有三维坐标。可以通过体素数据在立体空间内的相对位置关系表示场景或物体的三维信息。
1.首先将点云数据进行体素化
体素化(Voxelization)是利用体素来近似表示场景或物体的空间结构和几何形状的过程。体素化的基本原理是:在输入的点云数据上创建一个三维立体的网格,立体网格是一种微小的三维立方体的集合。然后,在每个三维立方体内,利用立方体内所有点云数据的重心点来近似表示网格内的所有点,网格处理后得到相应的体素云数据。体素云数据可以表示模型的表面几何特征和内部属性信息,并且利用体素数据的相对位置关系还可以表示三维信息。
体素化过程如下:

点云数据是杂乱、无组织结构的,但是通过体素化处理后,在体素空间内存在三
种拓扑结构:6 邻接、18 邻接以及 26 邻接。其中 6 邻接的两个体素具有 6 个公共面,
18 邻接的体素具有 12 条公共边和 6 个公共面,26 邻接体素在此基础上还具有 8 个
公共点。如图 3.3 所示,从左到右依次为 6 邻接、18 邻接以及 26 邻接。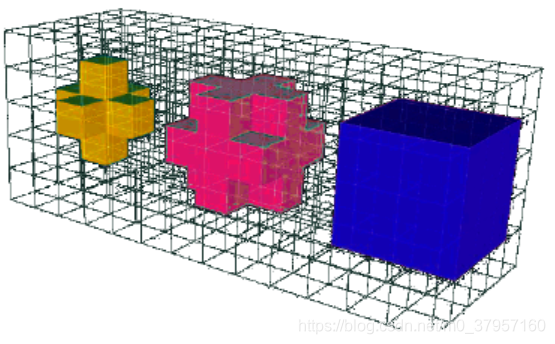
2.网格化处理
体素化处理后,利用网格化操作筛选种子体素,为聚类算法提供初始种子点。
首先在体素空间下进行网格化处理,网格化处理的分辨率为Rpatch。选择网格内最接近中心的体素作为初始种子体素。对于初始的候选种子体素进行过滤去噪处理,删除体素空间下孤立的种子点,保留位于物体表面上的种子体素。对于每个体素种子,建立一个半径为Rsearch的搜索区域,计算该种子点在邻域半径Rsearch下的体素数目,删除表面与搜索范围内相交区域内体素数目小于固定阈值的种子体素,如下图内黄色区域所示。
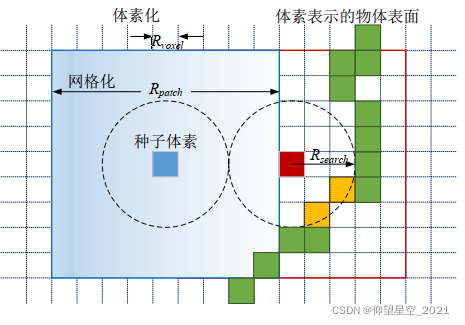
需要注意的是,网格化分辨率Rpatch要远大于体素分辨率Rvoxel。否则,在筛选种子的过程中无法准确判断网格的中心体素,或者无法正确剔除孤立种子点,使得流约束聚类算法在初始化的过程中产生误差,并且在聚类迭代的过程中不断增加,最终导致错误分割。同时,网格化分辨率对过分割得到的超体素具有直接的影响,网格分辨率的大小与超体素的大小成正比例。如上图所示,背景虚线网格表示体素化处理,网格化分辨率Rpatch>>Rvoxel。在红色种子体素的搜索范围内,与物体表面相交的体素数据只有两个,小于预先设置的固定阈值,则判断红色种子体素是空间内的孤立种子点,并将其删除。
种子体素选择、过滤结束后,需要综合考虑体素数据的特征向量,计算种子体素与连通邻接体素的相似性。
3. 特征计算与距离度量
3.1特征计算
在上述初始化的基础上,综合考虑点云数据的边缘属性、几何特征和空间距离来衡量体素之间的相似性,在37维的特征空间下对体素数据进行聚类,其中包括曲率值、XYZ三维空间和33维的点特征空间。体素数据在37维特征空间下的特征向量定义为:

其中,x,y,z是空间三维坐标;c表示体素数据的曲率值;FPFH1...33为快速点特征直方图(Fast Point Feature Histograms,FPFH),该直方图是由33个浮点数组成的特征向量。
3.2 距离度量
综合考虑边缘属性、几何特征和空间位置来衡量体素之间的相似性,利用曲率特征、FPFH和空间距离计算邻接体素的相似性距离。
通过限制每次聚类过程的搜索范围,可以使得该算法在接近相邻超体素的聚类中心时停止搜索。这意味着在聚类过程中,需要利用最大距离为![]() 的数据对空间距离Ds进行归一化处理。两种属性的相对重要性随着种子分辨率Rpatch变化。
的数据对空间距离Ds进行归一化处理。两种属性的相对重要性随着种子分辨率Rpatch变化。
定义D表示体素与邻接体素之间的距离,Ds是三维空间内体素的欧式距离值,Dc表示体素之间的曲率变化值,DHIK是体素点特征直方图的交叉核,![]() 分别对应空间距离和几何特征的影响因子,Cmax表示体素邻域范围内的最大曲率值,用来对体素之间的曲率距离进行归一化处理。邻接体素距离的计算公式如下:
分别对应空间距离和几何特征的影响因子,Cmax表示体素邻域范围内的最大曲率值,用来对体素之间的曲率距离进行归一化处理。邻接体素距离的计算公式如下:
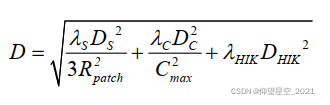

3.4 超体素聚类分割


如下为针对XYZ格式的点云使用超体素进行分割的结果:
- #include <pcl/console/parse.h>
- #include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
- #include <pcl/point_types.h>
- #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
- #include <pcl/segmentation/supervoxel_clustering.h>
- #include <pcl/filters/statistical_outlier_removal.h>
- #include<iostream>
- //VTK include needed for drawing graph lines
- #include <vtkPolyLine.h>
- #include"IO.h"
-
- using namespace pcl;
- using namespace std;
-
- typedef PointXYZ PointT;
- typedef PointXYZL PointTL;
- //-----------------------邻接线条可视化------------------------------------------
- void addSupervoxelConnectionsToViewer(PointXYZRGBA& supervoxel_center,
- PointCloud<PointXYZRGBA>& adjacent_supervoxel_centers,
- std::string supervoxel_name,
- pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr& viewer)
- {
- vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New();
- vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> cells = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New();
- vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyLine> polyLine = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyLine>::New();
-
- //遍历所有相邻点,并在相邻点对中添加一个中心点
- for (auto adjacent_itr = adjacent_supervoxel_centers.begin(); adjacent_itr != adjacent_supervoxel_centers.end(); ++adjacent_itr)
- {
- points->InsertNextPoint(supervoxel_center.data);
- points->InsertNextPoint(adjacent_itr->data);
- }
- // 创建一个polydata来存储所有内容
- vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New();
- // Add the points to the dataset
- polyData->SetPoints(points);
- polyLine->GetPointIds()->SetNumberOfIds(points->GetNumberOfPoints());
- for (unsigned int i = 0; i < points->GetNumberOfPoints(); i++)
- polyLine->GetPointIds()->SetId(i, i);
- cells->InsertNextCell(polyLine);
- // 将这些线添加到数据集
- polyData->SetLines(cells);
- viewer->addModelFromPolyData(polyData, supervoxel_name);
- }
- int main()
- {
- IO IOExample;
- //--------------------加载点云--------------------------
- PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr cloud(new PointCloud<PointT>);
- char *inputpath = "..//测试数据//desk.txt";
- vector<pcl::PointXYZ> allpoints;
- allpoints = IOExample.ReadPointXYZIntoVector(inputpath);
- cloud->width = allpoints.size();
- cloud->height = 1;
- cloud->is_dense = false;
- cloud->resize(cloud->width*cloud->height);
- for (int i = 0; i < allpoints.size(); i++)
- {
- cloud->points[i].x = allpoints[i].x;
- cloud->points[i].y = allpoints[i].y;
- cloud->points[i].z = allpoints[i].z;
- }
-
- //-------------------点云去噪---------------------------
- StatisticalOutlierRemoval<PointT>sor;
- PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr sor_cloud(new PointCloud<PointT>);
- sor.setInputCloud(cloud);
- sor.setMeanK(10);
- sor.setStddevMulThresh(1);
- sor.filter(*sor_cloud);
- //------------------构建超体素--------------------------
- float voxel_resultion = 0.01f;
- float seed_resultion = 0.1f;
- float color_importance = 0.0f;
- float spatial_importance = 0.4f;
- float normal_importance = 5.0f;
-
- SupervoxelClustering<PointT> super(voxel_resultion, seed_resultion);
- super.setInputCloud(sor_cloud);
- super.setNormalImportance(normal_importance);
- super.setColorImportance(color_importance);
- super.setSpatialImportance(spatial_importance);
- std::map<uint32_t, Supervoxel<PointT>::Ptr >supervoxl_clustering;
- super.extract(supervoxl_clustering);
-
- cout << "supervoxel number is" << supervoxl_clustering.size() << endl;
-
- visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer(new visualization::PCLVisualizer("VCCS"));
- PointCloud<PointT>::Ptr supervoxel_centroid_cloud = super.getVoxelCentroidCloud();
-
- viewer->addPointCloud(supervoxel_centroid_cloud, "supervoxel_centroid_cloud");
- viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "supervoxel_centroid_cloud");
- viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_OPACITY, 0.5, "supervoxel_centroid_cloud");
-
-
- PointCloud<PointTL>::Ptr supervoxel_cloud = super.getLabeledVoxelCloud();
- viewer->addPointCloud(supervoxel_cloud, "supervoxel_cloud");
- viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "supervoxel_cloud");
- viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_OPACITY, 0.5, "supervoxel_cloud");
- //-----------------可视化法向量--------------------------
- //PointCloud<PointNormal>::Ptr supervoxel_normal=super.makeSupervoxelNormalCloud(supervoxl_clustering);
- //viewer->addPointCloudNormals<PointNormal>(supervoxel_normal, 1, 0.2, "123");
-
- multimap<uint32_t, uint32_t>SupervoxelAdjacency;
- super.getSupervoxelAdjacency(SupervoxelAdjacency);
- //--------------获得体素点云的邻接单元-------------------
- for (auto label_itr = SupervoxelAdjacency.cbegin(); label_itr != SupervoxelAdjacency.cend();)
- {
- uint32_t super_label = label_itr->first;//获取体素单元的标签
- Supervoxel<PointT>::Ptr super_cloud = supervoxl_clustering.at(super_label);//把对应标签内的点云、体素质心、以及质心对应的法向量提取出来
- PointCloud<PointXYZRGBA> adjacent_supervoxel_centers;
- for (auto adjacent_itr = SupervoxelAdjacency.equal_range(super_label).first; adjacent_itr != SupervoxelAdjacency.equal_range(super_label).second; ++adjacent_itr) {
- Supervoxel<PointT>::Ptr neighbor_supervoxel = supervoxl_clustering.at(adjacent_itr->second);
- adjacent_supervoxel_centers.push_back(neighbor_supervoxel->centroid_);
- }
- std::stringstream ss;
- ss << "supervoxel_" << super_label;
- addSupervoxelConnectionsToViewer(super_cloud->centroid_, adjacent_supervoxel_centers, ss.str(), viewer);
- label_itr = SupervoxelAdjacency.upper_bound(super_label);
- }
- viewer->spin();
- return 0;
- }

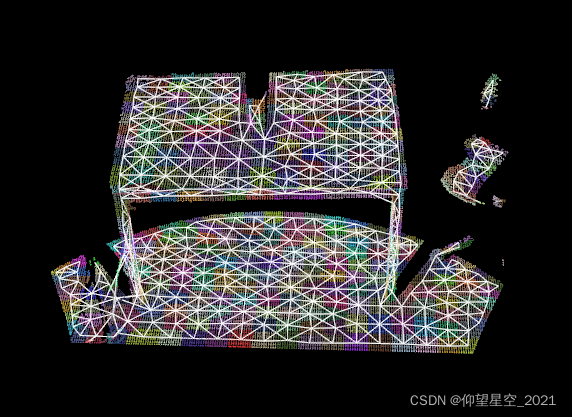
参考博库:与https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41918369/article/details/114436941


